User login
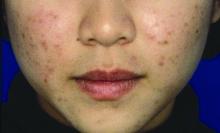
Ovarian reserve markers fall on isotretinoin, but rebound after stopping treatment
MILAN – according to data presented at the World Congress of Dermatology.
Although markers for ovarian reserve, including anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) serum levels, ovarian volume, and antral follicle count, were significantly lower during a period of isotretinoin use than at baseline, these values were were not significantly different from pretreatment levels by 1 month after stopping isotretinoin.
For patients taking isotretinoin at a dose of 0.5 mg/kg/day, AMH levels fell from a baseline level of 5.29 ng/mL to 4.16 ng/mL during treatment, but rebounded to 4.77 ng/mL 1 month after stopping treatment (P less than .001 for difference between baseline and on-drug values), Tuğba Özkök Akbulut, MD, said during a late-breaking abstracts session.
For women taking isotretinoin 1 mg/kg/day, AMH levels went from 5.14 ng/mL at baseline to 4.24 ng/mL on treatment, to 4.65 ng/mL 1 month after treatment (P less than .001 for difference between baseline and on-drug values), reported Dr. Akbulut a dermatologist at the Haseki Training Research Hospital, Istanbul.
Women on the higher dose of isotretinoin had a similar pattern of decline while on treatment and rebound after ceasing isotretinoin for ovarian volume and antral follicle count (P less than .001 for all values). These differences were not statistically significant for women taking 0.5 mg/kg/day of isotretinoin, except for right ovarian volume (P = 0.013).
Although values were numerically lower for many markers of ovarian reserve after ceasing treatment, compared with baseline figures, these differences were not statistically significantly different. Markers of ovarian reserve did not change significantly for a control group of women without acne.
Dr. Akbulut and her colleagues conducted this prospective case-control study of 42 women of reproductive age who sought dermatologist care for severe acne unresponsive to conservative therapy; 26 women who did not have acne constituted the control group. Smokers, patients with thyroid disease, and those with known polycystic ovary syndrome were excluded from participation.
The women with acne received oral isotretinoin dosed either at 0.5 or 1.0 mg/kg/day, with treatment lasting 5-9 months. For each patient, treatment was stopped when the cumulative dose reached 120 mg/kg.
After an initial visit at which blood was collected from all participants to measure serum AMH levels, those receiving isotretinoin were seen every 4 weeks to check serum lipid and liver enzyme levels.
At the 3-month mark during the study period and 1 month after the end of completing isotretinoin treatment, or at the end of the study period for the control group, blood samples also were drawn for AMH levels.
To measure hormone levels, also blood was drawn between days 2 and 5 of the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle. Participants received ultrasounds to measure antral follicle count and ovarian volume between days 2 and 5 of the menstrual cycle at the initial visit, at the 3-month visit, and at the final visit. Results were interpreted by a trained gynecologist.
Patients, who were mostly in their early 20s, had a mean body mass index of about 22 kg/m2. Hormone levels, ovarian volume, and antral follicle count did not differ among study arms at baseline.
“There are contradictory reports in the literature regarding the effect of retinoic acid on ovarian reserve,” noted Dr. Akbulut. Some preclinical studies found that retinoic acid increased fertility and ovarian reserve in rodents; however, some human studies had shown lower serum AMH concentrations in patients using isotretinoin.
This new demonstration of the reversibility of isotretinoin’s negative effect on ovarian reserve helps clarify a confused picture in the medical literature, said Dr. Akbulut. “The results of our study demonstrated that systemic isotretinoin had a reversible effect on ovarian reserve.”
Dr. Akbulut reported no outside sources of funding and that she had no relevant financial disclosures.
MILAN – according to data presented at the World Congress of Dermatology.
Although markers for ovarian reserve, including anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) serum levels, ovarian volume, and antral follicle count, were significantly lower during a period of isotretinoin use than at baseline, these values were were not significantly different from pretreatment levels by 1 month after stopping isotretinoin.
For patients taking isotretinoin at a dose of 0.5 mg/kg/day, AMH levels fell from a baseline level of 5.29 ng/mL to 4.16 ng/mL during treatment, but rebounded to 4.77 ng/mL 1 month after stopping treatment (P less than .001 for difference between baseline and on-drug values), Tuğba Özkök Akbulut, MD, said during a late-breaking abstracts session.
For women taking isotretinoin 1 mg/kg/day, AMH levels went from 5.14 ng/mL at baseline to 4.24 ng/mL on treatment, to 4.65 ng/mL 1 month after treatment (P less than .001 for difference between baseline and on-drug values), reported Dr. Akbulut a dermatologist at the Haseki Training Research Hospital, Istanbul.
Women on the higher dose of isotretinoin had a similar pattern of decline while on treatment and rebound after ceasing isotretinoin for ovarian volume and antral follicle count (P less than .001 for all values). These differences were not statistically significant for women taking 0.5 mg/kg/day of isotretinoin, except for right ovarian volume (P = 0.013).
Although values were numerically lower for many markers of ovarian reserve after ceasing treatment, compared with baseline figures, these differences were not statistically significantly different. Markers of ovarian reserve did not change significantly for a control group of women without acne.
Dr. Akbulut and her colleagues conducted this prospective case-control study of 42 women of reproductive age who sought dermatologist care for severe acne unresponsive to conservative therapy; 26 women who did not have acne constituted the control group. Smokers, patients with thyroid disease, and those with known polycystic ovary syndrome were excluded from participation.
The women with acne received oral isotretinoin dosed either at 0.5 or 1.0 mg/kg/day, with treatment lasting 5-9 months. For each patient, treatment was stopped when the cumulative dose reached 120 mg/kg.
After an initial visit at which blood was collected from all participants to measure serum AMH levels, those receiving isotretinoin were seen every 4 weeks to check serum lipid and liver enzyme levels.
At the 3-month mark during the study period and 1 month after the end of completing isotretinoin treatment, or at the end of the study period for the control group, blood samples also were drawn for AMH levels.
To measure hormone levels, also blood was drawn between days 2 and 5 of the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle. Participants received ultrasounds to measure antral follicle count and ovarian volume between days 2 and 5 of the menstrual cycle at the initial visit, at the 3-month visit, and at the final visit. Results were interpreted by a trained gynecologist.
Patients, who were mostly in their early 20s, had a mean body mass index of about 22 kg/m2. Hormone levels, ovarian volume, and antral follicle count did not differ among study arms at baseline.
“There are contradictory reports in the literature regarding the effect of retinoic acid on ovarian reserve,” noted Dr. Akbulut. Some preclinical studies found that retinoic acid increased fertility and ovarian reserve in rodents; however, some human studies had shown lower serum AMH concentrations in patients using isotretinoin.
This new demonstration of the reversibility of isotretinoin’s negative effect on ovarian reserve helps clarify a confused picture in the medical literature, said Dr. Akbulut. “The results of our study demonstrated that systemic isotretinoin had a reversible effect on ovarian reserve.”
Dr. Akbulut reported no outside sources of funding and that she had no relevant financial disclosures.
MILAN – according to data presented at the World Congress of Dermatology.
Although markers for ovarian reserve, including anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) serum levels, ovarian volume, and antral follicle count, were significantly lower during a period of isotretinoin use than at baseline, these values were were not significantly different from pretreatment levels by 1 month after stopping isotretinoin.
For patients taking isotretinoin at a dose of 0.5 mg/kg/day, AMH levels fell from a baseline level of 5.29 ng/mL to 4.16 ng/mL during treatment, but rebounded to 4.77 ng/mL 1 month after stopping treatment (P less than .001 for difference between baseline and on-drug values), Tuğba Özkök Akbulut, MD, said during a late-breaking abstracts session.
For women taking isotretinoin 1 mg/kg/day, AMH levels went from 5.14 ng/mL at baseline to 4.24 ng/mL on treatment, to 4.65 ng/mL 1 month after treatment (P less than .001 for difference between baseline and on-drug values), reported Dr. Akbulut a dermatologist at the Haseki Training Research Hospital, Istanbul.
Women on the higher dose of isotretinoin had a similar pattern of decline while on treatment and rebound after ceasing isotretinoin for ovarian volume and antral follicle count (P less than .001 for all values). These differences were not statistically significant for women taking 0.5 mg/kg/day of isotretinoin, except for right ovarian volume (P = 0.013).
Although values were numerically lower for many markers of ovarian reserve after ceasing treatment, compared with baseline figures, these differences were not statistically significantly different. Markers of ovarian reserve did not change significantly for a control group of women without acne.
Dr. Akbulut and her colleagues conducted this prospective case-control study of 42 women of reproductive age who sought dermatologist care for severe acne unresponsive to conservative therapy; 26 women who did not have acne constituted the control group. Smokers, patients with thyroid disease, and those with known polycystic ovary syndrome were excluded from participation.
The women with acne received oral isotretinoin dosed either at 0.5 or 1.0 mg/kg/day, with treatment lasting 5-9 months. For each patient, treatment was stopped when the cumulative dose reached 120 mg/kg.
After an initial visit at which blood was collected from all participants to measure serum AMH levels, those receiving isotretinoin were seen every 4 weeks to check serum lipid and liver enzyme levels.
At the 3-month mark during the study period and 1 month after the end of completing isotretinoin treatment, or at the end of the study period for the control group, blood samples also were drawn for AMH levels.
To measure hormone levels, also blood was drawn between days 2 and 5 of the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle. Participants received ultrasounds to measure antral follicle count and ovarian volume between days 2 and 5 of the menstrual cycle at the initial visit, at the 3-month visit, and at the final visit. Results were interpreted by a trained gynecologist.
Patients, who were mostly in their early 20s, had a mean body mass index of about 22 kg/m2. Hormone levels, ovarian volume, and antral follicle count did not differ among study arms at baseline.
“There are contradictory reports in the literature regarding the effect of retinoic acid on ovarian reserve,” noted Dr. Akbulut. Some preclinical studies found that retinoic acid increased fertility and ovarian reserve in rodents; however, some human studies had shown lower serum AMH concentrations in patients using isotretinoin.
This new demonstration of the reversibility of isotretinoin’s negative effect on ovarian reserve helps clarify a confused picture in the medical literature, said Dr. Akbulut. “The results of our study demonstrated that systemic isotretinoin had a reversible effect on ovarian reserve.”
Dr. Akbulut reported no outside sources of funding and that she had no relevant financial disclosures.
REPORTING FROM WCD2019
Review hints at improved semen quality after bariatric surgery
LOS ANGELES – On the male fertility front, obesity seems to hurt semen quality. So does weight-loss surgery reverse the trend? A new review of existing research suggests that there may be an effect, but the findings aren’t conclusive.
“We found something,” said Sikarin Upala, MD, a second-year endocrinology fellow at the University of Chicago, who pointed out that three of the four reports he and his colleagues reviewed suggested improvement in semen motility. “But we still need to study more about whether bariatric surgery will affect infertility,” he continued.
Dr. Upala, who led the systematic review and meta-analysis of research into bariatric surgery and semen quality, spoke in an interview after his presentation at the annual scientific and clinical congress of the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists.
As researchers explained in a 2018 report, “conflicting results have been observed in studies evaluating the correlation between [body mass index] and sperm parameters, such as sperm concentration and total sperm count.” However, they noted that it is “generally accepted” that men with obesity seem to be at higher risk of having a low sperm count or having azoospermia, which is the total lack of sperm in semen.
It’s also not clear whether weight loss directly improves male fertility. “We do know that androgen levels improve after weight-loss surgery, and that might be one factor among several that may contribute to improved male fertility,” Edward Lin, DO, MBA, FACS, professor of surgery and chief of gastrointestinal and general surgery at Emory University, Atlanta, said in an interview.
In their review, Dr. Upala and his colleagues analyzed four studies published between 2012 and 2018 that evaluated the effect of bariatric surgery on semen quality. All of the studies examined semen volume and sperm morphology and motility, and three examined sperm concentration.
A meta-analysis found that motility and volume improved after surgery; however, some of the studies (two for volume, one for motility) failed to show a statistically significant change.
There was no statistically significant difference in sperm morphology or concentration overall, although one study showed a statistically significant improvement in both categories.
Overall, “there might be a little bit of positive effect, but we couldn’t reach a good conclusion because there were too few studies,” Dr. Upala said.
Dr. Lin, director of the Emory Bariatrics Center, agreed that the review findings are limited. He said that although the findings hint at a positive effect on semen quality, “the jury is still out” when it comes to a link between bariatric surgery and male infertility.
“Multiple factors contribute to semen quality,” he added, pointing to vitamin deficiencies, micronutrient levels in the body, enzyme signaling pathways, and sperm chromatin integrity. “In fact, surgically or diet-induced weight loss may be associated with permissive malnutrition, which further exacerbates these deficiencies. Deficiencies in these areas can sometimes take months, if not years, to correct by taking vitamin D or copper or zinc, for example.”
Dr. Lin referred to a small study in which reporters observed semen abnormalities and subfertility after weight-loss surgery despite improvements in androgenic and quality of life levels.
Dr. Upala reported having no relevant disclosures.
LOS ANGELES – On the male fertility front, obesity seems to hurt semen quality. So does weight-loss surgery reverse the trend? A new review of existing research suggests that there may be an effect, but the findings aren’t conclusive.
“We found something,” said Sikarin Upala, MD, a second-year endocrinology fellow at the University of Chicago, who pointed out that three of the four reports he and his colleagues reviewed suggested improvement in semen motility. “But we still need to study more about whether bariatric surgery will affect infertility,” he continued.
Dr. Upala, who led the systematic review and meta-analysis of research into bariatric surgery and semen quality, spoke in an interview after his presentation at the annual scientific and clinical congress of the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists.
As researchers explained in a 2018 report, “conflicting results have been observed in studies evaluating the correlation between [body mass index] and sperm parameters, such as sperm concentration and total sperm count.” However, they noted that it is “generally accepted” that men with obesity seem to be at higher risk of having a low sperm count or having azoospermia, which is the total lack of sperm in semen.
It’s also not clear whether weight loss directly improves male fertility. “We do know that androgen levels improve after weight-loss surgery, and that might be one factor among several that may contribute to improved male fertility,” Edward Lin, DO, MBA, FACS, professor of surgery and chief of gastrointestinal and general surgery at Emory University, Atlanta, said in an interview.
In their review, Dr. Upala and his colleagues analyzed four studies published between 2012 and 2018 that evaluated the effect of bariatric surgery on semen quality. All of the studies examined semen volume and sperm morphology and motility, and three examined sperm concentration.
A meta-analysis found that motility and volume improved after surgery; however, some of the studies (two for volume, one for motility) failed to show a statistically significant change.
There was no statistically significant difference in sperm morphology or concentration overall, although one study showed a statistically significant improvement in both categories.
Overall, “there might be a little bit of positive effect, but we couldn’t reach a good conclusion because there were too few studies,” Dr. Upala said.
Dr. Lin, director of the Emory Bariatrics Center, agreed that the review findings are limited. He said that although the findings hint at a positive effect on semen quality, “the jury is still out” when it comes to a link between bariatric surgery and male infertility.
“Multiple factors contribute to semen quality,” he added, pointing to vitamin deficiencies, micronutrient levels in the body, enzyme signaling pathways, and sperm chromatin integrity. “In fact, surgically or diet-induced weight loss may be associated with permissive malnutrition, which further exacerbates these deficiencies. Deficiencies in these areas can sometimes take months, if not years, to correct by taking vitamin D or copper or zinc, for example.”
Dr. Lin referred to a small study in which reporters observed semen abnormalities and subfertility after weight-loss surgery despite improvements in androgenic and quality of life levels.
Dr. Upala reported having no relevant disclosures.
LOS ANGELES – On the male fertility front, obesity seems to hurt semen quality. So does weight-loss surgery reverse the trend? A new review of existing research suggests that there may be an effect, but the findings aren’t conclusive.
“We found something,” said Sikarin Upala, MD, a second-year endocrinology fellow at the University of Chicago, who pointed out that three of the four reports he and his colleagues reviewed suggested improvement in semen motility. “But we still need to study more about whether bariatric surgery will affect infertility,” he continued.
Dr. Upala, who led the systematic review and meta-analysis of research into bariatric surgery and semen quality, spoke in an interview after his presentation at the annual scientific and clinical congress of the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists.
As researchers explained in a 2018 report, “conflicting results have been observed in studies evaluating the correlation between [body mass index] and sperm parameters, such as sperm concentration and total sperm count.” However, they noted that it is “generally accepted” that men with obesity seem to be at higher risk of having a low sperm count or having azoospermia, which is the total lack of sperm in semen.
It’s also not clear whether weight loss directly improves male fertility. “We do know that androgen levels improve after weight-loss surgery, and that might be one factor among several that may contribute to improved male fertility,” Edward Lin, DO, MBA, FACS, professor of surgery and chief of gastrointestinal and general surgery at Emory University, Atlanta, said in an interview.
In their review, Dr. Upala and his colleagues analyzed four studies published between 2012 and 2018 that evaluated the effect of bariatric surgery on semen quality. All of the studies examined semen volume and sperm morphology and motility, and three examined sperm concentration.
A meta-analysis found that motility and volume improved after surgery; however, some of the studies (two for volume, one for motility) failed to show a statistically significant change.
There was no statistically significant difference in sperm morphology or concentration overall, although one study showed a statistically significant improvement in both categories.
Overall, “there might be a little bit of positive effect, but we couldn’t reach a good conclusion because there were too few studies,” Dr. Upala said.
Dr. Lin, director of the Emory Bariatrics Center, agreed that the review findings are limited. He said that although the findings hint at a positive effect on semen quality, “the jury is still out” when it comes to a link between bariatric surgery and male infertility.
“Multiple factors contribute to semen quality,” he added, pointing to vitamin deficiencies, micronutrient levels in the body, enzyme signaling pathways, and sperm chromatin integrity. “In fact, surgically or diet-induced weight loss may be associated with permissive malnutrition, which further exacerbates these deficiencies. Deficiencies in these areas can sometimes take months, if not years, to correct by taking vitamin D or copper or zinc, for example.”
Dr. Lin referred to a small study in which reporters observed semen abnormalities and subfertility after weight-loss surgery despite improvements in androgenic and quality of life levels.
Dr. Upala reported having no relevant disclosures.
REPORTING FROM AACE 2019
2019 Update: Contraceptives and unintended pregnancy rates
NASHVILLE, TENN. – The unintended pregnancy rate is declining after years of hovering at close to 50%.
While the rates among women of color remain high – currently at 58 and 79 per 1,000 women aged 15-44 years for Hispanic and black women, respectively – they have declined from 79 and 92 per 1,000 Hispanic and black women in that age group in 2008, and the overall rate is now at about 45%, Eve Espey, MD, said at the annual clinical and scientific meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
“Considering the scope and number of women affected by unplanned pregnancy, this is actually a huge public health achievement,” said Dr. Espey, professor and chair of the department of obstetrics & gynecology at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque.
she noted, adding that “another enormous determinant of this decrease in unintended pregnancy is the use of long-acting reversible contraception [LARC].” About 2% of women used contraceptives in 2002, and now, based on the latest cycle of data from 2015-2017, 16% of women use contraceptives.
In this video interview, Dr. Espey discusses the main points of her talk entitled “Contraceptives: What you need to know in 2019,” including:
- The importance of “following reproductive justice–based principles and counseling” when it comes to prescribing contraceptives.
- The latest data showing that certain LARC methods remain safe and effective beyond their approved duration of use.
- Trends with respect to tubal ligation and salpingectomy.
- The value of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s U.S. Medical Eligibility Criteria (MEC) for evidence-based guidance on selecting contraceptives based on patients’ individual needs.
“[MEC] is something every ob.gyn. should consider using,” she said, noting that access is available through a free app. “As our patients are more complex and have more comorbidities, it’s particularly helpful for matching up patients and their conditions with recommendations for specific contraceptive methods.”
Dr. Espey reported having no financial disclosures.
NASHVILLE, TENN. – The unintended pregnancy rate is declining after years of hovering at close to 50%.
While the rates among women of color remain high – currently at 58 and 79 per 1,000 women aged 15-44 years for Hispanic and black women, respectively – they have declined from 79 and 92 per 1,000 Hispanic and black women in that age group in 2008, and the overall rate is now at about 45%, Eve Espey, MD, said at the annual clinical and scientific meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
“Considering the scope and number of women affected by unplanned pregnancy, this is actually a huge public health achievement,” said Dr. Espey, professor and chair of the department of obstetrics & gynecology at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque.
she noted, adding that “another enormous determinant of this decrease in unintended pregnancy is the use of long-acting reversible contraception [LARC].” About 2% of women used contraceptives in 2002, and now, based on the latest cycle of data from 2015-2017, 16% of women use contraceptives.
In this video interview, Dr. Espey discusses the main points of her talk entitled “Contraceptives: What you need to know in 2019,” including:
- The importance of “following reproductive justice–based principles and counseling” when it comes to prescribing contraceptives.
- The latest data showing that certain LARC methods remain safe and effective beyond their approved duration of use.
- Trends with respect to tubal ligation and salpingectomy.
- The value of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s U.S. Medical Eligibility Criteria (MEC) for evidence-based guidance on selecting contraceptives based on patients’ individual needs.
“[MEC] is something every ob.gyn. should consider using,” she said, noting that access is available through a free app. “As our patients are more complex and have more comorbidities, it’s particularly helpful for matching up patients and their conditions with recommendations for specific contraceptive methods.”
Dr. Espey reported having no financial disclosures.
NASHVILLE, TENN. – The unintended pregnancy rate is declining after years of hovering at close to 50%.
While the rates among women of color remain high – currently at 58 and 79 per 1,000 women aged 15-44 years for Hispanic and black women, respectively – they have declined from 79 and 92 per 1,000 Hispanic and black women in that age group in 2008, and the overall rate is now at about 45%, Eve Espey, MD, said at the annual clinical and scientific meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
“Considering the scope and number of women affected by unplanned pregnancy, this is actually a huge public health achievement,” said Dr. Espey, professor and chair of the department of obstetrics & gynecology at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque.
she noted, adding that “another enormous determinant of this decrease in unintended pregnancy is the use of long-acting reversible contraception [LARC].” About 2% of women used contraceptives in 2002, and now, based on the latest cycle of data from 2015-2017, 16% of women use contraceptives.
In this video interview, Dr. Espey discusses the main points of her talk entitled “Contraceptives: What you need to know in 2019,” including:
- The importance of “following reproductive justice–based principles and counseling” when it comes to prescribing contraceptives.
- The latest data showing that certain LARC methods remain safe and effective beyond their approved duration of use.
- Trends with respect to tubal ligation and salpingectomy.
- The value of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s U.S. Medical Eligibility Criteria (MEC) for evidence-based guidance on selecting contraceptives based on patients’ individual needs.
“[MEC] is something every ob.gyn. should consider using,” she said, noting that access is available through a free app. “As our patients are more complex and have more comorbidities, it’s particularly helpful for matching up patients and their conditions with recommendations for specific contraceptive methods.”
Dr. Espey reported having no financial disclosures.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM ACOG 2019
Discuss compounded bioidentical hormones and cancer risk
The clinical scenario is as follows: A 62-year-old woman comes to see me for a new diagnosis of grade 1 endometrial cancer. She has a normal body mass index of 24 kg/m2, a history of four prior full-term pregnancies, no family history of malignancy, and no medical comorbidities. She is otherwise a specimen of good health, and has no clear identifiable risk factors for this malignancy. She then reports that she transitioned through menopause at age 52 years and developed severe hot flashes with sleep and mood disturbance. She did not wish to take conventional hormone replacement therapy (HT) because she had heard it causes cancer. She subsequently researched the Internet and found a provider who has been prescribing compounded bioidentical hormone therapy (CBHT) for her for the past 10 years. She submits saliva for testing of her estrogen levels, and the provider uses this data to compound the appropriate doses of “natural” estrogens and testosterone for her which she applies via vaginal or transdermal creams. She has been prescribed a progesterone suppository, but she doesn’t always take that because she doesn’t notice that it has any effect on how she feels.
My answer is, of course, I don’t know. Cancer is a complex disease with a complex array of causative and promoting factors. However, we do know that taking estrogen unopposed with adequate progesterone can cause the development of uterine cancer and its precursor state.1 If those bioidentical estrogens were effective at controlling her menopausal symptoms, they likely were effective at stimulating her endometrium at the same time.
What are compounded bioidentical hormones?
The term “bioidentical” refers to having the same molecular structure as that which is found in the human body. Examples of bioidentical estrogens include 17-beta-estradiol, estrone, and estriol – which are produced from yams and soy. Micronized progesterone is an example of a bioidentical progesterone. Many of these drugs are approved by the Food and Drug Administration, and prescribed and dispensed by conventional pharmacies.
An alternative, and increasingly popular, version of bioidentical hormones are CBHs. It should be recognized that this is a marketing, and not a scientific, term. These products utilize hormones, in some cases FDA-approved bioidentical hormones, that are broken down and blended by specialized pharmacies and reconstituted (compounded) into different, and sometimes “customized,” dosing and delivery methods (such as capsules, patches, gels, creams, lozenges, suppositories). Frequently used compounded products utilize multiple formulations of estrogens in doublets and triplets as well as progesterone, testosterone, and dehydroepiandrosterone.
How do they differ from synthetic hormones?
Distributors of CBHs state that they differ from conventional HT (synthetic and bioidentical) because of the customization process from which they promise greater efficacy and a sense of personalized medicine. The distributors frequently utilize assays from saliva, blood, vaginal secretions, and urine to measure a woman’s hormone levels, and titrate her compounded formulation based on those results. It should be noted that there is no data to support that titration of hormones to blood, salivary, or urine levels is efficacious or ensures greater safety than titration based on symptom management.
Critics of CBHT, which includes the North American Menopause Society2 and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists,3 highlight that the main difference between CBHT and HT is lack of FDA regulation over the CBHT industry. Many of these agents are delivered transdermally and therefore are classified as “dietary supplements.” As such, they do not require FDA regulation or proof of safety or efficacy.
Lack of FDA approval allows CBHs to be distributed without package inserts and boxed warnings (such as the standard warnings about MI, venous thromboembolic events, and breast cancer). The absence of FDA approval also allows them to avoid FDA-regulated guarantees about purity, potency, and efficacy. Audits of CBHs have shown high rates of discrepancy between stated and measured potency, including observations of both much lower and much higher than stated strength.4
Why would dosing accuracy be important in hormone therapy prescription? If a woman taking estrogen therapy is not receiving adequate cotreatment with progesterone because of either omission or a subtherapeutic product, she increases her risk for endometrial cancer.
What drives patients’ decision to use compounded bioidentical hormones?
After the Womens’ Health Initiative study was published in 20025, all FDA-regulated estrogen preparations were required to carry specific warnings, particularly in relation to the increased risk for MI, venous thromboembolic events, and breast cancer. There was a clear uptake in use of CBHT after this study was reported. By avoiding FDA regulations, distributors of CBHTs may have avoided providing Womens’ Health Initiative information to patients. The absence of an insert with a written warning, in and of itself, makes these preparations seem safer to the patient.
But is it entirely a lack of information that drives demand for CBHTs? Surveys of current or former users suggest the motivations are more complex than that. A survey of 21 past or present CBHT users inquired about reasons for use of CBHT over conventional HT.6 Their responses were categorized as either push motivations away from conventional therapy versus pull motivations toward CBHT. About 95% of current and former users cited distrust of the biomedicine and pharmaceutical industry as reasons for use of CBHT. Fear about the safety of conventional HT, particularly with respect to cancer risk, also was strongly cited at 81%. Motivations pulling toward CBHT included its efficacy (76%) and perception that CBHT is “safer” than conventional HT (76%).
Women in this study also appreciated the tailored, individualized approach that often is associated with CBHT, in which providers spend long consultations discussing individual patient needs and concerns. They enjoy the idea of a customized blend that is created, as opposed to a standard dosing regimen, and intuitively trust the reliability of blood and saliva testing as a prescriptive tool.
Are bioidentical hormones safe with respect to cancer risk?
Hormones themselves are not inert substances, including those derived in vivo and those from plants. They have powerful effects in the human body and can promote malignant transformation or proliferation, alter metabolic pathways, stimulate vascular tone, influence coagulation pathways, along with many other effects. A hormone’s potential for deleterious effect can be present regardless of how that hormone is synthesized, procured, or prepared. While there are no data to suggest that CBHT is associated with increased cancer risk, compared with conventional HT, there are by no means any data to suggest it is safer. Unopposed compounded estrogens place women at increased risk for endometrial cancers, and the prolonged use of hormonal therapy, compounded or otherwise, after menopause increases the risk for breast cancer.
How should we counsel patients?
Patients who desire compounded bioidentical hormone preparations should be counseled that little is known about the safety of these preparations, compared with conventional hormone preparations. The fact that the components are often plant based rather than synthetic does not inherently alter their potential negative impact on biologic pathways. Patients should be educated regarding the difference between FDA-regulated products and nonregulated products so that they can understand that lack of a boxed warning on a non-FDA regulated product does not mean an absence of risk. Women should be informed of the potential inaccuracies in dosing and strength of the CBH preparations they receive.
We should recognize that our patients strongly desire a relationship with their provider in which they are listened to, understood, and treated as individuals. If conversations regarding hormone use are approached with these principles, we will optimize the likelihood our patients are receptive to the highest quality information and not pulled in the direction of unregulated products.
Dr. Rossi is assistant professor in the division of gynecologic oncology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. She reported that she had no conflicts of interest. Email Dr. Rossi at obnews@mdedge.com.
References:
1. Maturitas. 2014 Jan;77(1):4-6.
2. Menopause. 2014 Dec;21(12):1298-300.
3. Fertil Steril. 2012 Aug;98(2):308-12.
4. Report: Limited FDA survey of compounded drug products (Silver Spring, Md.: U.S. Food and Drug Administration, 2009).
5. JAMA. 2002;288(3):321-33.
6. BMC Womens Health. 2017 Oct 2;17(1):97.
The clinical scenario is as follows: A 62-year-old woman comes to see me for a new diagnosis of grade 1 endometrial cancer. She has a normal body mass index of 24 kg/m2, a history of four prior full-term pregnancies, no family history of malignancy, and no medical comorbidities. She is otherwise a specimen of good health, and has no clear identifiable risk factors for this malignancy. She then reports that she transitioned through menopause at age 52 years and developed severe hot flashes with sleep and mood disturbance. She did not wish to take conventional hormone replacement therapy (HT) because she had heard it causes cancer. She subsequently researched the Internet and found a provider who has been prescribing compounded bioidentical hormone therapy (CBHT) for her for the past 10 years. She submits saliva for testing of her estrogen levels, and the provider uses this data to compound the appropriate doses of “natural” estrogens and testosterone for her which she applies via vaginal or transdermal creams. She has been prescribed a progesterone suppository, but she doesn’t always take that because she doesn’t notice that it has any effect on how she feels.
My answer is, of course, I don’t know. Cancer is a complex disease with a complex array of causative and promoting factors. However, we do know that taking estrogen unopposed with adequate progesterone can cause the development of uterine cancer and its precursor state.1 If those bioidentical estrogens were effective at controlling her menopausal symptoms, they likely were effective at stimulating her endometrium at the same time.
What are compounded bioidentical hormones?
The term “bioidentical” refers to having the same molecular structure as that which is found in the human body. Examples of bioidentical estrogens include 17-beta-estradiol, estrone, and estriol – which are produced from yams and soy. Micronized progesterone is an example of a bioidentical progesterone. Many of these drugs are approved by the Food and Drug Administration, and prescribed and dispensed by conventional pharmacies.
An alternative, and increasingly popular, version of bioidentical hormones are CBHs. It should be recognized that this is a marketing, and not a scientific, term. These products utilize hormones, in some cases FDA-approved bioidentical hormones, that are broken down and blended by specialized pharmacies and reconstituted (compounded) into different, and sometimes “customized,” dosing and delivery methods (such as capsules, patches, gels, creams, lozenges, suppositories). Frequently used compounded products utilize multiple formulations of estrogens in doublets and triplets as well as progesterone, testosterone, and dehydroepiandrosterone.
How do they differ from synthetic hormones?
Distributors of CBHs state that they differ from conventional HT (synthetic and bioidentical) because of the customization process from which they promise greater efficacy and a sense of personalized medicine. The distributors frequently utilize assays from saliva, blood, vaginal secretions, and urine to measure a woman’s hormone levels, and titrate her compounded formulation based on those results. It should be noted that there is no data to support that titration of hormones to blood, salivary, or urine levels is efficacious or ensures greater safety than titration based on symptom management.
Critics of CBHT, which includes the North American Menopause Society2 and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists,3 highlight that the main difference between CBHT and HT is lack of FDA regulation over the CBHT industry. Many of these agents are delivered transdermally and therefore are classified as “dietary supplements.” As such, they do not require FDA regulation or proof of safety or efficacy.
Lack of FDA approval allows CBHs to be distributed without package inserts and boxed warnings (such as the standard warnings about MI, venous thromboembolic events, and breast cancer). The absence of FDA approval also allows them to avoid FDA-regulated guarantees about purity, potency, and efficacy. Audits of CBHs have shown high rates of discrepancy between stated and measured potency, including observations of both much lower and much higher than stated strength.4
Why would dosing accuracy be important in hormone therapy prescription? If a woman taking estrogen therapy is not receiving adequate cotreatment with progesterone because of either omission or a subtherapeutic product, she increases her risk for endometrial cancer.
What drives patients’ decision to use compounded bioidentical hormones?
After the Womens’ Health Initiative study was published in 20025, all FDA-regulated estrogen preparations were required to carry specific warnings, particularly in relation to the increased risk for MI, venous thromboembolic events, and breast cancer. There was a clear uptake in use of CBHT after this study was reported. By avoiding FDA regulations, distributors of CBHTs may have avoided providing Womens’ Health Initiative information to patients. The absence of an insert with a written warning, in and of itself, makes these preparations seem safer to the patient.
But is it entirely a lack of information that drives demand for CBHTs? Surveys of current or former users suggest the motivations are more complex than that. A survey of 21 past or present CBHT users inquired about reasons for use of CBHT over conventional HT.6 Their responses were categorized as either push motivations away from conventional therapy versus pull motivations toward CBHT. About 95% of current and former users cited distrust of the biomedicine and pharmaceutical industry as reasons for use of CBHT. Fear about the safety of conventional HT, particularly with respect to cancer risk, also was strongly cited at 81%. Motivations pulling toward CBHT included its efficacy (76%) and perception that CBHT is “safer” than conventional HT (76%).
Women in this study also appreciated the tailored, individualized approach that often is associated with CBHT, in which providers spend long consultations discussing individual patient needs and concerns. They enjoy the idea of a customized blend that is created, as opposed to a standard dosing regimen, and intuitively trust the reliability of blood and saliva testing as a prescriptive tool.
Are bioidentical hormones safe with respect to cancer risk?
Hormones themselves are not inert substances, including those derived in vivo and those from plants. They have powerful effects in the human body and can promote malignant transformation or proliferation, alter metabolic pathways, stimulate vascular tone, influence coagulation pathways, along with many other effects. A hormone’s potential for deleterious effect can be present regardless of how that hormone is synthesized, procured, or prepared. While there are no data to suggest that CBHT is associated with increased cancer risk, compared with conventional HT, there are by no means any data to suggest it is safer. Unopposed compounded estrogens place women at increased risk for endometrial cancers, and the prolonged use of hormonal therapy, compounded or otherwise, after menopause increases the risk for breast cancer.
How should we counsel patients?
Patients who desire compounded bioidentical hormone preparations should be counseled that little is known about the safety of these preparations, compared with conventional hormone preparations. The fact that the components are often plant based rather than synthetic does not inherently alter their potential negative impact on biologic pathways. Patients should be educated regarding the difference between FDA-regulated products and nonregulated products so that they can understand that lack of a boxed warning on a non-FDA regulated product does not mean an absence of risk. Women should be informed of the potential inaccuracies in dosing and strength of the CBH preparations they receive.
We should recognize that our patients strongly desire a relationship with their provider in which they are listened to, understood, and treated as individuals. If conversations regarding hormone use are approached with these principles, we will optimize the likelihood our patients are receptive to the highest quality information and not pulled in the direction of unregulated products.
Dr. Rossi is assistant professor in the division of gynecologic oncology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. She reported that she had no conflicts of interest. Email Dr. Rossi at obnews@mdedge.com.
References:
1. Maturitas. 2014 Jan;77(1):4-6.
2. Menopause. 2014 Dec;21(12):1298-300.
3. Fertil Steril. 2012 Aug;98(2):308-12.
4. Report: Limited FDA survey of compounded drug products (Silver Spring, Md.: U.S. Food and Drug Administration, 2009).
5. JAMA. 2002;288(3):321-33.
6. BMC Womens Health. 2017 Oct 2;17(1):97.
The clinical scenario is as follows: A 62-year-old woman comes to see me for a new diagnosis of grade 1 endometrial cancer. She has a normal body mass index of 24 kg/m2, a history of four prior full-term pregnancies, no family history of malignancy, and no medical comorbidities. She is otherwise a specimen of good health, and has no clear identifiable risk factors for this malignancy. She then reports that she transitioned through menopause at age 52 years and developed severe hot flashes with sleep and mood disturbance. She did not wish to take conventional hormone replacement therapy (HT) because she had heard it causes cancer. She subsequently researched the Internet and found a provider who has been prescribing compounded bioidentical hormone therapy (CBHT) for her for the past 10 years. She submits saliva for testing of her estrogen levels, and the provider uses this data to compound the appropriate doses of “natural” estrogens and testosterone for her which she applies via vaginal or transdermal creams. She has been prescribed a progesterone suppository, but she doesn’t always take that because she doesn’t notice that it has any effect on how she feels.
My answer is, of course, I don’t know. Cancer is a complex disease with a complex array of causative and promoting factors. However, we do know that taking estrogen unopposed with adequate progesterone can cause the development of uterine cancer and its precursor state.1 If those bioidentical estrogens were effective at controlling her menopausal symptoms, they likely were effective at stimulating her endometrium at the same time.
What are compounded bioidentical hormones?
The term “bioidentical” refers to having the same molecular structure as that which is found in the human body. Examples of bioidentical estrogens include 17-beta-estradiol, estrone, and estriol – which are produced from yams and soy. Micronized progesterone is an example of a bioidentical progesterone. Many of these drugs are approved by the Food and Drug Administration, and prescribed and dispensed by conventional pharmacies.
An alternative, and increasingly popular, version of bioidentical hormones are CBHs. It should be recognized that this is a marketing, and not a scientific, term. These products utilize hormones, in some cases FDA-approved bioidentical hormones, that are broken down and blended by specialized pharmacies and reconstituted (compounded) into different, and sometimes “customized,” dosing and delivery methods (such as capsules, patches, gels, creams, lozenges, suppositories). Frequently used compounded products utilize multiple formulations of estrogens in doublets and triplets as well as progesterone, testosterone, and dehydroepiandrosterone.
How do they differ from synthetic hormones?
Distributors of CBHs state that they differ from conventional HT (synthetic and bioidentical) because of the customization process from which they promise greater efficacy and a sense of personalized medicine. The distributors frequently utilize assays from saliva, blood, vaginal secretions, and urine to measure a woman’s hormone levels, and titrate her compounded formulation based on those results. It should be noted that there is no data to support that titration of hormones to blood, salivary, or urine levels is efficacious or ensures greater safety than titration based on symptom management.
Critics of CBHT, which includes the North American Menopause Society2 and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists,3 highlight that the main difference between CBHT and HT is lack of FDA regulation over the CBHT industry. Many of these agents are delivered transdermally and therefore are classified as “dietary supplements.” As such, they do not require FDA regulation or proof of safety or efficacy.
Lack of FDA approval allows CBHs to be distributed without package inserts and boxed warnings (such as the standard warnings about MI, venous thromboembolic events, and breast cancer). The absence of FDA approval also allows them to avoid FDA-regulated guarantees about purity, potency, and efficacy. Audits of CBHs have shown high rates of discrepancy between stated and measured potency, including observations of both much lower and much higher than stated strength.4
Why would dosing accuracy be important in hormone therapy prescription? If a woman taking estrogen therapy is not receiving adequate cotreatment with progesterone because of either omission or a subtherapeutic product, she increases her risk for endometrial cancer.
What drives patients’ decision to use compounded bioidentical hormones?
After the Womens’ Health Initiative study was published in 20025, all FDA-regulated estrogen preparations were required to carry specific warnings, particularly in relation to the increased risk for MI, venous thromboembolic events, and breast cancer. There was a clear uptake in use of CBHT after this study was reported. By avoiding FDA regulations, distributors of CBHTs may have avoided providing Womens’ Health Initiative information to patients. The absence of an insert with a written warning, in and of itself, makes these preparations seem safer to the patient.
But is it entirely a lack of information that drives demand for CBHTs? Surveys of current or former users suggest the motivations are more complex than that. A survey of 21 past or present CBHT users inquired about reasons for use of CBHT over conventional HT.6 Their responses were categorized as either push motivations away from conventional therapy versus pull motivations toward CBHT. About 95% of current and former users cited distrust of the biomedicine and pharmaceutical industry as reasons for use of CBHT. Fear about the safety of conventional HT, particularly with respect to cancer risk, also was strongly cited at 81%. Motivations pulling toward CBHT included its efficacy (76%) and perception that CBHT is “safer” than conventional HT (76%).
Women in this study also appreciated the tailored, individualized approach that often is associated with CBHT, in which providers spend long consultations discussing individual patient needs and concerns. They enjoy the idea of a customized blend that is created, as opposed to a standard dosing regimen, and intuitively trust the reliability of blood and saliva testing as a prescriptive tool.
Are bioidentical hormones safe with respect to cancer risk?
Hormones themselves are not inert substances, including those derived in vivo and those from plants. They have powerful effects in the human body and can promote malignant transformation or proliferation, alter metabolic pathways, stimulate vascular tone, influence coagulation pathways, along with many other effects. A hormone’s potential for deleterious effect can be present regardless of how that hormone is synthesized, procured, or prepared. While there are no data to suggest that CBHT is associated with increased cancer risk, compared with conventional HT, there are by no means any data to suggest it is safer. Unopposed compounded estrogens place women at increased risk for endometrial cancers, and the prolonged use of hormonal therapy, compounded or otherwise, after menopause increases the risk for breast cancer.
How should we counsel patients?
Patients who desire compounded bioidentical hormone preparations should be counseled that little is known about the safety of these preparations, compared with conventional hormone preparations. The fact that the components are often plant based rather than synthetic does not inherently alter their potential negative impact on biologic pathways. Patients should be educated regarding the difference between FDA-regulated products and nonregulated products so that they can understand that lack of a boxed warning on a non-FDA regulated product does not mean an absence of risk. Women should be informed of the potential inaccuracies in dosing and strength of the CBH preparations they receive.
We should recognize that our patients strongly desire a relationship with their provider in which they are listened to, understood, and treated as individuals. If conversations regarding hormone use are approached with these principles, we will optimize the likelihood our patients are receptive to the highest quality information and not pulled in the direction of unregulated products.
Dr. Rossi is assistant professor in the division of gynecologic oncology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. She reported that she had no conflicts of interest. Email Dr. Rossi at obnews@mdedge.com.
References:
1. Maturitas. 2014 Jan;77(1):4-6.
2. Menopause. 2014 Dec;21(12):1298-300.
3. Fertil Steril. 2012 Aug;98(2):308-12.
4. Report: Limited FDA survey of compounded drug products (Silver Spring, Md.: U.S. Food and Drug Administration, 2009).
5. JAMA. 2002;288(3):321-33.
6. BMC Womens Health. 2017 Oct 2;17(1):97.
Is childhood cancer associated with assisted reproductive technology?
Recently, two studies were published addressing the potential association of childhood cancer and assisted reproductive technology. For more than a decade and a half, it has been acknowledged that ART is associated with increased concern both with structural birth defects, as well as imprinting disorders. As both of these issues have been linked to greater cancer risk in children, it is important to decipher the impact of ART on childhood cancer risk.
Published online April 1 in JAMA Pediatrics, the study, “Association of in vitro fertilization [IVF] with childhood cancer in the United States,”1 by LG Spector et al. looked retrospectively at birth and cancer registries in 14 states with 8 years of data on 275,686 children were conceived via ART through 2013, who were compared with 2,266,847 children selected randomly.
The overall cancer rate per 1,000,000 person-years was low in both groups: 252 for the IVF group and 193 for the control group, for an overall hazard risk of 1.17. Of note, the rate of hepatic tumors was higher among the IVF group than the non-IVF group (18 vs. 5.7; hazard ratio, 2.46). There appeared to be no association with specific IVF treatments, whether children were conceived by donor egg vs. autologous egg; frozen embryos vs. fresh embryos; use of intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) vs. none; assisted hatching vs. none; and day-3 vs. day-5 transfer. The researchers concluded that the “increased rate of embryonal cancers, particularly hepatic tumors, that could not be attributed to IVF rather than to underlying infertility.”
This first and largest cohort study of association between IVF and the risk of childhood cancer ever published showed little evidence of excess risk of most cancers, including more common cancers such as leukemia.
The authors did note limitations in their study. Mothers who conceived via IVF were more likely to be white, non-Hispanic, more educated, and older. Could this patient population undergoing ART be at greater risk of producing offspring with cancer concerns? If that were the case – and not great risk of childhood cancer in ART, per se – one therefore would extrapolate that couples undergoing ART vs. alternative infertility treatment should not show a treatment-biased risk (i.e., ART vs. non-ART).
This was demonstrated recently in the study, “Risk of cancer in children and young adults conceived by assisted reproductive technology.”2 This Dutch historical cohort study with prospective follow-up of a median 21 years evaluated 47,690 live-born children, of which 24,269 were ART conceived, 13,761 naturally conceived, and 9,660 conceived naturally or with fertility drugs but not by ART.
Overall, cancer risk was not increased in ART-conceived children, compared with naturally conceived subfertile women or even the general population. A nonsignificant increased risk was observed in children conceived by ICSI or cryopreservation.
On the basis of these two studies, there appears to be no significant increased risk of cancer in children conceived through fertility treatment, including ART.
Although these studies do not support the conclusion reached by a 2013 meta-analysis of 9 studies that specifically looked at ART and 16 other studies that looked at other types of medically assisted reproduction (such medically assisted reproduction as reproduction achieved through ovulation induction; controlled ovarian stimulation; ovulation triggering; intrauterine, intracervical, or intravaginal insemination) which reported a significant increased risk of overall cancers (1.33), including leukemia, CNS cancer, and neuroblastoma,3 they do agree more closely with two prospective studies conducted in the United Kingdom and Nordic countries.
In the U.K. study,4 there was no overall increased risk of cancer associated with ART, but two types of cancer were noted to be higher in the ART-conceived group – hepatoblastoma (3.27 risk) and rhabdomyosarcoma (2.62 risk) – but the absolute risk of these two types of cancer was small in this 17-year study of 106,013 children. This, of course, would be consistent with the JAMA Pediatrics study. In the Nordic study,5 similar to the Dutch Study, IVF was not associated with a significant increased risk of cancer (1.08). The Nordic study included 91,796 children born of ART-assisted pregnancies, compared with 358,419 children born after spontaneous conceptions.
The evidence so far shows that there appears to be no significant increased risk of cancer overall associated with fertility treatments, including IVF.
Dr. Miller is a clinical associate professor at the University of Illinois in Chicago and past president of the AAGL. He is a reproductive endocrinologist and minimally invasive gynecologic surgeon in metropolitan Chicago and the director of minimally invasive gynecologic surgery at Advocate Lutheran General Hospital, Park Ridge, Ill. He also is a member of Ob.Gyn. News editorial advisory board. Dr. Miller disclosed that he is president of the Advanced IVF Institute in Park Ridge and Naperville, Ill.
References
1. JAMA Pediatr. 2019 Apr 1. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.0392.
2. Hum Reprod. 2019 Apr 1;34(4):740-50.
3. Fertil Steril. 2013 Jul. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2013.03.017.
4. N Engl J Med. 2013 Nov 7;369(19):1819-27.
5. Hum Reprod. 2014 Sep;29(9):2050-7.
Recently, two studies were published addressing the potential association of childhood cancer and assisted reproductive technology. For more than a decade and a half, it has been acknowledged that ART is associated with increased concern both with structural birth defects, as well as imprinting disorders. As both of these issues have been linked to greater cancer risk in children, it is important to decipher the impact of ART on childhood cancer risk.
Published online April 1 in JAMA Pediatrics, the study, “Association of in vitro fertilization [IVF] with childhood cancer in the United States,”1 by LG Spector et al. looked retrospectively at birth and cancer registries in 14 states with 8 years of data on 275,686 children were conceived via ART through 2013, who were compared with 2,266,847 children selected randomly.
The overall cancer rate per 1,000,000 person-years was low in both groups: 252 for the IVF group and 193 for the control group, for an overall hazard risk of 1.17. Of note, the rate of hepatic tumors was higher among the IVF group than the non-IVF group (18 vs. 5.7; hazard ratio, 2.46). There appeared to be no association with specific IVF treatments, whether children were conceived by donor egg vs. autologous egg; frozen embryos vs. fresh embryos; use of intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) vs. none; assisted hatching vs. none; and day-3 vs. day-5 transfer. The researchers concluded that the “increased rate of embryonal cancers, particularly hepatic tumors, that could not be attributed to IVF rather than to underlying infertility.”
This first and largest cohort study of association between IVF and the risk of childhood cancer ever published showed little evidence of excess risk of most cancers, including more common cancers such as leukemia.
The authors did note limitations in their study. Mothers who conceived via IVF were more likely to be white, non-Hispanic, more educated, and older. Could this patient population undergoing ART be at greater risk of producing offspring with cancer concerns? If that were the case – and not great risk of childhood cancer in ART, per se – one therefore would extrapolate that couples undergoing ART vs. alternative infertility treatment should not show a treatment-biased risk (i.e., ART vs. non-ART).
This was demonstrated recently in the study, “Risk of cancer in children and young adults conceived by assisted reproductive technology.”2 This Dutch historical cohort study with prospective follow-up of a median 21 years evaluated 47,690 live-born children, of which 24,269 were ART conceived, 13,761 naturally conceived, and 9,660 conceived naturally or with fertility drugs but not by ART.
Overall, cancer risk was not increased in ART-conceived children, compared with naturally conceived subfertile women or even the general population. A nonsignificant increased risk was observed in children conceived by ICSI or cryopreservation.
On the basis of these two studies, there appears to be no significant increased risk of cancer in children conceived through fertility treatment, including ART.
Although these studies do not support the conclusion reached by a 2013 meta-analysis of 9 studies that specifically looked at ART and 16 other studies that looked at other types of medically assisted reproduction (such medically assisted reproduction as reproduction achieved through ovulation induction; controlled ovarian stimulation; ovulation triggering; intrauterine, intracervical, or intravaginal insemination) which reported a significant increased risk of overall cancers (1.33), including leukemia, CNS cancer, and neuroblastoma,3 they do agree more closely with two prospective studies conducted in the United Kingdom and Nordic countries.
In the U.K. study,4 there was no overall increased risk of cancer associated with ART, but two types of cancer were noted to be higher in the ART-conceived group – hepatoblastoma (3.27 risk) and rhabdomyosarcoma (2.62 risk) – but the absolute risk of these two types of cancer was small in this 17-year study of 106,013 children. This, of course, would be consistent with the JAMA Pediatrics study. In the Nordic study,5 similar to the Dutch Study, IVF was not associated with a significant increased risk of cancer (1.08). The Nordic study included 91,796 children born of ART-assisted pregnancies, compared with 358,419 children born after spontaneous conceptions.
The evidence so far shows that there appears to be no significant increased risk of cancer overall associated with fertility treatments, including IVF.
Dr. Miller is a clinical associate professor at the University of Illinois in Chicago and past president of the AAGL. He is a reproductive endocrinologist and minimally invasive gynecologic surgeon in metropolitan Chicago and the director of minimally invasive gynecologic surgery at Advocate Lutheran General Hospital, Park Ridge, Ill. He also is a member of Ob.Gyn. News editorial advisory board. Dr. Miller disclosed that he is president of the Advanced IVF Institute in Park Ridge and Naperville, Ill.
References
1. JAMA Pediatr. 2019 Apr 1. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.0392.
2. Hum Reprod. 2019 Apr 1;34(4):740-50.
3. Fertil Steril. 2013 Jul. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2013.03.017.
4. N Engl J Med. 2013 Nov 7;369(19):1819-27.
5. Hum Reprod. 2014 Sep;29(9):2050-7.
Recently, two studies were published addressing the potential association of childhood cancer and assisted reproductive technology. For more than a decade and a half, it has been acknowledged that ART is associated with increased concern both with structural birth defects, as well as imprinting disorders. As both of these issues have been linked to greater cancer risk in children, it is important to decipher the impact of ART on childhood cancer risk.
Published online April 1 in JAMA Pediatrics, the study, “Association of in vitro fertilization [IVF] with childhood cancer in the United States,”1 by LG Spector et al. looked retrospectively at birth and cancer registries in 14 states with 8 years of data on 275,686 children were conceived via ART through 2013, who were compared with 2,266,847 children selected randomly.
The overall cancer rate per 1,000,000 person-years was low in both groups: 252 for the IVF group and 193 for the control group, for an overall hazard risk of 1.17. Of note, the rate of hepatic tumors was higher among the IVF group than the non-IVF group (18 vs. 5.7; hazard ratio, 2.46). There appeared to be no association with specific IVF treatments, whether children were conceived by donor egg vs. autologous egg; frozen embryos vs. fresh embryos; use of intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) vs. none; assisted hatching vs. none; and day-3 vs. day-5 transfer. The researchers concluded that the “increased rate of embryonal cancers, particularly hepatic tumors, that could not be attributed to IVF rather than to underlying infertility.”
This first and largest cohort study of association between IVF and the risk of childhood cancer ever published showed little evidence of excess risk of most cancers, including more common cancers such as leukemia.
The authors did note limitations in their study. Mothers who conceived via IVF were more likely to be white, non-Hispanic, more educated, and older. Could this patient population undergoing ART be at greater risk of producing offspring with cancer concerns? If that were the case – and not great risk of childhood cancer in ART, per se – one therefore would extrapolate that couples undergoing ART vs. alternative infertility treatment should not show a treatment-biased risk (i.e., ART vs. non-ART).
This was demonstrated recently in the study, “Risk of cancer in children and young adults conceived by assisted reproductive technology.”2 This Dutch historical cohort study with prospective follow-up of a median 21 years evaluated 47,690 live-born children, of which 24,269 were ART conceived, 13,761 naturally conceived, and 9,660 conceived naturally or with fertility drugs but not by ART.
Overall, cancer risk was not increased in ART-conceived children, compared with naturally conceived subfertile women or even the general population. A nonsignificant increased risk was observed in children conceived by ICSI or cryopreservation.
On the basis of these two studies, there appears to be no significant increased risk of cancer in children conceived through fertility treatment, including ART.
Although these studies do not support the conclusion reached by a 2013 meta-analysis of 9 studies that specifically looked at ART and 16 other studies that looked at other types of medically assisted reproduction (such medically assisted reproduction as reproduction achieved through ovulation induction; controlled ovarian stimulation; ovulation triggering; intrauterine, intracervical, or intravaginal insemination) which reported a significant increased risk of overall cancers (1.33), including leukemia, CNS cancer, and neuroblastoma,3 they do agree more closely with two prospective studies conducted in the United Kingdom and Nordic countries.
In the U.K. study,4 there was no overall increased risk of cancer associated with ART, but two types of cancer were noted to be higher in the ART-conceived group – hepatoblastoma (3.27 risk) and rhabdomyosarcoma (2.62 risk) – but the absolute risk of these two types of cancer was small in this 17-year study of 106,013 children. This, of course, would be consistent with the JAMA Pediatrics study. In the Nordic study,5 similar to the Dutch Study, IVF was not associated with a significant increased risk of cancer (1.08). The Nordic study included 91,796 children born of ART-assisted pregnancies, compared with 358,419 children born after spontaneous conceptions.
The evidence so far shows that there appears to be no significant increased risk of cancer overall associated with fertility treatments, including IVF.
Dr. Miller is a clinical associate professor at the University of Illinois in Chicago and past president of the AAGL. He is a reproductive endocrinologist and minimally invasive gynecologic surgeon in metropolitan Chicago and the director of minimally invasive gynecologic surgery at Advocate Lutheran General Hospital, Park Ridge, Ill. He also is a member of Ob.Gyn. News editorial advisory board. Dr. Miller disclosed that he is president of the Advanced IVF Institute in Park Ridge and Naperville, Ill.
References
1. JAMA Pediatr. 2019 Apr 1. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.0392.
2. Hum Reprod. 2019 Apr 1;34(4):740-50.
3. Fertil Steril. 2013 Jul. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2013.03.017.
4. N Engl J Med. 2013 Nov 7;369(19):1819-27.
5. Hum Reprod. 2014 Sep;29(9):2050-7.
Fezolinetant looks good for hot flashes in phase 2b trial
NEW ORLEANS – Hot flash frequency was reduced by up to threefold in phase 2b results for fezolinetant, a novel nonhormonal therapy.

The neurokinin-3–receptor (NK3R) antagonist showed a significant reduction of 1.8-2.6 mean hot flashes daily from placebo in twice-daily dosing at the end of 12 weeks, despite a strong 55% response rate to placebo, Graeme Fraser, PhD, said at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
Once-daily dosing also significantly dropped the frequency of moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms by 2.1-2.6 events daily, compared with placebo at the end of 12 weeks.
“This phase 2b trial was really about looking at different dose levels and looking at the once-daily versus twice-daily dosing,” Dr. Fraser said in a video interview. “The efficacy of both, with regard to once-daily and twice-daily dosing, was clear.”
The investigators looked at doses ranging from 15 mg to 90 mg twice daily and 30-120 mg daily. Significant reductions in frequency of moderate to severe hot flashes were seen at all doses and frequencies at 4 weeks and 12 weeks.
A coprimary endpoint, vasomotor severity, was also significantly reduced at 12 weeks for the two highest twice-daily doses. Hot flash severity was similarly reduced at 12 weeks for the two highest once-daily doses.
The safety profile was generally good; there were no signs of suicidality, no changes in endometrial thickness judged by ultrasound or endometrial biopsy, and estradiol levels were unchanged. Plasma bone markers, other laboratory values, and electrocardiograms were also unchanged.
A total of nine women experienced asymptomatic elevations in liver enzymes without bilirubin elevation. Most of these elevations were below three times the upper limit of normal.
Across 51 study sites in the United States, a total of 352 women received one dose of study drug and were included in the safety analysis. Efficacy was analyzed for 349 women, and 287 (81%) were considered completers.
Women were included in the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study if they were naturally or surgically menopausal and aged 40-65 years, and experiencing at least 50 moderate to severe hot flashes weekly.
Fezolinetant acts on the KNDy neuron by replacing estrogen’s inhibitory effects. “Normally the firing is controlled by estrogen, but of course, in menopause, estrogen levels drop, and that control is lost,” explained Dr. Fraser. Fezolinetant exerts antagonism on the KNDy neuron’s NK3 receptor. “Why that’s important is that this neuron synapses at the thermoregulatory centers of the brain.”
Dr. Fraser said that discussions are underway with regulatory authorities to proceed to phase 3 clinical trials.
Dr. Fraser is a consultant to Astellas and was formerly a principal in Ogeda, the developer of fezolinetant. Ogeda is now a wholly owned subsidiary of Astellas, which funded the phase 2B trial.
NEW ORLEANS – Hot flash frequency was reduced by up to threefold in phase 2b results for fezolinetant, a novel nonhormonal therapy.

The neurokinin-3–receptor (NK3R) antagonist showed a significant reduction of 1.8-2.6 mean hot flashes daily from placebo in twice-daily dosing at the end of 12 weeks, despite a strong 55% response rate to placebo, Graeme Fraser, PhD, said at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
Once-daily dosing also significantly dropped the frequency of moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms by 2.1-2.6 events daily, compared with placebo at the end of 12 weeks.
“This phase 2b trial was really about looking at different dose levels and looking at the once-daily versus twice-daily dosing,” Dr. Fraser said in a video interview. “The efficacy of both, with regard to once-daily and twice-daily dosing, was clear.”
The investigators looked at doses ranging from 15 mg to 90 mg twice daily and 30-120 mg daily. Significant reductions in frequency of moderate to severe hot flashes were seen at all doses and frequencies at 4 weeks and 12 weeks.
A coprimary endpoint, vasomotor severity, was also significantly reduced at 12 weeks for the two highest twice-daily doses. Hot flash severity was similarly reduced at 12 weeks for the two highest once-daily doses.
The safety profile was generally good; there were no signs of suicidality, no changes in endometrial thickness judged by ultrasound or endometrial biopsy, and estradiol levels were unchanged. Plasma bone markers, other laboratory values, and electrocardiograms were also unchanged.
A total of nine women experienced asymptomatic elevations in liver enzymes without bilirubin elevation. Most of these elevations were below three times the upper limit of normal.
Across 51 study sites in the United States, a total of 352 women received one dose of study drug and were included in the safety analysis. Efficacy was analyzed for 349 women, and 287 (81%) were considered completers.
Women were included in the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study if they were naturally or surgically menopausal and aged 40-65 years, and experiencing at least 50 moderate to severe hot flashes weekly.
Fezolinetant acts on the KNDy neuron by replacing estrogen’s inhibitory effects. “Normally the firing is controlled by estrogen, but of course, in menopause, estrogen levels drop, and that control is lost,” explained Dr. Fraser. Fezolinetant exerts antagonism on the KNDy neuron’s NK3 receptor. “Why that’s important is that this neuron synapses at the thermoregulatory centers of the brain.”
Dr. Fraser said that discussions are underway with regulatory authorities to proceed to phase 3 clinical trials.
Dr. Fraser is a consultant to Astellas and was formerly a principal in Ogeda, the developer of fezolinetant. Ogeda is now a wholly owned subsidiary of Astellas, which funded the phase 2B trial.
NEW ORLEANS – Hot flash frequency was reduced by up to threefold in phase 2b results for fezolinetant, a novel nonhormonal therapy.

The neurokinin-3–receptor (NK3R) antagonist showed a significant reduction of 1.8-2.6 mean hot flashes daily from placebo in twice-daily dosing at the end of 12 weeks, despite a strong 55% response rate to placebo, Graeme Fraser, PhD, said at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
Once-daily dosing also significantly dropped the frequency of moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms by 2.1-2.6 events daily, compared with placebo at the end of 12 weeks.
“This phase 2b trial was really about looking at different dose levels and looking at the once-daily versus twice-daily dosing,” Dr. Fraser said in a video interview. “The efficacy of both, with regard to once-daily and twice-daily dosing, was clear.”
The investigators looked at doses ranging from 15 mg to 90 mg twice daily and 30-120 mg daily. Significant reductions in frequency of moderate to severe hot flashes were seen at all doses and frequencies at 4 weeks and 12 weeks.
A coprimary endpoint, vasomotor severity, was also significantly reduced at 12 weeks for the two highest twice-daily doses. Hot flash severity was similarly reduced at 12 weeks for the two highest once-daily doses.
The safety profile was generally good; there were no signs of suicidality, no changes in endometrial thickness judged by ultrasound or endometrial biopsy, and estradiol levels were unchanged. Plasma bone markers, other laboratory values, and electrocardiograms were also unchanged.
A total of nine women experienced asymptomatic elevations in liver enzymes without bilirubin elevation. Most of these elevations were below three times the upper limit of normal.
Across 51 study sites in the United States, a total of 352 women received one dose of study drug and were included in the safety analysis. Efficacy was analyzed for 349 women, and 287 (81%) were considered completers.
Women were included in the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study if they were naturally or surgically menopausal and aged 40-65 years, and experiencing at least 50 moderate to severe hot flashes weekly.
Fezolinetant acts on the KNDy neuron by replacing estrogen’s inhibitory effects. “Normally the firing is controlled by estrogen, but of course, in menopause, estrogen levels drop, and that control is lost,” explained Dr. Fraser. Fezolinetant exerts antagonism on the KNDy neuron’s NK3 receptor. “Why that’s important is that this neuron synapses at the thermoregulatory centers of the brain.”
Dr. Fraser said that discussions are underway with regulatory authorities to proceed to phase 3 clinical trials.
Dr. Fraser is a consultant to Astellas and was formerly a principal in Ogeda, the developer of fezolinetant. Ogeda is now a wholly owned subsidiary of Astellas, which funded the phase 2B trial.
REPORTING FROM ENDO 2019
No birth rate gains from levothyroxine in pregnancy
Treatment with levothyroxine does not improve the live birth rate in women with thyroid peroxidase antibodies before conception, according to data presented at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
Until now, the evidence for the use of levothyroxine in pregnant women with thyroid peroxidase antibodies but normal thyroid function has been inconclusive, Rima K. Dhillon-Smith, MBChB, PhD, of the University of Birmingham (England), and her coauthors said in a paper published simultaneously with the meeting presentation March 23 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Previous studies have shown that women with thyroid peroxidase antibodies but normal thyroid function have a nearly fourfold higher risk of miscarriage and twofold higher risk of preterm birth, compared with women who don’t have the antibodies.
In the new double-blind study, 952 women with thyroid peroxidase antibodies, normal thyroid function, and a history of miscarriage or infertility were randomized either to daily 50 mcg levothyroxine or placebo, taken from conception to the end of pregnancy.
The rate of pregnancy was similar in the levothyroxine and placebo groups (56.6% vs. 58.3%, respectively), as was the live birth rate (37.4% vs. 37.9%), despite the observation that the levothyroxine group had consistently lower serum thyrotropin and higher free T4 concentrations than did the placebo group.
There were also no significant differences between the two groups in secondary outcomes of miscarriage, preterm birth, or neonatal outcomes such as birth weight.
Researchers also saw no statistically significant differences in the rate of serious adverse events or in the number of women who showed abnormal results on thyroid function tests.
The authors noted that the dosage of levothyroxine used in the study was fixed, leaving the possibility that “the dose may need to be adjusted depending on the participant’s body weight, thyroid peroxidase antibody level, or thyrotropin concentration.”
Existing guidelines from the American Thyroid Association acknowledge the lack of evidence in favor of levothyroxine decreasing the risk of pregnancy loss. However, the guidelines also state that it can be considered in antibody-positive, euthyroid women with a history of loss, “given its potential benefits in comparison with its minimal risk.”
The study was supported by the National Institute for Health Research. No conflicts of interest were declared.
SOURCE: Dhillon-Smith R et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 March 23. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1812537
Treatment with levothyroxine does not improve the live birth rate in women with thyroid peroxidase antibodies before conception, according to data presented at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
Until now, the evidence for the use of levothyroxine in pregnant women with thyroid peroxidase antibodies but normal thyroid function has been inconclusive, Rima K. Dhillon-Smith, MBChB, PhD, of the University of Birmingham (England), and her coauthors said in a paper published simultaneously with the meeting presentation March 23 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Previous studies have shown that women with thyroid peroxidase antibodies but normal thyroid function have a nearly fourfold higher risk of miscarriage and twofold higher risk of preterm birth, compared with women who don’t have the antibodies.
In the new double-blind study, 952 women with thyroid peroxidase antibodies, normal thyroid function, and a history of miscarriage or infertility were randomized either to daily 50 mcg levothyroxine or placebo, taken from conception to the end of pregnancy.
The rate of pregnancy was similar in the levothyroxine and placebo groups (56.6% vs. 58.3%, respectively), as was the live birth rate (37.4% vs. 37.9%), despite the observation that the levothyroxine group had consistently lower serum thyrotropin and higher free T4 concentrations than did the placebo group.
There were also no significant differences between the two groups in secondary outcomes of miscarriage, preterm birth, or neonatal outcomes such as birth weight.
Researchers also saw no statistically significant differences in the rate of serious adverse events or in the number of women who showed abnormal results on thyroid function tests.
The authors noted that the dosage of levothyroxine used in the study was fixed, leaving the possibility that “the dose may need to be adjusted depending on the participant’s body weight, thyroid peroxidase antibody level, or thyrotropin concentration.”
Existing guidelines from the American Thyroid Association acknowledge the lack of evidence in favor of levothyroxine decreasing the risk of pregnancy loss. However, the guidelines also state that it can be considered in antibody-positive, euthyroid women with a history of loss, “given its potential benefits in comparison with its minimal risk.”
The study was supported by the National Institute for Health Research. No conflicts of interest were declared.
SOURCE: Dhillon-Smith R et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 March 23. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1812537
Treatment with levothyroxine does not improve the live birth rate in women with thyroid peroxidase antibodies before conception, according to data presented at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
Until now, the evidence for the use of levothyroxine in pregnant women with thyroid peroxidase antibodies but normal thyroid function has been inconclusive, Rima K. Dhillon-Smith, MBChB, PhD, of the University of Birmingham (England), and her coauthors said in a paper published simultaneously with the meeting presentation March 23 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Previous studies have shown that women with thyroid peroxidase antibodies but normal thyroid function have a nearly fourfold higher risk of miscarriage and twofold higher risk of preterm birth, compared with women who don’t have the antibodies.
In the new double-blind study, 952 women with thyroid peroxidase antibodies, normal thyroid function, and a history of miscarriage or infertility were randomized either to daily 50 mcg levothyroxine or placebo, taken from conception to the end of pregnancy.
The rate of pregnancy was similar in the levothyroxine and placebo groups (56.6% vs. 58.3%, respectively), as was the live birth rate (37.4% vs. 37.9%), despite the observation that the levothyroxine group had consistently lower serum thyrotropin and higher free T4 concentrations than did the placebo group.
There were also no significant differences between the two groups in secondary outcomes of miscarriage, preterm birth, or neonatal outcomes such as birth weight.
Researchers also saw no statistically significant differences in the rate of serious adverse events or in the number of women who showed abnormal results on thyroid function tests.
The authors noted that the dosage of levothyroxine used in the study was fixed, leaving the possibility that “the dose may need to be adjusted depending on the participant’s body weight, thyroid peroxidase antibody level, or thyrotropin concentration.”
Existing guidelines from the American Thyroid Association acknowledge the lack of evidence in favor of levothyroxine decreasing the risk of pregnancy loss. However, the guidelines also state that it can be considered in antibody-positive, euthyroid women with a history of loss, “given its potential benefits in comparison with its minimal risk.”
The study was supported by the National Institute for Health Research. No conflicts of interest were declared.
SOURCE: Dhillon-Smith R et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 March 23. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1812537
FROM ENDO 2019
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Pregnancy rates and outcomes were similar in women treated with levothyroxine and those treated with placebo.
Study details: Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial in 952 women.
Disclosures: The study was supported by the National Institute for Health Research. No conflicts of interest were declared.
Source: Dhillon-Smith R et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 March 23. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1812537
Survey: Reproductive counseling is often MIA in IBD
LAS VEGAS – Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) can disrupt both fertility and pregnancy, especially if it’s not fully controlled, and there’s a risk that the condition can be passed onto an unborn child. Still a new study suggests many patients with IBD don’t receive appropriate reproductive counseling.
Nearly two-thirds of 100 patients surveyed at a single center reported that no physician had talked to them about reproductive topics, and some said they’d considered not having children because of the condition. “Really fundamental subjects have not made their way into the interactions between patients and their care teams,” coauthor and gastroenterologist Sarah Streett, MD, AGAF, of Stanford (Calif.) University, said in an interview before the study was presented at the annual congress of the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation and the American Gastroenterological Association.
IBD can lower fertility in both sexes and boost complications in pregnancy. “The good news is that almost all the medications used for IBD appear safe,” Dr. Streett said. “In fact, the safety risks for the baby and the pregnancy revolve around not having IBD under good control.”
Unfortunately, she said, misinformation is common. “Patients who become pregnant or are trying to become pregnant, and are worried about potential harm to the baby, will stop the medications due to incorrect information. Or they’ll be told by their health care team to stop their medications.”
Dr. Streett and study lead author Aarti Rao, MD, a gastroenterology fellow at Stanford, launched their study of IBD clinic patients to gain more understanding about patient knowledge. “We know from research already published that those with IBD have a lot of concerns about starting families and don’t have a lot of information to base their decision making on,” Dr. Streett said. “We wanted to evaluate that in our population and see how much people knew and what the need was.”
In 2018 and 2019, Dr. Streett and Dr. Rao gave an anonymous, validated 17-question survey to patients aged 18-45 with IBD. One hundred patients responded (median age = 30, 54% female, 59% white, 66% with incomes over $100,000, 52% with ulcerative colitis, 21% with prior IBD surgery, 71% with prior IBD hospitalization).
Just over a third – 35% – of the patients said they’d been counseled about reproductive health by a physician. This finding reflects findings in previous research, said Dr. Rao, who spoke in an interview.
Just 15% of those who’d undergone IBD surgery reported getting guidance about the effects of surgery on fertility.
More than a third (35%) of women and 15% of men said they’d considered not having children because of their IBD. In fact, “most potential dads and moms have the chance to do very well,” Dr. Streett said.
Without reproductive counseling, she added, parents won’t know about the risks of passing on IBD. According to Dr. Rao, there’s an estimated less than 5% chance that IBD will be passed on to children if one parent has the condition; the risk is much higher if both parents have it.
Going forward, “there’s a really urgent need for proactive counseling on the part of gastroenterologists and health care teams to give people of childbearing age the right information so they can be informed to make the best decisions,” Dr. Streett said.
The study was funded by a philanthropic grant. The study authors report no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Rao A et al. Crohn’s & Colitis Congress, Abstract P009.
LAS VEGAS – Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) can disrupt both fertility and pregnancy, especially if it’s not fully controlled, and there’s a risk that the condition can be passed onto an unborn child. Still a new study suggests many patients with IBD don’t receive appropriate reproductive counseling.
Nearly two-thirds of 100 patients surveyed at a single center reported that no physician had talked to them about reproductive topics, and some said they’d considered not having children because of the condition. “Really fundamental subjects have not made their way into the interactions between patients and their care teams,” coauthor and gastroenterologist Sarah Streett, MD, AGAF, of Stanford (Calif.) University, said in an interview before the study was presented at the annual congress of the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation and the American Gastroenterological Association.
IBD can lower fertility in both sexes and boost complications in pregnancy. “The good news is that almost all the medications used for IBD appear safe,” Dr. Streett said. “In fact, the safety risks for the baby and the pregnancy revolve around not having IBD under good control.”
Unfortunately, she said, misinformation is common. “Patients who become pregnant or are trying to become pregnant, and are worried about potential harm to the baby, will stop the medications due to incorrect information. Or they’ll be told by their health care team to stop their medications.”
Dr. Streett and study lead author Aarti Rao, MD, a gastroenterology fellow at Stanford, launched their study of IBD clinic patients to gain more understanding about patient knowledge. “We know from research already published that those with IBD have a lot of concerns about starting families and don’t have a lot of information to base their decision making on,” Dr. Streett said. “We wanted to evaluate that in our population and see how much people knew and what the need was.”
In 2018 and 2019, Dr. Streett and Dr. Rao gave an anonymous, validated 17-question survey to patients aged 18-45 with IBD. One hundred patients responded (median age = 30, 54% female, 59% white, 66% with incomes over $100,000, 52% with ulcerative colitis, 21% with prior IBD surgery, 71% with prior IBD hospitalization).
Just over a third – 35% – of the patients said they’d been counseled about reproductive health by a physician. This finding reflects findings in previous research, said Dr. Rao, who spoke in an interview.
Just 15% of those who’d undergone IBD surgery reported getting guidance about the effects of surgery on fertility.
More than a third (35%) of women and 15% of men said they’d considered not having children because of their IBD. In fact, “most potential dads and moms have the chance to do very well,” Dr. Streett said.
Without reproductive counseling, she added, parents won’t know about the risks of passing on IBD. According to Dr. Rao, there’s an estimated less than 5% chance that IBD will be passed on to children if one parent has the condition; the risk is much higher if both parents have it.
Going forward, “there’s a really urgent need for proactive counseling on the part of gastroenterologists and health care teams to give people of childbearing age the right information so they can be informed to make the best decisions,” Dr. Streett said.
The study was funded by a philanthropic grant. The study authors report no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Rao A et al. Crohn’s & Colitis Congress, Abstract P009.
LAS VEGAS – Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) can disrupt both fertility and pregnancy, especially if it’s not fully controlled, and there’s a risk that the condition can be passed onto an unborn child. Still a new study suggests many patients with IBD don’t receive appropriate reproductive counseling.
Nearly two-thirds of 100 patients surveyed at a single center reported that no physician had talked to them about reproductive topics, and some said they’d considered not having children because of the condition. “Really fundamental subjects have not made their way into the interactions between patients and their care teams,” coauthor and gastroenterologist Sarah Streett, MD, AGAF, of Stanford (Calif.) University, said in an interview before the study was presented at the annual congress of the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation and the American Gastroenterological Association.
IBD can lower fertility in both sexes and boost complications in pregnancy. “The good news is that almost all the medications used for IBD appear safe,” Dr. Streett said. “In fact, the safety risks for the baby and the pregnancy revolve around not having IBD under good control.”
Unfortunately, she said, misinformation is common. “Patients who become pregnant or are trying to become pregnant, and are worried about potential harm to the baby, will stop the medications due to incorrect information. Or they’ll be told by their health care team to stop their medications.”
Dr. Streett and study lead author Aarti Rao, MD, a gastroenterology fellow at Stanford, launched their study of IBD clinic patients to gain more understanding about patient knowledge. “We know from research already published that those with IBD have a lot of concerns about starting families and don’t have a lot of information to base their decision making on,” Dr. Streett said. “We wanted to evaluate that in our population and see how much people knew and what the need was.”
In 2018 and 2019, Dr. Streett and Dr. Rao gave an anonymous, validated 17-question survey to patients aged 18-45 with IBD. One hundred patients responded (median age = 30, 54% female, 59% white, 66% with incomes over $100,000, 52% with ulcerative colitis, 21% with prior IBD surgery, 71% with prior IBD hospitalization).
Just over a third – 35% – of the patients said they’d been counseled about reproductive health by a physician. This finding reflects findings in previous research, said Dr. Rao, who spoke in an interview.
Just 15% of those who’d undergone IBD surgery reported getting guidance about the effects of surgery on fertility.
More than a third (35%) of women and 15% of men said they’d considered not having children because of their IBD. In fact, “most potential dads and moms have the chance to do very well,” Dr. Streett said.
Without reproductive counseling, she added, parents won’t know about the risks of passing on IBD. According to Dr. Rao, there’s an estimated less than 5% chance that IBD will be passed on to children if one parent has the condition; the risk is much higher if both parents have it.
Going forward, “there’s a really urgent need for proactive counseling on the part of gastroenterologists and health care teams to give people of childbearing age the right information so they can be informed to make the best decisions,” Dr. Streett said.
The study was funded by a philanthropic grant. The study authors report no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Rao A et al. Crohn’s & Colitis Congress, Abstract P009.
REPORTING FROM THE CROHN’S & COLITIS CONGRESS
Key clinical point: Patients with inflammatory bowel disease aren’t getting proper guidance regarding fertility, pregnancy, and genetic risks.
Major finding: Among surveyed patients, 65% said they’d never received reproductive counseling from a physician.
Study details: Single-center survey of 100 patients (median age = 30, 54% female).
Disclosures: The study was funded by a philanthropic grant. The study authors report no relevant disclosures.
Source: Rao A et al. Crohn’s & Colitis Congress 2019, Abstract P009.
Product Update: Bijuva; Liletta; Aegea Vapor System; Natural Cycles
TREATMENT FOR VASOMOTOR SYMPTOMS
BIJUVA™ has been US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved as the first oral treatment for moderate-to-severe vasomotor symptoms due to menopause in women with a uterus. BIJUVA offers a combination of bioidentical estradiol to reduce moderate-to-severe hot flashes and bioidentical progesterone to reduce the risk for endometrial hyperplasia.
TherapeuticsMD says that BIJUVA will be available Spring 2019 and is a proven treatment option for women who are experiencing bothersome symptoms of menopause, with clinical trial data demonstrating a statistically significant reduction in both the frequency and severity of moderate-to-severe vasomotor symptoms. The manufacturer also says that BIJUVA is developed to be identical in molecular structure to the hormones already produced by the body and is designed to help women restore what is lost during menopause.
BIJUVA estradiol and progesterone combination (1 mg/100 mg) will be available in capsule form.
FOR MORE INFORMATION, VISIT:https://bijuva.com/discover/
LILETTA USE EXTENDED
The FDA has approved LILETTA® (levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system) 52 mg for 5-year use. This approval is based on efficacy and safety data from ACCESS IUS, the largest ongoing intrauterine device (IUD) Phase 3 clinical trial in the United States. Previously, LILETTA was indicated for use up to 4 years.
LILETTA continues to be greater than 99% effective in preventing pregnancy in a broad range of women, regardless of age, race, body mass index, or parity, according to Allergan and Medicines360. The extended duration and proven efficacy across a diverse population enables more women in the United States to obtain effective birth control, as the IUD is now available for a low cost at public health clinics.
FOR MORE INFORMATION, VISIT: https://www.liletta.com
Continue to: ENDOMETRIAL ABLATION TECHNOLOGY
ENDOMETRIAL ABLATION TECHNOLOGY
AEGEA Medical introduces the AEGEA Vapor SystemTM, an innovative solution for endometrial ablation to treat menorrhagia.
The system uses Adaptive Vapor Ablation and is the first endometrial ablation system specifically designed for use in the doctor’s office, allowing minimal anesthesia/analgesia and rapid recovery, says AEGEA Medical.
AEGEA Medical describes the AEGEA Vapor System as a fully automated safety monitoring and vapor delivery system that uses a slender, flexible Vapor Probe with SmartSealTM technology and the Integrity ProTM safety feature, for an added level of confidence. The 4-minute procedure time includes 2 minutes of vapor treatment and can be performed in patients with a wider range of uterine anatomies than indicated for use with currently available treatments, says AEGEA Medical.
FOR MORE INFORMATION, VISIT: http://aegeamedical.com/
NATURAL CYCLES
The FDA has cleared Natural Cycles as the first digital method of birth control in the United States. Delivered in the form of an app, Natural Cycles is a fertility awareness–based contraceptive that uses a sophisticated algorithm to accurately and conveniently determine a woman’s daily fertility based on basal body temperature.
That data builds into a personalized fertility indicator that informs her when she needs to use protection to minimize the chance of conception. The app also can be used to help plan a pregnancy when the time is right, according to Natural Cycles.
A clinical study showed that the efficacy of a contraceptive mobile application is higher than usually reported for traditional fertility awareness–based methods. The application may contribute to reducing the unmet need for contraception, says Natural Cycles.
FOR MORE INFORMATION, VISIT: https://www.naturalcycles.com/en/hcp
TREATMENT FOR VASOMOTOR SYMPTOMS
BIJUVA™ has been US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved as the first oral treatment for moderate-to-severe vasomotor symptoms due to menopause in women with a uterus. BIJUVA offers a combination of bioidentical estradiol to reduce moderate-to-severe hot flashes and bioidentical progesterone to reduce the risk for endometrial hyperplasia.
TherapeuticsMD says that BIJUVA will be available Spring 2019 and is a proven treatment option for women who are experiencing bothersome symptoms of menopause, with clinical trial data demonstrating a statistically significant reduction in both the frequency and severity of moderate-to-severe vasomotor symptoms. The manufacturer also says that BIJUVA is developed to be identical in molecular structure to the hormones already produced by the body and is designed to help women restore what is lost during menopause.
BIJUVA estradiol and progesterone combination (1 mg/100 mg) will be available in capsule form.
FOR MORE INFORMATION, VISIT:https://bijuva.com/discover/
LILETTA USE EXTENDED
The FDA has approved LILETTA® (levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system) 52 mg for 5-year use. This approval is based on efficacy and safety data from ACCESS IUS, the largest ongoing intrauterine device (IUD) Phase 3 clinical trial in the United States. Previously, LILETTA was indicated for use up to 4 years.
LILETTA continues to be greater than 99% effective in preventing pregnancy in a broad range of women, regardless of age, race, body mass index, or parity, according to Allergan and Medicines360. The extended duration and proven efficacy across a diverse population enables more women in the United States to obtain effective birth control, as the IUD is now available for a low cost at public health clinics.
FOR MORE INFORMATION, VISIT: https://www.liletta.com
Continue to: ENDOMETRIAL ABLATION TECHNOLOGY
ENDOMETRIAL ABLATION TECHNOLOGY
AEGEA Medical introduces the AEGEA Vapor SystemTM, an innovative solution for endometrial ablation to treat menorrhagia.
The system uses Adaptive Vapor Ablation and is the first endometrial ablation system specifically designed for use in the doctor’s office, allowing minimal anesthesia/analgesia and rapid recovery, says AEGEA Medical.
AEGEA Medical describes the AEGEA Vapor System as a fully automated safety monitoring and vapor delivery system that uses a slender, flexible Vapor Probe with SmartSealTM technology and the Integrity ProTM safety feature, for an added level of confidence. The 4-minute procedure time includes 2 minutes of vapor treatment and can be performed in patients with a wider range of uterine anatomies than indicated for use with currently available treatments, says AEGEA Medical.
FOR MORE INFORMATION, VISIT: http://aegeamedical.com/
NATURAL CYCLES
The FDA has cleared Natural Cycles as the first digital method of birth control in the United States. Delivered in the form of an app, Natural Cycles is a fertility awareness–based contraceptive that uses a sophisticated algorithm to accurately and conveniently determine a woman’s daily fertility based on basal body temperature.
That data builds into a personalized fertility indicator that informs her when she needs to use protection to minimize the chance of conception. The app also can be used to help plan a pregnancy when the time is right, according to Natural Cycles.
A clinical study showed that the efficacy of a contraceptive mobile application is higher than usually reported for traditional fertility awareness–based methods. The application may contribute to reducing the unmet need for contraception, says Natural Cycles.
FOR MORE INFORMATION, VISIT: https://www.naturalcycles.com/en/hcp
TREATMENT FOR VASOMOTOR SYMPTOMS
BIJUVA™ has been US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved as the first oral treatment for moderate-to-severe vasomotor symptoms due to menopause in women with a uterus. BIJUVA offers a combination of bioidentical estradiol to reduce moderate-to-severe hot flashes and bioidentical progesterone to reduce the risk for endometrial hyperplasia.
TherapeuticsMD says that BIJUVA will be available Spring 2019 and is a proven treatment option for women who are experiencing bothersome symptoms of menopause, with clinical trial data demonstrating a statistically significant reduction in both the frequency and severity of moderate-to-severe vasomotor symptoms. The manufacturer also says that BIJUVA is developed to be identical in molecular structure to the hormones already produced by the body and is designed to help women restore what is lost during menopause.
BIJUVA estradiol and progesterone combination (1 mg/100 mg) will be available in capsule form.
FOR MORE INFORMATION, VISIT:https://bijuva.com/discover/
LILETTA USE EXTENDED
The FDA has approved LILETTA® (levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system) 52 mg for 5-year use. This approval is based on efficacy and safety data from ACCESS IUS, the largest ongoing intrauterine device (IUD) Phase 3 clinical trial in the United States. Previously, LILETTA was indicated for use up to 4 years.
LILETTA continues to be greater than 99% effective in preventing pregnancy in a broad range of women, regardless of age, race, body mass index, or parity, according to Allergan and Medicines360. The extended duration and proven efficacy across a diverse population enables more women in the United States to obtain effective birth control, as the IUD is now available for a low cost at public health clinics.
FOR MORE INFORMATION, VISIT: https://www.liletta.com
Continue to: ENDOMETRIAL ABLATION TECHNOLOGY
ENDOMETRIAL ABLATION TECHNOLOGY
AEGEA Medical introduces the AEGEA Vapor SystemTM, an innovative solution for endometrial ablation to treat menorrhagia.
The system uses Adaptive Vapor Ablation and is the first endometrial ablation system specifically designed for use in the doctor’s office, allowing minimal anesthesia/analgesia and rapid recovery, says AEGEA Medical.
AEGEA Medical describes the AEGEA Vapor System as a fully automated safety monitoring and vapor delivery system that uses a slender, flexible Vapor Probe with SmartSealTM technology and the Integrity ProTM safety feature, for an added level of confidence. The 4-minute procedure time includes 2 minutes of vapor treatment and can be performed in patients with a wider range of uterine anatomies than indicated for use with currently available treatments, says AEGEA Medical.
FOR MORE INFORMATION, VISIT: http://aegeamedical.com/
NATURAL CYCLES
The FDA has cleared Natural Cycles as the first digital method of birth control in the United States. Delivered in the form of an app, Natural Cycles is a fertility awareness–based contraceptive that uses a sophisticated algorithm to accurately and conveniently determine a woman’s daily fertility based on basal body temperature.
That data builds into a personalized fertility indicator that informs her when she needs to use protection to minimize the chance of conception. The app also can be used to help plan a pregnancy when the time is right, according to Natural Cycles.
A clinical study showed that the efficacy of a contraceptive mobile application is higher than usually reported for traditional fertility awareness–based methods. The application may contribute to reducing the unmet need for contraception, says Natural Cycles.
FOR MORE INFORMATION, VISIT: https://www.naturalcycles.com/en/hcp
Insulin may be toxic to the placenta in early pregnancy
, according to findings from an experimental in vitro study published in Fertility and Sterility.
“Collectively these results demonstrate that insulin itself may be directly toxic to the early human placenta but that metformin can prevent these deleterious effects,” wrote Mario Vega, MD, of Columbia University Fertility Center, New York, and his colleagues. “If confirmed in animal and human studies, this would indicate that screening and treatment for insulin resistance should focus on hyperinsulinemia.”
Dr. Vega and his colleagues cultivated trophoblast cells from three healthy women scheduled for manual vacuum aspiration during the first trimester of pregnancy to study the effects of insulin exposure alone, while trophoblast cells were cultured from a different set of women for the insulin and metformin follow-up experiments. The researchers tested each experiment against a control group of cultivated lung fibroblast cells. Insulin was measured in doses of 0.2 nmol, 1 nmol, and 5 nmol, while metformin was measured at 10 micromol. The primary outcome measures examined were gamma-H2AX for DNA damage, cell proliferation assay for cell survival, and cleaved caspase-3 for apoptosis.
Within 48 hours, the cultures showed DNA damage and induction of apoptosis when exposed to 1 nmol of insulin, but researchers said pretreatment with metformin prevented these effects. Exposing cells to metformin after insulin reduced but did not eliminate the effects of insulin.
The researchers noted the study is limited because the effects of insulin and metformin have not been examined in vivo, and it is not known at what level insulin causes damage. In addition, they suggested downregulation of genes in trophoblasts caused by insulin could cause apoptosis and DNA damage to trophoblast cells.
“Although studies performed on kidney and colon cells suggest that one possible mechanism of action for insulin-mediated genotoxicity is through AKT activation of mitochondria and subsequent reactive oxygen species production, the exact mechanism is poorly understood,” Dr. Vega and colleagues said. “Future studies will be necessary to determine variability among subjects, as well as mechanisms of action through which insulin exerts its cytotoxicity and genotoxicity.”
This study was funded by a grant from the National Institutes of Health Human Placenta Project. The authors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Vega M et al. Fertil Steril. 2019. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2018.11.032.
, according to findings from an experimental in vitro study published in Fertility and Sterility.
“Collectively these results demonstrate that insulin itself may be directly toxic to the early human placenta but that metformin can prevent these deleterious effects,” wrote Mario Vega, MD, of Columbia University Fertility Center, New York, and his colleagues. “If confirmed in animal and human studies, this would indicate that screening and treatment for insulin resistance should focus on hyperinsulinemia.”
Dr. Vega and his colleagues cultivated trophoblast cells from three healthy women scheduled for manual vacuum aspiration during the first trimester of pregnancy to study the effects of insulin exposure alone, while trophoblast cells were cultured from a different set of women for the insulin and metformin follow-up experiments. The researchers tested each experiment against a control group of cultivated lung fibroblast cells. Insulin was measured in doses of 0.2 nmol, 1 nmol, and 5 nmol, while metformin was measured at 10 micromol. The primary outcome measures examined were gamma-H2AX for DNA damage, cell proliferation assay for cell survival, and cleaved caspase-3 for apoptosis.
Within 48 hours, the cultures showed DNA damage and induction of apoptosis when exposed to 1 nmol of insulin, but researchers said pretreatment with metformin prevented these effects. Exposing cells to metformin after insulin reduced but did not eliminate the effects of insulin.
The researchers noted the study is limited because the effects of insulin and metformin have not been examined in vivo, and it is not known at what level insulin causes damage. In addition, they suggested downregulation of genes in trophoblasts caused by insulin could cause apoptosis and DNA damage to trophoblast cells.
“Although studies performed on kidney and colon cells suggest that one possible mechanism of action for insulin-mediated genotoxicity is through AKT activation of mitochondria and subsequent reactive oxygen species production, the exact mechanism is poorly understood,” Dr. Vega and colleagues said. “Future studies will be necessary to determine variability among subjects, as well as mechanisms of action through which insulin exerts its cytotoxicity and genotoxicity.”
This study was funded by a grant from the National Institutes of Health Human Placenta Project. The authors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Vega M et al. Fertil Steril. 2019. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2018.11.032.
, according to findings from an experimental in vitro study published in Fertility and Sterility.
“Collectively these results demonstrate that insulin itself may be directly toxic to the early human placenta but that metformin can prevent these deleterious effects,” wrote Mario Vega, MD, of Columbia University Fertility Center, New York, and his colleagues. “If confirmed in animal and human studies, this would indicate that screening and treatment for insulin resistance should focus on hyperinsulinemia.”
Dr. Vega and his colleagues cultivated trophoblast cells from three healthy women scheduled for manual vacuum aspiration during the first trimester of pregnancy to study the effects of insulin exposure alone, while trophoblast cells were cultured from a different set of women for the insulin and metformin follow-up experiments. The researchers tested each experiment against a control group of cultivated lung fibroblast cells. Insulin was measured in doses of 0.2 nmol, 1 nmol, and 5 nmol, while metformin was measured at 10 micromol. The primary outcome measures examined were gamma-H2AX for DNA damage, cell proliferation assay for cell survival, and cleaved caspase-3 for apoptosis.
Within 48 hours, the cultures showed DNA damage and induction of apoptosis when exposed to 1 nmol of insulin, but researchers said pretreatment with metformin prevented these effects. Exposing cells to metformin after insulin reduced but did not eliminate the effects of insulin.
The researchers noted the study is limited because the effects of insulin and metformin have not been examined in vivo, and it is not known at what level insulin causes damage. In addition, they suggested downregulation of genes in trophoblasts caused by insulin could cause apoptosis and DNA damage to trophoblast cells.
“Although studies performed on kidney and colon cells suggest that one possible mechanism of action for insulin-mediated genotoxicity is through AKT activation of mitochondria and subsequent reactive oxygen species production, the exact mechanism is poorly understood,” Dr. Vega and colleagues said. “Future studies will be necessary to determine variability among subjects, as well as mechanisms of action through which insulin exerts its cytotoxicity and genotoxicity.”
This study was funded by a grant from the National Institutes of Health Human Placenta Project. The authors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Vega M et al. Fertil Steril. 2019. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2018.11.032.
FROM FERTILITY & STERILITY
Key clinical point: Trophoblasts cultured during the first trimester of pregnancy exposed to insulin were more likely to have increased apoptosis, DNA damage, and decreased cell survival, while pretreatment with metformin prior to exposure with insulin prevented these effects.
Major finding: DNA damage and rate of apoptosis increased in trophoblast cells exposed to 1 nmol of insulin, and cell survival decreased, compared with primary lung fibroblast cells; treating the cells with metformin prior to exposure with insulin resulted in prevention of these effects.
Study details: An experimental in vitro study of first trimester trophoblast cells exposed to insulin and metformin.
Disclosures: This study was funded by a grant from the National Institutes of Health Human Placenta Project. The authors reported they had no relevant financial disclosures.
Source: Vega M et al. Fertil Steril. 2019. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2018.11.032.