User login
Branding tattoo removal helps sex trafficking survivor close door on painful past
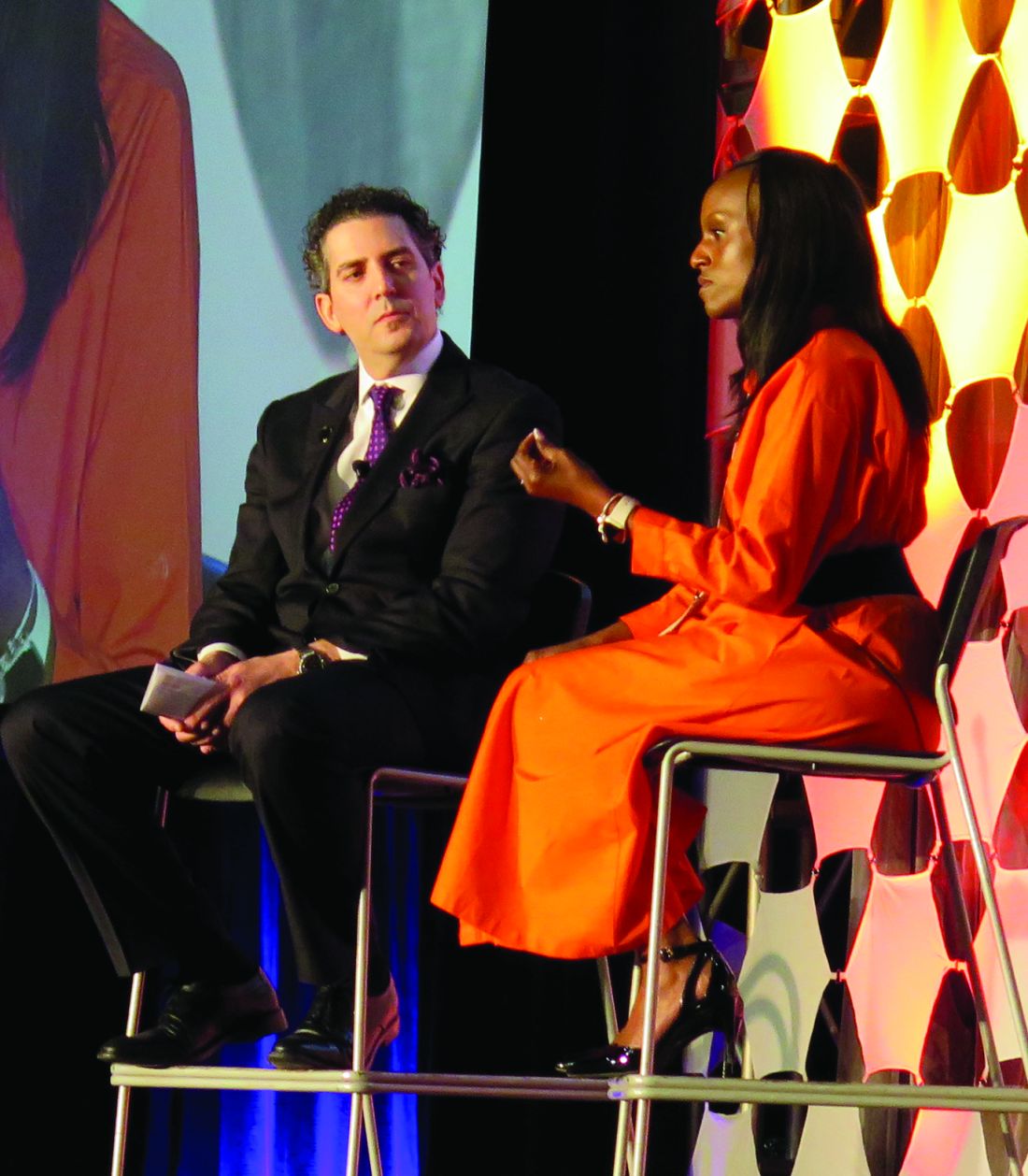
PHOENIX – When Kathy Givens walked onstage during a plenary session at the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery to reflect on her 9-month ordeal being sex trafficked in Texas more than 20 years ago, you could hear a pin drop.
“One of the scariest things about the life of sex trafficking is not knowing who’s going to be on the other side,” said Ms. Givens, who now lives in Houston. “There was some violence. There were some horrible things that happened. But you know what was really scary? When I got out. People may ask, ‘How’s that so? You escaped your trafficker. The past is behind you. Why were you afraid?’ I was afraid because I didn’t know that I had community. I didn’t know that community or that society would care about someone like me.”
She said that she found herself immobilized by fear of being shamed in society and labeled a sex trafficking victim, and wondered if she could overcome that fear and if anyone would view her as human again. Once free from her trafficker, she began a “healing journey,” which included getting married, raising four children, and re-enrolling in college with hopes of becoming a social worker. In 2020, she and her husband founded Twelve 11 Partners, an organization committed to supporting human trafficking survivors.
“I was working in the anti-trafficking field helping other survivors ... who have experienced this horrific crime,” she said. “I thought I was on my way.” But one “stain” from her sex trafficking past remained: The name of her trafficker was tattooed on her skin, “a reminder of what I’d gone through.”
Ms. Givens was eventually introduced to Paul M. Friedman, MD, the current ASLMS president and one of the that was formed in 2022. According to a survey that Dr. Friedman and colleagues presented at the 2022 annual ASLMS conference, an estimated 1 in 2 sex trafficking survivors have branding tattoos, and at least 1,000 survivors a year could benefit from removal of those tattoos.
“To date, 87 physicians in the U.S. and one in Canada have stepped forward to volunteer their services to be part of this program,” Dr. Friedman, who directs the Dermatology and Laser Surgery Center in Houston, said at this year’s meeting. “My goal is to double this number by the next annual conference,” he added, noting that trauma-informed training is part of the program, “to support the survivor experience during the treatment process.”
ASLMS is also working on this issue in partnership with the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) Ad Hoc Task Force on Dermatological Resources for the Intervention and Prevention of Human Trafficking, which is headed by Boston dermatologist Shadi Kourosh, MD.
“Dermatologists are uniquely positioned to aid in efforts to assist those experiences in trafficking with our training to recognize and diagnose relevant signs on the skin and to assist patients with certain aspects of care and recovery including the treatment of the disease of scars and tattoos,” Dr. Friedman said. “Ultimately, we hope to create a database together to improve recognition of branding tattoos to aid in identifying sex trafficking victims.”
Ms. Givens, who sits on the U.S. Advisory Council on Human Trafficking, said that she was able to truly close the door on her sex trafficking past thanks to the tattoo removal Dr. Friedman performed as part of New Beginnings. “It means the world to me to know that I can now be an advocate for other individuals who have experienced human trafficking,” she told meeting attendees.
“Again, one of the scariest things is not knowing that you have community. I was scared of losing hope, but I’m standing here today. I have all the hope that I need. You have the power to change lives.”
PHOENIX – When Kathy Givens walked onstage during a plenary session at the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery to reflect on her 9-month ordeal being sex trafficked in Texas more than 20 years ago, you could hear a pin drop.
“One of the scariest things about the life of sex trafficking is not knowing who’s going to be on the other side,” said Ms. Givens, who now lives in Houston. “There was some violence. There were some horrible things that happened. But you know what was really scary? When I got out. People may ask, ‘How’s that so? You escaped your trafficker. The past is behind you. Why were you afraid?’ I was afraid because I didn’t know that I had community. I didn’t know that community or that society would care about someone like me.”
She said that she found herself immobilized by fear of being shamed in society and labeled a sex trafficking victim, and wondered if she could overcome that fear and if anyone would view her as human again. Once free from her trafficker, she began a “healing journey,” which included getting married, raising four children, and re-enrolling in college with hopes of becoming a social worker. In 2020, she and her husband founded Twelve 11 Partners, an organization committed to supporting human trafficking survivors.
“I was working in the anti-trafficking field helping other survivors ... who have experienced this horrific crime,” she said. “I thought I was on my way.” But one “stain” from her sex trafficking past remained: The name of her trafficker was tattooed on her skin, “a reminder of what I’d gone through.”
Ms. Givens was eventually introduced to Paul M. Friedman, MD, the current ASLMS president and one of the that was formed in 2022. According to a survey that Dr. Friedman and colleagues presented at the 2022 annual ASLMS conference, an estimated 1 in 2 sex trafficking survivors have branding tattoos, and at least 1,000 survivors a year could benefit from removal of those tattoos.
“To date, 87 physicians in the U.S. and one in Canada have stepped forward to volunteer their services to be part of this program,” Dr. Friedman, who directs the Dermatology and Laser Surgery Center in Houston, said at this year’s meeting. “My goal is to double this number by the next annual conference,” he added, noting that trauma-informed training is part of the program, “to support the survivor experience during the treatment process.”
ASLMS is also working on this issue in partnership with the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) Ad Hoc Task Force on Dermatological Resources for the Intervention and Prevention of Human Trafficking, which is headed by Boston dermatologist Shadi Kourosh, MD.
“Dermatologists are uniquely positioned to aid in efforts to assist those experiences in trafficking with our training to recognize and diagnose relevant signs on the skin and to assist patients with certain aspects of care and recovery including the treatment of the disease of scars and tattoos,” Dr. Friedman said. “Ultimately, we hope to create a database together to improve recognition of branding tattoos to aid in identifying sex trafficking victims.”
Ms. Givens, who sits on the U.S. Advisory Council on Human Trafficking, said that she was able to truly close the door on her sex trafficking past thanks to the tattoo removal Dr. Friedman performed as part of New Beginnings. “It means the world to me to know that I can now be an advocate for other individuals who have experienced human trafficking,” she told meeting attendees.
“Again, one of the scariest things is not knowing that you have community. I was scared of losing hope, but I’m standing here today. I have all the hope that I need. You have the power to change lives.”
PHOENIX – When Kathy Givens walked onstage during a plenary session at the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery to reflect on her 9-month ordeal being sex trafficked in Texas more than 20 years ago, you could hear a pin drop.
“One of the scariest things about the life of sex trafficking is not knowing who’s going to be on the other side,” said Ms. Givens, who now lives in Houston. “There was some violence. There were some horrible things that happened. But you know what was really scary? When I got out. People may ask, ‘How’s that so? You escaped your trafficker. The past is behind you. Why were you afraid?’ I was afraid because I didn’t know that I had community. I didn’t know that community or that society would care about someone like me.”
She said that she found herself immobilized by fear of being shamed in society and labeled a sex trafficking victim, and wondered if she could overcome that fear and if anyone would view her as human again. Once free from her trafficker, she began a “healing journey,” which included getting married, raising four children, and re-enrolling in college with hopes of becoming a social worker. In 2020, she and her husband founded Twelve 11 Partners, an organization committed to supporting human trafficking survivors.
“I was working in the anti-trafficking field helping other survivors ... who have experienced this horrific crime,” she said. “I thought I was on my way.” But one “stain” from her sex trafficking past remained: The name of her trafficker was tattooed on her skin, “a reminder of what I’d gone through.”
Ms. Givens was eventually introduced to Paul M. Friedman, MD, the current ASLMS president and one of the that was formed in 2022. According to a survey that Dr. Friedman and colleagues presented at the 2022 annual ASLMS conference, an estimated 1 in 2 sex trafficking survivors have branding tattoos, and at least 1,000 survivors a year could benefit from removal of those tattoos.
“To date, 87 physicians in the U.S. and one in Canada have stepped forward to volunteer their services to be part of this program,” Dr. Friedman, who directs the Dermatology and Laser Surgery Center in Houston, said at this year’s meeting. “My goal is to double this number by the next annual conference,” he added, noting that trauma-informed training is part of the program, “to support the survivor experience during the treatment process.”
ASLMS is also working on this issue in partnership with the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) Ad Hoc Task Force on Dermatological Resources for the Intervention and Prevention of Human Trafficking, which is headed by Boston dermatologist Shadi Kourosh, MD.
“Dermatologists are uniquely positioned to aid in efforts to assist those experiences in trafficking with our training to recognize and diagnose relevant signs on the skin and to assist patients with certain aspects of care and recovery including the treatment of the disease of scars and tattoos,” Dr. Friedman said. “Ultimately, we hope to create a database together to improve recognition of branding tattoos to aid in identifying sex trafficking victims.”
Ms. Givens, who sits on the U.S. Advisory Council on Human Trafficking, said that she was able to truly close the door on her sex trafficking past thanks to the tattoo removal Dr. Friedman performed as part of New Beginnings. “It means the world to me to know that I can now be an advocate for other individuals who have experienced human trafficking,” she told meeting attendees.
“Again, one of the scariest things is not knowing that you have community. I was scared of losing hope, but I’m standing here today. I have all the hope that I need. You have the power to change lives.”
AT ASLMS 2023
Small study finds IPL-radiofrequency combination effective for dry eye disease
PHOENIX – and improved meibum quality in both upper and lower eyelids, results from an ongoing, novel study showed.
Dry eye disease affects a large proportion of people in the United States “and the factors that contribute to that are certainly not going away,” lead study author James G. Chelnis MD, said at the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery, where he presented the results during an abstract session. “Prepandemic, we used to have meetings in person; now most are on a computer screen,” a common risk factor for worsening dry eyes, he said. Telltale dry eye symptoms include blurry vision, irritation, and corneal damage – mostly caused by meibomian gland dysfunction – which impacts the quality and quantity of meibum secreted. Common treatments include warm compresses, doxycycline, and artificial tears.
While some studies have shown IPL is helpful in treating dry eye disease caused by meibomian gland dysfunction, little information is available on its use alone or in combination with topical RF to preserve and improve the function of meibomian glands, said Dr. Chelnis, an ophthalmic plastic surgeon in New York City. “The theory here is that the radiofrequency would be able to vibrate the water molecules inside the meibomian glands, which would allow you to turn over the meibum faster, as well as improve the blink reflex response by building supporting collagen,” he said. “Our novel study explores the ability of this combined modality treatment to improve upon meibomian gland health.”
Study design, results
Dr. Chelnis and his colleagues enrolled 11 individuals with a previous diagnosis of dry eye disease and meibomian gland dysfunction with Ocular Surface Disease Index (OSDI) survey scores higher than 23, which indicate at least moderate dry eye symptoms. Inclusion criteria were being 22 years of age or older, signs of meibomian gland dysfunction as detected by biomicroscopy, a modified meibomian gland score over 12 in the lower eyelid of at least one eye, and type I-IV skin.
All patients received four treatments (each 2 weeks apart) of IPL to the lower eyelid, surrounding malar region, and nose, followed by 7 minutes of topical RF treatments at 1 MHz and 4 MHz extending to the inferior, lateral, and superior orbital rim. Evaluation of meibomian gland expression and quality of meibum upon expression was conducted following each treatment session, with a final evaluation 4 weeks after the final treatment session.
Meibum quality was evaluated on a scale of 0-3 representing clear (0), cloudy (1), inspissated (2), and blocked (3) meibum, respectively.
Following treatment, meibomian gland expression and meibum quality improved in all eyelids in all 11 patients. Specifically, in the right eye, the number of upper lid expressible glands increased from an average of 13 to 27.9 and the number of lower lid expressible glands increased from an average of 14.6 to 28.2; and in the left eye, the number of upper lid expressible glands increased from an average of 13.3 to 27.3 and the number of lower lid expressible glands increased from an average of 14.8 to 26.8 (P < .001 for all associations).
The overall percentage improvement in meibomian gland expression in the right eye was 82.7% for the upper lids and 136.6% for the lower lids, and in the left eye, 82.9% for the upper lids, and 112.2% for the lower lids.
When comparing upper against lower lids, meibomian gland expression increased 124.4% and 82.8%, respectively. Meibum quality improved in all four eyelids, although upper eyelids displayed a superior improvement compared with lower eyelids.
“We are finding that combining IPL plus RF produces a more complete and comprehensive improvement in the quality of their meibomian gland health, and as such, their dry eyes,” with “a large decrease in their symptom profile,” he concluded.
More patients to be studied
Dr. Chelnis acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the small number of patients, but he and his colleagues have added an additional clinical site to expand the sample size. “Larger scale studies are needed to evaluate long-term effectiveness of IPL plus RF as well as a comparison with other treatment options.”
During a question-and-answer session Mathew M. Avram, MD, JD, director of laser, cosmetics, and dermatologic surgery at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, who served as one of the abstract session moderators, asked Dr. Chelnis to comment on what the mechanism of action of the IPL-RF combination in improving meibomian gland health.
“It’s not fully understood, but part of it is improved vascularity at the lid margin,” said Dr. Chelnis, who holds a faculty position in the department of ophthalmology at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. “Your ocular surface is sort of like your screen door; it catches everything that’s in the environment. An increase in vascularity and immunologic cytokines occurs in response to that. If you’re looking at the eye with a slit lamp, you can see a lot of vascularity that occurs at the lid margin and crowds the meibomian glands. When you decrease that crowding and immunogenic response, you move towards a normally functioning lid margin.”
Dr. Chelnis disclosed that he is a consultant to or an adviser for Lumenis, Horizon Therapeutics, and Soniquence.
PHOENIX – and improved meibum quality in both upper and lower eyelids, results from an ongoing, novel study showed.
Dry eye disease affects a large proportion of people in the United States “and the factors that contribute to that are certainly not going away,” lead study author James G. Chelnis MD, said at the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery, where he presented the results during an abstract session. “Prepandemic, we used to have meetings in person; now most are on a computer screen,” a common risk factor for worsening dry eyes, he said. Telltale dry eye symptoms include blurry vision, irritation, and corneal damage – mostly caused by meibomian gland dysfunction – which impacts the quality and quantity of meibum secreted. Common treatments include warm compresses, doxycycline, and artificial tears.
While some studies have shown IPL is helpful in treating dry eye disease caused by meibomian gland dysfunction, little information is available on its use alone or in combination with topical RF to preserve and improve the function of meibomian glands, said Dr. Chelnis, an ophthalmic plastic surgeon in New York City. “The theory here is that the radiofrequency would be able to vibrate the water molecules inside the meibomian glands, which would allow you to turn over the meibum faster, as well as improve the blink reflex response by building supporting collagen,” he said. “Our novel study explores the ability of this combined modality treatment to improve upon meibomian gland health.”
Study design, results
Dr. Chelnis and his colleagues enrolled 11 individuals with a previous diagnosis of dry eye disease and meibomian gland dysfunction with Ocular Surface Disease Index (OSDI) survey scores higher than 23, which indicate at least moderate dry eye symptoms. Inclusion criteria were being 22 years of age or older, signs of meibomian gland dysfunction as detected by biomicroscopy, a modified meibomian gland score over 12 in the lower eyelid of at least one eye, and type I-IV skin.
All patients received four treatments (each 2 weeks apart) of IPL to the lower eyelid, surrounding malar region, and nose, followed by 7 minutes of topical RF treatments at 1 MHz and 4 MHz extending to the inferior, lateral, and superior orbital rim. Evaluation of meibomian gland expression and quality of meibum upon expression was conducted following each treatment session, with a final evaluation 4 weeks after the final treatment session.
Meibum quality was evaluated on a scale of 0-3 representing clear (0), cloudy (1), inspissated (2), and blocked (3) meibum, respectively.
Following treatment, meibomian gland expression and meibum quality improved in all eyelids in all 11 patients. Specifically, in the right eye, the number of upper lid expressible glands increased from an average of 13 to 27.9 and the number of lower lid expressible glands increased from an average of 14.6 to 28.2; and in the left eye, the number of upper lid expressible glands increased from an average of 13.3 to 27.3 and the number of lower lid expressible glands increased from an average of 14.8 to 26.8 (P < .001 for all associations).
The overall percentage improvement in meibomian gland expression in the right eye was 82.7% for the upper lids and 136.6% for the lower lids, and in the left eye, 82.9% for the upper lids, and 112.2% for the lower lids.
When comparing upper against lower lids, meibomian gland expression increased 124.4% and 82.8%, respectively. Meibum quality improved in all four eyelids, although upper eyelids displayed a superior improvement compared with lower eyelids.
“We are finding that combining IPL plus RF produces a more complete and comprehensive improvement in the quality of their meibomian gland health, and as such, their dry eyes,” with “a large decrease in their symptom profile,” he concluded.
More patients to be studied
Dr. Chelnis acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the small number of patients, but he and his colleagues have added an additional clinical site to expand the sample size. “Larger scale studies are needed to evaluate long-term effectiveness of IPL plus RF as well as a comparison with other treatment options.”
During a question-and-answer session Mathew M. Avram, MD, JD, director of laser, cosmetics, and dermatologic surgery at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, who served as one of the abstract session moderators, asked Dr. Chelnis to comment on what the mechanism of action of the IPL-RF combination in improving meibomian gland health.
“It’s not fully understood, but part of it is improved vascularity at the lid margin,” said Dr. Chelnis, who holds a faculty position in the department of ophthalmology at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. “Your ocular surface is sort of like your screen door; it catches everything that’s in the environment. An increase in vascularity and immunologic cytokines occurs in response to that. If you’re looking at the eye with a slit lamp, you can see a lot of vascularity that occurs at the lid margin and crowds the meibomian glands. When you decrease that crowding and immunogenic response, you move towards a normally functioning lid margin.”
Dr. Chelnis disclosed that he is a consultant to or an adviser for Lumenis, Horizon Therapeutics, and Soniquence.
PHOENIX – and improved meibum quality in both upper and lower eyelids, results from an ongoing, novel study showed.
Dry eye disease affects a large proportion of people in the United States “and the factors that contribute to that are certainly not going away,” lead study author James G. Chelnis MD, said at the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery, where he presented the results during an abstract session. “Prepandemic, we used to have meetings in person; now most are on a computer screen,” a common risk factor for worsening dry eyes, he said. Telltale dry eye symptoms include blurry vision, irritation, and corneal damage – mostly caused by meibomian gland dysfunction – which impacts the quality and quantity of meibum secreted. Common treatments include warm compresses, doxycycline, and artificial tears.
While some studies have shown IPL is helpful in treating dry eye disease caused by meibomian gland dysfunction, little information is available on its use alone or in combination with topical RF to preserve and improve the function of meibomian glands, said Dr. Chelnis, an ophthalmic plastic surgeon in New York City. “The theory here is that the radiofrequency would be able to vibrate the water molecules inside the meibomian glands, which would allow you to turn over the meibum faster, as well as improve the blink reflex response by building supporting collagen,” he said. “Our novel study explores the ability of this combined modality treatment to improve upon meibomian gland health.”
Study design, results
Dr. Chelnis and his colleagues enrolled 11 individuals with a previous diagnosis of dry eye disease and meibomian gland dysfunction with Ocular Surface Disease Index (OSDI) survey scores higher than 23, which indicate at least moderate dry eye symptoms. Inclusion criteria were being 22 years of age or older, signs of meibomian gland dysfunction as detected by biomicroscopy, a modified meibomian gland score over 12 in the lower eyelid of at least one eye, and type I-IV skin.
All patients received four treatments (each 2 weeks apart) of IPL to the lower eyelid, surrounding malar region, and nose, followed by 7 minutes of topical RF treatments at 1 MHz and 4 MHz extending to the inferior, lateral, and superior orbital rim. Evaluation of meibomian gland expression and quality of meibum upon expression was conducted following each treatment session, with a final evaluation 4 weeks after the final treatment session.
Meibum quality was evaluated on a scale of 0-3 representing clear (0), cloudy (1), inspissated (2), and blocked (3) meibum, respectively.
Following treatment, meibomian gland expression and meibum quality improved in all eyelids in all 11 patients. Specifically, in the right eye, the number of upper lid expressible glands increased from an average of 13 to 27.9 and the number of lower lid expressible glands increased from an average of 14.6 to 28.2; and in the left eye, the number of upper lid expressible glands increased from an average of 13.3 to 27.3 and the number of lower lid expressible glands increased from an average of 14.8 to 26.8 (P < .001 for all associations).
The overall percentage improvement in meibomian gland expression in the right eye was 82.7% for the upper lids and 136.6% for the lower lids, and in the left eye, 82.9% for the upper lids, and 112.2% for the lower lids.
When comparing upper against lower lids, meibomian gland expression increased 124.4% and 82.8%, respectively. Meibum quality improved in all four eyelids, although upper eyelids displayed a superior improvement compared with lower eyelids.
“We are finding that combining IPL plus RF produces a more complete and comprehensive improvement in the quality of their meibomian gland health, and as such, their dry eyes,” with “a large decrease in their symptom profile,” he concluded.
More patients to be studied
Dr. Chelnis acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the small number of patients, but he and his colleagues have added an additional clinical site to expand the sample size. “Larger scale studies are needed to evaluate long-term effectiveness of IPL plus RF as well as a comparison with other treatment options.”
During a question-and-answer session Mathew M. Avram, MD, JD, director of laser, cosmetics, and dermatologic surgery at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, who served as one of the abstract session moderators, asked Dr. Chelnis to comment on what the mechanism of action of the IPL-RF combination in improving meibomian gland health.
“It’s not fully understood, but part of it is improved vascularity at the lid margin,” said Dr. Chelnis, who holds a faculty position in the department of ophthalmology at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. “Your ocular surface is sort of like your screen door; it catches everything that’s in the environment. An increase in vascularity and immunologic cytokines occurs in response to that. If you’re looking at the eye with a slit lamp, you can see a lot of vascularity that occurs at the lid margin and crowds the meibomian glands. When you decrease that crowding and immunogenic response, you move towards a normally functioning lid margin.”
Dr. Chelnis disclosed that he is a consultant to or an adviser for Lumenis, Horizon Therapeutics, and Soniquence.
AT ASLMS 2023
Ten-year analysis finds relatively low complication rate from fractional resurfacing lasers
PHOENIX – over a decade showed.
To investigate, Dr. Hashemi, a third-year dermatology resident at Harvard University and Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and Mathew M. Avram, MD, JD, director of laser, cosmetics, and dermatologic surgery at MGH, drew from the FDA’s Manufacturer and User Facility Device Experience (MAUDE) database, which compiles medical device reports for suspected injuries from device use or malfunction and represents the largest repository of device adverse effects. Medical device reports are submitted by manufacturers, clinicians, patients, and others.
The researchers limited their query to MDRs related to ablative and nonablative fractional resurfacing lasers over the 10-year period from 2013 to 2022. The query was performed in January 2023 using a comprehensive list of product names and manufacturers.
The initial search yielded 240 MDRs, which were individually reviewed for duplicate records or insufficient data, and the final analysis included 165 MDRs. The 10 most reported adverse events were burns (30%), followed by dyspigmentation (14%), scarring (12%), other (11%), postoperative infection (8%), blisters (6%), pain (5%), hypertrophic scar (4%), post-treatment inflammation (4%), and textural changes (3%). Within the 10-year period analyzed, 56% of MDRs occurred between 2016 and 2019, with a disproportionately low percentage of MDRs occurring in 2022 (5%).
“Adverse events due to ablative and nonablative fractional resurfacing lasers are rare but potentially serious,” Dr. Hashemi concluded. “Care must be taken with counseling, patient selection, and treatment settings to optimize safety, informed consent, and patient satisfaction. Given the relatively low number of adverse events seen with fractional resurfacing lasers, factors driving their safety should be further explored.”
He added that he was surprised by the relatively low number of reported issues, referring to the total of 165 cases over 10 years. By comparison, he said, body contouring had 660 cases reported over a 7-year period in one recent study.
According to the MAUDE website, submitting MDRs to MAUDE is mandatory for manufacturers, importers, and device user facilities, and are voluntary for other groups, such as health care professionals, patients, and consumers.
Dr. Hashemi disclosed that he is a consultant for Castle Biosciences. He is also an entrepreneur in residence for Gore Range Capital.
PHOENIX – over a decade showed.
To investigate, Dr. Hashemi, a third-year dermatology resident at Harvard University and Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and Mathew M. Avram, MD, JD, director of laser, cosmetics, and dermatologic surgery at MGH, drew from the FDA’s Manufacturer and User Facility Device Experience (MAUDE) database, which compiles medical device reports for suspected injuries from device use or malfunction and represents the largest repository of device adverse effects. Medical device reports are submitted by manufacturers, clinicians, patients, and others.
The researchers limited their query to MDRs related to ablative and nonablative fractional resurfacing lasers over the 10-year period from 2013 to 2022. The query was performed in January 2023 using a comprehensive list of product names and manufacturers.
The initial search yielded 240 MDRs, which were individually reviewed for duplicate records or insufficient data, and the final analysis included 165 MDRs. The 10 most reported adverse events were burns (30%), followed by dyspigmentation (14%), scarring (12%), other (11%), postoperative infection (8%), blisters (6%), pain (5%), hypertrophic scar (4%), post-treatment inflammation (4%), and textural changes (3%). Within the 10-year period analyzed, 56% of MDRs occurred between 2016 and 2019, with a disproportionately low percentage of MDRs occurring in 2022 (5%).
“Adverse events due to ablative and nonablative fractional resurfacing lasers are rare but potentially serious,” Dr. Hashemi concluded. “Care must be taken with counseling, patient selection, and treatment settings to optimize safety, informed consent, and patient satisfaction. Given the relatively low number of adverse events seen with fractional resurfacing lasers, factors driving their safety should be further explored.”
He added that he was surprised by the relatively low number of reported issues, referring to the total of 165 cases over 10 years. By comparison, he said, body contouring had 660 cases reported over a 7-year period in one recent study.
According to the MAUDE website, submitting MDRs to MAUDE is mandatory for manufacturers, importers, and device user facilities, and are voluntary for other groups, such as health care professionals, patients, and consumers.
Dr. Hashemi disclosed that he is a consultant for Castle Biosciences. He is also an entrepreneur in residence for Gore Range Capital.
PHOENIX – over a decade showed.
To investigate, Dr. Hashemi, a third-year dermatology resident at Harvard University and Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and Mathew M. Avram, MD, JD, director of laser, cosmetics, and dermatologic surgery at MGH, drew from the FDA’s Manufacturer and User Facility Device Experience (MAUDE) database, which compiles medical device reports for suspected injuries from device use or malfunction and represents the largest repository of device adverse effects. Medical device reports are submitted by manufacturers, clinicians, patients, and others.
The researchers limited their query to MDRs related to ablative and nonablative fractional resurfacing lasers over the 10-year period from 2013 to 2022. The query was performed in January 2023 using a comprehensive list of product names and manufacturers.
The initial search yielded 240 MDRs, which were individually reviewed for duplicate records or insufficient data, and the final analysis included 165 MDRs. The 10 most reported adverse events were burns (30%), followed by dyspigmentation (14%), scarring (12%), other (11%), postoperative infection (8%), blisters (6%), pain (5%), hypertrophic scar (4%), post-treatment inflammation (4%), and textural changes (3%). Within the 10-year period analyzed, 56% of MDRs occurred between 2016 and 2019, with a disproportionately low percentage of MDRs occurring in 2022 (5%).
“Adverse events due to ablative and nonablative fractional resurfacing lasers are rare but potentially serious,” Dr. Hashemi concluded. “Care must be taken with counseling, patient selection, and treatment settings to optimize safety, informed consent, and patient satisfaction. Given the relatively low number of adverse events seen with fractional resurfacing lasers, factors driving their safety should be further explored.”
He added that he was surprised by the relatively low number of reported issues, referring to the total of 165 cases over 10 years. By comparison, he said, body contouring had 660 cases reported over a 7-year period in one recent study.
According to the MAUDE website, submitting MDRs to MAUDE is mandatory for manufacturers, importers, and device user facilities, and are voluntary for other groups, such as health care professionals, patients, and consumers.
Dr. Hashemi disclosed that he is a consultant for Castle Biosciences. He is also an entrepreneur in residence for Gore Range Capital.
AT ASLMS 2023
Poor representation of patients with darker skin phototypes in laser and light device studies
, according to a systematic review of the literature, the authors reported.
“While there broadly appears to be skin of color representation [in such studies], a more granular understanding of the data shows a large discrepancy in representation between ‘lighter’ and ‘darker’ skin of color patients,” Priya Manjaly and associates wrote in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology.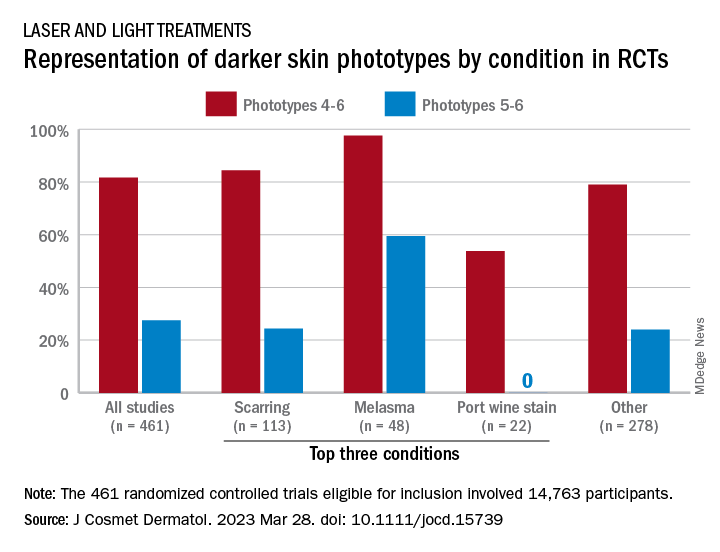
Among the 461 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) eligible for inclusion, most (81.7%) included participants with skin phototypes 4-6, which is considered skin of color. When only phototypes 5 and 6 were included, however, representation in studies involving laser and light devices was only 27.5%, said Ms. Manjaly, a research fellow in the department of dermatology at Boston University, and associates.
“This trend of excluding darker skin phototypes persisted when the results were stratified by condition, laser of study, study location, journal type, and funding source,” the investigators noted.
RCTs of laser/light devices for scarring, the most common dermatologic condition represented, included phototypes 5 and 6 in 24.4% of studies, compared with 84.4% for phototypes 4-6. The gap was smaller for melasma, but not for port wine stains. Among the devices examined, RCTs of diode lasers and intense pulsed light had the smallest gaps between inclusion of the two groups of phototypes, while pulsed-dye laser studies had the largest, they reported.
Stratification by journal showed the largest gap in studies published by Lasers in Medical Science and the smallest gap coming from Lasers in Surgery and Medicine. Funding was not specified for the majority of the eligible device RCTs, but those funded by industry had the smallest discrepancy between types 5-6 and types 4-6 and those supported by foundations/nonprofits the largest, Ms. Manjaly and associates said.
“With projections estimating that more than 50% of the U.S. population is set to identify as Hispanic or nonwhite by 2045 ... the lack of information has important consequences for clinical practice, as clinicians are unable to counsel patients on the efficacy and possible complications of various devices in patient with skin of color,” they wrote.
The investigators did not declare any conflicts of interest or funding sources.
, according to a systematic review of the literature, the authors reported.
“While there broadly appears to be skin of color representation [in such studies], a more granular understanding of the data shows a large discrepancy in representation between ‘lighter’ and ‘darker’ skin of color patients,” Priya Manjaly and associates wrote in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology.
Among the 461 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) eligible for inclusion, most (81.7%) included participants with skin phototypes 4-6, which is considered skin of color. When only phototypes 5 and 6 were included, however, representation in studies involving laser and light devices was only 27.5%, said Ms. Manjaly, a research fellow in the department of dermatology at Boston University, and associates.
“This trend of excluding darker skin phototypes persisted when the results were stratified by condition, laser of study, study location, journal type, and funding source,” the investigators noted.
RCTs of laser/light devices for scarring, the most common dermatologic condition represented, included phototypes 5 and 6 in 24.4% of studies, compared with 84.4% for phototypes 4-6. The gap was smaller for melasma, but not for port wine stains. Among the devices examined, RCTs of diode lasers and intense pulsed light had the smallest gaps between inclusion of the two groups of phototypes, while pulsed-dye laser studies had the largest, they reported.
Stratification by journal showed the largest gap in studies published by Lasers in Medical Science and the smallest gap coming from Lasers in Surgery and Medicine. Funding was not specified for the majority of the eligible device RCTs, but those funded by industry had the smallest discrepancy between types 5-6 and types 4-6 and those supported by foundations/nonprofits the largest, Ms. Manjaly and associates said.
“With projections estimating that more than 50% of the U.S. population is set to identify as Hispanic or nonwhite by 2045 ... the lack of information has important consequences for clinical practice, as clinicians are unable to counsel patients on the efficacy and possible complications of various devices in patient with skin of color,” they wrote.
The investigators did not declare any conflicts of interest or funding sources.
, according to a systematic review of the literature, the authors reported.
“While there broadly appears to be skin of color representation [in such studies], a more granular understanding of the data shows a large discrepancy in representation between ‘lighter’ and ‘darker’ skin of color patients,” Priya Manjaly and associates wrote in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology.
Among the 461 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) eligible for inclusion, most (81.7%) included participants with skin phototypes 4-6, which is considered skin of color. When only phototypes 5 and 6 were included, however, representation in studies involving laser and light devices was only 27.5%, said Ms. Manjaly, a research fellow in the department of dermatology at Boston University, and associates.
“This trend of excluding darker skin phototypes persisted when the results were stratified by condition, laser of study, study location, journal type, and funding source,” the investigators noted.
RCTs of laser/light devices for scarring, the most common dermatologic condition represented, included phototypes 5 and 6 in 24.4% of studies, compared with 84.4% for phototypes 4-6. The gap was smaller for melasma, but not for port wine stains. Among the devices examined, RCTs of diode lasers and intense pulsed light had the smallest gaps between inclusion of the two groups of phototypes, while pulsed-dye laser studies had the largest, they reported.
Stratification by journal showed the largest gap in studies published by Lasers in Medical Science and the smallest gap coming from Lasers in Surgery and Medicine. Funding was not specified for the majority of the eligible device RCTs, but those funded by industry had the smallest discrepancy between types 5-6 and types 4-6 and those supported by foundations/nonprofits the largest, Ms. Manjaly and associates said.
“With projections estimating that more than 50% of the U.S. population is set to identify as Hispanic or nonwhite by 2045 ... the lack of information has important consequences for clinical practice, as clinicians are unable to counsel patients on the efficacy and possible complications of various devices in patient with skin of color,” they wrote.
The investigators did not declare any conflicts of interest or funding sources.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF COSMETIC DERMATOLOGY
Cleansing balms
A skin care trend, particularly in the Korean beauty product market and now worldwide, cleansing balms are a soft, yet solid variation of an oil-based cleanser. The solid oily component is combined with a surfactant or emulsifier. The cream balm texture melts into more of an oil texture once warmed with fingertips and applied to facial skin. The oils are effective at breaking down or attracting skin care products, oil, and grime on the skin surface. Once warm water is added, the oil emulsifies, and after it is wiped or rinsed off, what’s left behind is clean, hydrated skin.
They don’t tend to compromise the moisture barrier or disrupt skin pH, thus, resulting in less dry skin and have less potential to cause irritation. These products are particularly useful during drier, colder months, or in dry climates, and for those who have dry skin or eczema.
The popularity of cleansing balms has largely been based on their ability to remove makeup, similar to an oil cleanser, without the need to necessarily “double cleanse” with a regular cleanser afterward.
Alternatives to remove makeup besides cleansing balms, oil cleansers, and regular liquid water-based cleansers include micellar water (oil in water), chemical makeup removing cloths, and nonchemical makeup removing pads used with water. Micellar water is also gentle on the skin; it requires a cotton pad, tip, or cloth to remove makeup, without the need for water or washing. Both are effective, but it may be easier to remove makeup with cleansing balms, without the need for rubbing dry skin, than with micellar water. A study published in 2020 of 20 individuals reported that waterproof sunscreen was more effectively removed with a cleansing oil than a non–oil-based cleanser, with less irritation and dryness. Both were effective at removing non-waterproof sunscreen.
Both cleansing balms and oil-based cleansers need to be kept at room temperature (not in the refrigerator), since they may separate or solidify at low temperatures.
Most cleansing balms can be applied to dry skin, massaged, and rinsed off with warm water, but they are sometimes easier to remove with a wet cloth (typically either cotton or muslin). Many are nonirritating to the eyes, which is important when used to remove eye makeup and mascara on delicate skin. While many cleansing balms are noncomedogenic, residue from balms that are too thick or not rinsed off properly can contribute to comedones or milia. If residue is present after use, then “double-cleansing” with a water-based cleanser is reasonable, but not necessary for most users.
Did the development of Ponds cold cream mark the beginning of this trend? Yes and no. The creation of the first cold cream prototype has been attributed to the Greek physician, Galen (who lived in Rome), a combination of rose water, beeswax, and olive oil in 150 CE. While Ponds also has manufactured a cleansing balm, the original cold cream is a 50% moisturizer in a cleanser. So while similar in containing an oil, water, emulsifier, and thickener, and effective, it is more of a moisturizer and less of a solid oil/balm in its consistency.
Dr. Wesley practices dermatology in Beverly Hills, Calif. Write to her at dermnews@mdedge.com. She had no relevant disclosures.
A skin care trend, particularly in the Korean beauty product market and now worldwide, cleansing balms are a soft, yet solid variation of an oil-based cleanser. The solid oily component is combined with a surfactant or emulsifier. The cream balm texture melts into more of an oil texture once warmed with fingertips and applied to facial skin. The oils are effective at breaking down or attracting skin care products, oil, and grime on the skin surface. Once warm water is added, the oil emulsifies, and after it is wiped or rinsed off, what’s left behind is clean, hydrated skin.
They don’t tend to compromise the moisture barrier or disrupt skin pH, thus, resulting in less dry skin and have less potential to cause irritation. These products are particularly useful during drier, colder months, or in dry climates, and for those who have dry skin or eczema.
The popularity of cleansing balms has largely been based on their ability to remove makeup, similar to an oil cleanser, without the need to necessarily “double cleanse” with a regular cleanser afterward.
Alternatives to remove makeup besides cleansing balms, oil cleansers, and regular liquid water-based cleansers include micellar water (oil in water), chemical makeup removing cloths, and nonchemical makeup removing pads used with water. Micellar water is also gentle on the skin; it requires a cotton pad, tip, or cloth to remove makeup, without the need for water or washing. Both are effective, but it may be easier to remove makeup with cleansing balms, without the need for rubbing dry skin, than with micellar water. A study published in 2020 of 20 individuals reported that waterproof sunscreen was more effectively removed with a cleansing oil than a non–oil-based cleanser, with less irritation and dryness. Both were effective at removing non-waterproof sunscreen.
Both cleansing balms and oil-based cleansers need to be kept at room temperature (not in the refrigerator), since they may separate or solidify at low temperatures.
Most cleansing balms can be applied to dry skin, massaged, and rinsed off with warm water, but they are sometimes easier to remove with a wet cloth (typically either cotton or muslin). Many are nonirritating to the eyes, which is important when used to remove eye makeup and mascara on delicate skin. While many cleansing balms are noncomedogenic, residue from balms that are too thick or not rinsed off properly can contribute to comedones or milia. If residue is present after use, then “double-cleansing” with a water-based cleanser is reasonable, but not necessary for most users.
Did the development of Ponds cold cream mark the beginning of this trend? Yes and no. The creation of the first cold cream prototype has been attributed to the Greek physician, Galen (who lived in Rome), a combination of rose water, beeswax, and olive oil in 150 CE. While Ponds also has manufactured a cleansing balm, the original cold cream is a 50% moisturizer in a cleanser. So while similar in containing an oil, water, emulsifier, and thickener, and effective, it is more of a moisturizer and less of a solid oil/balm in its consistency.
Dr. Wesley practices dermatology in Beverly Hills, Calif. Write to her at dermnews@mdedge.com. She had no relevant disclosures.
A skin care trend, particularly in the Korean beauty product market and now worldwide, cleansing balms are a soft, yet solid variation of an oil-based cleanser. The solid oily component is combined with a surfactant or emulsifier. The cream balm texture melts into more of an oil texture once warmed with fingertips and applied to facial skin. The oils are effective at breaking down or attracting skin care products, oil, and grime on the skin surface. Once warm water is added, the oil emulsifies, and after it is wiped or rinsed off, what’s left behind is clean, hydrated skin.
They don’t tend to compromise the moisture barrier or disrupt skin pH, thus, resulting in less dry skin and have less potential to cause irritation. These products are particularly useful during drier, colder months, or in dry climates, and for those who have dry skin or eczema.
The popularity of cleansing balms has largely been based on their ability to remove makeup, similar to an oil cleanser, without the need to necessarily “double cleanse” with a regular cleanser afterward.
Alternatives to remove makeup besides cleansing balms, oil cleansers, and regular liquid water-based cleansers include micellar water (oil in water), chemical makeup removing cloths, and nonchemical makeup removing pads used with water. Micellar water is also gentle on the skin; it requires a cotton pad, tip, or cloth to remove makeup, without the need for water or washing. Both are effective, but it may be easier to remove makeup with cleansing balms, without the need for rubbing dry skin, than with micellar water. A study published in 2020 of 20 individuals reported that waterproof sunscreen was more effectively removed with a cleansing oil than a non–oil-based cleanser, with less irritation and dryness. Both were effective at removing non-waterproof sunscreen.
Both cleansing balms and oil-based cleansers need to be kept at room temperature (not in the refrigerator), since they may separate or solidify at low temperatures.
Most cleansing balms can be applied to dry skin, massaged, and rinsed off with warm water, but they are sometimes easier to remove with a wet cloth (typically either cotton or muslin). Many are nonirritating to the eyes, which is important when used to remove eye makeup and mascara on delicate skin. While many cleansing balms are noncomedogenic, residue from balms that are too thick or not rinsed off properly can contribute to comedones or milia. If residue is present after use, then “double-cleansing” with a water-based cleanser is reasonable, but not necessary for most users.
Did the development of Ponds cold cream mark the beginning of this trend? Yes and no. The creation of the first cold cream prototype has been attributed to the Greek physician, Galen (who lived in Rome), a combination of rose water, beeswax, and olive oil in 150 CE. While Ponds also has manufactured a cleansing balm, the original cold cream is a 50% moisturizer in a cleanser. So while similar in containing an oil, water, emulsifier, and thickener, and effective, it is more of a moisturizer and less of a solid oil/balm in its consistency.
Dr. Wesley practices dermatology in Beverly Hills, Calif. Write to her at dermnews@mdedge.com. She had no relevant disclosures.
Bergamot
Citrus bergamia (bergamot) is a fruit tree thought to originate in the Mediterranean area; its fruit has been a part of the diet in that region since the early 18th century.1 Bergamot is known to confer antioxidant as well as anti-inflammatory activity, and yields proapoptotic effects in the sebaceous gland.2,3 The plant contains the natural furocoumarin bergapten, which is also known as 5-methoxypsoralen.4
5 In this capacity, bergamot oil has been used for photodynamic therapy of cutaneous conditions such as vitiligo.6 In fact, for several years 5-methoxypsoralen and 8-methoxypsoralen have been used to achieve acceptable clearance rates of psoriasis and vitiligo.7 This column focuses on bergapten, as well as the cutaneous conditions for which bergamot has been shown to have some benefits warranting application or further investigation.
Bergapten
In a 2021 literature review, Liang et al. cited the anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, anticancer, and other salutary effects associated with bergapten. Based on numerous citations, they also cautioned about the phototoxicity of the compound combined with ultraviolet (UV) light while noting the photoactivation of bergapten for anticancer uses.4
The following year, Quetglas-Llabrés et al. acknowledged, in another literature review, the numerous preclinical and in vitro studies demonstrating the therapeutic activity of bergapten and highlighted clinical trials revealing notable lesion clearance rates of psoriasis or vitiligo imparted by oral or topical bergapten along with UV irradiation. Bergapten was also found to be effective as hypolipemic therapy.5
Anti-inflammatory topical uses
In a 2017 study by Han et al. of 10 essential oils, bergamot was among the investigated oils, all of which exhibited significant anti-proliferative activity in a preinflamed human dermal fibroblast system simulating chronic inflammation. Bergamot was among three essential oils that also suppressed protein molecules involved with inflammation, immune responses, and tissue remodeling, indicating anti-inflammatory and wound healing characteristics.8
More recently, Cristiano et al. reported that ultradeformable nanocarriers containing bergamot essential oil and ammonium glycyrrhizinate were demonstrated in healthy human volunteers to be characterized by the appropriate mean size, size distribution, surface charge, and long-term stability for topical administration. Topical administration on human volunteers also revealed greater activity of the combined agents as compared with a nanosystem loaded only with ammonium glycyrrhizinate. The researchers concluded that this combination of ingredients in ultradeformable vesicles shows potential as topical anti-inflammatory treatment.3
Acne
In a 2020 study using golden hamsters, Sun et al. assessed the effects of the juice and essential oils of bergamot and sweet orange on acne vulgaris engendered by excessive androgen secretion. Among 80 male hamsters randomly divided into 10 groups ranging from low to high doses, all results demonstrated improvement with treatment as seen by decreased growth rates of sebaceous glands, suppressed triglyceride accumulation, lowered inflammatory cytokine release, and apoptosis promotion in sebaceous glands. The authors noted that the essential oils yielded better dose-dependent effects than the juices.2
Psoriasis
In 2019, Perna et al. conducted a literature review on the effects of bergamot essential oil, extract, juice, and polyphenolic fraction on various health metrics. Thirty-one studies (20 involving humans with 1,709 subjects and 11 in rats and mice) were identified. Animal models indicated that bergamot essential oil (10 mg/kg or 20 mg/kg daily for 20 weeks) reduced psoriatic plaques, increased skin collagen content, and fostered hair growth and that bergamot juice (20 mg/kg) diminished proinflammatory cytokines. Human studies showed that bergamot extract and essential oil may reduce blood pressure and improve mental conditions.9
Vitiligo
In 2019, Shaaban et al. prepared elastic nanocarriers (spanlastics) to deliver psoralen-containing bergamot oil along with PUVB with the intention of harnessing melanogenic activity to treat vitiligo. Histopathologic assessment on rat skin was conducted before clinical treatment in patients with vitiligo. The spanlastics were deemed to be of suitable nanosize and deformable, yielding consistent bergamot oil release. The bergamot oil included in the nanocarrier was found to enhance photostability and photodynamic activity, with the researchers concluding that bergamot oil nanospanlastics with psoralen-UVB therapy shows potential as a vitiligo therapy.10
Two years later, Shaaban evaluated bergamot oil formulated in nanostructured lipid carriers as a photosensitizer for photodynamic treatment of vitiligo. The botanical oil was effectively used in the nanostructured lipid carriers with a gel consistency that delivered sustained release of the oil for 24 hours. Preclinical and clinical results in patients were encouraging for the topical photodynamic treatment of vitiligo, with the nanostructured lipid carriers improving the photostability and photodynamic activity of bergamot oil.6
Photoaging, photoprotection, and safety concerns
Three decades ago, an international cooperative study of the photophysical, photomutagenic, and photocarcinogenic characteristics of bergamot oil and the effect of UVA and UVB sunscreens found that UVB and UVA sunscreens at low concentration (0.5%-1%) in perfumes could not inhibit the phototoxicity of bergamot oil on human skin.11
In a 2015 study assessing the impact of 38% bergamot polyphenolic fraction (a highly concentrated Citrus bergamia fruit extract) on UVB-generated photoaging, Nisticò et al. found that the bergamot compound dose-dependently protected HaCaT cells against UVB-caused oxidative stress and photoaging markers. Suggesting that the high-antioxidant bergamot polyphenolic fraction has potential for use in skin care formulations, the researchers added that the extract seems to induce antiproliferative, immune-modulating, and antiaging activity.12In 2022, Alexa et al. performed in vitro tests and found that natural preparations containing bergamot, orange, and clove essential oils do not significantly alter physiological skin parameters and were deemed safe for topical use. An emulsion with bergamot essential oil was also found to reduce the viability of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells.13
Conclusion
As a photosensitizing agent, bergamot has an established role in skin care. Beyond its niche role in treatments for vitiligo and psoriasis, this botanical product appears to show potential as an anti-inflammatory agent as well as an ingredient to combat photoaging and skin cancer. Much more research is needed to elucidate the possible wider benefits of this Mediterranean staple.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur in Miami. She founded the division of cosmetic dermatology at the University of Miami in 1997. The third edition of her bestselling textbook, “Cosmetic Dermatology,” was published in 2022. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Johnson & Johnson, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions Inc., a SaaS company used to generate skin care routines in office and as an ecommerce solution. Write to her at dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Juber M. Health benefits of bergamot. WebMD. November 29, 2022. Accessed March 21, 2023.
2. Sun P et al. Mediators Inflamm. 2020 Oct 6;2020:8868107.
3. Cristiano MC et al. Biomedicines. 2022 Apr 30;10(5):1039.
4. Liang Y et al. Phytother Res. 2021 Nov;35(11):6131-47.
5. Quetglas-Llabrés MM et al. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Apr 25;2022:8615242.
6. Shaaban M et al. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2021 Jan;18(1):139-50.
7. McNeely W, Goa KL. Drugs. 1998 Oct;56(4):667-90.
8. Han X, Beaumont C, Stevens N. Biochim Open. 2017 Apr 26;5:1-7.
9. Perna S et al. Food Sci Nutr. 2019 Jan 25;7(2):369-84.
10. Shaaban M et al. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2019 Dec;9(6):1106-16.
11. Dubertret L et al. J Photochem Photobiol B. 1990 Nov;7(2-4):251-9.
12. Nisticò S et al. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2015 Jul-Sep;29(3):723-8.
13. Alexa VT et al. Molecules. 2022 Feb 1;27(3):990.
Citrus bergamia (bergamot) is a fruit tree thought to originate in the Mediterranean area; its fruit has been a part of the diet in that region since the early 18th century.1 Bergamot is known to confer antioxidant as well as anti-inflammatory activity, and yields proapoptotic effects in the sebaceous gland.2,3 The plant contains the natural furocoumarin bergapten, which is also known as 5-methoxypsoralen.4
5 In this capacity, bergamot oil has been used for photodynamic therapy of cutaneous conditions such as vitiligo.6 In fact, for several years 5-methoxypsoralen and 8-methoxypsoralen have been used to achieve acceptable clearance rates of psoriasis and vitiligo.7 This column focuses on bergapten, as well as the cutaneous conditions for which bergamot has been shown to have some benefits warranting application or further investigation.
Bergapten
In a 2021 literature review, Liang et al. cited the anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, anticancer, and other salutary effects associated with bergapten. Based on numerous citations, they also cautioned about the phototoxicity of the compound combined with ultraviolet (UV) light while noting the photoactivation of bergapten for anticancer uses.4
The following year, Quetglas-Llabrés et al. acknowledged, in another literature review, the numerous preclinical and in vitro studies demonstrating the therapeutic activity of bergapten and highlighted clinical trials revealing notable lesion clearance rates of psoriasis or vitiligo imparted by oral or topical bergapten along with UV irradiation. Bergapten was also found to be effective as hypolipemic therapy.5
Anti-inflammatory topical uses
In a 2017 study by Han et al. of 10 essential oils, bergamot was among the investigated oils, all of which exhibited significant anti-proliferative activity in a preinflamed human dermal fibroblast system simulating chronic inflammation. Bergamot was among three essential oils that also suppressed protein molecules involved with inflammation, immune responses, and tissue remodeling, indicating anti-inflammatory and wound healing characteristics.8
More recently, Cristiano et al. reported that ultradeformable nanocarriers containing bergamot essential oil and ammonium glycyrrhizinate were demonstrated in healthy human volunteers to be characterized by the appropriate mean size, size distribution, surface charge, and long-term stability for topical administration. Topical administration on human volunteers also revealed greater activity of the combined agents as compared with a nanosystem loaded only with ammonium glycyrrhizinate. The researchers concluded that this combination of ingredients in ultradeformable vesicles shows potential as topical anti-inflammatory treatment.3
Acne
In a 2020 study using golden hamsters, Sun et al. assessed the effects of the juice and essential oils of bergamot and sweet orange on acne vulgaris engendered by excessive androgen secretion. Among 80 male hamsters randomly divided into 10 groups ranging from low to high doses, all results demonstrated improvement with treatment as seen by decreased growth rates of sebaceous glands, suppressed triglyceride accumulation, lowered inflammatory cytokine release, and apoptosis promotion in sebaceous glands. The authors noted that the essential oils yielded better dose-dependent effects than the juices.2
Psoriasis
In 2019, Perna et al. conducted a literature review on the effects of bergamot essential oil, extract, juice, and polyphenolic fraction on various health metrics. Thirty-one studies (20 involving humans with 1,709 subjects and 11 in rats and mice) were identified. Animal models indicated that bergamot essential oil (10 mg/kg or 20 mg/kg daily for 20 weeks) reduced psoriatic plaques, increased skin collagen content, and fostered hair growth and that bergamot juice (20 mg/kg) diminished proinflammatory cytokines. Human studies showed that bergamot extract and essential oil may reduce blood pressure and improve mental conditions.9
Vitiligo
In 2019, Shaaban et al. prepared elastic nanocarriers (spanlastics) to deliver psoralen-containing bergamot oil along with PUVB with the intention of harnessing melanogenic activity to treat vitiligo. Histopathologic assessment on rat skin was conducted before clinical treatment in patients with vitiligo. The spanlastics were deemed to be of suitable nanosize and deformable, yielding consistent bergamot oil release. The bergamot oil included in the nanocarrier was found to enhance photostability and photodynamic activity, with the researchers concluding that bergamot oil nanospanlastics with psoralen-UVB therapy shows potential as a vitiligo therapy.10
Two years later, Shaaban evaluated bergamot oil formulated in nanostructured lipid carriers as a photosensitizer for photodynamic treatment of vitiligo. The botanical oil was effectively used in the nanostructured lipid carriers with a gel consistency that delivered sustained release of the oil for 24 hours. Preclinical and clinical results in patients were encouraging for the topical photodynamic treatment of vitiligo, with the nanostructured lipid carriers improving the photostability and photodynamic activity of bergamot oil.6
Photoaging, photoprotection, and safety concerns
Three decades ago, an international cooperative study of the photophysical, photomutagenic, and photocarcinogenic characteristics of bergamot oil and the effect of UVA and UVB sunscreens found that UVB and UVA sunscreens at low concentration (0.5%-1%) in perfumes could not inhibit the phototoxicity of bergamot oil on human skin.11
In a 2015 study assessing the impact of 38% bergamot polyphenolic fraction (a highly concentrated Citrus bergamia fruit extract) on UVB-generated photoaging, Nisticò et al. found that the bergamot compound dose-dependently protected HaCaT cells against UVB-caused oxidative stress and photoaging markers. Suggesting that the high-antioxidant bergamot polyphenolic fraction has potential for use in skin care formulations, the researchers added that the extract seems to induce antiproliferative, immune-modulating, and antiaging activity.12In 2022, Alexa et al. performed in vitro tests and found that natural preparations containing bergamot, orange, and clove essential oils do not significantly alter physiological skin parameters and were deemed safe for topical use. An emulsion with bergamot essential oil was also found to reduce the viability of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells.13
Conclusion
As a photosensitizing agent, bergamot has an established role in skin care. Beyond its niche role in treatments for vitiligo and psoriasis, this botanical product appears to show potential as an anti-inflammatory agent as well as an ingredient to combat photoaging and skin cancer. Much more research is needed to elucidate the possible wider benefits of this Mediterranean staple.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur in Miami. She founded the division of cosmetic dermatology at the University of Miami in 1997. The third edition of her bestselling textbook, “Cosmetic Dermatology,” was published in 2022. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Johnson & Johnson, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions Inc., a SaaS company used to generate skin care routines in office and as an ecommerce solution. Write to her at dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Juber M. Health benefits of bergamot. WebMD. November 29, 2022. Accessed March 21, 2023.
2. Sun P et al. Mediators Inflamm. 2020 Oct 6;2020:8868107.
3. Cristiano MC et al. Biomedicines. 2022 Apr 30;10(5):1039.
4. Liang Y et al. Phytother Res. 2021 Nov;35(11):6131-47.
5. Quetglas-Llabrés MM et al. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Apr 25;2022:8615242.
6. Shaaban M et al. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2021 Jan;18(1):139-50.
7. McNeely W, Goa KL. Drugs. 1998 Oct;56(4):667-90.
8. Han X, Beaumont C, Stevens N. Biochim Open. 2017 Apr 26;5:1-7.
9. Perna S et al. Food Sci Nutr. 2019 Jan 25;7(2):369-84.
10. Shaaban M et al. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2019 Dec;9(6):1106-16.
11. Dubertret L et al. J Photochem Photobiol B. 1990 Nov;7(2-4):251-9.
12. Nisticò S et al. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2015 Jul-Sep;29(3):723-8.
13. Alexa VT et al. Molecules. 2022 Feb 1;27(3):990.
Citrus bergamia (bergamot) is a fruit tree thought to originate in the Mediterranean area; its fruit has been a part of the diet in that region since the early 18th century.1 Bergamot is known to confer antioxidant as well as anti-inflammatory activity, and yields proapoptotic effects in the sebaceous gland.2,3 The plant contains the natural furocoumarin bergapten, which is also known as 5-methoxypsoralen.4
5 In this capacity, bergamot oil has been used for photodynamic therapy of cutaneous conditions such as vitiligo.6 In fact, for several years 5-methoxypsoralen and 8-methoxypsoralen have been used to achieve acceptable clearance rates of psoriasis and vitiligo.7 This column focuses on bergapten, as well as the cutaneous conditions for which bergamot has been shown to have some benefits warranting application or further investigation.
Bergapten
In a 2021 literature review, Liang et al. cited the anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, anticancer, and other salutary effects associated with bergapten. Based on numerous citations, they also cautioned about the phototoxicity of the compound combined with ultraviolet (UV) light while noting the photoactivation of bergapten for anticancer uses.4
The following year, Quetglas-Llabrés et al. acknowledged, in another literature review, the numerous preclinical and in vitro studies demonstrating the therapeutic activity of bergapten and highlighted clinical trials revealing notable lesion clearance rates of psoriasis or vitiligo imparted by oral or topical bergapten along with UV irradiation. Bergapten was also found to be effective as hypolipemic therapy.5
Anti-inflammatory topical uses
In a 2017 study by Han et al. of 10 essential oils, bergamot was among the investigated oils, all of which exhibited significant anti-proliferative activity in a preinflamed human dermal fibroblast system simulating chronic inflammation. Bergamot was among three essential oils that also suppressed protein molecules involved with inflammation, immune responses, and tissue remodeling, indicating anti-inflammatory and wound healing characteristics.8
More recently, Cristiano et al. reported that ultradeformable nanocarriers containing bergamot essential oil and ammonium glycyrrhizinate were demonstrated in healthy human volunteers to be characterized by the appropriate mean size, size distribution, surface charge, and long-term stability for topical administration. Topical administration on human volunteers also revealed greater activity of the combined agents as compared with a nanosystem loaded only with ammonium glycyrrhizinate. The researchers concluded that this combination of ingredients in ultradeformable vesicles shows potential as topical anti-inflammatory treatment.3
Acne
In a 2020 study using golden hamsters, Sun et al. assessed the effects of the juice and essential oils of bergamot and sweet orange on acne vulgaris engendered by excessive androgen secretion. Among 80 male hamsters randomly divided into 10 groups ranging from low to high doses, all results demonstrated improvement with treatment as seen by decreased growth rates of sebaceous glands, suppressed triglyceride accumulation, lowered inflammatory cytokine release, and apoptosis promotion in sebaceous glands. The authors noted that the essential oils yielded better dose-dependent effects than the juices.2
Psoriasis
In 2019, Perna et al. conducted a literature review on the effects of bergamot essential oil, extract, juice, and polyphenolic fraction on various health metrics. Thirty-one studies (20 involving humans with 1,709 subjects and 11 in rats and mice) were identified. Animal models indicated that bergamot essential oil (10 mg/kg or 20 mg/kg daily for 20 weeks) reduced psoriatic plaques, increased skin collagen content, and fostered hair growth and that bergamot juice (20 mg/kg) diminished proinflammatory cytokines. Human studies showed that bergamot extract and essential oil may reduce blood pressure and improve mental conditions.9
Vitiligo
In 2019, Shaaban et al. prepared elastic nanocarriers (spanlastics) to deliver psoralen-containing bergamot oil along with PUVB with the intention of harnessing melanogenic activity to treat vitiligo. Histopathologic assessment on rat skin was conducted before clinical treatment in patients with vitiligo. The spanlastics were deemed to be of suitable nanosize and deformable, yielding consistent bergamot oil release. The bergamot oil included in the nanocarrier was found to enhance photostability and photodynamic activity, with the researchers concluding that bergamot oil nanospanlastics with psoralen-UVB therapy shows potential as a vitiligo therapy.10
Two years later, Shaaban evaluated bergamot oil formulated in nanostructured lipid carriers as a photosensitizer for photodynamic treatment of vitiligo. The botanical oil was effectively used in the nanostructured lipid carriers with a gel consistency that delivered sustained release of the oil for 24 hours. Preclinical and clinical results in patients were encouraging for the topical photodynamic treatment of vitiligo, with the nanostructured lipid carriers improving the photostability and photodynamic activity of bergamot oil.6
Photoaging, photoprotection, and safety concerns
Three decades ago, an international cooperative study of the photophysical, photomutagenic, and photocarcinogenic characteristics of bergamot oil and the effect of UVA and UVB sunscreens found that UVB and UVA sunscreens at low concentration (0.5%-1%) in perfumes could not inhibit the phototoxicity of bergamot oil on human skin.11
In a 2015 study assessing the impact of 38% bergamot polyphenolic fraction (a highly concentrated Citrus bergamia fruit extract) on UVB-generated photoaging, Nisticò et al. found that the bergamot compound dose-dependently protected HaCaT cells against UVB-caused oxidative stress and photoaging markers. Suggesting that the high-antioxidant bergamot polyphenolic fraction has potential for use in skin care formulations, the researchers added that the extract seems to induce antiproliferative, immune-modulating, and antiaging activity.12In 2022, Alexa et al. performed in vitro tests and found that natural preparations containing bergamot, orange, and clove essential oils do not significantly alter physiological skin parameters and were deemed safe for topical use. An emulsion with bergamot essential oil was also found to reduce the viability of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells.13
Conclusion
As a photosensitizing agent, bergamot has an established role in skin care. Beyond its niche role in treatments for vitiligo and psoriasis, this botanical product appears to show potential as an anti-inflammatory agent as well as an ingredient to combat photoaging and skin cancer. Much more research is needed to elucidate the possible wider benefits of this Mediterranean staple.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur in Miami. She founded the division of cosmetic dermatology at the University of Miami in 1997. The third edition of her bestselling textbook, “Cosmetic Dermatology,” was published in 2022. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Johnson & Johnson, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions Inc., a SaaS company used to generate skin care routines in office and as an ecommerce solution. Write to her at dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Juber M. Health benefits of bergamot. WebMD. November 29, 2022. Accessed March 21, 2023.
2. Sun P et al. Mediators Inflamm. 2020 Oct 6;2020:8868107.
3. Cristiano MC et al. Biomedicines. 2022 Apr 30;10(5):1039.
4. Liang Y et al. Phytother Res. 2021 Nov;35(11):6131-47.
5. Quetglas-Llabrés MM et al. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Apr 25;2022:8615242.
6. Shaaban M et al. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2021 Jan;18(1):139-50.
7. McNeely W, Goa KL. Drugs. 1998 Oct;56(4):667-90.
8. Han X, Beaumont C, Stevens N. Biochim Open. 2017 Apr 26;5:1-7.
9. Perna S et al. Food Sci Nutr. 2019 Jan 25;7(2):369-84.
10. Shaaban M et al. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2019 Dec;9(6):1106-16.
11. Dubertret L et al. J Photochem Photobiol B. 1990 Nov;7(2-4):251-9.
12. Nisticò S et al. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2015 Jul-Sep;29(3):723-8.
13. Alexa VT et al. Molecules. 2022 Feb 1;27(3):990.
What happens to melanocytic nevi during laser hair removal?
PHOENIX – , while common histologic changes include mild atypia and thermal damage, according to results from a systematic review of literature on the topic. To date, no severe cases of severe dysplasia or melanoma have been reported.
“That’s reassuring,” study author Ahuva Cices, MD, said in an interview at the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery, where she presented the results during an abstract session. “But, with that in mind, we want to avoid treating nevi with laser hair removal to avoid changes that could be concerning. We also recommend baseline skin exams so we know what we’re looking at before we start treating with lasers, and any changes can be recognized from that baseline status. It’s important to keep an eye out for changes and always be evaluating.”
In December of 2022, Dr. Cices, chief dermatology resident at Mount Sinai Health System, New York, searched PubMed for articles that evaluated changes in melanocytic nevi after laser hair removal procedures. She used the search terms “nevi laser hair removal,” “nevi diode,” “nevi long pulse alexandrite,” “nevi long pulse neodymium doped yttrium aluminum garnet,” and “melanoma laser hair removal,” and limited the analysis to English language patient-based reports that discussed incidental treatment of melanocytic nevi while undergoing hair removal with a laser.
Reports excluded from the analysis were those that focused on changes following hair removal with nonlaser devices such as intense pulsed light (IPL), those evaluating nonmelanocytic nevi such as Becker’s nevus or nevus of Ota, and those evaluating the intentional ablation or removal of melanocytic lesions.
The search yielded 10 relevant studies for systematic review: seven case reports or series and three observational trials, two of which were prospective and one retrospective.
The results of the review, according to Dr. Cices, revealed that clinical and dermoscopic changes were noted to present as early as 15 days after treatment and persist to the maximum follow up time, at 3 years. Commonly reported changes included regression, decreased size, laser-induced asymmetry, bleaching, darkening, and altered pattern on dermoscopy. Histologic changes included mild atypia, thermal damage, scar formation, and regression.
“Although some of the clinical and dermoscopic alterations may be concerning for malignancy, to our knowledge, there are no documented cases of malignant transformation of nevi following treatment with laser hair removal,” she wrote in the abstract.
Dr. Cices acknowledged certain limitations of the systematic review, including the low number of relevant reports and their generally small sample size, many of which were limited to single cases.
Omar A. Ibrahimi, MD, PhD, medical director of the Connecticut Skin Institute, Stamford, who was asked to comment on the review, characterized the findings as important because laser hair removal is such a commonly performed procedure.
While the study is limited by the small number of studies on the subject matter, “it brings up an important discussion,” Dr. Ibrahimi said in an interview. “Generally speaking, we know that most hair removal lasers do indeed target melanin pigment and can be absorbed by melanocytes. While the wavelengths used for LHR [laser hair removal] will not result in DNA damage or cause mutations that can lead to melanoma, they can sometimes alter the appearance of pigmented lesions and that may change the dermatologist’s ability to monitor them for atypia,” he noted.
“For that reason, I would recommend all patients see a dermatologist for evaluation of their nevi prior to any treatments and they consider very carefully where they get their laser treatments. If they have any atypical pigmented lesions, then that information should be disclosed with the person performing the laser hair removal procedure particularly if there are lesions that are being specifically monitored.”
Dr. Cices reported having no disclosures. Dr. Ibrahimi disclosed that he is a member of the advisory board for Accure Acne, AbbVie, Cutera, Lutronic, Blueberry Therapeutics, Cytrellis, and Quthero. He also holds stock in many device and pharmaceutical companies.
PHOENIX – , while common histologic changes include mild atypia and thermal damage, according to results from a systematic review of literature on the topic. To date, no severe cases of severe dysplasia or melanoma have been reported.
“That’s reassuring,” study author Ahuva Cices, MD, said in an interview at the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery, where she presented the results during an abstract session. “But, with that in mind, we want to avoid treating nevi with laser hair removal to avoid changes that could be concerning. We also recommend baseline skin exams so we know what we’re looking at before we start treating with lasers, and any changes can be recognized from that baseline status. It’s important to keep an eye out for changes and always be evaluating.”
In December of 2022, Dr. Cices, chief dermatology resident at Mount Sinai Health System, New York, searched PubMed for articles that evaluated changes in melanocytic nevi after laser hair removal procedures. She used the search terms “nevi laser hair removal,” “nevi diode,” “nevi long pulse alexandrite,” “nevi long pulse neodymium doped yttrium aluminum garnet,” and “melanoma laser hair removal,” and limited the analysis to English language patient-based reports that discussed incidental treatment of melanocytic nevi while undergoing hair removal with a laser.
Reports excluded from the analysis were those that focused on changes following hair removal with nonlaser devices such as intense pulsed light (IPL), those evaluating nonmelanocytic nevi such as Becker’s nevus or nevus of Ota, and those evaluating the intentional ablation or removal of melanocytic lesions.
The search yielded 10 relevant studies for systematic review: seven case reports or series and three observational trials, two of which were prospective and one retrospective.
The results of the review, according to Dr. Cices, revealed that clinical and dermoscopic changes were noted to present as early as 15 days after treatment and persist to the maximum follow up time, at 3 years. Commonly reported changes included regression, decreased size, laser-induced asymmetry, bleaching, darkening, and altered pattern on dermoscopy. Histologic changes included mild atypia, thermal damage, scar formation, and regression.
“Although some of the clinical and dermoscopic alterations may be concerning for malignancy, to our knowledge, there are no documented cases of malignant transformation of nevi following treatment with laser hair removal,” she wrote in the abstract.
Dr. Cices acknowledged certain limitations of the systematic review, including the low number of relevant reports and their generally small sample size, many of which were limited to single cases.
Omar A. Ibrahimi, MD, PhD, medical director of the Connecticut Skin Institute, Stamford, who was asked to comment on the review, characterized the findings as important because laser hair removal is such a commonly performed procedure.
While the study is limited by the small number of studies on the subject matter, “it brings up an important discussion,” Dr. Ibrahimi said in an interview. “Generally speaking, we know that most hair removal lasers do indeed target melanin pigment and can be absorbed by melanocytes. While the wavelengths used for LHR [laser hair removal] will not result in DNA damage or cause mutations that can lead to melanoma, they can sometimes alter the appearance of pigmented lesions and that may change the dermatologist’s ability to monitor them for atypia,” he noted.
“For that reason, I would recommend all patients see a dermatologist for evaluation of their nevi prior to any treatments and they consider very carefully where they get their laser treatments. If they have any atypical pigmented lesions, then that information should be disclosed with the person performing the laser hair removal procedure particularly if there are lesions that are being specifically monitored.”
Dr. Cices reported having no disclosures. Dr. Ibrahimi disclosed that he is a member of the advisory board for Accure Acne, AbbVie, Cutera, Lutronic, Blueberry Therapeutics, Cytrellis, and Quthero. He also holds stock in many device and pharmaceutical companies.
PHOENIX – , while common histologic changes include mild atypia and thermal damage, according to results from a systematic review of literature on the topic. To date, no severe cases of severe dysplasia or melanoma have been reported.
“That’s reassuring,” study author Ahuva Cices, MD, said in an interview at the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery, where she presented the results during an abstract session. “But, with that in mind, we want to avoid treating nevi with laser hair removal to avoid changes that could be concerning. We also recommend baseline skin exams so we know what we’re looking at before we start treating with lasers, and any changes can be recognized from that baseline status. It’s important to keep an eye out for changes and always be evaluating.”
In December of 2022, Dr. Cices, chief dermatology resident at Mount Sinai Health System, New York, searched PubMed for articles that evaluated changes in melanocytic nevi after laser hair removal procedures. She used the search terms “nevi laser hair removal,” “nevi diode,” “nevi long pulse alexandrite,” “nevi long pulse neodymium doped yttrium aluminum garnet,” and “melanoma laser hair removal,” and limited the analysis to English language patient-based reports that discussed incidental treatment of melanocytic nevi while undergoing hair removal with a laser.
Reports excluded from the analysis were those that focused on changes following hair removal with nonlaser devices such as intense pulsed light (IPL), those evaluating nonmelanocytic nevi such as Becker’s nevus or nevus of Ota, and those evaluating the intentional ablation or removal of melanocytic lesions.
The search yielded 10 relevant studies for systematic review: seven case reports or series and three observational trials, two of which were prospective and one retrospective.
The results of the review, according to Dr. Cices, revealed that clinical and dermoscopic changes were noted to present as early as 15 days after treatment and persist to the maximum follow up time, at 3 years. Commonly reported changes included regression, decreased size, laser-induced asymmetry, bleaching, darkening, and altered pattern on dermoscopy. Histologic changes included mild atypia, thermal damage, scar formation, and regression.
“Although some of the clinical and dermoscopic alterations may be concerning for malignancy, to our knowledge, there are no documented cases of malignant transformation of nevi following treatment with laser hair removal,” she wrote in the abstract.
Dr. Cices acknowledged certain limitations of the systematic review, including the low number of relevant reports and their generally small sample size, many of which were limited to single cases.
Omar A. Ibrahimi, MD, PhD, medical director of the Connecticut Skin Institute, Stamford, who was asked to comment on the review, characterized the findings as important because laser hair removal is such a commonly performed procedure.
While the study is limited by the small number of studies on the subject matter, “it brings up an important discussion,” Dr. Ibrahimi said in an interview. “Generally speaking, we know that most hair removal lasers do indeed target melanin pigment and can be absorbed by melanocytes. While the wavelengths used for LHR [laser hair removal] will not result in DNA damage or cause mutations that can lead to melanoma, they can sometimes alter the appearance of pigmented lesions and that may change the dermatologist’s ability to monitor them for atypia,” he noted.
“For that reason, I would recommend all patients see a dermatologist for evaluation of their nevi prior to any treatments and they consider very carefully where they get their laser treatments. If they have any atypical pigmented lesions, then that information should be disclosed with the person performing the laser hair removal procedure particularly if there are lesions that are being specifically monitored.”
Dr. Cices reported having no disclosures. Dr. Ibrahimi disclosed that he is a member of the advisory board for Accure Acne, AbbVie, Cutera, Lutronic, Blueberry Therapeutics, Cytrellis, and Quthero. He also holds stock in many device and pharmaceutical companies.
AT ASLMS 2023
FDA clears first patch to treat axillary hyperhidrosis
The Food and Drug Administration on April 13 cleared the first patch to reduce excessive underarm sweating for adults with primary axillary hyperhidrosis.
The single-use, disposable, prescription-only patch will be marketed as Brella. It consists of a sodium sheet with an adhesive overlay. A health care provider applies it to the patient’s underarm for up to 3 minutes and then repeats the process on the other underarm.
The developer, Candesant Biomedical, says the patch uses the company’s patented targeted alkali thermolysis (TAT) technology, which was built on the principle that heat is generated when sodium reacts with water in sweat. “The thermal energy created by the sodium sheet is precisely localized, microtargeting sweat glands to significantly reduce sweat production,” according to the company’s press release announcing the FDA decision.
FDA clearance was based on data from the pivotal randomized, double-blind, multicenter SAHARA study, which indicated that the product is effective and well tolerated.
Patients experienced a reduction in sweat that was maintained for 3 months or longer, according to trial results.
The SAHARA trial results were reported in a late-breaking abstract at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology in March.
The trial enrolled 110 individuals with Hyperhidrosis Disease Severity Scale (HDSS) scores of 3 or 4 (indicating frequent sweating or sweating that always interferes with daily activities). Trial participants were randomly assigned to receive either an active TAT or a sham patch, which was applied for up to 3 minutes.
At the meeting, lead investigator David M. Pariser, MD, a dermatologist practicing in Norfolk, Va., reported that at 4 weeks, 63.6% of patients in the active patch group achieved an HDSS score of 1 or 2, compared with 44.2% of those in the sham treatment group (P = .0332). Also, 43.2% of those in the active-patch group achieved an improvement of 2 points or greater on the HDSS, as compared with 16.3% of those in the sham treatment group (P = .0107) .
In addition, 9.1% of those in the active-patch group achieved a 3-point improvement on the HDSS, compared with none in the sham group. “That’s an amazing improvement; you’re basically going from moderate or severe to none,” Dr. Pariser said at the meeting.
As for adverse events (AEs), 13 patients in the active-patch group experienced AEs at the treatment site. Six patients experienced erythema; four experienced erosion; two experienced burning, itching, or stinging; and one had underarm odor.
“The two procedure-related AEs in the TAT-treated group were compensatory sweating and irritant contact dermatitis due to the adhesive,” Dr. Pariser said. He noted that most AEs resolved in fewer than 2 weeks, and all AEs were mild to moderate.
According to the International Hyperhidrosis Society, about 1.3 million people in the United States have axillary hyperhidrosis, and about a third report that sweating is barely tolerable and frequently interferes with daily activities or is intolerable and always interferes with daily activities.
The patch will be available within months in select U.S. markets beginning in late summer. The company says the markets will be listed on its website.
A company representative told this news organization that because it is an in-office procedure, pricing will vary, depending on the practice. “With that said, Candesant expects doctors will charge about the same for one session of the Brella SweatControl Patch as they would for a high-end, in-office facial or chemical peel,” the representative said.
Dr. Pariser is a consultant or investigator for Bickel Biotechnology, Biofrontera AG, Bristol-Myers Squibb, the Celgene Corporation, Novartis Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration on April 13 cleared the first patch to reduce excessive underarm sweating for adults with primary axillary hyperhidrosis.
The single-use, disposable, prescription-only patch will be marketed as Brella. It consists of a sodium sheet with an adhesive overlay. A health care provider applies it to the patient’s underarm for up to 3 minutes and then repeats the process on the other underarm.
The developer, Candesant Biomedical, says the patch uses the company’s patented targeted alkali thermolysis (TAT) technology, which was built on the principle that heat is generated when sodium reacts with water in sweat. “The thermal energy created by the sodium sheet is precisely localized, microtargeting sweat glands to significantly reduce sweat production,” according to the company’s press release announcing the FDA decision.
FDA clearance was based on data from the pivotal randomized, double-blind, multicenter SAHARA study, which indicated that the product is effective and well tolerated.
Patients experienced a reduction in sweat that was maintained for 3 months or longer, according to trial results.
The SAHARA trial results were reported in a late-breaking abstract at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology in March.
The trial enrolled 110 individuals with Hyperhidrosis Disease Severity Scale (HDSS) scores of 3 or 4 (indicating frequent sweating or sweating that always interferes with daily activities). Trial participants were randomly assigned to receive either an active TAT or a sham patch, which was applied for up to 3 minutes.
At the meeting, lead investigator David M. Pariser, MD, a dermatologist practicing in Norfolk, Va., reported that at 4 weeks, 63.6% of patients in the active patch group achieved an HDSS score of 1 or 2, compared with 44.2% of those in the sham treatment group (P = .0332). Also, 43.2% of those in the active-patch group achieved an improvement of 2 points or greater on the HDSS, as compared with 16.3% of those in the sham treatment group (P = .0107) .
In addition, 9.1% of those in the active-patch group achieved a 3-point improvement on the HDSS, compared with none in the sham group. “That’s an amazing improvement; you’re basically going from moderate or severe to none,” Dr. Pariser said at the meeting.
As for adverse events (AEs), 13 patients in the active-patch group experienced AEs at the treatment site. Six patients experienced erythema; four experienced erosion; two experienced burning, itching, or stinging; and one had underarm odor.
“The two procedure-related AEs in the TAT-treated group were compensatory sweating and irritant contact dermatitis due to the adhesive,” Dr. Pariser said. He noted that most AEs resolved in fewer than 2 weeks, and all AEs were mild to moderate.
According to the International Hyperhidrosis Society, about 1.3 million people in the United States have axillary hyperhidrosis, and about a third report that sweating is barely tolerable and frequently interferes with daily activities or is intolerable and always interferes with daily activities.
The patch will be available within months in select U.S. markets beginning in late summer. The company says the markets will be listed on its website.
A company representative told this news organization that because it is an in-office procedure, pricing will vary, depending on the practice. “With that said, Candesant expects doctors will charge about the same for one session of the Brella SweatControl Patch as they would for a high-end, in-office facial or chemical peel,” the representative said.
Dr. Pariser is a consultant or investigator for Bickel Biotechnology, Biofrontera AG, Bristol-Myers Squibb, the Celgene Corporation, Novartis Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration on April 13 cleared the first patch to reduce excessive underarm sweating for adults with primary axillary hyperhidrosis.
The single-use, disposable, prescription-only patch will be marketed as Brella. It consists of a sodium sheet with an adhesive overlay. A health care provider applies it to the patient’s underarm for up to 3 minutes and then repeats the process on the other underarm.
The developer, Candesant Biomedical, says the patch uses the company’s patented targeted alkali thermolysis (TAT) technology, which was built on the principle that heat is generated when sodium reacts with water in sweat. “The thermal energy created by the sodium sheet is precisely localized, microtargeting sweat glands to significantly reduce sweat production,” according to the company’s press release announcing the FDA decision.
FDA clearance was based on data from the pivotal randomized, double-blind, multicenter SAHARA study, which indicated that the product is effective and well tolerated.
Patients experienced a reduction in sweat that was maintained for 3 months or longer, according to trial results.
The SAHARA trial results were reported in a late-breaking abstract at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology in March.
The trial enrolled 110 individuals with Hyperhidrosis Disease Severity Scale (HDSS) scores of 3 or 4 (indicating frequent sweating or sweating that always interferes with daily activities). Trial participants were randomly assigned to receive either an active TAT or a sham patch, which was applied for up to 3 minutes.
At the meeting, lead investigator David M. Pariser, MD, a dermatologist practicing in Norfolk, Va., reported that at 4 weeks, 63.6% of patients in the active patch group achieved an HDSS score of 1 or 2, compared with 44.2% of those in the sham treatment group (P = .0332). Also, 43.2% of those in the active-patch group achieved an improvement of 2 points or greater on the HDSS, as compared with 16.3% of those in the sham treatment group (P = .0107) .
In addition, 9.1% of those in the active-patch group achieved a 3-point improvement on the HDSS, compared with none in the sham group. “That’s an amazing improvement; you’re basically going from moderate or severe to none,” Dr. Pariser said at the meeting.
As for adverse events (AEs), 13 patients in the active-patch group experienced AEs at the treatment site. Six patients experienced erythema; four experienced erosion; two experienced burning, itching, or stinging; and one had underarm odor.
“The two procedure-related AEs in the TAT-treated group were compensatory sweating and irritant contact dermatitis due to the adhesive,” Dr. Pariser said. He noted that most AEs resolved in fewer than 2 weeks, and all AEs were mild to moderate.
According to the International Hyperhidrosis Society, about 1.3 million people in the United States have axillary hyperhidrosis, and about a third report that sweating is barely tolerable and frequently interferes with daily activities or is intolerable and always interferes with daily activities.
The patch will be available within months in select U.S. markets beginning in late summer. The company says the markets will be listed on its website.
A company representative told this news organization that because it is an in-office procedure, pricing will vary, depending on the practice. “With that said, Candesant expects doctors will charge about the same for one session of the Brella SweatControl Patch as they would for a high-end, in-office facial or chemical peel,” the representative said.
Dr. Pariser is a consultant or investigator for Bickel Biotechnology, Biofrontera AG, Bristol-Myers Squibb, the Celgene Corporation, Novartis Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Treatment of craniofacial hyperhidrosis
Hyperhidrosis has a significant impact on a person’s physical, psychological, and social aspects of life. The lack of treatment options and associated stigma limits access to care and treatment options.
Primary hyperhidrosis does not have an underlying cause; is symmetrical; can worsen with anxiety, fear, or stress; and may have a familial component. Palmar and axillary hyperhidrosis are the most common types of hyperhidrosis. The incidence of craniofacial hyperhidrosis has not been clearly defined but it is most commonly reported on the forehead, where the concentration of eccrine sweat glands is highest.
Treatment options for craniofacial hyperhidrosis include topical aluminum chloride, which blocks the eccrine sweat duct or causes eccrine cell atrophy. Although this option is a common treatment for palmar and axillary hyperhidrosis, use on the face has not been thoroughly studied, and may also cause skin irritation.
Topical and oral glycopyrrolate can be effective for all types of hyperhidrosis, but must be used daily and can have systemic side effects, with variable efficacy and longevity. Oral oxybutynin, beta-blockers, clonidine, and benzodiazepines have also been used with some limited studies available in patients with generalized hyperhidrosis.
Surgical treatments such as videothoracoscopy sympathectomy can be used in severe or recalcitrant cases of hyperhidrosis with good efficacy. However, surgical complications and inherent surgical risks limit these treatment options unless other modalities are exhausted.
OnabotulinumtoxinA is Food and Drug Administration approved for treating severe primary axillary hyperhidrosis, but is used off label for palmar, plantar, and craniofacial hyperhidrosis with great results and few side effects. Clinical pearls and guidelines for the use of botulinum toxin A in craniofacial hyperhidrosis were outlined by Wolosker and colleagues in a review article. As with any injection of neurotoxin, knowledge of the facial anatomy is critical to avoiding muscle paralysis.
double diluted. Treatment effects usually last 3 months, similar to cosmetic uses. Wolosker uses a dilution of 100 U botulinum toxin in 1.0 mL saline, which I find slightly more difficult to control and more likely to have loss of toxin.
In my experience, I have found the following dosing to be most effective with the least side effects for the following (dosages vary and can be titrated up to response):
- Upper lip: 6-10 U.
- Chin: 6-10 U.
- Forehead: 15-30 U. (Avoid 1 cm above the brow unless risks of brow drop are reviewed and acceptable to the patient. In my experience patients would rather have a lower brow than obstructive sweating in their brow that can irritate the eyes, blur vision, and smudge skincare and makeup.)
- Nose: 10 U
- Cheeks: 10 U per side (staying very superficial with injections).
- Scalp: 30-50 U (using serial injections 1-2 cm apart in the area affected by hyperhidrosis).
Side effects include temporary erythema, bruising, and edema, as well as muscle paralysis and asymmetry if proper injection technique is not used, the dose is not diluted properly, or the injection is too deep.
There are scattered case studies of symbiotic techniques to help the penetration of botulinum toxin when treating craniofacial hyperhidrosis, including microneedling, radiofrequency, long-pulsed diode laser, and ultrasound. But the safety and efficacy of these procedures have not been properly evaluated.
In all of my patients with craniofacial hyperhidrosis treated with botulinum toxin, quality of life is significantly improved with almost no complications. Botulinum toxin is a safe, relatively quick in-office procedure to treat craniofacial hyperhidrosis that can be used to help patients – particularly those who experience anxiety or have social and occupational impairment related to their disease.
This procedure is cosmetic in nature, and therefore, not covered by insurance.
Dr. Talakoub is in private practice in McLean, Va. Write to her at dermnews@mdedge.com. She had no relevant disclosures.
References
Parashar K et al. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2023 Mar;24(2):187-98.
Doolittle J et al. Arch Dermatol Res. 2016 Dec;308(10):743-9.
Wolosker N et al. J Vasc Bras. 2020 Nov 16;19:e20190152.
Garcia-Souto F et al. Dermatol Ther. 2021 Jan;34(1):e14658.
Ebrahim H et al. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2022 Sep;15(9):40-4.
Campanati A et al. Toxins (Basel). 2022 May 27;14(6):3727.
Hyperhidrosis has a significant impact on a person’s physical, psychological, and social aspects of life. The lack of treatment options and associated stigma limits access to care and treatment options.
Primary hyperhidrosis does not have an underlying cause; is symmetrical; can worsen with anxiety, fear, or stress; and may have a familial component. Palmar and axillary hyperhidrosis are the most common types of hyperhidrosis. The incidence of craniofacial hyperhidrosis has not been clearly defined but it is most commonly reported on the forehead, where the concentration of eccrine sweat glands is highest.
Treatment options for craniofacial hyperhidrosis include topical aluminum chloride, which blocks the eccrine sweat duct or causes eccrine cell atrophy. Although this option is a common treatment for palmar and axillary hyperhidrosis, use on the face has not been thoroughly studied, and may also cause skin irritation.
Topical and oral glycopyrrolate can be effective for all types of hyperhidrosis, but must be used daily and can have systemic side effects, with variable efficacy and longevity. Oral oxybutynin, beta-blockers, clonidine, and benzodiazepines have also been used with some limited studies available in patients with generalized hyperhidrosis.
Surgical treatments such as videothoracoscopy sympathectomy can be used in severe or recalcitrant cases of hyperhidrosis with good efficacy. However, surgical complications and inherent surgical risks limit these treatment options unless other modalities are exhausted.
OnabotulinumtoxinA is Food and Drug Administration approved for treating severe primary axillary hyperhidrosis, but is used off label for palmar, plantar, and craniofacial hyperhidrosis with great results and few side effects. Clinical pearls and guidelines for the use of botulinum toxin A in craniofacial hyperhidrosis were outlined by Wolosker and colleagues in a review article. As with any injection of neurotoxin, knowledge of the facial anatomy is critical to avoiding muscle paralysis.
double diluted. Treatment effects usually last 3 months, similar to cosmetic uses. Wolosker uses a dilution of 100 U botulinum toxin in 1.0 mL saline, which I find slightly more difficult to control and more likely to have loss of toxin.
In my experience, I have found the following dosing to be most effective with the least side effects for the following (dosages vary and can be titrated up to response):
- Upper lip: 6-10 U.
- Chin: 6-10 U.
- Forehead: 15-30 U. (Avoid 1 cm above the brow unless risks of brow drop are reviewed and acceptable to the patient. In my experience patients would rather have a lower brow than obstructive sweating in their brow that can irritate the eyes, blur vision, and smudge skincare and makeup.)
- Nose: 10 U
- Cheeks: 10 U per side (staying very superficial with injections).
- Scalp: 30-50 U (using serial injections 1-2 cm apart in the area affected by hyperhidrosis).
Side effects include temporary erythema, bruising, and edema, as well as muscle paralysis and asymmetry if proper injection technique is not used, the dose is not diluted properly, or the injection is too deep.
There are scattered case studies of symbiotic techniques to help the penetration of botulinum toxin when treating craniofacial hyperhidrosis, including microneedling, radiofrequency, long-pulsed diode laser, and ultrasound. But the safety and efficacy of these procedures have not been properly evaluated.
In all of my patients with craniofacial hyperhidrosis treated with botulinum toxin, quality of life is significantly improved with almost no complications. Botulinum toxin is a safe, relatively quick in-office procedure to treat craniofacial hyperhidrosis that can be used to help patients – particularly those who experience anxiety or have social and occupational impairment related to their disease.
This procedure is cosmetic in nature, and therefore, not covered by insurance.
Dr. Talakoub is in private practice in McLean, Va. Write to her at dermnews@mdedge.com. She had no relevant disclosures.
References
Parashar K et al. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2023 Mar;24(2):187-98.
Doolittle J et al. Arch Dermatol Res. 2016 Dec;308(10):743-9.
Wolosker N et al. J Vasc Bras. 2020 Nov 16;19:e20190152.
Garcia-Souto F et al. Dermatol Ther. 2021 Jan;34(1):e14658.
Ebrahim H et al. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2022 Sep;15(9):40-4.
Campanati A et al. Toxins (Basel). 2022 May 27;14(6):3727.
Hyperhidrosis has a significant impact on a person’s physical, psychological, and social aspects of life. The lack of treatment options and associated stigma limits access to care and treatment options.
Primary hyperhidrosis does not have an underlying cause; is symmetrical; can worsen with anxiety, fear, or stress; and may have a familial component. Palmar and axillary hyperhidrosis are the most common types of hyperhidrosis. The incidence of craniofacial hyperhidrosis has not been clearly defined but it is most commonly reported on the forehead, where the concentration of eccrine sweat glands is highest.
Treatment options for craniofacial hyperhidrosis include topical aluminum chloride, which blocks the eccrine sweat duct or causes eccrine cell atrophy. Although this option is a common treatment for palmar and axillary hyperhidrosis, use on the face has not been thoroughly studied, and may also cause skin irritation.
Topical and oral glycopyrrolate can be effective for all types of hyperhidrosis, but must be used daily and can have systemic side effects, with variable efficacy and longevity. Oral oxybutynin, beta-blockers, clonidine, and benzodiazepines have also been used with some limited studies available in patients with generalized hyperhidrosis.
Surgical treatments such as videothoracoscopy sympathectomy can be used in severe or recalcitrant cases of hyperhidrosis with good efficacy. However, surgical complications and inherent surgical risks limit these treatment options unless other modalities are exhausted.
OnabotulinumtoxinA is Food and Drug Administration approved for treating severe primary axillary hyperhidrosis, but is used off label for palmar, plantar, and craniofacial hyperhidrosis with great results and few side effects. Clinical pearls and guidelines for the use of botulinum toxin A in craniofacial hyperhidrosis were outlined by Wolosker and colleagues in a review article. As with any injection of neurotoxin, knowledge of the facial anatomy is critical to avoiding muscle paralysis.
double diluted. Treatment effects usually last 3 months, similar to cosmetic uses. Wolosker uses a dilution of 100 U botulinum toxin in 1.0 mL saline, which I find slightly more difficult to control and more likely to have loss of toxin.
In my experience, I have found the following dosing to be most effective with the least side effects for the following (dosages vary and can be titrated up to response):
- Upper lip: 6-10 U.
- Chin: 6-10 U.
- Forehead: 15-30 U. (Avoid 1 cm above the brow unless risks of brow drop are reviewed and acceptable to the patient. In my experience patients would rather have a lower brow than obstructive sweating in their brow that can irritate the eyes, blur vision, and smudge skincare and makeup.)
- Nose: 10 U
- Cheeks: 10 U per side (staying very superficial with injections).
- Scalp: 30-50 U (using serial injections 1-2 cm apart in the area affected by hyperhidrosis).
Side effects include temporary erythema, bruising, and edema, as well as muscle paralysis and asymmetry if proper injection technique is not used, the dose is not diluted properly, or the injection is too deep.
There are scattered case studies of symbiotic techniques to help the penetration of botulinum toxin when treating craniofacial hyperhidrosis, including microneedling, radiofrequency, long-pulsed diode laser, and ultrasound. But the safety and efficacy of these procedures have not been properly evaluated.
In all of my patients with craniofacial hyperhidrosis treated with botulinum toxin, quality of life is significantly improved with almost no complications. Botulinum toxin is a safe, relatively quick in-office procedure to treat craniofacial hyperhidrosis that can be used to help patients – particularly those who experience anxiety or have social and occupational impairment related to their disease.
This procedure is cosmetic in nature, and therefore, not covered by insurance.
Dr. Talakoub is in private practice in McLean, Va. Write to her at dermnews@mdedge.com. She had no relevant disclosures.
References
Parashar K et al. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2023 Mar;24(2):187-98.
Doolittle J et al. Arch Dermatol Res. 2016 Dec;308(10):743-9.
Wolosker N et al. J Vasc Bras. 2020 Nov 16;19:e20190152.
Garcia-Souto F et al. Dermatol Ther. 2021 Jan;34(1):e14658.
Ebrahim H et al. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2022 Sep;15(9):40-4.
Campanati A et al. Toxins (Basel). 2022 May 27;14(6):3727.
Racial morphing: A conundrum in cosmetic dermatology
HONOLULU – In the opinion of Nazanin A. Saedi, MD, social media-induced dissatisfaction with appearance is getting out of hand in the field of cosmetic dermatology, with the emergence of apps to filter and edit images to the patient’s liking.
This, coupled with
“Overexposure of celebrity images and altered faces on social media have led to a trend of overarching brows, sculpted noses, enlarged cheeks, and sharply defined jawlines,” Dr. Saedi, cochair of the laser and aesthetics surgery center at Dermatology Associates of Plymouth Meeting, Pa., said at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by MedscapeLIVE! “These trends have made people of different ethnicities morph into a similar appearance.”
At the meeting, she showed early career images of celebrities from different ethnic backgrounds, “and they all have unique features that make them look great,” said Dr. Saedi, clinical associate professor of dermatology at Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia. She then showed images of the same celebrities after they had undergone cosmetic procedures, “and they look so much more similar,” with overarched brows, sculpted noses, enlarged cheeks, and sharply defined jawlines. “Whereas they were all beautiful before individually, now they look very similar,” she said. “This is what we see on social media.”
Referring to the Kardashians as an example of celebrities who have had a lot of aesthetic treatments, look different than they did years ago, and are seen “more and more,” she added, “it’s this repeated overexposure to people on social media, to celebrities, that’s created this different trend of attractiveness.”
This trend also affects patients seeking cosmetic treatments, she noted. Individuals can use an app to alter their appearance, “changing the way they look to create the best version of themselves, they might say, or a filtered version of themselves,” said Dr. Saedi, one of the authors of a commentary on patient perception of beauty on social media published several years ago.
“I tell people, ‘Don’t use filters in your photos. Embrace your beauty.’ I have patients coming in who want to look like the social media photos they’ve curated, maybe larger lips or more definition in their jawline. What they don’t understand is that it takes a long time for that to happen. It’s a process.” In other cases, their desired outcome is not possible due to limits of their individual facial anatomy.
In a study published almost 20 years ago in the journal Perception, Irish researchers manipulated the familiarity of typical and distinctive faces to measure the effect on attractiveness. They found that episodic familiarity affects attractiveness ratings independently of general or structural familiarity.
“So, the more you saw a face, the more familiar that face was to you,” said Dr. Saedi, who was not involved with the study. “Over time, you felt that to be more attractive. I think that’s a lot of what’s going on in the trends that we’re seeing – both in real life and on social media. I do think we need to be more mindful of maintaining features that make an individual unique, while also maintaining their ethnic beauty.”
In an interview at the meeting, Jacqueline D. Watchmaker, MD, a board-certified cosmetic and medical dermatologist who practices in Scottsdale, Ariz., said that she identifies with the notion of racial morphing in her own clinical experience. “Patients come in and specifically ask for chiseled jawlines, high cheekbones, and bigger lips,” Dr. Watchmaker said. “It’s a tricky situation when they ask for [a treatment] you don’t think they need. I prefer a more staged approach to maintain their individuality while giving them a little bit of the aesthetic benefit that they’re looking for.”
Dr. Saedi disclosed ties with AbbVie, Aerolase, Allergan, Alma, Cartessa, Cynosure, Galderma Laboratories, LP, Grand Cosmetics, Revelle Aesthetics, and Revision Skincare. Dr. Watchmaker reported having no financial disclosures.
Medscape and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
HONOLULU – In the opinion of Nazanin A. Saedi, MD, social media-induced dissatisfaction with appearance is getting out of hand in the field of cosmetic dermatology, with the emergence of apps to filter and edit images to the patient’s liking.
This, coupled with
“Overexposure of celebrity images and altered faces on social media have led to a trend of overarching brows, sculpted noses, enlarged cheeks, and sharply defined jawlines,” Dr. Saedi, cochair of the laser and aesthetics surgery center at Dermatology Associates of Plymouth Meeting, Pa., said at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by MedscapeLIVE! “These trends have made people of different ethnicities morph into a similar appearance.”
At the meeting, she showed early career images of celebrities from different ethnic backgrounds, “and they all have unique features that make them look great,” said Dr. Saedi, clinical associate professor of dermatology at Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia. She then showed images of the same celebrities after they had undergone cosmetic procedures, “and they look so much more similar,” with overarched brows, sculpted noses, enlarged cheeks, and sharply defined jawlines. “Whereas they were all beautiful before individually, now they look very similar,” she said. “This is what we see on social media.”
Referring to the Kardashians as an example of celebrities who have had a lot of aesthetic treatments, look different than they did years ago, and are seen “more and more,” she added, “it’s this repeated overexposure to people on social media, to celebrities, that’s created this different trend of attractiveness.”
This trend also affects patients seeking cosmetic treatments, she noted. Individuals can use an app to alter their appearance, “changing the way they look to create the best version of themselves, they might say, or a filtered version of themselves,” said Dr. Saedi, one of the authors of a commentary on patient perception of beauty on social media published several years ago.
“I tell people, ‘Don’t use filters in your photos. Embrace your beauty.’ I have patients coming in who want to look like the social media photos they’ve curated, maybe larger lips or more definition in their jawline. What they don’t understand is that it takes a long time for that to happen. It’s a process.” In other cases, their desired outcome is not possible due to limits of their individual facial anatomy.
In a study published almost 20 years ago in the journal Perception, Irish researchers manipulated the familiarity of typical and distinctive faces to measure the effect on attractiveness. They found that episodic familiarity affects attractiveness ratings independently of general or structural familiarity.
“So, the more you saw a face, the more familiar that face was to you,” said Dr. Saedi, who was not involved with the study. “Over time, you felt that to be more attractive. I think that’s a lot of what’s going on in the trends that we’re seeing – both in real life and on social media. I do think we need to be more mindful of maintaining features that make an individual unique, while also maintaining their ethnic beauty.”
In an interview at the meeting, Jacqueline D. Watchmaker, MD, a board-certified cosmetic and medical dermatologist who practices in Scottsdale, Ariz., said that she identifies with the notion of racial morphing in her own clinical experience. “Patients come in and specifically ask for chiseled jawlines, high cheekbones, and bigger lips,” Dr. Watchmaker said. “It’s a tricky situation when they ask for [a treatment] you don’t think they need. I prefer a more staged approach to maintain their individuality while giving them a little bit of the aesthetic benefit that they’re looking for.”
Dr. Saedi disclosed ties with AbbVie, Aerolase, Allergan, Alma, Cartessa, Cynosure, Galderma Laboratories, LP, Grand Cosmetics, Revelle Aesthetics, and Revision Skincare. Dr. Watchmaker reported having no financial disclosures.
Medscape and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
HONOLULU – In the opinion of Nazanin A. Saedi, MD, social media-induced dissatisfaction with appearance is getting out of hand in the field of cosmetic dermatology, with the emergence of apps to filter and edit images to the patient’s liking.
This, coupled with
“Overexposure of celebrity images and altered faces on social media have led to a trend of overarching brows, sculpted noses, enlarged cheeks, and sharply defined jawlines,” Dr. Saedi, cochair of the laser and aesthetics surgery center at Dermatology Associates of Plymouth Meeting, Pa., said at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by MedscapeLIVE! “These trends have made people of different ethnicities morph into a similar appearance.”
At the meeting, she showed early career images of celebrities from different ethnic backgrounds, “and they all have unique features that make them look great,” said Dr. Saedi, clinical associate professor of dermatology at Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia. She then showed images of the same celebrities after they had undergone cosmetic procedures, “and they look so much more similar,” with overarched brows, sculpted noses, enlarged cheeks, and sharply defined jawlines. “Whereas they were all beautiful before individually, now they look very similar,” she said. “This is what we see on social media.”
Referring to the Kardashians as an example of celebrities who have had a lot of aesthetic treatments, look different than they did years ago, and are seen “more and more,” she added, “it’s this repeated overexposure to people on social media, to celebrities, that’s created this different trend of attractiveness.”
This trend also affects patients seeking cosmetic treatments, she noted. Individuals can use an app to alter their appearance, “changing the way they look to create the best version of themselves, they might say, or a filtered version of themselves,” said Dr. Saedi, one of the authors of a commentary on patient perception of beauty on social media published several years ago.
“I tell people, ‘Don’t use filters in your photos. Embrace your beauty.’ I have patients coming in who want to look like the social media photos they’ve curated, maybe larger lips or more definition in their jawline. What they don’t understand is that it takes a long time for that to happen. It’s a process.” In other cases, their desired outcome is not possible due to limits of their individual facial anatomy.
In a study published almost 20 years ago in the journal Perception, Irish researchers manipulated the familiarity of typical and distinctive faces to measure the effect on attractiveness. They found that episodic familiarity affects attractiveness ratings independently of general or structural familiarity.
“So, the more you saw a face, the more familiar that face was to you,” said Dr. Saedi, who was not involved with the study. “Over time, you felt that to be more attractive. I think that’s a lot of what’s going on in the trends that we’re seeing – both in real life and on social media. I do think we need to be more mindful of maintaining features that make an individual unique, while also maintaining their ethnic beauty.”
In an interview at the meeting, Jacqueline D. Watchmaker, MD, a board-certified cosmetic and medical dermatologist who practices in Scottsdale, Ariz., said that she identifies with the notion of racial morphing in her own clinical experience. “Patients come in and specifically ask for chiseled jawlines, high cheekbones, and bigger lips,” Dr. Watchmaker said. “It’s a tricky situation when they ask for [a treatment] you don’t think they need. I prefer a more staged approach to maintain their individuality while giving them a little bit of the aesthetic benefit that they’re looking for.”
Dr. Saedi disclosed ties with AbbVie, Aerolase, Allergan, Alma, Cartessa, Cynosure, Galderma Laboratories, LP, Grand Cosmetics, Revelle Aesthetics, and Revision Skincare. Dr. Watchmaker reported having no financial disclosures.
Medscape and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
AT THE MEDSCAPELIVE! HAWAII DERMATOLOGY SEMINAR

















