User login
Exploring the Relationship Between Psoriasis and Mobility Among US Adults
To the Editor:
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects individuals in various extracutaneous ways.1 Prior studies have documented a decrease in exercise intensity among patients with psoriasis2; however, few studies have specifically investigated baseline mobility in this population. Baseline mobility denotes an individual’s fundamental ability to walk or move around without assistance of any kind. Impaired mobility—when baseline mobility is compromised—is an aspect of the wider diversity, equity, and inclusion framework that underscores the significance of recognizing challenges and promoting inclusive measures, both at the point of care and in research.3 study sought to analyze the relationship between psoriasis and baseline mobility among US adults (aged 45 to 80 years) utilizing the latest data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) database for psoriasis.4 We used three 2-year cycles of NHANES data to create a 2009-2014 dataset.
The overall NHANES response rate among adults aged 45 to 80 years between 2009 and 2014 was 67.9%. Patients were categorized as having impaired mobility if they responded “yes” to the following question: “Because of a health problem, do you have difficulty walking without using any special equipment?” Psoriasis status was assessed by the following question: “Have you ever been told by a doctor or other health professional that you had psoriasis?” Multivariable logistic regression analyses were performed using Stata/SE 18.0 software (StataCorp LLC) to assess the relationship between psoriasis and impaired mobility. Age, income, education, sex, race, tobacco use, diabetes status, body mass index, and arthritis status were controlled for in our models.
Our analysis initially included 9982 participants; 14 did not respond to questions assessing psoriasis and impaired mobility and were excluded. The prevalence of impaired mobility in patients with psoriasis was 17.1% compared with 10.9% among those without psoriasis (Table 1). There was a significant association between psoriasis and impaired mobility among patients aged 45 to 80 years after adjusting for potential confounding variables (adjusted odds ratio [AOR], 1.54; 95% CI, 1.04- 2.29; P=.032)(Table 2). Analyses of subgroups yielded no statistically significant results.
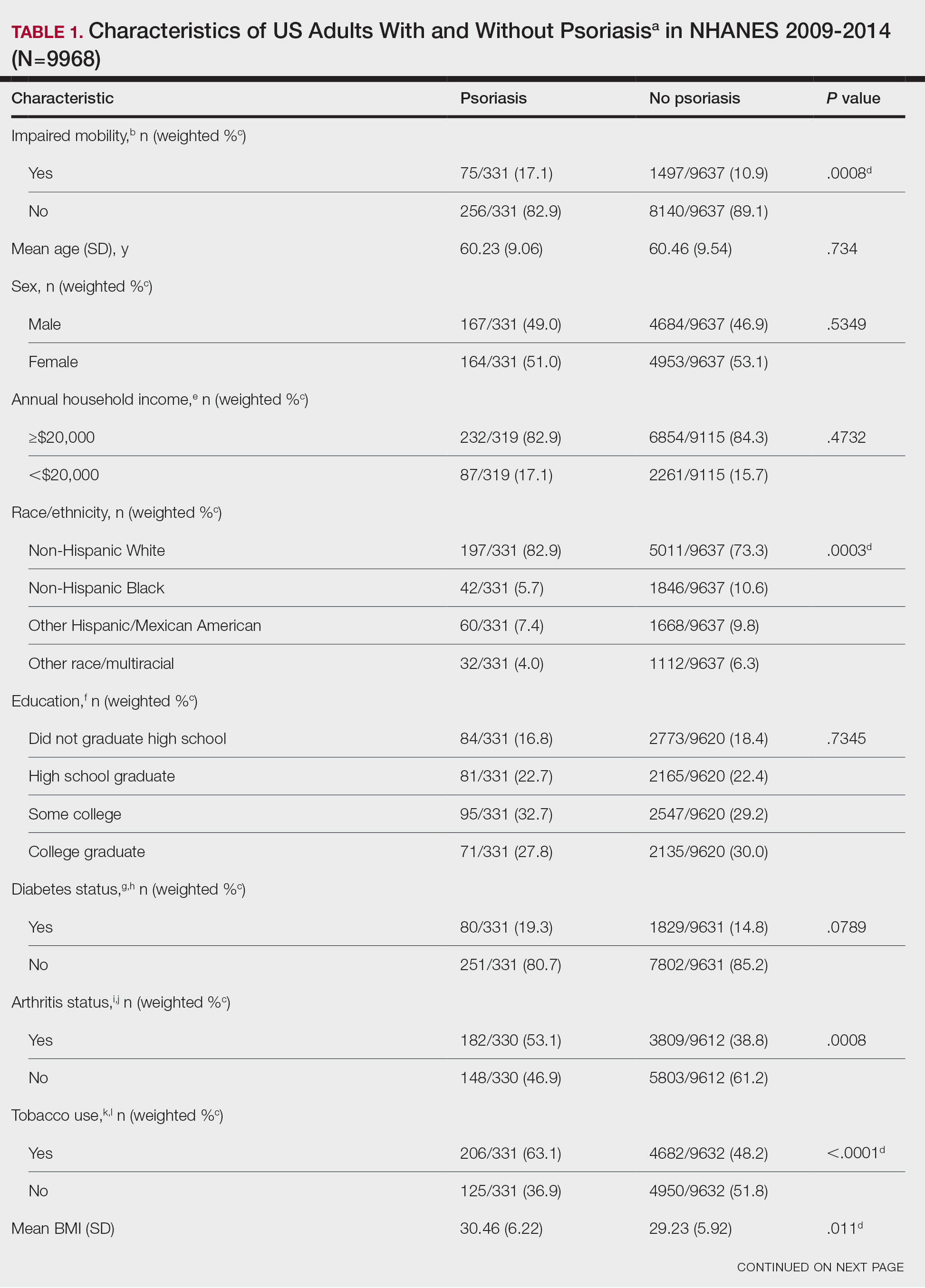

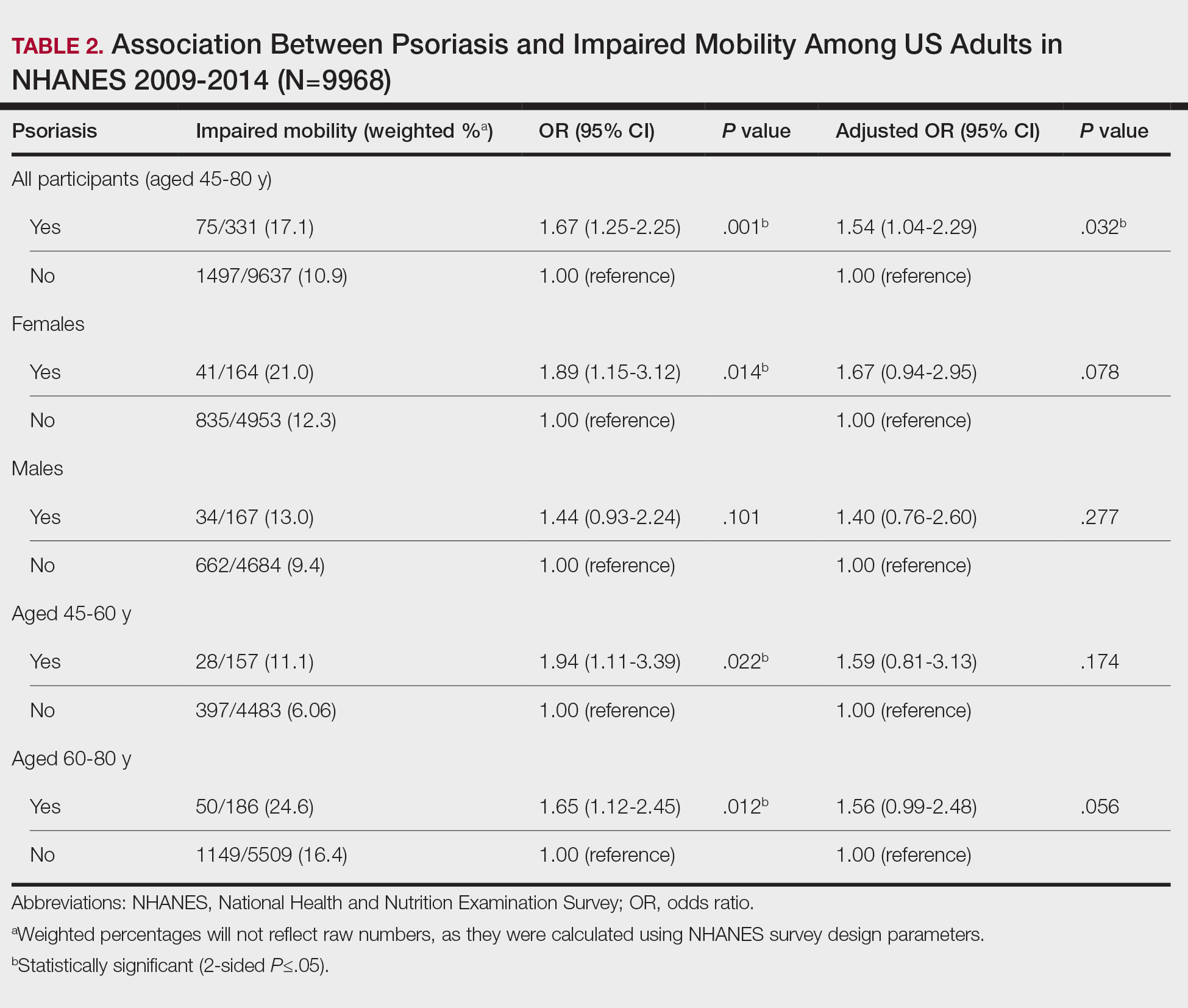
Our study demonstrated a statistically significant difference in mobility between individuals with psoriasis compared with the general population, which remained significant when controlling for arthritis, obesity, and diabetes (P=.032). This may be the result of several influences. First, the location of the psoriasis may impact mobility. Plantar psoriasis—a manifestation on the soles of the feet—can cause discomfort and pain, which can hinder walking and standing.5 Second, a study by Lasselin et al6 found that systemic inflammation contributes to mobility impairment through alterations in gait and posture, which suggests that the inflammatory processes inherent in psoriasis could intrinsically modify walking speed and stride, potentially exacerbating mobility difficulties independent of other comorbid conditions. These findings suggest that psoriasis may disproportionately affect individuals with impaired mobility, independent of comorbid arthritis, obesity, and diabetes.
These findings have broad implications for diversity, equity, and inclusion. They should prompt us to consider the practical challenges faced by this patient population and the ways that we can address barriers to care. Offering telehealth appointments, making primary care referrals for impaired mobility workups, and advising patients of direct-to-home delivery of prescriptions are good places to start.
Limitations to our study include the lack of specificity in the survey question, self-reporting bias, and the inability to control for the psoriasis location. Further investigations are warranted in large, representative US adult populations to assess the implications of impaired mobility in patients with psoriasis.
- Elmets CA, Leonardi CL, Davis DMR, et al. Joint AAD-NPF guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with awareness and attention to comorbidities. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1073-1113. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2018.11.058
- Zheng Q, Sun XY, Miao X, et al. Association between physical activity and risk of prevalent psoriasis: A MOOSE-compliant meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97:e11394. doi: 10.1097 /MD.0000000000011394
- Mullin AE, Coe IR, Gooden EA, et al. Inclusion, diversity, equity, and accessibility: from organizational responsibility to leadership competency. Healthc Manage Forum. 2021;34311-315. doi: 10.1177/08404704211038232
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. NHANES questionnaires, datasets, and related documentation. Accessed October 21, 2023. https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/
- Romani M, Biela G, Farr K, et al. Plantar psoriasis: a review of the literature. Clin Podiatr Med Surg. 2021;38:541-552. doi: 10.1016 /j.cpm.2021.06.009
- Lasselin J, Sundelin T, Wayne PM, et al. Biological motion during inflammation in humans. Brain Behav Immun. 2020;84:147-153. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2019.11.019
To the Editor:
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects individuals in various extracutaneous ways.1 Prior studies have documented a decrease in exercise intensity among patients with psoriasis2; however, few studies have specifically investigated baseline mobility in this population. Baseline mobility denotes an individual’s fundamental ability to walk or move around without assistance of any kind. Impaired mobility—when baseline mobility is compromised—is an aspect of the wider diversity, equity, and inclusion framework that underscores the significance of recognizing challenges and promoting inclusive measures, both at the point of care and in research.3 study sought to analyze the relationship between psoriasis and baseline mobility among US adults (aged 45 to 80 years) utilizing the latest data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) database for psoriasis.4 We used three 2-year cycles of NHANES data to create a 2009-2014 dataset.
The overall NHANES response rate among adults aged 45 to 80 years between 2009 and 2014 was 67.9%. Patients were categorized as having impaired mobility if they responded “yes” to the following question: “Because of a health problem, do you have difficulty walking without using any special equipment?” Psoriasis status was assessed by the following question: “Have you ever been told by a doctor or other health professional that you had psoriasis?” Multivariable logistic regression analyses were performed using Stata/SE 18.0 software (StataCorp LLC) to assess the relationship between psoriasis and impaired mobility. Age, income, education, sex, race, tobacco use, diabetes status, body mass index, and arthritis status were controlled for in our models.
Our analysis initially included 9982 participants; 14 did not respond to questions assessing psoriasis and impaired mobility and were excluded. The prevalence of impaired mobility in patients with psoriasis was 17.1% compared with 10.9% among those without psoriasis (Table 1). There was a significant association between psoriasis and impaired mobility among patients aged 45 to 80 years after adjusting for potential confounding variables (adjusted odds ratio [AOR], 1.54; 95% CI, 1.04- 2.29; P=.032)(Table 2). Analyses of subgroups yielded no statistically significant results.



Our study demonstrated a statistically significant difference in mobility between individuals with psoriasis compared with the general population, which remained significant when controlling for arthritis, obesity, and diabetes (P=.032). This may be the result of several influences. First, the location of the psoriasis may impact mobility. Plantar psoriasis—a manifestation on the soles of the feet—can cause discomfort and pain, which can hinder walking and standing.5 Second, a study by Lasselin et al6 found that systemic inflammation contributes to mobility impairment through alterations in gait and posture, which suggests that the inflammatory processes inherent in psoriasis could intrinsically modify walking speed and stride, potentially exacerbating mobility difficulties independent of other comorbid conditions. These findings suggest that psoriasis may disproportionately affect individuals with impaired mobility, independent of comorbid arthritis, obesity, and diabetes.
These findings have broad implications for diversity, equity, and inclusion. They should prompt us to consider the practical challenges faced by this patient population and the ways that we can address barriers to care. Offering telehealth appointments, making primary care referrals for impaired mobility workups, and advising patients of direct-to-home delivery of prescriptions are good places to start.
Limitations to our study include the lack of specificity in the survey question, self-reporting bias, and the inability to control for the psoriasis location. Further investigations are warranted in large, representative US adult populations to assess the implications of impaired mobility in patients with psoriasis.
To the Editor:
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects individuals in various extracutaneous ways.1 Prior studies have documented a decrease in exercise intensity among patients with psoriasis2; however, few studies have specifically investigated baseline mobility in this population. Baseline mobility denotes an individual’s fundamental ability to walk or move around without assistance of any kind. Impaired mobility—when baseline mobility is compromised—is an aspect of the wider diversity, equity, and inclusion framework that underscores the significance of recognizing challenges and promoting inclusive measures, both at the point of care and in research.3 study sought to analyze the relationship between psoriasis and baseline mobility among US adults (aged 45 to 80 years) utilizing the latest data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) database for psoriasis.4 We used three 2-year cycles of NHANES data to create a 2009-2014 dataset.
The overall NHANES response rate among adults aged 45 to 80 years between 2009 and 2014 was 67.9%. Patients were categorized as having impaired mobility if they responded “yes” to the following question: “Because of a health problem, do you have difficulty walking without using any special equipment?” Psoriasis status was assessed by the following question: “Have you ever been told by a doctor or other health professional that you had psoriasis?” Multivariable logistic regression analyses were performed using Stata/SE 18.0 software (StataCorp LLC) to assess the relationship between psoriasis and impaired mobility. Age, income, education, sex, race, tobacco use, diabetes status, body mass index, and arthritis status were controlled for in our models.
Our analysis initially included 9982 participants; 14 did not respond to questions assessing psoriasis and impaired mobility and were excluded. The prevalence of impaired mobility in patients with psoriasis was 17.1% compared with 10.9% among those without psoriasis (Table 1). There was a significant association between psoriasis and impaired mobility among patients aged 45 to 80 years after adjusting for potential confounding variables (adjusted odds ratio [AOR], 1.54; 95% CI, 1.04- 2.29; P=.032)(Table 2). Analyses of subgroups yielded no statistically significant results.



Our study demonstrated a statistically significant difference in mobility between individuals with psoriasis compared with the general population, which remained significant when controlling for arthritis, obesity, and diabetes (P=.032). This may be the result of several influences. First, the location of the psoriasis may impact mobility. Plantar psoriasis—a manifestation on the soles of the feet—can cause discomfort and pain, which can hinder walking and standing.5 Second, a study by Lasselin et al6 found that systemic inflammation contributes to mobility impairment through alterations in gait and posture, which suggests that the inflammatory processes inherent in psoriasis could intrinsically modify walking speed and stride, potentially exacerbating mobility difficulties independent of other comorbid conditions. These findings suggest that psoriasis may disproportionately affect individuals with impaired mobility, independent of comorbid arthritis, obesity, and diabetes.
These findings have broad implications for diversity, equity, and inclusion. They should prompt us to consider the practical challenges faced by this patient population and the ways that we can address barriers to care. Offering telehealth appointments, making primary care referrals for impaired mobility workups, and advising patients of direct-to-home delivery of prescriptions are good places to start.
Limitations to our study include the lack of specificity in the survey question, self-reporting bias, and the inability to control for the psoriasis location. Further investigations are warranted in large, representative US adult populations to assess the implications of impaired mobility in patients with psoriasis.
- Elmets CA, Leonardi CL, Davis DMR, et al. Joint AAD-NPF guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with awareness and attention to comorbidities. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1073-1113. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2018.11.058
- Zheng Q, Sun XY, Miao X, et al. Association between physical activity and risk of prevalent psoriasis: A MOOSE-compliant meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97:e11394. doi: 10.1097 /MD.0000000000011394
- Mullin AE, Coe IR, Gooden EA, et al. Inclusion, diversity, equity, and accessibility: from organizational responsibility to leadership competency. Healthc Manage Forum. 2021;34311-315. doi: 10.1177/08404704211038232
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. NHANES questionnaires, datasets, and related documentation. Accessed October 21, 2023. https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/
- Romani M, Biela G, Farr K, et al. Plantar psoriasis: a review of the literature. Clin Podiatr Med Surg. 2021;38:541-552. doi: 10.1016 /j.cpm.2021.06.009
- Lasselin J, Sundelin T, Wayne PM, et al. Biological motion during inflammation in humans. Brain Behav Immun. 2020;84:147-153. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2019.11.019
- Elmets CA, Leonardi CL, Davis DMR, et al. Joint AAD-NPF guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with awareness and attention to comorbidities. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1073-1113. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2018.11.058
- Zheng Q, Sun XY, Miao X, et al. Association between physical activity and risk of prevalent psoriasis: A MOOSE-compliant meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97:e11394. doi: 10.1097 /MD.0000000000011394
- Mullin AE, Coe IR, Gooden EA, et al. Inclusion, diversity, equity, and accessibility: from organizational responsibility to leadership competency. Healthc Manage Forum. 2021;34311-315. doi: 10.1177/08404704211038232
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. NHANES questionnaires, datasets, and related documentation. Accessed October 21, 2023. https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/
- Romani M, Biela G, Farr K, et al. Plantar psoriasis: a review of the literature. Clin Podiatr Med Surg. 2021;38:541-552. doi: 10.1016 /j.cpm.2021.06.009
- Lasselin J, Sundelin T, Wayne PM, et al. Biological motion during inflammation in humans. Brain Behav Immun. 2020;84:147-153. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2019.11.019
Exploring the Relationship Between Psoriasis and Mobility Among US Adults
Exploring the Relationship Between Psoriasis and Mobility Among US Adults
PRACTICE POINTS
- Mobility issues are more common in patients who have psoriasis than in those who do not.
- It is important to assess patients with psoriasis for mobility issues regardless of age or comorbid conditions such as arthritis, obesity, and diabetes.
- Dermatologists can help patients with psoriasis and impaired mobility overcome potential barriers to care by incorporating telehealth services into their practices and informing patients of direct-to-home delivery of prescriptions.