User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Patient Navigators for Serious Illnesses Can Now Bill Under New Medicare Codes
In a move that acknowledges the gauntlet the US health system poses for people facing serious and fatal illnesses, Medicare will pay for a new class of workers to help patients manage treatments for conditions like cancer and heart failure.
The 2024 Medicare physician fee schedule includes new billing codes, including G0023, to pay for 60 minutes a month of care coordination by certified or trained auxiliary personnel working under the direction of a clinician.
A diagnosis of cancer or another serious illness takes a toll beyond the physical effects of the disease. Patients often scramble to make adjustments in family and work schedules to manage treatment, said Samyukta Mullangi, MD, MBA, medical director of oncology at Thyme Care, a Nashville, Tennessee–based firm that provides navigation and coordination services to oncology practices and insurers.
“It just really does create a bit of a pressure cooker for patients,” Dr. Mullangi told this news organization.
Medicare has for many years paid for medical professionals to help patients cope with the complexities of disease, such as chronic care management (CCM) provided by physicians, nurses, and physician assistants.
The new principal illness navigation (PIN) payments are intended to pay for work that to date typically has been done by people without medical degrees, including those involved in peer support networks and community health programs. The US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services(CMS) expects these navigators will undergo training and work under the supervision of clinicians.
The new navigators may coordinate care transitions between medical settings, follow up with patients after emergency department (ED) visits, or communicate with skilled nursing facilities regarding the psychosocial needs and functional deficits of a patient, among other functions.
CMS expects the new navigators may:
- Conduct assessments to understand a patient’s life story, strengths, needs, goals, preferences, and desired outcomes, including understanding cultural and linguistic factors.
- Provide support to accomplish the clinician’s treatment plan.
- Coordinate the receipt of needed services from healthcare facilities, home- and community-based service providers, and caregivers.
Peers as Navigators
The new navigators can be former patients who have undergone similar treatments for serious diseases, CMS said. This approach sets the new program apart from other care management services Medicare already covers, program officials wrote in the 2024 physician fee schedule.
“For some conditions, patients are best able to engage with the healthcare system and access care if they have assistance from a single, dedicated individual who has ‘lived experience,’ ” according to the rule.
The agency has taken a broad initial approach in defining what kinds of illnesses a patient may have to qualify for services. Patients must have a serious condition that is expected to last at least 3 months, such as cancer, heart failure, or substance use disorder.
But those without a definitive diagnosis may also qualify to receive navigator services.
In the rule, CMS cited a case in which a CT scan identified a suspicious mass in a patient’s colon. A clinician might decide this person would benefit from navigation services due to the potential risks for an undiagnosed illness.
“Regardless of the definitive diagnosis of the mass, presence of a colonic mass for that patient may be a serious high-risk condition that could, for example, cause obstruction and lead the patient to present to the emergency department, as well as be potentially indicative of an underlying life-threatening illness such as colon cancer,” CMS wrote in the rule.
Navigators often start their work when cancer patients are screened and guide them through initial diagnosis, potential surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy, said Sharon Gentry, MSN, RN, a former nurse navigator who is now the editor in chief of the Journal of the Academy of Oncology Nurse & Patient Navigators.
The navigators are meant to be a trusted and continual presence for patients, who otherwise might be left to start anew in finding help at each phase of care.
The navigators “see the whole picture. They see the whole journey the patient takes, from pre-diagnosis all the way through diagnosis care out through survival,” Ms. Gentry said.
Gaining a special Medicare payment for these kinds of services will elevate this work, she said.
Many newer drugs can target specific mechanisms and proteins of cancer. Often, oncology treatment involves testing to find out if mutations are allowing the cancer cells to evade a patient’s immune system.
Checking these biomarkers takes time, however. Patients sometimes become frustrated because they are anxious to begin treatment. Patients may receive inaccurate information from friends or family who went through treatment previously. Navigators can provide knowledge on the current state of care for a patient’s disease, helping them better manage anxieties.
“You have to explain to them that things have changed since the guy you drink coffee with was diagnosed with cancer, and there may be a drug that could target that,” Ms. Gentry said.
Potential Challenges
Initial uptake of the new PIN codes may be slow going, however, as clinicians and health systems may already use well-established codes. These include CCM and principal care management services, which may pay higher rates, Mullangi said.
“There might be sensitivity around not wanting to cannibalize existing programs with a new program,” Dr. Mullangi said.
In addition, many patients will have a copay for the services of principal illness navigators, Dr. Mullangi said.
While many patients have additional insurance that would cover the service, not all do. People with traditional Medicare coverage can sometimes pay 20% of the cost of some medical services.
“I think that may give patients pause, particularly if they’re already feeling the financial burden of a cancer treatment journey,” Dr. Mullangi said.
Pay rates for PIN services involve calculations of regional price differences, which are posted publicly by CMS, and potential added fees for services provided by hospital-affiliated organizations.
Consider payments for code G0023, covering 60 minutes of principal navigation services provided in a single month.
A set reimbursement for patients cared for in independent medical practices exists, with variation for local costs. Medicare’s non-facility price for G0023 would be $102.41 in some parts of Silicon Valley in California, including San Jose. In Arkansas, where costs are lower, reimbursement would be $73.14 for this same service.
Patients who get services covered by code G0023 in independent medical practices would have monthly copays of about $15-$20, depending on where they live.
The tab for patients tends to be higher for these same services if delivered through a medical practice owned by a hospital, as this would trigger the addition of facility fees to the payments made to cover the services. Facility fees are difficult for the public to ascertain before getting a treatment or service.
Dr. Mullangi and Ms. Gentry reported no relevant financial disclosures outside of their employers.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a move that acknowledges the gauntlet the US health system poses for people facing serious and fatal illnesses, Medicare will pay for a new class of workers to help patients manage treatments for conditions like cancer and heart failure.
The 2024 Medicare physician fee schedule includes new billing codes, including G0023, to pay for 60 minutes a month of care coordination by certified or trained auxiliary personnel working under the direction of a clinician.
A diagnosis of cancer or another serious illness takes a toll beyond the physical effects of the disease. Patients often scramble to make adjustments in family and work schedules to manage treatment, said Samyukta Mullangi, MD, MBA, medical director of oncology at Thyme Care, a Nashville, Tennessee–based firm that provides navigation and coordination services to oncology practices and insurers.
“It just really does create a bit of a pressure cooker for patients,” Dr. Mullangi told this news organization.
Medicare has for many years paid for medical professionals to help patients cope with the complexities of disease, such as chronic care management (CCM) provided by physicians, nurses, and physician assistants.
The new principal illness navigation (PIN) payments are intended to pay for work that to date typically has been done by people without medical degrees, including those involved in peer support networks and community health programs. The US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services(CMS) expects these navigators will undergo training and work under the supervision of clinicians.
The new navigators may coordinate care transitions between medical settings, follow up with patients after emergency department (ED) visits, or communicate with skilled nursing facilities regarding the psychosocial needs and functional deficits of a patient, among other functions.
CMS expects the new navigators may:
- Conduct assessments to understand a patient’s life story, strengths, needs, goals, preferences, and desired outcomes, including understanding cultural and linguistic factors.
- Provide support to accomplish the clinician’s treatment plan.
- Coordinate the receipt of needed services from healthcare facilities, home- and community-based service providers, and caregivers.
Peers as Navigators
The new navigators can be former patients who have undergone similar treatments for serious diseases, CMS said. This approach sets the new program apart from other care management services Medicare already covers, program officials wrote in the 2024 physician fee schedule.
“For some conditions, patients are best able to engage with the healthcare system and access care if they have assistance from a single, dedicated individual who has ‘lived experience,’ ” according to the rule.
The agency has taken a broad initial approach in defining what kinds of illnesses a patient may have to qualify for services. Patients must have a serious condition that is expected to last at least 3 months, such as cancer, heart failure, or substance use disorder.
But those without a definitive diagnosis may also qualify to receive navigator services.
In the rule, CMS cited a case in which a CT scan identified a suspicious mass in a patient’s colon. A clinician might decide this person would benefit from navigation services due to the potential risks for an undiagnosed illness.
“Regardless of the definitive diagnosis of the mass, presence of a colonic mass for that patient may be a serious high-risk condition that could, for example, cause obstruction and lead the patient to present to the emergency department, as well as be potentially indicative of an underlying life-threatening illness such as colon cancer,” CMS wrote in the rule.
Navigators often start their work when cancer patients are screened and guide them through initial diagnosis, potential surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy, said Sharon Gentry, MSN, RN, a former nurse navigator who is now the editor in chief of the Journal of the Academy of Oncology Nurse & Patient Navigators.
The navigators are meant to be a trusted and continual presence for patients, who otherwise might be left to start anew in finding help at each phase of care.
The navigators “see the whole picture. They see the whole journey the patient takes, from pre-diagnosis all the way through diagnosis care out through survival,” Ms. Gentry said.
Gaining a special Medicare payment for these kinds of services will elevate this work, she said.
Many newer drugs can target specific mechanisms and proteins of cancer. Often, oncology treatment involves testing to find out if mutations are allowing the cancer cells to evade a patient’s immune system.
Checking these biomarkers takes time, however. Patients sometimes become frustrated because they are anxious to begin treatment. Patients may receive inaccurate information from friends or family who went through treatment previously. Navigators can provide knowledge on the current state of care for a patient’s disease, helping them better manage anxieties.
“You have to explain to them that things have changed since the guy you drink coffee with was diagnosed with cancer, and there may be a drug that could target that,” Ms. Gentry said.
Potential Challenges
Initial uptake of the new PIN codes may be slow going, however, as clinicians and health systems may already use well-established codes. These include CCM and principal care management services, which may pay higher rates, Mullangi said.
“There might be sensitivity around not wanting to cannibalize existing programs with a new program,” Dr. Mullangi said.
In addition, many patients will have a copay for the services of principal illness navigators, Dr. Mullangi said.
While many patients have additional insurance that would cover the service, not all do. People with traditional Medicare coverage can sometimes pay 20% of the cost of some medical services.
“I think that may give patients pause, particularly if they’re already feeling the financial burden of a cancer treatment journey,” Dr. Mullangi said.
Pay rates for PIN services involve calculations of regional price differences, which are posted publicly by CMS, and potential added fees for services provided by hospital-affiliated organizations.
Consider payments for code G0023, covering 60 minutes of principal navigation services provided in a single month.
A set reimbursement for patients cared for in independent medical practices exists, with variation for local costs. Medicare’s non-facility price for G0023 would be $102.41 in some parts of Silicon Valley in California, including San Jose. In Arkansas, where costs are lower, reimbursement would be $73.14 for this same service.
Patients who get services covered by code G0023 in independent medical practices would have monthly copays of about $15-$20, depending on where they live.
The tab for patients tends to be higher for these same services if delivered through a medical practice owned by a hospital, as this would trigger the addition of facility fees to the payments made to cover the services. Facility fees are difficult for the public to ascertain before getting a treatment or service.
Dr. Mullangi and Ms. Gentry reported no relevant financial disclosures outside of their employers.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a move that acknowledges the gauntlet the US health system poses for people facing serious and fatal illnesses, Medicare will pay for a new class of workers to help patients manage treatments for conditions like cancer and heart failure.
The 2024 Medicare physician fee schedule includes new billing codes, including G0023, to pay for 60 minutes a month of care coordination by certified or trained auxiliary personnel working under the direction of a clinician.
A diagnosis of cancer or another serious illness takes a toll beyond the physical effects of the disease. Patients often scramble to make adjustments in family and work schedules to manage treatment, said Samyukta Mullangi, MD, MBA, medical director of oncology at Thyme Care, a Nashville, Tennessee–based firm that provides navigation and coordination services to oncology practices and insurers.
“It just really does create a bit of a pressure cooker for patients,” Dr. Mullangi told this news organization.
Medicare has for many years paid for medical professionals to help patients cope with the complexities of disease, such as chronic care management (CCM) provided by physicians, nurses, and physician assistants.
The new principal illness navigation (PIN) payments are intended to pay for work that to date typically has been done by people without medical degrees, including those involved in peer support networks and community health programs. The US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services(CMS) expects these navigators will undergo training and work under the supervision of clinicians.
The new navigators may coordinate care transitions between medical settings, follow up with patients after emergency department (ED) visits, or communicate with skilled nursing facilities regarding the psychosocial needs and functional deficits of a patient, among other functions.
CMS expects the new navigators may:
- Conduct assessments to understand a patient’s life story, strengths, needs, goals, preferences, and desired outcomes, including understanding cultural and linguistic factors.
- Provide support to accomplish the clinician’s treatment plan.
- Coordinate the receipt of needed services from healthcare facilities, home- and community-based service providers, and caregivers.
Peers as Navigators
The new navigators can be former patients who have undergone similar treatments for serious diseases, CMS said. This approach sets the new program apart from other care management services Medicare already covers, program officials wrote in the 2024 physician fee schedule.
“For some conditions, patients are best able to engage with the healthcare system and access care if they have assistance from a single, dedicated individual who has ‘lived experience,’ ” according to the rule.
The agency has taken a broad initial approach in defining what kinds of illnesses a patient may have to qualify for services. Patients must have a serious condition that is expected to last at least 3 months, such as cancer, heart failure, or substance use disorder.
But those without a definitive diagnosis may also qualify to receive navigator services.
In the rule, CMS cited a case in which a CT scan identified a suspicious mass in a patient’s colon. A clinician might decide this person would benefit from navigation services due to the potential risks for an undiagnosed illness.
“Regardless of the definitive diagnosis of the mass, presence of a colonic mass for that patient may be a serious high-risk condition that could, for example, cause obstruction and lead the patient to present to the emergency department, as well as be potentially indicative of an underlying life-threatening illness such as colon cancer,” CMS wrote in the rule.
Navigators often start their work when cancer patients are screened and guide them through initial diagnosis, potential surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy, said Sharon Gentry, MSN, RN, a former nurse navigator who is now the editor in chief of the Journal of the Academy of Oncology Nurse & Patient Navigators.
The navigators are meant to be a trusted and continual presence for patients, who otherwise might be left to start anew in finding help at each phase of care.
The navigators “see the whole picture. They see the whole journey the patient takes, from pre-diagnosis all the way through diagnosis care out through survival,” Ms. Gentry said.
Gaining a special Medicare payment for these kinds of services will elevate this work, she said.
Many newer drugs can target specific mechanisms and proteins of cancer. Often, oncology treatment involves testing to find out if mutations are allowing the cancer cells to evade a patient’s immune system.
Checking these biomarkers takes time, however. Patients sometimes become frustrated because they are anxious to begin treatment. Patients may receive inaccurate information from friends or family who went through treatment previously. Navigators can provide knowledge on the current state of care for a patient’s disease, helping them better manage anxieties.
“You have to explain to them that things have changed since the guy you drink coffee with was diagnosed with cancer, and there may be a drug that could target that,” Ms. Gentry said.
Potential Challenges
Initial uptake of the new PIN codes may be slow going, however, as clinicians and health systems may already use well-established codes. These include CCM and principal care management services, which may pay higher rates, Mullangi said.
“There might be sensitivity around not wanting to cannibalize existing programs with a new program,” Dr. Mullangi said.
In addition, many patients will have a copay for the services of principal illness navigators, Dr. Mullangi said.
While many patients have additional insurance that would cover the service, not all do. People with traditional Medicare coverage can sometimes pay 20% of the cost of some medical services.
“I think that may give patients pause, particularly if they’re already feeling the financial burden of a cancer treatment journey,” Dr. Mullangi said.
Pay rates for PIN services involve calculations of regional price differences, which are posted publicly by CMS, and potential added fees for services provided by hospital-affiliated organizations.
Consider payments for code G0023, covering 60 minutes of principal navigation services provided in a single month.
A set reimbursement for patients cared for in independent medical practices exists, with variation for local costs. Medicare’s non-facility price for G0023 would be $102.41 in some parts of Silicon Valley in California, including San Jose. In Arkansas, where costs are lower, reimbursement would be $73.14 for this same service.
Patients who get services covered by code G0023 in independent medical practices would have monthly copays of about $15-$20, depending on where they live.
The tab for patients tends to be higher for these same services if delivered through a medical practice owned by a hospital, as this would trigger the addition of facility fees to the payments made to cover the services. Facility fees are difficult for the public to ascertain before getting a treatment or service.
Dr. Mullangi and Ms. Gentry reported no relevant financial disclosures outside of their employers.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.

How to explain physician compounding to legislators
In Ohio, new limits on drug compounding in physicians’ offices went into effect in April and have become a real hindrance to care for dermatology patients. The State of Ohio Board of Pharmacy has defined compounding as combining two or more prescription drugs and has required that physicians who perform this “compounding” must obtain a “Terminal Distributor of Dangerous Drugs” license. Ohio is the “test state,” and these rules, unless vigorously opposed, will be coming to your state.
[polldaddy:9779752]
The rules state that “compounded” drugs used within 6 hours of preparation must be prepared in a designated clean medication area with proper hand hygiene and the use of powder-free gloves. “Compounded” drugs that are used more than 6 hours after preparation, require a designated clean room with access limited to authorized personnel, environmental control devices such as a laminar flow hood, and additional equipment and training of personnel to maintain an aseptic environment. A separate license is required for each office location.
The state pharmacy boards are eager to restrict physicians – as well as dentists and veterinarians – and to collect annual licensing fees. Additionally, according to an article from the Ohio State Medical Association, noncompliant physicians can be fined by the pharmacy board.
We are talking big money, power, and dreams of clinical relevancy (and billable activities) here.
What can dermatologists do to prevent this regulatory overreach? I encourage you to plan a visit to your state representative, where you can demonstrate how these restrictions affect you and your patients – an exercise that should be both fun and compelling. All you need to illustrate your case is a simple kit that includes a syringe (but no needles in the statehouse!), a bottle of lidocaine with epinephrine, a bottle of 8.4% bicarbonate, alcohol pads, and gloves.
First, explain to your audience that there is a skin cancer epidemic with more than 5.4 million new cases a year and that, over the past 20 years, the incidence of skin cancer has doubled and is projected to double again over the next 20 years. Further, explain that dermatologists treat more than 70% of these cases in the office setting, under local anesthesia, at a huge cost savings to the public and government (it costs an average of 12 times as much to remove these cancers in the outpatient department at the hospital). Remember, states foot most of the bill for Medicaid and Medicare gap indigent coverage.
Take the bottle of lidocaine with epinephrine and open the syringe pack (Staffers love this demonstration; everyone is fascinated with shots.). Put on your gloves, wipe the top of the lidocaine bottle with an alcohol swab, and explain that this medicine is the anesthetic preferred for skin cancer surgery. Explain how it not only numbs the skin, but also causes vasoconstriction, so that the cancer can be easily and safely removed in the office.
Then explain that, in order for the epinephrine to be stable, the solution has to be very acidic (a pH of 4.2, in fact). Explain that this makes it burn like hell unless you add 0.1 cc per cc of 8.4% bicarbonate, in which case the perceived pain on a 10-point scale will drop from 8 to 2. Then pick up the bottle of bicarbonate and explain that you will no longer be able to mix these two components anymore without a “Terminal Distributor of Dangerous Drugs” license because your state pharmacy board considers this compounding. Your representative is likely to give you looks of astonishment, disbelief, and then a dawning realization of the absurdity of the situation.
Follow-up questions may include “Why can’t you buy buffered lidocaine with epinephrine from the compounding pharmacy?” Easy answer: because each patient needs an individual prescription, and you may not know in advance which patient will need it, and how much the patient will need, and it becomes unstable once it has been buffered. It also will cost the patient $45 per 5-cc syringe, and it will be degraded by the time the patient returns from the compounding pharmacy. Explain further that it costs you only 84 cents to make a 5-cc syringe of buffered lidocaine; that some patients may need as many as 10 syringes; and that these costs are all included in the surgery (free!) if the physician draws it up in the office.
A simple summary is – less pain, less cost – and no history of infections or complications.
It is an eye-opener when you demonstrate how ridiculous the compounding rules being imposed are for physicians and patients. I’ve used this demonstration at the state and federal legislative level, and more recently, at the Food and Drug Administration.
If you get the chance, when a state legislator is in your office, become an advocate for your patients and fellow physicians. Make sure physician offices are excluded from these definitions of com
This column was updated June 22, 2017.
Dr. Coldiron is in private practice but maintains a clinical assistant professorship at the University of Cincinnati. He cares for patients, teaches medical students and residents, and has several active clinical research projects. Dr. Coldiron is the author of more than 80 scientific letters, papers, and several book chapters, and he speaks frequently on a variety of topics. He is a past president of the American Academy of Dermatology. Write to him at dermnews@frontlinemedcom.com.
In Ohio, new limits on drug compounding in physicians’ offices went into effect in April and have become a real hindrance to care for dermatology patients. The State of Ohio Board of Pharmacy has defined compounding as combining two or more prescription drugs and has required that physicians who perform this “compounding” must obtain a “Terminal Distributor of Dangerous Drugs” license. Ohio is the “test state,” and these rules, unless vigorously opposed, will be coming to your state.
[polldaddy:9779752]
The rules state that “compounded” drugs used within 6 hours of preparation must be prepared in a designated clean medication area with proper hand hygiene and the use of powder-free gloves. “Compounded” drugs that are used more than 6 hours after preparation, require a designated clean room with access limited to authorized personnel, environmental control devices such as a laminar flow hood, and additional equipment and training of personnel to maintain an aseptic environment. A separate license is required for each office location.
The state pharmacy boards are eager to restrict physicians – as well as dentists and veterinarians – and to collect annual licensing fees. Additionally, according to an article from the Ohio State Medical Association, noncompliant physicians can be fined by the pharmacy board.
We are talking big money, power, and dreams of clinical relevancy (and billable activities) here.
What can dermatologists do to prevent this regulatory overreach? I encourage you to plan a visit to your state representative, where you can demonstrate how these restrictions affect you and your patients – an exercise that should be both fun and compelling. All you need to illustrate your case is a simple kit that includes a syringe (but no needles in the statehouse!), a bottle of lidocaine with epinephrine, a bottle of 8.4% bicarbonate, alcohol pads, and gloves.
First, explain to your audience that there is a skin cancer epidemic with more than 5.4 million new cases a year and that, over the past 20 years, the incidence of skin cancer has doubled and is projected to double again over the next 20 years. Further, explain that dermatologists treat more than 70% of these cases in the office setting, under local anesthesia, at a huge cost savings to the public and government (it costs an average of 12 times as much to remove these cancers in the outpatient department at the hospital). Remember, states foot most of the bill for Medicaid and Medicare gap indigent coverage.
Take the bottle of lidocaine with epinephrine and open the syringe pack (Staffers love this demonstration; everyone is fascinated with shots.). Put on your gloves, wipe the top of the lidocaine bottle with an alcohol swab, and explain that this medicine is the anesthetic preferred for skin cancer surgery. Explain how it not only numbs the skin, but also causes vasoconstriction, so that the cancer can be easily and safely removed in the office.
Then explain that, in order for the epinephrine to be stable, the solution has to be very acidic (a pH of 4.2, in fact). Explain that this makes it burn like hell unless you add 0.1 cc per cc of 8.4% bicarbonate, in which case the perceived pain on a 10-point scale will drop from 8 to 2. Then pick up the bottle of bicarbonate and explain that you will no longer be able to mix these two components anymore without a “Terminal Distributor of Dangerous Drugs” license because your state pharmacy board considers this compounding. Your representative is likely to give you looks of astonishment, disbelief, and then a dawning realization of the absurdity of the situation.
Follow-up questions may include “Why can’t you buy buffered lidocaine with epinephrine from the compounding pharmacy?” Easy answer: because each patient needs an individual prescription, and you may not know in advance which patient will need it, and how much the patient will need, and it becomes unstable once it has been buffered. It also will cost the patient $45 per 5-cc syringe, and it will be degraded by the time the patient returns from the compounding pharmacy. Explain further that it costs you only 84 cents to make a 5-cc syringe of buffered lidocaine; that some patients may need as many as 10 syringes; and that these costs are all included in the surgery (free!) if the physician draws it up in the office.
A simple summary is – less pain, less cost – and no history of infections or complications.
It is an eye-opener when you demonstrate how ridiculous the compounding rules being imposed are for physicians and patients. I’ve used this demonstration at the state and federal legislative level, and more recently, at the Food and Drug Administration.
If you get the chance, when a state legislator is in your office, become an advocate for your patients and fellow physicians. Make sure physician offices are excluded from these definitions of com
This column was updated June 22, 2017.
Dr. Coldiron is in private practice but maintains a clinical assistant professorship at the University of Cincinnati. He cares for patients, teaches medical students and residents, and has several active clinical research projects. Dr. Coldiron is the author of more than 80 scientific letters, papers, and several book chapters, and he speaks frequently on a variety of topics. He is a past president of the American Academy of Dermatology. Write to him at dermnews@frontlinemedcom.com.
In Ohio, new limits on drug compounding in physicians’ offices went into effect in April and have become a real hindrance to care for dermatology patients. The State of Ohio Board of Pharmacy has defined compounding as combining two or more prescription drugs and has required that physicians who perform this “compounding” must obtain a “Terminal Distributor of Dangerous Drugs” license. Ohio is the “test state,” and these rules, unless vigorously opposed, will be coming to your state.
[polldaddy:9779752]
The rules state that “compounded” drugs used within 6 hours of preparation must be prepared in a designated clean medication area with proper hand hygiene and the use of powder-free gloves. “Compounded” drugs that are used more than 6 hours after preparation, require a designated clean room with access limited to authorized personnel, environmental control devices such as a laminar flow hood, and additional equipment and training of personnel to maintain an aseptic environment. A separate license is required for each office location.
The state pharmacy boards are eager to restrict physicians – as well as dentists and veterinarians – and to collect annual licensing fees. Additionally, according to an article from the Ohio State Medical Association, noncompliant physicians can be fined by the pharmacy board.
We are talking big money, power, and dreams of clinical relevancy (and billable activities) here.
What can dermatologists do to prevent this regulatory overreach? I encourage you to plan a visit to your state representative, where you can demonstrate how these restrictions affect you and your patients – an exercise that should be both fun and compelling. All you need to illustrate your case is a simple kit that includes a syringe (but no needles in the statehouse!), a bottle of lidocaine with epinephrine, a bottle of 8.4% bicarbonate, alcohol pads, and gloves.
First, explain to your audience that there is a skin cancer epidemic with more than 5.4 million new cases a year and that, over the past 20 years, the incidence of skin cancer has doubled and is projected to double again over the next 20 years. Further, explain that dermatologists treat more than 70% of these cases in the office setting, under local anesthesia, at a huge cost savings to the public and government (it costs an average of 12 times as much to remove these cancers in the outpatient department at the hospital). Remember, states foot most of the bill for Medicaid and Medicare gap indigent coverage.
Take the bottle of lidocaine with epinephrine and open the syringe pack (Staffers love this demonstration; everyone is fascinated with shots.). Put on your gloves, wipe the top of the lidocaine bottle with an alcohol swab, and explain that this medicine is the anesthetic preferred for skin cancer surgery. Explain how it not only numbs the skin, but also causes vasoconstriction, so that the cancer can be easily and safely removed in the office.
Then explain that, in order for the epinephrine to be stable, the solution has to be very acidic (a pH of 4.2, in fact). Explain that this makes it burn like hell unless you add 0.1 cc per cc of 8.4% bicarbonate, in which case the perceived pain on a 10-point scale will drop from 8 to 2. Then pick up the bottle of bicarbonate and explain that you will no longer be able to mix these two components anymore without a “Terminal Distributor of Dangerous Drugs” license because your state pharmacy board considers this compounding. Your representative is likely to give you looks of astonishment, disbelief, and then a dawning realization of the absurdity of the situation.
Follow-up questions may include “Why can’t you buy buffered lidocaine with epinephrine from the compounding pharmacy?” Easy answer: because each patient needs an individual prescription, and you may not know in advance which patient will need it, and how much the patient will need, and it becomes unstable once it has been buffered. It also will cost the patient $45 per 5-cc syringe, and it will be degraded by the time the patient returns from the compounding pharmacy. Explain further that it costs you only 84 cents to make a 5-cc syringe of buffered lidocaine; that some patients may need as many as 10 syringes; and that these costs are all included in the surgery (free!) if the physician draws it up in the office.
A simple summary is – less pain, less cost – and no history of infections or complications.
It is an eye-opener when you demonstrate how ridiculous the compounding rules being imposed are for physicians and patients. I’ve used this demonstration at the state and federal legislative level, and more recently, at the Food and Drug Administration.
If you get the chance, when a state legislator is in your office, become an advocate for your patients and fellow physicians. Make sure physician offices are excluded from these definitions of com
This column was updated June 22, 2017.
Dr. Coldiron is in private practice but maintains a clinical assistant professorship at the University of Cincinnati. He cares for patients, teaches medical students and residents, and has several active clinical research projects. Dr. Coldiron is the author of more than 80 scientific letters, papers, and several book chapters, and he speaks frequently on a variety of topics. He is a past president of the American Academy of Dermatology. Write to him at dermnews@frontlinemedcom.com.
Best Practices: Protecting Dry Vulnerable Skin with CeraVe® Healing Ointment
A supplement to Dermatology News. This advertising supplement is sponsored by Valeant Pharmaceuticals.
- Reinforcing the Skin Barrier
- NEA Seal of Acceptance
- A Preventative Approach to Dry, Cracked Skin
- CeraVe Ointment in the Clinical Setting
Faculty/Faculty Disclosure
Sheila Fallon Friedlander, MD
Professor of Clinical Dermatology & Pediatrics
Director, Pediatric Dermatology Fellowship Training Program
University of California at San Diego School of Medicine
Rady Children’s Hospital,
San Diego, California
Dr. Friedlander was compensated for her participation in the development of this article.
CeraVe is a registered trademark of Valeant Pharmaceuticals International, Inc. or its affiliates.
A supplement to Dermatology News. This advertising supplement is sponsored by Valeant Pharmaceuticals.
- Reinforcing the Skin Barrier
- NEA Seal of Acceptance
- A Preventative Approach to Dry, Cracked Skin
- CeraVe Ointment in the Clinical Setting
Faculty/Faculty Disclosure
Sheila Fallon Friedlander, MD
Professor of Clinical Dermatology & Pediatrics
Director, Pediatric Dermatology Fellowship Training Program
University of California at San Diego School of Medicine
Rady Children’s Hospital,
San Diego, California
Dr. Friedlander was compensated for her participation in the development of this article.
CeraVe is a registered trademark of Valeant Pharmaceuticals International, Inc. or its affiliates.
A supplement to Dermatology News. This advertising supplement is sponsored by Valeant Pharmaceuticals.
- Reinforcing the Skin Barrier
- NEA Seal of Acceptance
- A Preventative Approach to Dry, Cracked Skin
- CeraVe Ointment in the Clinical Setting
Faculty/Faculty Disclosure
Sheila Fallon Friedlander, MD
Professor of Clinical Dermatology & Pediatrics
Director, Pediatric Dermatology Fellowship Training Program
University of California at San Diego School of Medicine
Rady Children’s Hospital,
San Diego, California
Dr. Friedlander was compensated for her participation in the development of this article.
CeraVe is a registered trademark of Valeant Pharmaceuticals International, Inc. or its affiliates.
Dermatology on Duty: Pathways to a Career in Military Medicine
Dermatology on Duty: Pathways to a Career in Military Medicine
Serving those who serve has been one of the most meaningful parts of my career. A career in military medicine offers dermatologists not only a chance to practice within a unique and diverse patient population but also an opportunity to contribute to something larger than themselves. Whether working with active-duty service members and their families within the Military Health System (MHS) or caring for veterans through the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), the experience can be both enriching and rewarding. This article will explore the various pathways available to dermatologists to serve military communities, whether they are at the start of their careers or are looking for a change of pace within their established practice.
Care Pathways for Military and Veterans
To care for uniformed service members, their families, and retired personnel, dermatologists typically serve within the MHS—a global, integrated network of military hospitals and clinics dedicated to delivering health care to this population.1 TRICARE is the health insurance program that covers those eligible for care within the system, including active-duty and retired service members.2 In this context, it is important to clarify what the term retired actually means, as it differs from the term veteran when it comes to accessing health care options, and these terms frequently are conflated. A retired service member is an individual who completed at least 20 years of active-duty service or who has been medically retired because of a condition or injury incurred while on active duty.3 In contrast, a veteran may not have completed 20 years of service but has separated honorably after serving at least 24 continuous months.4 Veterans typically receive care through the VA system.5
Serving on Active Duty
In general, there are 2 main pathways to serve as a dermatologist within the MHS. The first is to commission in the military and serve on active duty. Most often, this pathway begins with a premedical student applying to medical school. Those considering military service typically explore scholarship programs such as the Health Professions Scholarship Program (HPSP)(https://www.medicineandthemilitary.com/applying-and-what-to-expect/medical-school-programs/hpsp) or the Health Services Collegiate Program (HSCP), or they apply to the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences (USU)(https://www.usuhs.edu/about). The HPSP and HSCP programs financially support medical students training at civilian medical schools, though in different ways—the HPSP covers tuition and fees, while the HSCP provides a salary during training but does not cover tuition.6 In contrast, students of USU attend the nation’s only military medical school, serving in uniform for 4 years while earning the pay and benefits of a junior officer in their respective service branch. Any premedical student considering the HPSP, HSCP or USU routes for service must meet the commissioning standards of their chosen branch—Army, Navy, or Air Force—and enter service as an officer before beginning medical school.
While direct commission prior to medical school is the most common route to active-duty service, board-certified dermatologists also can join a military branch later through what is called Direct Accession or Direct Commission; for example, the Navy offers a Residency to Direct Accession program, which commissions residents in their final year of training to join the Navy upon graduation. In some cases, commissioning at this stage includes a bonus of up to $600,000 in exchange for a 4-year active-duty commitment.7 The Army and Air Force offer similar direct commission programs, though specific incentives vary.8 Interested residents or practitioners can contact a local recruiting office within their branch of interest to learn more. Direct accession is open at many points in a dermatologist’s career—after residency, after fellowship, or even as an established civilian practitioner—and the initial commissioning rank and bonus generally reflect one’s level of experience.
Serving as a Civilian
Outside of uniformed service, dermatologists can find opportunities to provide care for active-duty service members, veterans, and military families through employment as General Schedule (GS) employees. The GS is a role classification and pay system that covers most federal employees in professional, administrative, and technical positions (eg, physicians). The GS system classifies most of these employees based on the complexity, responsibility, and qualifications required for their role.9 Such positions often are at the highest level of the GS pay scale, reflecting the expertise and years of education required to become a dermatologist, though pay varies by location and experience. In contrast, physicians employed through the VA system are classified as Title 38 federal employees, governed by a different pay structure and regulatory framework under the US Code of Federal Regulations.10 These regulations govern the hiring, retention, and firing guidelines for VA physicians, which differ from those of GS physicians. A full explanation is outside of the scope of this article, however.
Final Thoughts
In summary, uniformed or federal service as a dermatologist offers a meaningful and impactful way to give back to those who have served our country. Opportunities exist throughout the United States for dermatologists interested in serving within the MHS or VA. The most transparent and up-to-date resource for identifying open positions in both large metropolitan areas and smaller communities is USAJOBS.gov. While financial compensation may not always match that of private practice, the intangible benefits are considerable—stable employment, comprehensive benefits, malpractice coverage, and secure retirement, among others. There is something deeply fulfilling about using one’s medical skills in service of a larger mission. The relationships built with service members, the sense of shared purpose, and the opportunity to contribute to the readiness and well-being of those who serve all make this career path profoundly rewarding. For dermatologists seeking a practice that combines professional growth with purpose and patriotism, military medicine offers a truly special calling.
- Military Health System. Elements of the military health system. Accessed October 11, 2025. https://www.health.mil/About-MHS/MHS-Elements
- TRICARE. Plans and eligibility. Accessed October 11, 2025. https://tricare.mil/Plans/Eligibility
- Military Benefit. TRICARE for retirees. Accessed October 11, 2025. https://www.militarybenefit.org/get-educated/tricareforretirees/
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Eligibility for VA health care. Accessed October 11, 2025. https://www.va.gov/health-care/eligibility/
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA priority groups. Accessed October 11, 2025. https://www.va.gov/health-care/eligibility/priority-groups/
- Navy Medicine. Health Professions Scholarship Program (HPSP) and Financial Assistance Program (FAP). Accessed October 12, 2025. https://www.med.navy.mil/Accessions/Health-Professions-Scholarship-Program-HPSP-and-Financial-Assistance-Program-FAP/
- US Navy. Navy Medicine R2DA program. Accessed October 12, 2025. https://www.navy.com/navy-medicine
- US Army Medical Department. Student programs. Accessed October 12, 2025. https://goamedd.com/student-programs
- US Office of Personnel Management. General Schedule. Accessed October 12, 2025. https://www.opm.gov/policy-data-oversight/pay-leave/pay-systems/general-schedule/
- Pines Federal Employment Attorneys. Title 38 employees: medical professionals. Accessed October 12, 2025. https://www.pinesfederal.com/va-federal-employees/title-38-employees-medical-professionals/
Serving those who serve has been one of the most meaningful parts of my career. A career in military medicine offers dermatologists not only a chance to practice within a unique and diverse patient population but also an opportunity to contribute to something larger than themselves. Whether working with active-duty service members and their families within the Military Health System (MHS) or caring for veterans through the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), the experience can be both enriching and rewarding. This article will explore the various pathways available to dermatologists to serve military communities, whether they are at the start of their careers or are looking for a change of pace within their established practice.
Care Pathways for Military and Veterans
To care for uniformed service members, their families, and retired personnel, dermatologists typically serve within the MHS—a global, integrated network of military hospitals and clinics dedicated to delivering health care to this population.1 TRICARE is the health insurance program that covers those eligible for care within the system, including active-duty and retired service members.2 In this context, it is important to clarify what the term retired actually means, as it differs from the term veteran when it comes to accessing health care options, and these terms frequently are conflated. A retired service member is an individual who completed at least 20 years of active-duty service or who has been medically retired because of a condition or injury incurred while on active duty.3 In contrast, a veteran may not have completed 20 years of service but has separated honorably after serving at least 24 continuous months.4 Veterans typically receive care through the VA system.5
Serving on Active Duty
In general, there are 2 main pathways to serve as a dermatologist within the MHS. The first is to commission in the military and serve on active duty. Most often, this pathway begins with a premedical student applying to medical school. Those considering military service typically explore scholarship programs such as the Health Professions Scholarship Program (HPSP)(https://www.medicineandthemilitary.com/applying-and-what-to-expect/medical-school-programs/hpsp) or the Health Services Collegiate Program (HSCP), or they apply to the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences (USU)(https://www.usuhs.edu/about). The HPSP and HSCP programs financially support medical students training at civilian medical schools, though in different ways—the HPSP covers tuition and fees, while the HSCP provides a salary during training but does not cover tuition.6 In contrast, students of USU attend the nation’s only military medical school, serving in uniform for 4 years while earning the pay and benefits of a junior officer in their respective service branch. Any premedical student considering the HPSP, HSCP or USU routes for service must meet the commissioning standards of their chosen branch—Army, Navy, or Air Force—and enter service as an officer before beginning medical school.
While direct commission prior to medical school is the most common route to active-duty service, board-certified dermatologists also can join a military branch later through what is called Direct Accession or Direct Commission; for example, the Navy offers a Residency to Direct Accession program, which commissions residents in their final year of training to join the Navy upon graduation. In some cases, commissioning at this stage includes a bonus of up to $600,000 in exchange for a 4-year active-duty commitment.7 The Army and Air Force offer similar direct commission programs, though specific incentives vary.8 Interested residents or practitioners can contact a local recruiting office within their branch of interest to learn more. Direct accession is open at many points in a dermatologist’s career—after residency, after fellowship, or even as an established civilian practitioner—and the initial commissioning rank and bonus generally reflect one’s level of experience.
Serving as a Civilian
Outside of uniformed service, dermatologists can find opportunities to provide care for active-duty service members, veterans, and military families through employment as General Schedule (GS) employees. The GS is a role classification and pay system that covers most federal employees in professional, administrative, and technical positions (eg, physicians). The GS system classifies most of these employees based on the complexity, responsibility, and qualifications required for their role.9 Such positions often are at the highest level of the GS pay scale, reflecting the expertise and years of education required to become a dermatologist, though pay varies by location and experience. In contrast, physicians employed through the VA system are classified as Title 38 federal employees, governed by a different pay structure and regulatory framework under the US Code of Federal Regulations.10 These regulations govern the hiring, retention, and firing guidelines for VA physicians, which differ from those of GS physicians. A full explanation is outside of the scope of this article, however.
Final Thoughts
In summary, uniformed or federal service as a dermatologist offers a meaningful and impactful way to give back to those who have served our country. Opportunities exist throughout the United States for dermatologists interested in serving within the MHS or VA. The most transparent and up-to-date resource for identifying open positions in both large metropolitan areas and smaller communities is USAJOBS.gov. While financial compensation may not always match that of private practice, the intangible benefits are considerable—stable employment, comprehensive benefits, malpractice coverage, and secure retirement, among others. There is something deeply fulfilling about using one’s medical skills in service of a larger mission. The relationships built with service members, the sense of shared purpose, and the opportunity to contribute to the readiness and well-being of those who serve all make this career path profoundly rewarding. For dermatologists seeking a practice that combines professional growth with purpose and patriotism, military medicine offers a truly special calling.
Serving those who serve has been one of the most meaningful parts of my career. A career in military medicine offers dermatologists not only a chance to practice within a unique and diverse patient population but also an opportunity to contribute to something larger than themselves. Whether working with active-duty service members and their families within the Military Health System (MHS) or caring for veterans through the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), the experience can be both enriching and rewarding. This article will explore the various pathways available to dermatologists to serve military communities, whether they are at the start of their careers or are looking for a change of pace within their established practice.
Care Pathways for Military and Veterans
To care for uniformed service members, their families, and retired personnel, dermatologists typically serve within the MHS—a global, integrated network of military hospitals and clinics dedicated to delivering health care to this population.1 TRICARE is the health insurance program that covers those eligible for care within the system, including active-duty and retired service members.2 In this context, it is important to clarify what the term retired actually means, as it differs from the term veteran when it comes to accessing health care options, and these terms frequently are conflated. A retired service member is an individual who completed at least 20 years of active-duty service or who has been medically retired because of a condition or injury incurred while on active duty.3 In contrast, a veteran may not have completed 20 years of service but has separated honorably after serving at least 24 continuous months.4 Veterans typically receive care through the VA system.5
Serving on Active Duty
In general, there are 2 main pathways to serve as a dermatologist within the MHS. The first is to commission in the military and serve on active duty. Most often, this pathway begins with a premedical student applying to medical school. Those considering military service typically explore scholarship programs such as the Health Professions Scholarship Program (HPSP)(https://www.medicineandthemilitary.com/applying-and-what-to-expect/medical-school-programs/hpsp) or the Health Services Collegiate Program (HSCP), or they apply to the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences (USU)(https://www.usuhs.edu/about). The HPSP and HSCP programs financially support medical students training at civilian medical schools, though in different ways—the HPSP covers tuition and fees, while the HSCP provides a salary during training but does not cover tuition.6 In contrast, students of USU attend the nation’s only military medical school, serving in uniform for 4 years while earning the pay and benefits of a junior officer in their respective service branch. Any premedical student considering the HPSP, HSCP or USU routes for service must meet the commissioning standards of their chosen branch—Army, Navy, or Air Force—and enter service as an officer before beginning medical school.
While direct commission prior to medical school is the most common route to active-duty service, board-certified dermatologists also can join a military branch later through what is called Direct Accession or Direct Commission; for example, the Navy offers a Residency to Direct Accession program, which commissions residents in their final year of training to join the Navy upon graduation. In some cases, commissioning at this stage includes a bonus of up to $600,000 in exchange for a 4-year active-duty commitment.7 The Army and Air Force offer similar direct commission programs, though specific incentives vary.8 Interested residents or practitioners can contact a local recruiting office within their branch of interest to learn more. Direct accession is open at many points in a dermatologist’s career—after residency, after fellowship, or even as an established civilian practitioner—and the initial commissioning rank and bonus generally reflect one’s level of experience.
Serving as a Civilian
Outside of uniformed service, dermatologists can find opportunities to provide care for active-duty service members, veterans, and military families through employment as General Schedule (GS) employees. The GS is a role classification and pay system that covers most federal employees in professional, administrative, and technical positions (eg, physicians). The GS system classifies most of these employees based on the complexity, responsibility, and qualifications required for their role.9 Such positions often are at the highest level of the GS pay scale, reflecting the expertise and years of education required to become a dermatologist, though pay varies by location and experience. In contrast, physicians employed through the VA system are classified as Title 38 federal employees, governed by a different pay structure and regulatory framework under the US Code of Federal Regulations.10 These regulations govern the hiring, retention, and firing guidelines for VA physicians, which differ from those of GS physicians. A full explanation is outside of the scope of this article, however.
Final Thoughts
In summary, uniformed or federal service as a dermatologist offers a meaningful and impactful way to give back to those who have served our country. Opportunities exist throughout the United States for dermatologists interested in serving within the MHS or VA. The most transparent and up-to-date resource for identifying open positions in both large metropolitan areas and smaller communities is USAJOBS.gov. While financial compensation may not always match that of private practice, the intangible benefits are considerable—stable employment, comprehensive benefits, malpractice coverage, and secure retirement, among others. There is something deeply fulfilling about using one’s medical skills in service of a larger mission. The relationships built with service members, the sense of shared purpose, and the opportunity to contribute to the readiness and well-being of those who serve all make this career path profoundly rewarding. For dermatologists seeking a practice that combines professional growth with purpose and patriotism, military medicine offers a truly special calling.
- Military Health System. Elements of the military health system. Accessed October 11, 2025. https://www.health.mil/About-MHS/MHS-Elements
- TRICARE. Plans and eligibility. Accessed October 11, 2025. https://tricare.mil/Plans/Eligibility
- Military Benefit. TRICARE for retirees. Accessed October 11, 2025. https://www.militarybenefit.org/get-educated/tricareforretirees/
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Eligibility for VA health care. Accessed October 11, 2025. https://www.va.gov/health-care/eligibility/
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA priority groups. Accessed October 11, 2025. https://www.va.gov/health-care/eligibility/priority-groups/
- Navy Medicine. Health Professions Scholarship Program (HPSP) and Financial Assistance Program (FAP). Accessed October 12, 2025. https://www.med.navy.mil/Accessions/Health-Professions-Scholarship-Program-HPSP-and-Financial-Assistance-Program-FAP/
- US Navy. Navy Medicine R2DA program. Accessed October 12, 2025. https://www.navy.com/navy-medicine
- US Army Medical Department. Student programs. Accessed October 12, 2025. https://goamedd.com/student-programs
- US Office of Personnel Management. General Schedule. Accessed October 12, 2025. https://www.opm.gov/policy-data-oversight/pay-leave/pay-systems/general-schedule/
- Pines Federal Employment Attorneys. Title 38 employees: medical professionals. Accessed October 12, 2025. https://www.pinesfederal.com/va-federal-employees/title-38-employees-medical-professionals/
- Military Health System. Elements of the military health system. Accessed October 11, 2025. https://www.health.mil/About-MHS/MHS-Elements
- TRICARE. Plans and eligibility. Accessed October 11, 2025. https://tricare.mil/Plans/Eligibility
- Military Benefit. TRICARE for retirees. Accessed October 11, 2025. https://www.militarybenefit.org/get-educated/tricareforretirees/
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Eligibility for VA health care. Accessed October 11, 2025. https://www.va.gov/health-care/eligibility/
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA priority groups. Accessed October 11, 2025. https://www.va.gov/health-care/eligibility/priority-groups/
- Navy Medicine. Health Professions Scholarship Program (HPSP) and Financial Assistance Program (FAP). Accessed October 12, 2025. https://www.med.navy.mil/Accessions/Health-Professions-Scholarship-Program-HPSP-and-Financial-Assistance-Program-FAP/
- US Navy. Navy Medicine R2DA program. Accessed October 12, 2025. https://www.navy.com/navy-medicine
- US Army Medical Department. Student programs. Accessed October 12, 2025. https://goamedd.com/student-programs
- US Office of Personnel Management. General Schedule. Accessed October 12, 2025. https://www.opm.gov/policy-data-oversight/pay-leave/pay-systems/general-schedule/
- Pines Federal Employment Attorneys. Title 38 employees: medical professionals. Accessed October 12, 2025. https://www.pinesfederal.com/va-federal-employees/title-38-employees-medical-professionals/
Dermatology on Duty: Pathways to a Career in Military Medicine
Dermatology on Duty: Pathways to a Career in Military Medicine
PRACTICE POINTS
- Dermatologists have diverse pathways to serve the military and veteran communities, either in uniform or as civilians.
- For those considering a military career, options include medical school scholarships or direct commission after residency.
- Those who prefer to remain civilians can find employment opportunities with the Military Heath System or the Department of Veterans Affairs that provide a way to care for this population without a service commitment.
The Habit of Curiosity: How Writing Shapes Clinical Thinking in Medical Training
The Habit of Curiosity: How Writing Shapes Clinical Thinking in Medical Training
I was accepted into my fellowship almost 1 year ago: major milestones on my curriculum vitae are now met, fellowship application materials are complete, and the stress of the match is long gone. At the start of my fellowship, I had 2 priorities: (1) to learn as much as I could about dermatologic surgery and (2) to be the best dad possible to my newborn son, Jay. However, most nights I still find myself up late editing a manuscript draft or chasing down references, long after the “need” to publish has passed. Recently, my wife asked me why—what’s left to prove?
I’ll be the first to admit it: early on, publishing felt almost purely transactional. Each project was little more than a line on an application or a way to stand out or meet a new mentor. I have reflected before on how easily that mindset can slip into a kind of research arms race, in which productivity overshadows purpose.1 This time, I wanted to explore the other side of that equation: the “why” behind it all.
I have learned that writing forces me to slow down and actually think about what I am seeing every day. It turns routine work into something I must understand well enough to explain. Even a small write-up can make me notice details I would otherwise skim past in clinic or surgery. These days, most of my projects start small: a case that taught me something, an observation that made me pause and think. Those seemingly small questions are what eventually grow into bigger ones. The clinical trial I am designing now did not begin as a grand plan—it started because I could not stop thinking about how we manage pain and analgesia after Mohs surgery. That curiosity, shaped by the experience of writing those earlier “smaller” papers, evolved into a study that might actually help improve patient care one day. Still, most of what I write will not revolutionize the field. It is not cutting-edge science or paradigm-shifting data; it is mostly modest analyses with a few interesting conclusions or surgical pearls that might cut down on a patient’s procedural time or save a dermatologist somewhere a few sutures. But it still feels worth doing.
While rotating with Dr. Anna Bar at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, I noticed a poster hanging on the wall titled, “Top 10 Reasons Why Our Faculty Are Dedicated to Academics and Teaching,” based on the wisdom of Dr. Jane M. Grant-Kels.2 My favorite line on the poster reads, “Residents make us better by asking questions.” I think this philosophy is the main reason why I still write. Even though I am not a resident anymore, I am still asking questions. But if I had to sum up my “why” into a neat list, here is what it might look like:
Because asking questions keeps your brain wired for curiosity. Even small projects train us to remain curious, and this curiosity can mean the difference between just doing your job and continuing to evolve within it. As Dr. Rodolfo Neirotti reminds us, “Questions are useful tools—they open communication, improve understanding, and drive scientific research. In medicine, doing things without knowing why is risky.”3
Because the small stuff builds the culture. Dermatology is a small world. Even short case series, pearls, or “how we do it” pieces can shape how we practice. They may not change paradigms, but they can refine them. Over time, those small practical contributions become part of the field’s collective muscle memory.
Because it preserves perspective. Residency, fellowship, and early practice can blur together. A tiny project can become a timestamp of what you were learning or caring about at that specific moment. Years later, you may remember the case through the paper.
Because the act of writing is the point. Writing forces clarity. You cannot hide behind saying, “That’s just how I do things,” when you have to explain it to others. The discipline of organizing your thoughts sharpens your clinical reasoning and keeps you honest about what you actually know.
Because sometimes it is simply about participating. Publishing, even small pieces, is a way of staying in touch with your field. It says, “I’m still here. I’m still paying attention.”
I think about how Dr. Frederic Mohs developed the technique that now bears his name while he was still a medical student.4 He could have said, “I already made it into medical school. That’s enough.” But he did not. I guess my point is not that we are all on the verge of inventing something revolutionary; it is that innovation happens only when curiosity keeps moving us forward. So no, I do not write to check boxes anymore. I write because it keeps me curious, and I have realized that curiosity is a habit I never want to outgrow.
Or maybe it’s because Jay keeps me up at night, and I have nothing better to do.
- Jeha GM. A roadmap to research opportunities for dermatology residents. Cutis. 2024;114:E53-E56.
- Grant-Kels J. The gift that keeps on giving. UConn Health Dermatology. Accessed November 24, 2025. https://health.uconn.edu/dermatology/education/
- Neirotti RA. The importance of asking questions and doing things for a reason. Braz J Cardiovasc Surg. 2021;36:I-II.
- Trost LB, Bailin PL. History of Mohs surgery. Dermatol Clin. 2011;29:135-139, vii.
I was accepted into my fellowship almost 1 year ago: major milestones on my curriculum vitae are now met, fellowship application materials are complete, and the stress of the match is long gone. At the start of my fellowship, I had 2 priorities: (1) to learn as much as I could about dermatologic surgery and (2) to be the best dad possible to my newborn son, Jay. However, most nights I still find myself up late editing a manuscript draft or chasing down references, long after the “need” to publish has passed. Recently, my wife asked me why—what’s left to prove?
I’ll be the first to admit it: early on, publishing felt almost purely transactional. Each project was little more than a line on an application or a way to stand out or meet a new mentor. I have reflected before on how easily that mindset can slip into a kind of research arms race, in which productivity overshadows purpose.1 This time, I wanted to explore the other side of that equation: the “why” behind it all.
I have learned that writing forces me to slow down and actually think about what I am seeing every day. It turns routine work into something I must understand well enough to explain. Even a small write-up can make me notice details I would otherwise skim past in clinic or surgery. These days, most of my projects start small: a case that taught me something, an observation that made me pause and think. Those seemingly small questions are what eventually grow into bigger ones. The clinical trial I am designing now did not begin as a grand plan—it started because I could not stop thinking about how we manage pain and analgesia after Mohs surgery. That curiosity, shaped by the experience of writing those earlier “smaller” papers, evolved into a study that might actually help improve patient care one day. Still, most of what I write will not revolutionize the field. It is not cutting-edge science or paradigm-shifting data; it is mostly modest analyses with a few interesting conclusions or surgical pearls that might cut down on a patient’s procedural time or save a dermatologist somewhere a few sutures. But it still feels worth doing.
While rotating with Dr. Anna Bar at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, I noticed a poster hanging on the wall titled, “Top 10 Reasons Why Our Faculty Are Dedicated to Academics and Teaching,” based on the wisdom of Dr. Jane M. Grant-Kels.2 My favorite line on the poster reads, “Residents make us better by asking questions.” I think this philosophy is the main reason why I still write. Even though I am not a resident anymore, I am still asking questions. But if I had to sum up my “why” into a neat list, here is what it might look like:
Because asking questions keeps your brain wired for curiosity. Even small projects train us to remain curious, and this curiosity can mean the difference between just doing your job and continuing to evolve within it. As Dr. Rodolfo Neirotti reminds us, “Questions are useful tools—they open communication, improve understanding, and drive scientific research. In medicine, doing things without knowing why is risky.”3
Because the small stuff builds the culture. Dermatology is a small world. Even short case series, pearls, or “how we do it” pieces can shape how we practice. They may not change paradigms, but they can refine them. Over time, those small practical contributions become part of the field’s collective muscle memory.
Because it preserves perspective. Residency, fellowship, and early practice can blur together. A tiny project can become a timestamp of what you were learning or caring about at that specific moment. Years later, you may remember the case through the paper.
Because the act of writing is the point. Writing forces clarity. You cannot hide behind saying, “That’s just how I do things,” when you have to explain it to others. The discipline of organizing your thoughts sharpens your clinical reasoning and keeps you honest about what you actually know.
Because sometimes it is simply about participating. Publishing, even small pieces, is a way of staying in touch with your field. It says, “I’m still here. I’m still paying attention.”
I think about how Dr. Frederic Mohs developed the technique that now bears his name while he was still a medical student.4 He could have said, “I already made it into medical school. That’s enough.” But he did not. I guess my point is not that we are all on the verge of inventing something revolutionary; it is that innovation happens only when curiosity keeps moving us forward. So no, I do not write to check boxes anymore. I write because it keeps me curious, and I have realized that curiosity is a habit I never want to outgrow.
Or maybe it’s because Jay keeps me up at night, and I have nothing better to do.
I was accepted into my fellowship almost 1 year ago: major milestones on my curriculum vitae are now met, fellowship application materials are complete, and the stress of the match is long gone. At the start of my fellowship, I had 2 priorities: (1) to learn as much as I could about dermatologic surgery and (2) to be the best dad possible to my newborn son, Jay. However, most nights I still find myself up late editing a manuscript draft or chasing down references, long after the “need” to publish has passed. Recently, my wife asked me why—what’s left to prove?
I’ll be the first to admit it: early on, publishing felt almost purely transactional. Each project was little more than a line on an application or a way to stand out or meet a new mentor. I have reflected before on how easily that mindset can slip into a kind of research arms race, in which productivity overshadows purpose.1 This time, I wanted to explore the other side of that equation: the “why” behind it all.
I have learned that writing forces me to slow down and actually think about what I am seeing every day. It turns routine work into something I must understand well enough to explain. Even a small write-up can make me notice details I would otherwise skim past in clinic or surgery. These days, most of my projects start small: a case that taught me something, an observation that made me pause and think. Those seemingly small questions are what eventually grow into bigger ones. The clinical trial I am designing now did not begin as a grand plan—it started because I could not stop thinking about how we manage pain and analgesia after Mohs surgery. That curiosity, shaped by the experience of writing those earlier “smaller” papers, evolved into a study that might actually help improve patient care one day. Still, most of what I write will not revolutionize the field. It is not cutting-edge science or paradigm-shifting data; it is mostly modest analyses with a few interesting conclusions or surgical pearls that might cut down on a patient’s procedural time or save a dermatologist somewhere a few sutures. But it still feels worth doing.
While rotating with Dr. Anna Bar at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, I noticed a poster hanging on the wall titled, “Top 10 Reasons Why Our Faculty Are Dedicated to Academics and Teaching,” based on the wisdom of Dr. Jane M. Grant-Kels.2 My favorite line on the poster reads, “Residents make us better by asking questions.” I think this philosophy is the main reason why I still write. Even though I am not a resident anymore, I am still asking questions. But if I had to sum up my “why” into a neat list, here is what it might look like:
Because asking questions keeps your brain wired for curiosity. Even small projects train us to remain curious, and this curiosity can mean the difference between just doing your job and continuing to evolve within it. As Dr. Rodolfo Neirotti reminds us, “Questions are useful tools—they open communication, improve understanding, and drive scientific research. In medicine, doing things without knowing why is risky.”3
Because the small stuff builds the culture. Dermatology is a small world. Even short case series, pearls, or “how we do it” pieces can shape how we practice. They may not change paradigms, but they can refine them. Over time, those small practical contributions become part of the field’s collective muscle memory.
Because it preserves perspective. Residency, fellowship, and early practice can blur together. A tiny project can become a timestamp of what you were learning or caring about at that specific moment. Years later, you may remember the case through the paper.
Because the act of writing is the point. Writing forces clarity. You cannot hide behind saying, “That’s just how I do things,” when you have to explain it to others. The discipline of organizing your thoughts sharpens your clinical reasoning and keeps you honest about what you actually know.
Because sometimes it is simply about participating. Publishing, even small pieces, is a way of staying in touch with your field. It says, “I’m still here. I’m still paying attention.”
I think about how Dr. Frederic Mohs developed the technique that now bears his name while he was still a medical student.4 He could have said, “I already made it into medical school. That’s enough.” But he did not. I guess my point is not that we are all on the verge of inventing something revolutionary; it is that innovation happens only when curiosity keeps moving us forward. So no, I do not write to check boxes anymore. I write because it keeps me curious, and I have realized that curiosity is a habit I never want to outgrow.
Or maybe it’s because Jay keeps me up at night, and I have nothing better to do.
- Jeha GM. A roadmap to research opportunities for dermatology residents. Cutis. 2024;114:E53-E56.
- Grant-Kels J. The gift that keeps on giving. UConn Health Dermatology. Accessed November 24, 2025. https://health.uconn.edu/dermatology/education/
- Neirotti RA. The importance of asking questions and doing things for a reason. Braz J Cardiovasc Surg. 2021;36:I-II.
- Trost LB, Bailin PL. History of Mohs surgery. Dermatol Clin. 2011;29:135-139, vii.
- Jeha GM. A roadmap to research opportunities for dermatology residents. Cutis. 2024;114:E53-E56.
- Grant-Kels J. The gift that keeps on giving. UConn Health Dermatology. Accessed November 24, 2025. https://health.uconn.edu/dermatology/education/
- Neirotti RA. The importance of asking questions and doing things for a reason. Braz J Cardiovasc Surg. 2021;36:I-II.
- Trost LB, Bailin PL. History of Mohs surgery. Dermatol Clin. 2011;29:135-139, vii.
The Habit of Curiosity: How Writing Shapes Clinical Thinking in Medical Training
The Habit of Curiosity: How Writing Shapes Clinical Thinking in Medical Training
Practice Points
- Writing about everyday clinical experiences forces trainees to slow down, think more carefully, and better understand why they do what they do. Being able to write clearly about a clinical scenario reflects true understanding.
- The act of writing sharpens clinical judgment by requiring clarity, honesty, and reflection rather than relying on habit or routine.
- Writing fosters habits of curiosity that support continued professional growth and ongoing engagement with one’s field beyond formal training milestones.
Progressive Dystrophy of the Fingernails and Toenails
Progressive Dystrophy of the Fingernails and Toenails
THE DIAGNOSIS: Nail Lichen Planus
The biopsy results showed features of hypergranulosis of the matricial epithelium, irregular acanthosis, apoptotic keratinocytes along the basal layer, and a lichenoid infiltrate consistent with nail lichen planus. The patient was started on topical clobetasol propionate 0.05% applied once daily under overnight occlusion. Additionally, intramatricial triamcinolone acetonide (2.5 mg/mL; 0.1 mL per injection) was administered into the affected nail matrix at 4-week intervals for a total of 2 sessions. At the 2-month follow-up visit, the patient reported improvement in longitudinal ridging; however, he subsequently was lost to follow-up.
Nail lichen planus is a chronic inflammatory disorder that occurs in 10% to 15% of patients with lichen planus worldwide and is more common in adults than children.1 It can manifest independently or concurrently with cutaneous and/or oral mucosal involvement. The fingernails are more commonly affected than the toenails.2 The clinical features of nail lichen planus can be classified based on involvement of the nail matrix (longitudinal ridging, red lunula, thinning of the nail plate, koilonychia, trachyonychia, pterygium, and anonychia) or nail bed (onycholysis, subungual hyperkeratosis, and splinter hemorrhages).1
In our patient, who presented with chronic progressive nail dystrophy affecting all 20 nails, onychomycosis, nail psoriasis, onychotillomania, and idiopathic trachyonychia were included in the differential.1
Onychomycosis manifests as white or yellow-brown discoloration of the nail, onycholysis, subungual hyperkeratosis, and thickening of the nail plate. Diagnosis is confirmed by the presence of septate hyphae (dermatophytes) or budding yeast cells (Candida species) on a potassium hydroxide mount. Other diagnostic modalities include dermoscopy, fungal culture, and histopathology of nail clippings, with demonstration of fungal elements identified on periodic acid-Schiff staining (eFigure 1).3
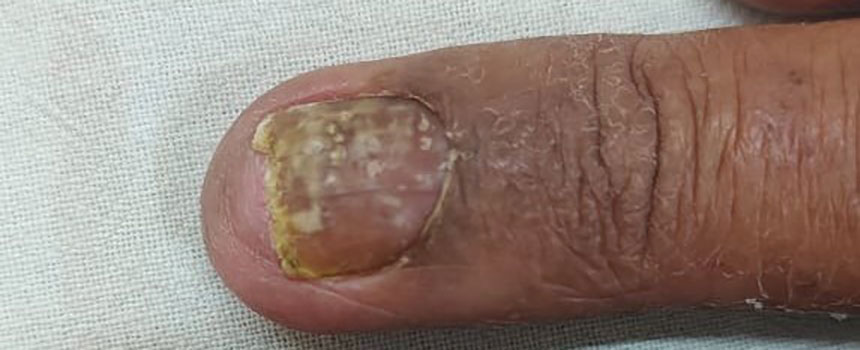
Nail psoriasis characteristically manifests as deep irregular pitting of the nails. Other features favoring psoriasis include involvement of the nail matrix manifesting as leukonychia, red lunula, and crumbling, as well as involvement of the nail bed manifesting as onycholysis, subungual hyperkeratosis, salmon patches/oil spots, and splinter hemorrhages (eFigure 2).4 Diagnosis primarily is clinical, supported by histopathology when uncertainty exists.
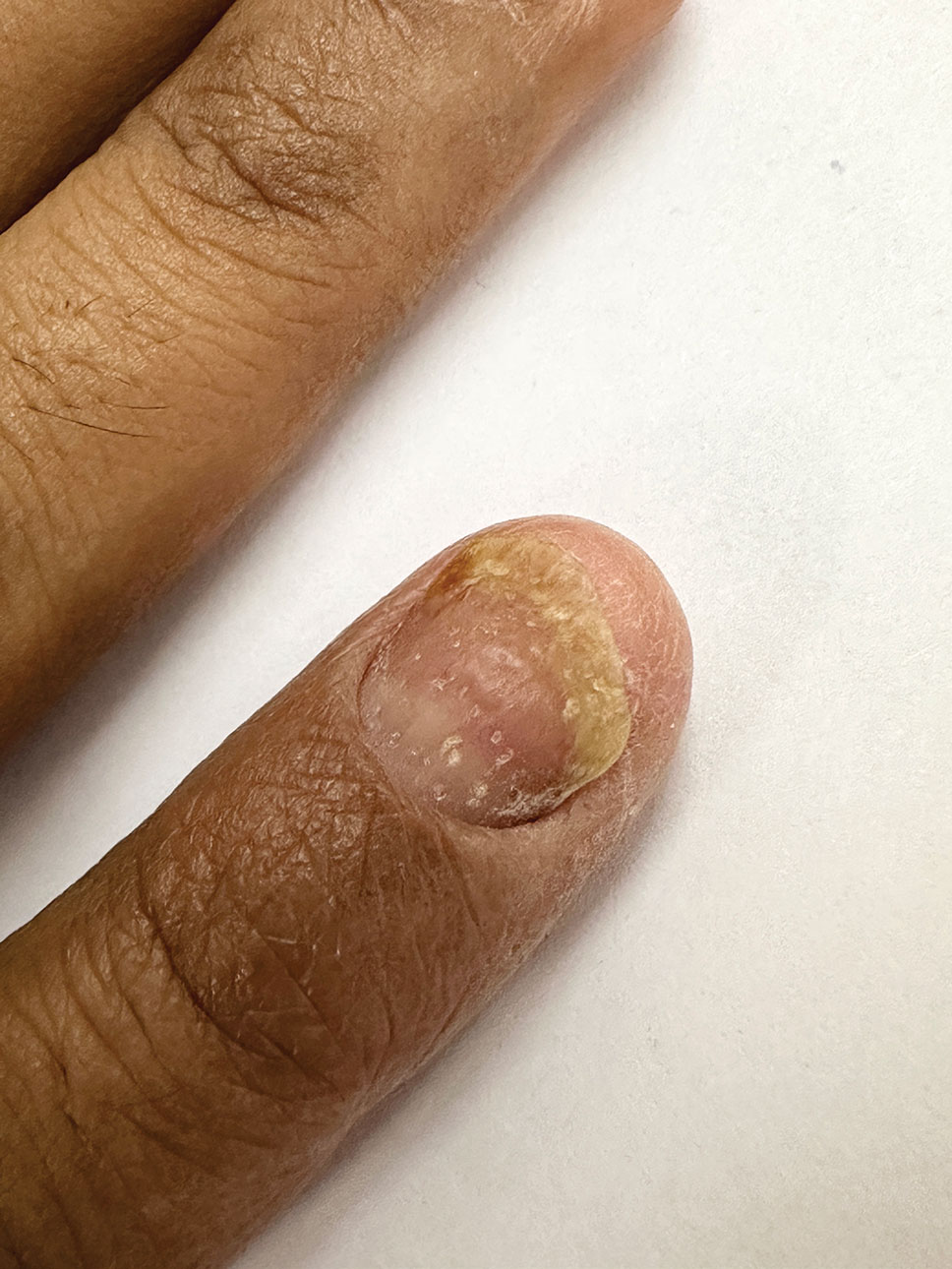
Onychotillomania is a behavioral disorder characterized by an irresistible urge or impulse in patients to either pick or pull at their fingernails and/or toenails. Clinicopathologic features of the involved nails are nonspecific and atypical, with possible involvement of periungual and digital skin. Diagnosis of onychotillomania is challenging.5 Dermoscopic features including anonychia with multiple obliquely arranged nail bed hemorrhages, gray pigmentation of the nail bed, and wavy lines, has been proposed to aid the diagnosis of onychotillomania.6
Idiopathic trachyonychia is isolated nail involvement characterized by rough, ridged, and thin nails affecting multiple or all of the fingernails and toenails without an underlying systemic or dermatologic condition (eFigure 3). The terms trachyonychia and 20-nail dystrophy have been used interchangeably in the literature; however, trachyonychia does not always involve all 20 nails. Other conditions causing widespread dystrophy of all 20 nails cannot be diagnosed as 20-nail dystrophy or trachyonychia without the distinct morphologic features of thin brittle nails with pronounced longitudinal ridging.7
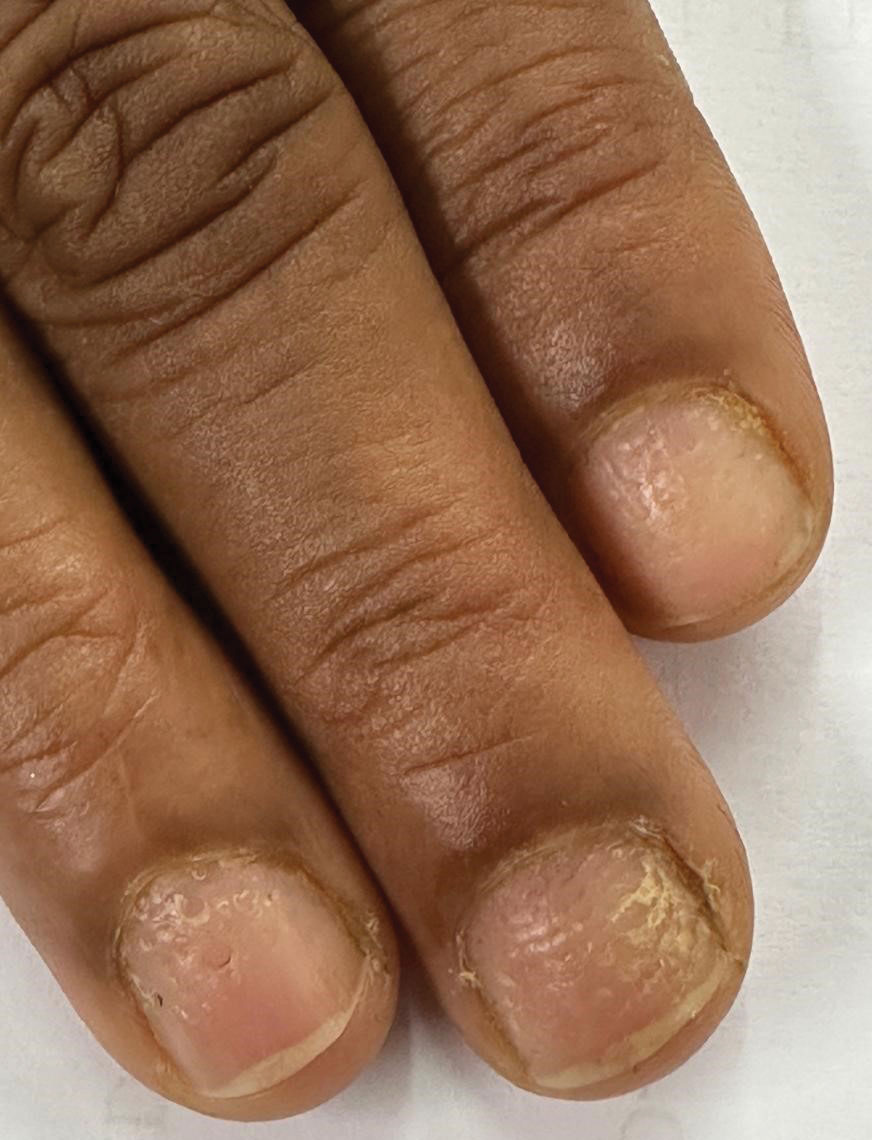
Prompt diagnosis and early intervention in nail lichen planus is crucial due to the potential for irreversible scarring. First-line treatment options include intramatricial and intramuscular triamcinolone acetonide for 3 to 6 months.4 Second-line therapies include oral retinoids such as acitretin and alitretinoin and immunosuppressive agents such as azathioprine, mycophenolate mofetil, and cyclosporine. Other reported treatment options include clobetasol propionate, tacrolimus, dapsone, griseofulvin, etanercept, hydroxychloroquine, methotrexate, and UV therapy.4
- Gupta MK, Lipner SR. Review of nail lichen planus: epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. Dermatol Clin. 2021;39:221-230. doi:10.1016/j.det.2020.12.002
- Iorizzo M, Tosti A, Starace M, et al. Isolated nail lichen planus: an expert consensus on treatment of the classical form. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1717-1723. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.02.056
- Leung AKC, Lam JM, Leong KF, et al. Onychomycosis: an updated review. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2020;14:32-45. doi:10.2174/1872213X13666191026090713
- Hwang JK, Grover C, Iorizzo M, et al. Nail psoriasis and nail lichen planus: updates on diagnosis and management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2024;90:585-596. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2023.11.024
- Sidiropoulou P, Sgouros D, Theodoropoulos K, et al. Onychotillomania: a chameleon-like disorder: case report and review of literature. Skin Appendage Disord. 2019;5:104-107. doi:10.1159/000489941
- Maddy AJ, Tosti A. Dermoscopic features of onychotillomania: a study of 36 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:702-705. doi:10.1016 /j.jaad.2018.04.015
- Haber JS, Chairatchaneeboon M, Rubin AI. Trachyonychia: review and update on clinical aspects, histology, and therapy. Skin Appendage Disord. 2017;2:109-115. doi:10.1159/000449063
THE DIAGNOSIS: Nail Lichen Planus
The biopsy results showed features of hypergranulosis of the matricial epithelium, irregular acanthosis, apoptotic keratinocytes along the basal layer, and a lichenoid infiltrate consistent with nail lichen planus. The patient was started on topical clobetasol propionate 0.05% applied once daily under overnight occlusion. Additionally, intramatricial triamcinolone acetonide (2.5 mg/mL; 0.1 mL per injection) was administered into the affected nail matrix at 4-week intervals for a total of 2 sessions. At the 2-month follow-up visit, the patient reported improvement in longitudinal ridging; however, he subsequently was lost to follow-up.
Nail lichen planus is a chronic inflammatory disorder that occurs in 10% to 15% of patients with lichen planus worldwide and is more common in adults than children.1 It can manifest independently or concurrently with cutaneous and/or oral mucosal involvement. The fingernails are more commonly affected than the toenails.2 The clinical features of nail lichen planus can be classified based on involvement of the nail matrix (longitudinal ridging, red lunula, thinning of the nail plate, koilonychia, trachyonychia, pterygium, and anonychia) or nail bed (onycholysis, subungual hyperkeratosis, and splinter hemorrhages).1
In our patient, who presented with chronic progressive nail dystrophy affecting all 20 nails, onychomycosis, nail psoriasis, onychotillomania, and idiopathic trachyonychia were included in the differential.1
Onychomycosis manifests as white or yellow-brown discoloration of the nail, onycholysis, subungual hyperkeratosis, and thickening of the nail plate. Diagnosis is confirmed by the presence of septate hyphae (dermatophytes) or budding yeast cells (Candida species) on a potassium hydroxide mount. Other diagnostic modalities include dermoscopy, fungal culture, and histopathology of nail clippings, with demonstration of fungal elements identified on periodic acid-Schiff staining (eFigure 1).3

Nail psoriasis characteristically manifests as deep irregular pitting of the nails. Other features favoring psoriasis include involvement of the nail matrix manifesting as leukonychia, red lunula, and crumbling, as well as involvement of the nail bed manifesting as onycholysis, subungual hyperkeratosis, salmon patches/oil spots, and splinter hemorrhages (eFigure 2).4 Diagnosis primarily is clinical, supported by histopathology when uncertainty exists.

Onychotillomania is a behavioral disorder characterized by an irresistible urge or impulse in patients to either pick or pull at their fingernails and/or toenails. Clinicopathologic features of the involved nails are nonspecific and atypical, with possible involvement of periungual and digital skin. Diagnosis of onychotillomania is challenging.5 Dermoscopic features including anonychia with multiple obliquely arranged nail bed hemorrhages, gray pigmentation of the nail bed, and wavy lines, has been proposed to aid the diagnosis of onychotillomania.6
Idiopathic trachyonychia is isolated nail involvement characterized by rough, ridged, and thin nails affecting multiple or all of the fingernails and toenails without an underlying systemic or dermatologic condition (eFigure 3). The terms trachyonychia and 20-nail dystrophy have been used interchangeably in the literature; however, trachyonychia does not always involve all 20 nails. Other conditions causing widespread dystrophy of all 20 nails cannot be diagnosed as 20-nail dystrophy or trachyonychia without the distinct morphologic features of thin brittle nails with pronounced longitudinal ridging.7

Prompt diagnosis and early intervention in nail lichen planus is crucial due to the potential for irreversible scarring. First-line treatment options include intramatricial and intramuscular triamcinolone acetonide for 3 to 6 months.4 Second-line therapies include oral retinoids such as acitretin and alitretinoin and immunosuppressive agents such as azathioprine, mycophenolate mofetil, and cyclosporine. Other reported treatment options include clobetasol propionate, tacrolimus, dapsone, griseofulvin, etanercept, hydroxychloroquine, methotrexate, and UV therapy.4
THE DIAGNOSIS: Nail Lichen Planus
The biopsy results showed features of hypergranulosis of the matricial epithelium, irregular acanthosis, apoptotic keratinocytes along the basal layer, and a lichenoid infiltrate consistent with nail lichen planus. The patient was started on topical clobetasol propionate 0.05% applied once daily under overnight occlusion. Additionally, intramatricial triamcinolone acetonide (2.5 mg/mL; 0.1 mL per injection) was administered into the affected nail matrix at 4-week intervals for a total of 2 sessions. At the 2-month follow-up visit, the patient reported improvement in longitudinal ridging; however, he subsequently was lost to follow-up.
Nail lichen planus is a chronic inflammatory disorder that occurs in 10% to 15% of patients with lichen planus worldwide and is more common in adults than children.1 It can manifest independently or concurrently with cutaneous and/or oral mucosal involvement. The fingernails are more commonly affected than the toenails.2 The clinical features of nail lichen planus can be classified based on involvement of the nail matrix (longitudinal ridging, red lunula, thinning of the nail plate, koilonychia, trachyonychia, pterygium, and anonychia) or nail bed (onycholysis, subungual hyperkeratosis, and splinter hemorrhages).1
In our patient, who presented with chronic progressive nail dystrophy affecting all 20 nails, onychomycosis, nail psoriasis, onychotillomania, and idiopathic trachyonychia were included in the differential.1
Onychomycosis manifests as white or yellow-brown discoloration of the nail, onycholysis, subungual hyperkeratosis, and thickening of the nail plate. Diagnosis is confirmed by the presence of septate hyphae (dermatophytes) or budding yeast cells (Candida species) on a potassium hydroxide mount. Other diagnostic modalities include dermoscopy, fungal culture, and histopathology of nail clippings, with demonstration of fungal elements identified on periodic acid-Schiff staining (eFigure 1).3

Nail psoriasis characteristically manifests as deep irregular pitting of the nails. Other features favoring psoriasis include involvement of the nail matrix manifesting as leukonychia, red lunula, and crumbling, as well as involvement of the nail bed manifesting as onycholysis, subungual hyperkeratosis, salmon patches/oil spots, and splinter hemorrhages (eFigure 2).4 Diagnosis primarily is clinical, supported by histopathology when uncertainty exists.

Onychotillomania is a behavioral disorder characterized by an irresistible urge or impulse in patients to either pick or pull at their fingernails and/or toenails. Clinicopathologic features of the involved nails are nonspecific and atypical, with possible involvement of periungual and digital skin. Diagnosis of onychotillomania is challenging.5 Dermoscopic features including anonychia with multiple obliquely arranged nail bed hemorrhages, gray pigmentation of the nail bed, and wavy lines, has been proposed to aid the diagnosis of onychotillomania.6
Idiopathic trachyonychia is isolated nail involvement characterized by rough, ridged, and thin nails affecting multiple or all of the fingernails and toenails without an underlying systemic or dermatologic condition (eFigure 3). The terms trachyonychia and 20-nail dystrophy have been used interchangeably in the literature; however, trachyonychia does not always involve all 20 nails. Other conditions causing widespread dystrophy of all 20 nails cannot be diagnosed as 20-nail dystrophy or trachyonychia without the distinct morphologic features of thin brittle nails with pronounced longitudinal ridging.7

Prompt diagnosis and early intervention in nail lichen planus is crucial due to the potential for irreversible scarring. First-line treatment options include intramatricial and intramuscular triamcinolone acetonide for 3 to 6 months.4 Second-line therapies include oral retinoids such as acitretin and alitretinoin and immunosuppressive agents such as azathioprine, mycophenolate mofetil, and cyclosporine. Other reported treatment options include clobetasol propionate, tacrolimus, dapsone, griseofulvin, etanercept, hydroxychloroquine, methotrexate, and UV therapy.4
- Gupta MK, Lipner SR. Review of nail lichen planus: epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. Dermatol Clin. 2021;39:221-230. doi:10.1016/j.det.2020.12.002
- Iorizzo M, Tosti A, Starace M, et al. Isolated nail lichen planus: an expert consensus on treatment of the classical form. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1717-1723. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.02.056
- Leung AKC, Lam JM, Leong KF, et al. Onychomycosis: an updated review. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2020;14:32-45. doi:10.2174/1872213X13666191026090713
- Hwang JK, Grover C, Iorizzo M, et al. Nail psoriasis and nail lichen planus: updates on diagnosis and management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2024;90:585-596. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2023.11.024
- Sidiropoulou P, Sgouros D, Theodoropoulos K, et al. Onychotillomania: a chameleon-like disorder: case report and review of literature. Skin Appendage Disord. 2019;5:104-107. doi:10.1159/000489941
- Maddy AJ, Tosti A. Dermoscopic features of onychotillomania: a study of 36 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:702-705. doi:10.1016 /j.jaad.2018.04.015
- Haber JS, Chairatchaneeboon M, Rubin AI. Trachyonychia: review and update on clinical aspects, histology, and therapy. Skin Appendage Disord. 2017;2:109-115. doi:10.1159/000449063
- Gupta MK, Lipner SR. Review of nail lichen planus: epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. Dermatol Clin. 2021;39:221-230. doi:10.1016/j.det.2020.12.002
- Iorizzo M, Tosti A, Starace M, et al. Isolated nail lichen planus: an expert consensus on treatment of the classical form. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1717-1723. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.02.056
- Leung AKC, Lam JM, Leong KF, et al. Onychomycosis: an updated review. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2020;14:32-45. doi:10.2174/1872213X13666191026090713
- Hwang JK, Grover C, Iorizzo M, et al. Nail psoriasis and nail lichen planus: updates on diagnosis and management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2024;90:585-596. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2023.11.024
- Sidiropoulou P, Sgouros D, Theodoropoulos K, et al. Onychotillomania: a chameleon-like disorder: case report and review of literature. Skin Appendage Disord. 2019;5:104-107. doi:10.1159/000489941
- Maddy AJ, Tosti A. Dermoscopic features of onychotillomania: a study of 36 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:702-705. doi:10.1016 /j.jaad.2018.04.015
- Haber JS, Chairatchaneeboon M, Rubin AI. Trachyonychia: review and update on clinical aspects, histology, and therapy. Skin Appendage Disord. 2017;2:109-115. doi:10.1159/000449063
Progressive Dystrophy of the Fingernails and Toenails
Progressive Dystrophy of the Fingernails and Toenails
A 35-year-old man presented to the dermatology department with gradually progressive dystrophy of the fingernails and toenails of 20 years’ duration. The patient reported no history of other dermatologic conditions. Physical examination revealed longitudinal ridging of all 20 nails and discoloration of the nail plates, as well as a few nails showing pterygium and anonychia; the skin and mucosal surfaces were otherwise normal, and nail plate thinning was not observed. A potassium hydroxide mount was negative. A biopsy of the nail matrix on the left thumbnail was performed.
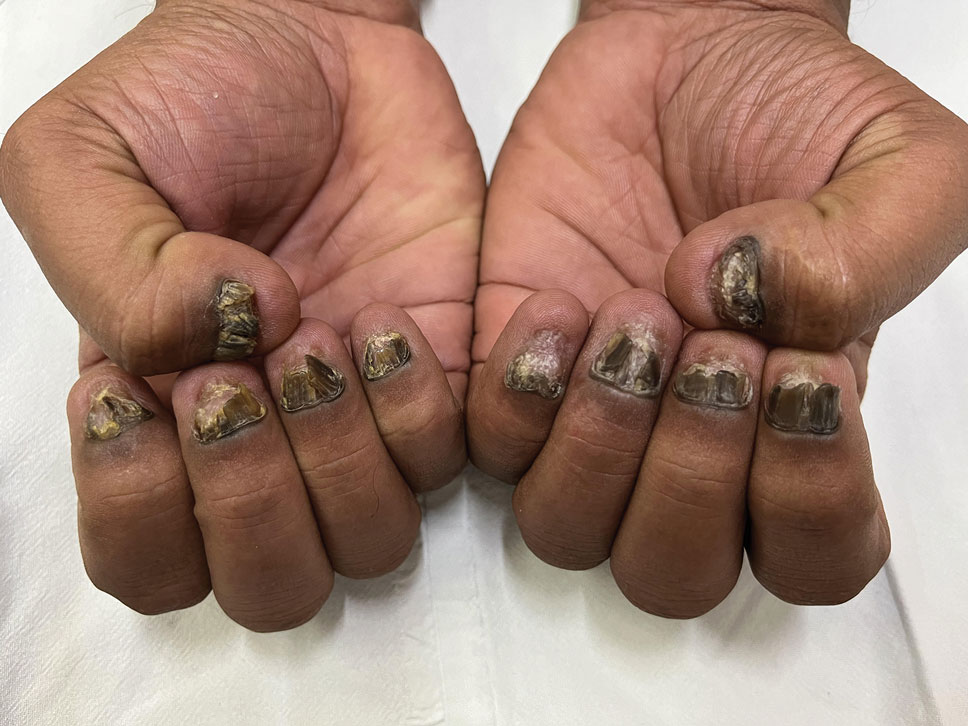
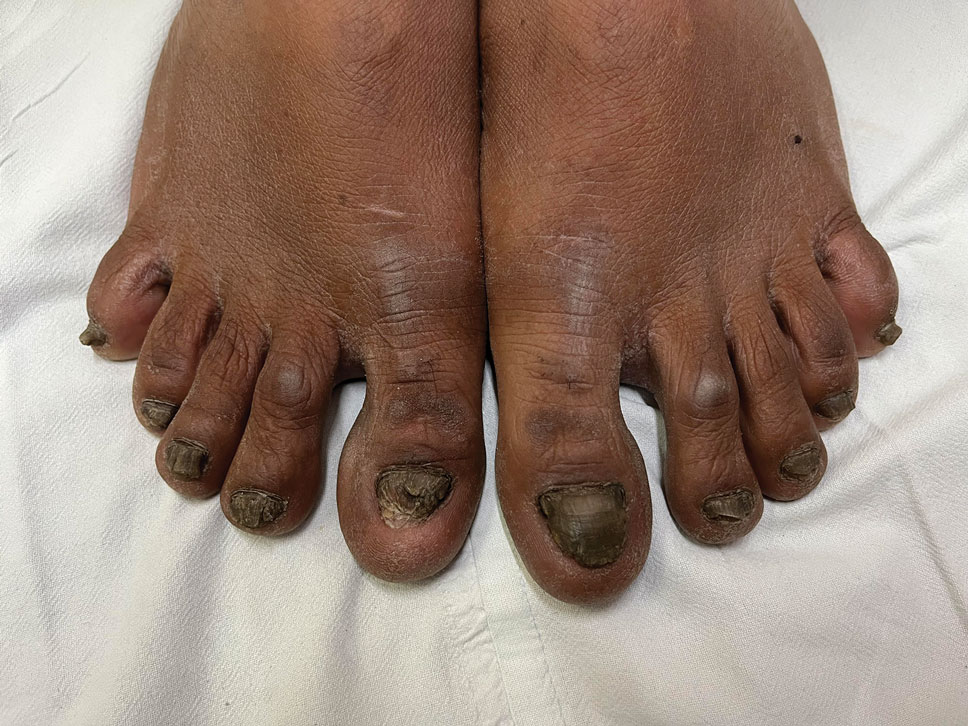
The Road Less Traveled: Why Rural Dermatology Could Be Your Path After Residency
The Road Less Traveled: Why Rural Dermatology Could Be Your Path After Residency
The myths persist: You will lack colleagues. Your practice will be thin. You must sacrifice academic engagement. In reality, rural practice offers variety, leadership opportunities, and the chance to influence the health of entire communities in profound ways. In this article, we aim to unpack what rural dermatology actually looks like as a potential career path for residents, with a focus on private-academic hybrid and hospital-based practice models.
Definitions of the term rural vary. For the US Census Bureau, it is synonymous with nonurban, and for the Office of Management and Budget, the term nonmetropolitan is preferred. The US Department of Agriculture’s Rural-Urban Commuting Area codes recognize a continuum of classifications from micropolitan to remote. In practice, the term rural covers a wide spectrum: the rolling farmlands of the Midwest, the mountains of Montana, the bayous of the South, the Native American reservations in New Mexico, and everything in between. It is not one uniform reality—rural America is diverse, resilient, and deeply connected.
Daily clinic flow may look familiar: a full schedule, a mix of new and established patients, and frequent simple procedures such as biopsies and corticosteroid injections. But the scope of practice is wider. You become the dermatologist for hundreds of miles in every direction, managing most conditions locally while referring select cases to subspecialty centers.
Case variety is striking. Neglected tumors, unusual inflammatory presentations, pediatric conditions, and occupational dermatoses/injuries appear alongside the routine. Each day requires flexibility, judgment, confidence, and the ability to think outside the box. You must consider how a patient’s seasonal work, such as ranching or farming, and/or their total commute time impacts the risk-benefit discussion around treatment recommendations.
Matthew P. Shaffer, MD (Salina, Kansas), who has practiced rural dermatology for more than 20 years, explained that the breadth of dermatologic cases in which he served as the expert was both exciting and intimidating, but it became clear that this was the right professional path for him (email communication, September 5, 2025). In small communities, your role extends beyond the clinic walls. You will see patients at the grocery store, the library, and school events. That continuity fosters loyalty and accountability in ways that are hard to quantify.
Many practice structures exist: independent clinics, multispecialty groups, hospital employment, and increasingly, hybrid partnerships with academic centers.
Academic institutions have recognized the importance of rural exposure, and many now collaborate with rural dermatologists. For example, Heartland Dermatology in Salina, Kansas, where 2 of the authors (B.R.L. and T.G.) practice, partners with St. Louis University in Missouri to provide a residency track and rotations in rural clinics.
Rural-based hospital systems can create similar structures. Monument Health Dermatology in Spearfish, South Dakota, is integrated into the fabric of the community’s larger rural health care model. The physician (M.E.L.) collaborates daily with primary care providers, surgeons, and oncologists through a shared electronic health record (sometimes even through telephone speed-dial given the close collegiality of small-town providers). Patients come from across 4 states, some driving 6 hours each way. Patients who once doubted whether dermatology was worth the trip will consistently return for follow-up care once trust is earned. The stability of hospital employment supports volunteer faculty positions and a free satellite clinic in partnership with a local Lakota Tribal health center. There is never a dull day: the providers see urgent add-ons daily, which keeps them on their toes but in exchange brings immense reward. This includes a recent case from rural Wyoming: a complex mixed infantile hemangioma on the mid face just entering the rapid proliferation phase. Propranolol was started immediately, as opposed to months later when it was too late—a common complication for the majority of rural patients by the time to get to a dermatologist.
Complex cases can overwhelm rural practices, and this is when the hub-and-spoke model is invaluable. Dermatologists embed in local communities as spokes, while subspecialty services such as pediatric dermatology, dermatopathology, or Mohs micrographic surgery remain centralized at hubs. The hubs can be but do not have to be academic institutions; for Heartland Dermatology in Kansas, private practices fulfill both hub and spoke roles. With that said, 10 states do not have academic dermatology programs.1 Mohs surgeons and pediatric dermatologists still can establish robust and successful independent rural subspecialty practices outside academic hubs. Christopher Gasbarre, DO (Spearfish, South Dakota), a board-certified, fellowship-trained Mohs surgeon in rural practice, advises residents to be confident in their abilities and to trust their training, noting that they often will be asked to manage complicated cases because of patient travel and cost constraints; however, clinicians should recognize their own limitations and those of nearby specialists and develop a referral network for cases that require multidisciplinary care (text communication, September 14, 2025).
The hub-and-spoke models—whether they entail an academic center as the hub with private practices as the spokes, or a network of private practices that include rural subspecialists—allows rural dermatologists to remain trusted local experts while ensuring that patients can access advanced care via a more streamlined referral process/network. The challenge is triage: what can be managed locally and what must patients travel for? As Dr. Shaffer explained, decisions about whether care is managed locally or referred to a hub often depend on the experience and comfort level of both the physician and the patient (email communication, September 5, 2025). Ultimately, continuity and trust are central. Patients rely on their local dermatologist to guide these decisions, and that guidance makes the model effective.
The idea that rural practice means being stuck in a small solo clinic is outdated. Multiple pathways exist, each with strengths and challenges. Independent private practice offers maximum autonomy and deep community integration, though financial and staffing risks are yours to manage. Hospital employment with outreach clinics provides stability, benefits, and collegiality, but bureaucracy can limit innovation and efficiency. Private equity platforms supply resources and rapid growth, but alignment with mission and autonomy must be weighed carefully. Hybrid joint ventures with hospitals combine private control and institutional support, but contracts can be complex. Locum tenens–to-permanent arrangements let you try rural life with minimal commitment, but continuity with patients may be sacrificed. A self-screener can clarify your path: How much autonomy do I want? Do I prefer predictability or variety? How important are procedures, teaching, or community roles? Answer these questions honestly and pair that insight with mentor guidance.
Launching a rural dermatology clinic is equal parts vision and structure. A focused 90-day plan can make the difference between a smooth opening and early frustration. Think in 4 domains: site selection, employment and licensing, credentialing and contracting, and operations. Even in a compressed timeline, dozens of small but crucial tasks may surface. There are resources—such as the Medical Group Management Association’s practice start-up checklist—that can provide a roadmap, ensuring no detail is overlooked as you transform a vision into a functioning clinic.2
Site Selection—First, determine whether you are opening a new standalone clinic, extending an existing practice, or creating a part-time satellite. Referral mapping with local primary care providers is essential, as is a scan of payer mix and dermatologist density in the region to ensure sustainability.
Employment and Licensing—Confirm state licensure and Drug Enforcement Administration registration and initiate hospital privileges early. These processes can stretch across the entire 90-day window, so starting immediately is critical.
Credentialing and Contracting—Applications with commercial and federal payers, along with Council for Affordable Quality Healthcare updates, often consume weeks if not months. If you plan to perform office microscopy or establish a dermatopathology laboratory, begin the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments certification process in parallel.
Operations—Once the regulatory wheels are in motion, shift to building your practice infrastructure. Secure space, weigh lease vs purchase, and consider partnerships with local hospitals for shared clinic facilities. Recruit staff with dermatology-specific skills such as clinical photography and biopsy assistance. Implement an electronic health record, set up payroll and malpractice insurance, and establish supply chains for everything from liquid nitrogen to surgical trays. Decide whether revenue cycle management will be in-house or outsourced and finalize dermatopathology workflows including courier and transport agreements.
Compensation in rural dermatology mirrors that of other clinical settings: base salary with productivity bonuses, revenue pooling, or relative value unit structures. Financial planning is crucial. Develop a pro forma that models patient volume, expenses, and realistic growth. Risks exist, including payer mix, staffing, and competition, but the demand for care in underserved areas often offsets these, and communities may support practices with reduced overhead and strong loyalty. Hospital systems may add stipends for supervising advanced practitioners or outreach travel. Loan repayment programs, tax credits, and grants can further enhance packages. Consider checking with the state’s Office of Rural Health.
Career sustainability ultimately depends on more than finances. Geography, amenities, schedule flexibility, autonomy in medical decision-making, work-life balance, the value of being part of and serving a community, and other personal values will shape your “best-fit” practice model. Ask whether you can envision yourself thriving in the community you would be serving.
No one builds a rural dermatology practice alone. That is why one of the authors (M.E.L.) created the Rural Access to Dermatology Society (https://www.radsociety.org/), a nonprofit organization connecting dermatologists, residents, and medical students with a shared mission. The organization supports residents through scholarships, mentorship, and telementoring. Faculty can contribute through advocacy, residency track development, and outreach to uniquely underserved rural populations such as Native American reservations where access to dermatology care remains severely limited. Joining can be as simple as attending a webinar, finding a mentor, or volunteering at a free clinic. You do not need to launch your own clinic to get involved; you can begin by connecting with a network already laying the foundation.
Teledermatology and academic initiatives enhance rural care but do not replace in-person practice. Store-and-forward consultations extend reach but cannot match the continuity and trust of long-term patient relationships. Academic rural tracks prepare residents for unique challenges, but someone must staff the clinics. Private and hybrid models remain the backbone of rural access, where dermatologists take on the responsibility and the joy of being the local expert.
So here’s the invitation: bring one question to your mentor about rural practice and identify one rural site you could visit. The road less traveled in dermatology is closer than you think—and it might just be your path.
- Association of American Medical Colleges. ERAS Directory: Dermatology. Accessed December 11, 2025. https://systems.aamc.org/eras/erasstats/par/display.cfm?NAV_ROW=PAR&SPEC_CD=080
- Medical Group Management Association. Large group or organization practice startup checklist. Accessed December 11, 2025. https://www.mgma.com/member-tools/large-group-or-organization -practice-startup-checklist
The myths persist: You will lack colleagues. Your practice will be thin. You must sacrifice academic engagement. In reality, rural practice offers variety, leadership opportunities, and the chance to influence the health of entire communities in profound ways. In this article, we aim to unpack what rural dermatology actually looks like as a potential career path for residents, with a focus on private-academic hybrid and hospital-based practice models.
Definitions of the term rural vary. For the US Census Bureau, it is synonymous with nonurban, and for the Office of Management and Budget, the term nonmetropolitan is preferred. The US Department of Agriculture’s Rural-Urban Commuting Area codes recognize a continuum of classifications from micropolitan to remote. In practice, the term rural covers a wide spectrum: the rolling farmlands of the Midwest, the mountains of Montana, the bayous of the South, the Native American reservations in New Mexico, and everything in between. It is not one uniform reality—rural America is diverse, resilient, and deeply connected.
Daily clinic flow may look familiar: a full schedule, a mix of new and established patients, and frequent simple procedures such as biopsies and corticosteroid injections. But the scope of practice is wider. You become the dermatologist for hundreds of miles in every direction, managing most conditions locally while referring select cases to subspecialty centers.
Case variety is striking. Neglected tumors, unusual inflammatory presentations, pediatric conditions, and occupational dermatoses/injuries appear alongside the routine. Each day requires flexibility, judgment, confidence, and the ability to think outside the box. You must consider how a patient’s seasonal work, such as ranching or farming, and/or their total commute time impacts the risk-benefit discussion around treatment recommendations.
Matthew P. Shaffer, MD (Salina, Kansas), who has practiced rural dermatology for more than 20 years, explained that the breadth of dermatologic cases in which he served as the expert was both exciting and intimidating, but it became clear that this was the right professional path for him (email communication, September 5, 2025). In small communities, your role extends beyond the clinic walls. You will see patients at the grocery store, the library, and school events. That continuity fosters loyalty and accountability in ways that are hard to quantify.
Many practice structures exist: independent clinics, multispecialty groups, hospital employment, and increasingly, hybrid partnerships with academic centers.
Academic institutions have recognized the importance of rural exposure, and many now collaborate with rural dermatologists. For example, Heartland Dermatology in Salina, Kansas, where 2 of the authors (B.R.L. and T.G.) practice, partners with St. Louis University in Missouri to provide a residency track and rotations in rural clinics.
Rural-based hospital systems can create similar structures. Monument Health Dermatology in Spearfish, South Dakota, is integrated into the fabric of the community’s larger rural health care model. The physician (M.E.L.) collaborates daily with primary care providers, surgeons, and oncologists through a shared electronic health record (sometimes even through telephone speed-dial given the close collegiality of small-town providers). Patients come from across 4 states, some driving 6 hours each way. Patients who once doubted whether dermatology was worth the trip will consistently return for follow-up care once trust is earned. The stability of hospital employment supports volunteer faculty positions and a free satellite clinic in partnership with a local Lakota Tribal health center. There is never a dull day: the providers see urgent add-ons daily, which keeps them on their toes but in exchange brings immense reward. This includes a recent case from rural Wyoming: a complex mixed infantile hemangioma on the mid face just entering the rapid proliferation phase. Propranolol was started immediately, as opposed to months later when it was too late—a common complication for the majority of rural patients by the time to get to a dermatologist.
Complex cases can overwhelm rural practices, and this is when the hub-and-spoke model is invaluable. Dermatologists embed in local communities as spokes, while subspecialty services such as pediatric dermatology, dermatopathology, or Mohs micrographic surgery remain centralized at hubs. The hubs can be but do not have to be academic institutions; for Heartland Dermatology in Kansas, private practices fulfill both hub and spoke roles. With that said, 10 states do not have academic dermatology programs.1 Mohs surgeons and pediatric dermatologists still can establish robust and successful independent rural subspecialty practices outside academic hubs. Christopher Gasbarre, DO (Spearfish, South Dakota), a board-certified, fellowship-trained Mohs surgeon in rural practice, advises residents to be confident in their abilities and to trust their training, noting that they often will be asked to manage complicated cases because of patient travel and cost constraints; however, clinicians should recognize their own limitations and those of nearby specialists and develop a referral network for cases that require multidisciplinary care (text communication, September 14, 2025).
The hub-and-spoke models—whether they entail an academic center as the hub with private practices as the spokes, or a network of private practices that include rural subspecialists—allows rural dermatologists to remain trusted local experts while ensuring that patients can access advanced care via a more streamlined referral process/network. The challenge is triage: what can be managed locally and what must patients travel for? As Dr. Shaffer explained, decisions about whether care is managed locally or referred to a hub often depend on the experience and comfort level of both the physician and the patient (email communication, September 5, 2025). Ultimately, continuity and trust are central. Patients rely on their local dermatologist to guide these decisions, and that guidance makes the model effective.
The idea that rural practice means being stuck in a small solo clinic is outdated. Multiple pathways exist, each with strengths and challenges. Independent private practice offers maximum autonomy and deep community integration, though financial and staffing risks are yours to manage. Hospital employment with outreach clinics provides stability, benefits, and collegiality, but bureaucracy can limit innovation and efficiency. Private equity platforms supply resources and rapid growth, but alignment with mission and autonomy must be weighed carefully. Hybrid joint ventures with hospitals combine private control and institutional support, but contracts can be complex. Locum tenens–to-permanent arrangements let you try rural life with minimal commitment, but continuity with patients may be sacrificed. A self-screener can clarify your path: How much autonomy do I want? Do I prefer predictability or variety? How important are procedures, teaching, or community roles? Answer these questions honestly and pair that insight with mentor guidance.
Launching a rural dermatology clinic is equal parts vision and structure. A focused 90-day plan can make the difference between a smooth opening and early frustration. Think in 4 domains: site selection, employment and licensing, credentialing and contracting, and operations. Even in a compressed timeline, dozens of small but crucial tasks may surface. There are resources—such as the Medical Group Management Association’s practice start-up checklist—that can provide a roadmap, ensuring no detail is overlooked as you transform a vision into a functioning clinic.2
Site Selection—First, determine whether you are opening a new standalone clinic, extending an existing practice, or creating a part-time satellite. Referral mapping with local primary care providers is essential, as is a scan of payer mix and dermatologist density in the region to ensure sustainability.
Employment and Licensing—Confirm state licensure and Drug Enforcement Administration registration and initiate hospital privileges early. These processes can stretch across the entire 90-day window, so starting immediately is critical.
Credentialing and Contracting—Applications with commercial and federal payers, along with Council for Affordable Quality Healthcare updates, often consume weeks if not months. If you plan to perform office microscopy or establish a dermatopathology laboratory, begin the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments certification process in parallel.
Operations—Once the regulatory wheels are in motion, shift to building your practice infrastructure. Secure space, weigh lease vs purchase, and consider partnerships with local hospitals for shared clinic facilities. Recruit staff with dermatology-specific skills such as clinical photography and biopsy assistance. Implement an electronic health record, set up payroll and malpractice insurance, and establish supply chains for everything from liquid nitrogen to surgical trays. Decide whether revenue cycle management will be in-house or outsourced and finalize dermatopathology workflows including courier and transport agreements.
Compensation in rural dermatology mirrors that of other clinical settings: base salary with productivity bonuses, revenue pooling, or relative value unit structures. Financial planning is crucial. Develop a pro forma that models patient volume, expenses, and realistic growth. Risks exist, including payer mix, staffing, and competition, but the demand for care in underserved areas often offsets these, and communities may support practices with reduced overhead and strong loyalty. Hospital systems may add stipends for supervising advanced practitioners or outreach travel. Loan repayment programs, tax credits, and grants can further enhance packages. Consider checking with the state’s Office of Rural Health.
Career sustainability ultimately depends on more than finances. Geography, amenities, schedule flexibility, autonomy in medical decision-making, work-life balance, the value of being part of and serving a community, and other personal values will shape your “best-fit” practice model. Ask whether you can envision yourself thriving in the community you would be serving.
No one builds a rural dermatology practice alone. That is why one of the authors (M.E.L.) created the Rural Access to Dermatology Society (https://www.radsociety.org/), a nonprofit organization connecting dermatologists, residents, and medical students with a shared mission. The organization supports residents through scholarships, mentorship, and telementoring. Faculty can contribute through advocacy, residency track development, and outreach to uniquely underserved rural populations such as Native American reservations where access to dermatology care remains severely limited. Joining can be as simple as attending a webinar, finding a mentor, or volunteering at a free clinic. You do not need to launch your own clinic to get involved; you can begin by connecting with a network already laying the foundation.
Teledermatology and academic initiatives enhance rural care but do not replace in-person practice. Store-and-forward consultations extend reach but cannot match the continuity and trust of long-term patient relationships. Academic rural tracks prepare residents for unique challenges, but someone must staff the clinics. Private and hybrid models remain the backbone of rural access, where dermatologists take on the responsibility and the joy of being the local expert.
So here’s the invitation: bring one question to your mentor about rural practice and identify one rural site you could visit. The road less traveled in dermatology is closer than you think—and it might just be your path.
The myths persist: You will lack colleagues. Your practice will be thin. You must sacrifice academic engagement. In reality, rural practice offers variety, leadership opportunities, and the chance to influence the health of entire communities in profound ways. In this article, we aim to unpack what rural dermatology actually looks like as a potential career path for residents, with a focus on private-academic hybrid and hospital-based practice models.
Definitions of the term rural vary. For the US Census Bureau, it is synonymous with nonurban, and for the Office of Management and Budget, the term nonmetropolitan is preferred. The US Department of Agriculture’s Rural-Urban Commuting Area codes recognize a continuum of classifications from micropolitan to remote. In practice, the term rural covers a wide spectrum: the rolling farmlands of the Midwest, the mountains of Montana, the bayous of the South, the Native American reservations in New Mexico, and everything in between. It is not one uniform reality—rural America is diverse, resilient, and deeply connected.
Daily clinic flow may look familiar: a full schedule, a mix of new and established patients, and frequent simple procedures such as biopsies and corticosteroid injections. But the scope of practice is wider. You become the dermatologist for hundreds of miles in every direction, managing most conditions locally while referring select cases to subspecialty centers.
Case variety is striking. Neglected tumors, unusual inflammatory presentations, pediatric conditions, and occupational dermatoses/injuries appear alongside the routine. Each day requires flexibility, judgment, confidence, and the ability to think outside the box. You must consider how a patient’s seasonal work, such as ranching or farming, and/or their total commute time impacts the risk-benefit discussion around treatment recommendations.
Matthew P. Shaffer, MD (Salina, Kansas), who has practiced rural dermatology for more than 20 years, explained that the breadth of dermatologic cases in which he served as the expert was both exciting and intimidating, but it became clear that this was the right professional path for him (email communication, September 5, 2025). In small communities, your role extends beyond the clinic walls. You will see patients at the grocery store, the library, and school events. That continuity fosters loyalty and accountability in ways that are hard to quantify.
Many practice structures exist: independent clinics, multispecialty groups, hospital employment, and increasingly, hybrid partnerships with academic centers.
Academic institutions have recognized the importance of rural exposure, and many now collaborate with rural dermatologists. For example, Heartland Dermatology in Salina, Kansas, where 2 of the authors (B.R.L. and T.G.) practice, partners with St. Louis University in Missouri to provide a residency track and rotations in rural clinics.
Rural-based hospital systems can create similar structures. Monument Health Dermatology in Spearfish, South Dakota, is integrated into the fabric of the community’s larger rural health care model. The physician (M.E.L.) collaborates daily with primary care providers, surgeons, and oncologists through a shared electronic health record (sometimes even through telephone speed-dial given the close collegiality of small-town providers). Patients come from across 4 states, some driving 6 hours each way. Patients who once doubted whether dermatology was worth the trip will consistently return for follow-up care once trust is earned. The stability of hospital employment supports volunteer faculty positions and a free satellite clinic in partnership with a local Lakota Tribal health center. There is never a dull day: the providers see urgent add-ons daily, which keeps them on their toes but in exchange brings immense reward. This includes a recent case from rural Wyoming: a complex mixed infantile hemangioma on the mid face just entering the rapid proliferation phase. Propranolol was started immediately, as opposed to months later when it was too late—a common complication for the majority of rural patients by the time to get to a dermatologist.
Complex cases can overwhelm rural practices, and this is when the hub-and-spoke model is invaluable. Dermatologists embed in local communities as spokes, while subspecialty services such as pediatric dermatology, dermatopathology, or Mohs micrographic surgery remain centralized at hubs. The hubs can be but do not have to be academic institutions; for Heartland Dermatology in Kansas, private practices fulfill both hub and spoke roles. With that said, 10 states do not have academic dermatology programs.1 Mohs surgeons and pediatric dermatologists still can establish robust and successful independent rural subspecialty practices outside academic hubs. Christopher Gasbarre, DO (Spearfish, South Dakota), a board-certified, fellowship-trained Mohs surgeon in rural practice, advises residents to be confident in their abilities and to trust their training, noting that they often will be asked to manage complicated cases because of patient travel and cost constraints; however, clinicians should recognize their own limitations and those of nearby specialists and develop a referral network for cases that require multidisciplinary care (text communication, September 14, 2025).
The hub-and-spoke models—whether they entail an academic center as the hub with private practices as the spokes, or a network of private practices that include rural subspecialists—allows rural dermatologists to remain trusted local experts while ensuring that patients can access advanced care via a more streamlined referral process/network. The challenge is triage: what can be managed locally and what must patients travel for? As Dr. Shaffer explained, decisions about whether care is managed locally or referred to a hub often depend on the experience and comfort level of both the physician and the patient (email communication, September 5, 2025). Ultimately, continuity and trust are central. Patients rely on their local dermatologist to guide these decisions, and that guidance makes the model effective.
The idea that rural practice means being stuck in a small solo clinic is outdated. Multiple pathways exist, each with strengths and challenges. Independent private practice offers maximum autonomy and deep community integration, though financial and staffing risks are yours to manage. Hospital employment with outreach clinics provides stability, benefits, and collegiality, but bureaucracy can limit innovation and efficiency. Private equity platforms supply resources and rapid growth, but alignment with mission and autonomy must be weighed carefully. Hybrid joint ventures with hospitals combine private control and institutional support, but contracts can be complex. Locum tenens–to-permanent arrangements let you try rural life with minimal commitment, but continuity with patients may be sacrificed. A self-screener can clarify your path: How much autonomy do I want? Do I prefer predictability or variety? How important are procedures, teaching, or community roles? Answer these questions honestly and pair that insight with mentor guidance.
Launching a rural dermatology clinic is equal parts vision and structure. A focused 90-day plan can make the difference between a smooth opening and early frustration. Think in 4 domains: site selection, employment and licensing, credentialing and contracting, and operations. Even in a compressed timeline, dozens of small but crucial tasks may surface. There are resources—such as the Medical Group Management Association’s practice start-up checklist—that can provide a roadmap, ensuring no detail is overlooked as you transform a vision into a functioning clinic.2
Site Selection—First, determine whether you are opening a new standalone clinic, extending an existing practice, or creating a part-time satellite. Referral mapping with local primary care providers is essential, as is a scan of payer mix and dermatologist density in the region to ensure sustainability.
Employment and Licensing—Confirm state licensure and Drug Enforcement Administration registration and initiate hospital privileges early. These processes can stretch across the entire 90-day window, so starting immediately is critical.
Credentialing and Contracting—Applications with commercial and federal payers, along with Council for Affordable Quality Healthcare updates, often consume weeks if not months. If you plan to perform office microscopy or establish a dermatopathology laboratory, begin the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments certification process in parallel.
Operations—Once the regulatory wheels are in motion, shift to building your practice infrastructure. Secure space, weigh lease vs purchase, and consider partnerships with local hospitals for shared clinic facilities. Recruit staff with dermatology-specific skills such as clinical photography and biopsy assistance. Implement an electronic health record, set up payroll and malpractice insurance, and establish supply chains for everything from liquid nitrogen to surgical trays. Decide whether revenue cycle management will be in-house or outsourced and finalize dermatopathology workflows including courier and transport agreements.
Compensation in rural dermatology mirrors that of other clinical settings: base salary with productivity bonuses, revenue pooling, or relative value unit structures. Financial planning is crucial. Develop a pro forma that models patient volume, expenses, and realistic growth. Risks exist, including payer mix, staffing, and competition, but the demand for care in underserved areas often offsets these, and communities may support practices with reduced overhead and strong loyalty. Hospital systems may add stipends for supervising advanced practitioners or outreach travel. Loan repayment programs, tax credits, and grants can further enhance packages. Consider checking with the state’s Office of Rural Health.
Career sustainability ultimately depends on more than finances. Geography, amenities, schedule flexibility, autonomy in medical decision-making, work-life balance, the value of being part of and serving a community, and other personal values will shape your “best-fit” practice model. Ask whether you can envision yourself thriving in the community you would be serving.
No one builds a rural dermatology practice alone. That is why one of the authors (M.E.L.) created the Rural Access to Dermatology Society (https://www.radsociety.org/), a nonprofit organization connecting dermatologists, residents, and medical students with a shared mission. The organization supports residents through scholarships, mentorship, and telementoring. Faculty can contribute through advocacy, residency track development, and outreach to uniquely underserved rural populations such as Native American reservations where access to dermatology care remains severely limited. Joining can be as simple as attending a webinar, finding a mentor, or volunteering at a free clinic. You do not need to launch your own clinic to get involved; you can begin by connecting with a network already laying the foundation.
Teledermatology and academic initiatives enhance rural care but do not replace in-person practice. Store-and-forward consultations extend reach but cannot match the continuity and trust of long-term patient relationships. Academic rural tracks prepare residents for unique challenges, but someone must staff the clinics. Private and hybrid models remain the backbone of rural access, where dermatologists take on the responsibility and the joy of being the local expert.
So here’s the invitation: bring one question to your mentor about rural practice and identify one rural site you could visit. The road less traveled in dermatology is closer than you think—and it might just be your path.
- Association of American Medical Colleges. ERAS Directory: Dermatology. Accessed December 11, 2025. https://systems.aamc.org/eras/erasstats/par/display.cfm?NAV_ROW=PAR&SPEC_CD=080
- Medical Group Management Association. Large group or organization practice startup checklist. Accessed December 11, 2025. https://www.mgma.com/member-tools/large-group-or-organization -practice-startup-checklist
- Association of American Medical Colleges. ERAS Directory: Dermatology. Accessed December 11, 2025. https://systems.aamc.org/eras/erasstats/par/display.cfm?NAV_ROW=PAR&SPEC_CD=080
- Medical Group Management Association. Large group or organization practice startup checklist. Accessed December 11, 2025. https://www.mgma.com/member-tools/large-group-or-organization -practice-startup-checklist
The Road Less Traveled: Why Rural Dermatology Could Be Your Path After Residency
The Road Less Traveled: Why Rural Dermatology Could Be Your Path After Residency
Cobblestonelike Papules on the Neck
The Diagnosis: Fibroelastolytic Papulosis
Histopathology demonstrated decreased density and fragmentation of elastic fibers in the superficial reticular and papillary dermis consistent with an elastolytic disease process (Figure). Of note, elastolysis typically is visualized with Verhoeff-van Gieson stain but cannot be visualized well with standard hematoxylin and eosin staining. Additional staining with Congo red was negative for amyloid, and colloidal iron did not show any increase in dermal mucin, ruling out amyloidosis and scleromyxedema, respectively. Based on the histopathologic findings and the clinical history, a diagnosis of fibroelastolytic papulosis (FP) was made. Given the benign nature of the condition, the patient was prescribed a topical steroid (clobetasol 0.05%) for symptomatic relief.
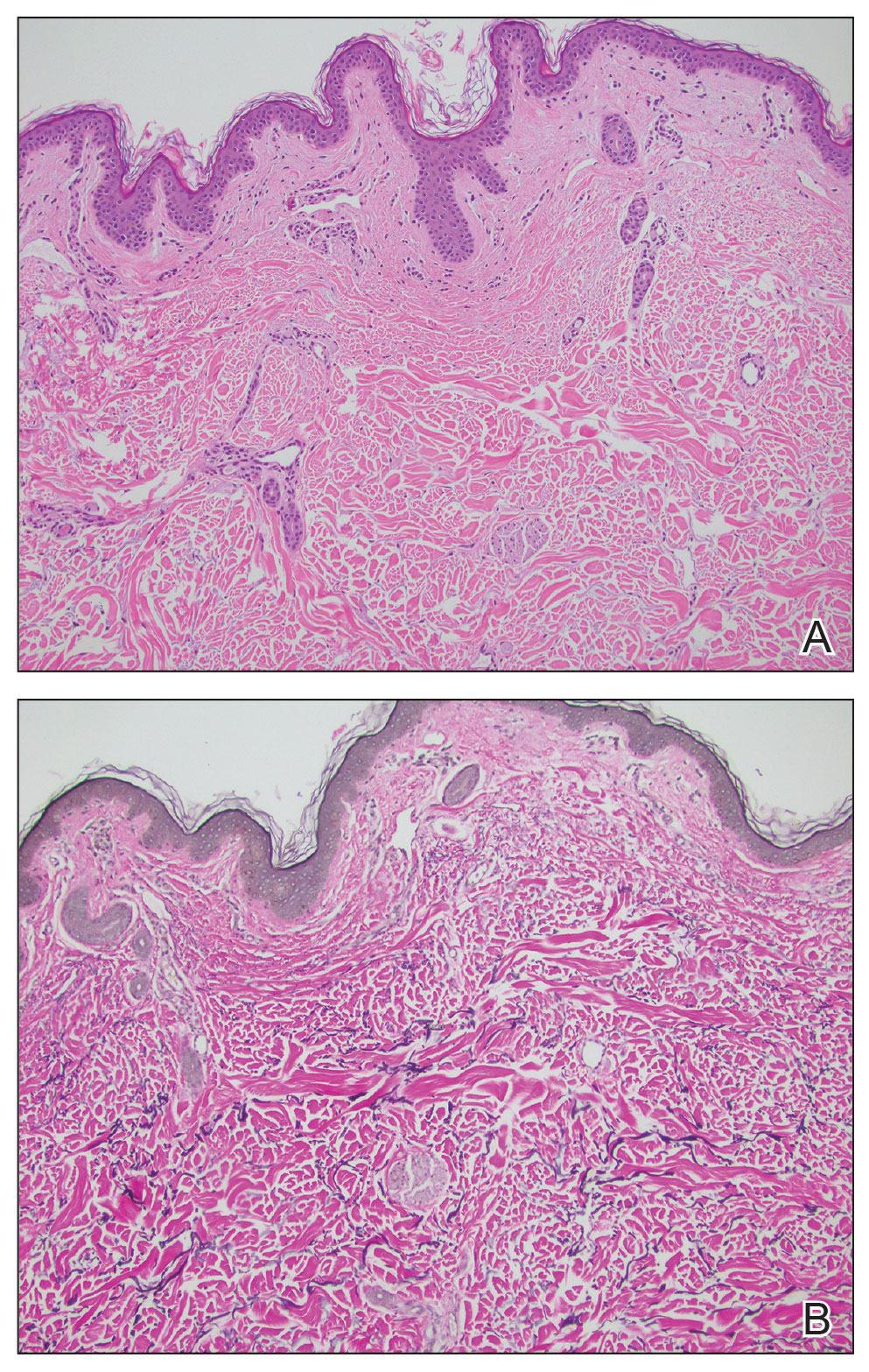
Cutaneous conditions can arise from abnormalities in the elastin composition of connective tissue due to abnormal elastin formation or degradation (elastolysis).1 Fibroelastolytic papulosis is a distinct elastolytic disorder diagnosed histologically by a notable loss of elastic fibers localized to the papillary dermis.2 Fibroelastolytic papulosis is an acquired condition linked to exposure to UV radiation, abnormal elastogenesis, and hormonal factors that commonly involves the neck, supraclavicular area, and upper back.1-3 Predominantly affecting elderly women, FP is characterized by soft white papules that often coalesce into a cobblestonelike plaque.2 Because the condition rarely is seen in men, there is speculation that it may involve genetic, hereditary, and hormonal factors that have yet to be identified.1
Fibroelastolytic papulosis can be classified as either pseudoxanthoma elasticum–like papillary dermal elastolysis or white fibrous papulosis.2,3 White fibrous papulosis manifests with haphazardly arranged collagen fibers in the reticular and deep dermis with papillary dermal elastolysis and most commonly develops on the neck.3 Although our patient’s lesion was on the neck, the absence of thickened collagen bands on histology supported classification as the pseudoxanthoma elasticum– like papillary dermal elastolysis subtype.
Fibroelastolytic papulosis can be distinguished from other elastic abnormalities by its characteristic clinical appearance, demographic distribution, and associated histopathologic findings. The differential diagnosis of FP includes pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE), anetoderma, scleromyxedema, and lichen amyloidosis.
Pseudoxanthoma elasticum is a hereditary or acquired multisystem disease characterized by fragmentation and calcification of elastic fibers in the mid dermis.1,4 Its clinical presentation resembles that of FP, appearing as small, asymptomatic, yellowish or flesh-colored papules in a reticular pattern that progressively coalesce into larger plaques with a cobblestonelike appearance.1 Like FP, PXE commonly affects the flexural creases in women but in contrast may manifest earlier (ie, second or third decades of life). Additionally, the pathogenesis of PXE is not related to UV radiation exposure. The hereditary form develops due to a gene variation, whereas the acquired form may be due to conditions associated with physiologic and/or mechanical stress.1
Anetoderma, also known as macular atrophy, is another condition that demonstrates elastic tissue loss in the dermis on histopathology.1 Anetoderma commonly is seen in younger patients and can be differentiated from FP by the antecedent presence of an inflammatory process. Anetoderma is classified as primary or secondary. Primary anetoderma is associated with prothrombotic abnormalities, while secondary anetoderma is associated with systemic disease including but not limited to sarcoidosis, systemic lupus erythematous, and Graves disease.1
Neither lichen myxedematosus (LM) nor lichen amyloidosis (LA) are true elastolytic conditions. Lichen myxedematosus is considered in the differential diagnosis of FP due to the associated loss of elastin observed with disease progression. An idiopathic cutaneous mucinosis, LM is a localized form of scleromyxedema, which is characterized by small, firm, waxy papules; mucin deposition in the skin; fibroblast proliferation; and fibrosis. On histologic analysis, typical findings of LM include irregularly arranged fibroblasts, diffuse mucin deposition within the upper and mid reticular dermis, increased collagen deposition, and a decrease in elastin fibers.5
Lichen amyloidosis is a subtype of primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis, a rare condition characterized by the extracellular deposition of amyloid proteins in the skin and a lack of systemic involvement. Although it is not an elastolytic condition, LA is clinically similar to FP, often manifesting as multiple localized, pruritic, hyperpigmented papules that can coalesce into larger plaques; it tends to develop on the shins, calves, ankles, and thighs.6,7 The condition commonly manifests in the fifth and sixth decades of life; however, in contrast to FP, LA is more prevalent in men and individuals from Central and South American as well as Middle Eastern and non-Chinese Asian populations.8 Lichen amyloidosis is a keratin-derived amyloidosis with cytokeratin-based amyloid precursors that only deposit in the dermis.6 Histopathology reveals colloid bodies due to the presence of apoptotic basal keratinocytes. The etiology of LA is unknown, but on rare occasions it has been associated with multiple endocrine neoplasia 2A rearranged during transfection mutations.6
In summary, FP is an uncommonly diagnosed elastolytic condition that often is asymptomatic or associated with mild pruritus. Biopsy is warranted to help differentiate it from mimicker conditions that may be associated with systemic disease. Currently, there is no established therapy that provides successful treatment. Research suggests unsatisfactory results with the use of topical tretinoin or topical antioxidants.3 More recently, nonablative fractional resurfacing lasers have been evaluated as a possible therapeutic strategy of promise for elastic disorders.9
- Andrés-Ramos I, Alegría-Landa V, Gimeno I, et al. Cutaneous elastic tissue anomalies. Am J Dermatopathol. 2019;41:85-117. doi:10.1097/DAD.0000000000001275
- Valbuena V, Assaad D, Yeung J. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum-like papillary dermal elastolysis: a single case report. J Cutan Med Surg. 2017;21:345-347. doi:10.1177/1203475417699407
- Dokic Y, Tschen J. White fibrous papulosis of the axillae and neck. Cureus. 2020;12:E7635. doi:10.7759/cureus.7635
- Recio-Monescillo M, Torre-Castro J, Manzanas C, et al. Papillary dermal elastolysis histopathology mimicking folliculotropic mycosis fungoides. J Cutan Pathol. 2023;50:430-433. doi:10.1111/cup.14402
- Cokonis Georgakis CD, Falasca G, Georgakis A, et al. Scleromyxedema. Clin Dermatol. 2006;24:493-497. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2006.07.011
- Weidner T, Illing T, Elsner P. Primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis: a systematic treatment review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2017;18:629-642. doi:10.1007/s40257-017-0278-9
- Ladizinski B, Lee KC. Lichen amyloidosis. CMAJ. 2014;186:532. doi:10.1503/cmaj.130698
- Chen JF, Chen YF. Answer: can you identify this condition? Can Fam Physician. 2012;58:1234-1235.
- Foering K, Torbeck RL, Frank MP, et al. Treatment of pseudoxanthoma elasticum-like papillary dermal elastolysis with nonablative fractional resurfacing laser resulting in clinical and histologic improvement in elastin and collagen. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2018;20:382-384. doi:10.1080/14764172.2017.1358457
The Diagnosis: Fibroelastolytic Papulosis
Histopathology demonstrated decreased density and fragmentation of elastic fibers in the superficial reticular and papillary dermis consistent with an elastolytic disease process (Figure). Of note, elastolysis typically is visualized with Verhoeff-van Gieson stain but cannot be visualized well with standard hematoxylin and eosin staining. Additional staining with Congo red was negative for amyloid, and colloidal iron did not show any increase in dermal mucin, ruling out amyloidosis and scleromyxedema, respectively. Based on the histopathologic findings and the clinical history, a diagnosis of fibroelastolytic papulosis (FP) was made. Given the benign nature of the condition, the patient was prescribed a topical steroid (clobetasol 0.05%) for symptomatic relief.

Cutaneous conditions can arise from abnormalities in the elastin composition of connective tissue due to abnormal elastin formation or degradation (elastolysis).1 Fibroelastolytic papulosis is a distinct elastolytic disorder diagnosed histologically by a notable loss of elastic fibers localized to the papillary dermis.2 Fibroelastolytic papulosis is an acquired condition linked to exposure to UV radiation, abnormal elastogenesis, and hormonal factors that commonly involves the neck, supraclavicular area, and upper back.1-3 Predominantly affecting elderly women, FP is characterized by soft white papules that often coalesce into a cobblestonelike plaque.2 Because the condition rarely is seen in men, there is speculation that it may involve genetic, hereditary, and hormonal factors that have yet to be identified.1
Fibroelastolytic papulosis can be classified as either pseudoxanthoma elasticum–like papillary dermal elastolysis or white fibrous papulosis.2,3 White fibrous papulosis manifests with haphazardly arranged collagen fibers in the reticular and deep dermis with papillary dermal elastolysis and most commonly develops on the neck.3 Although our patient’s lesion was on the neck, the absence of thickened collagen bands on histology supported classification as the pseudoxanthoma elasticum– like papillary dermal elastolysis subtype.
Fibroelastolytic papulosis can be distinguished from other elastic abnormalities by its characteristic clinical appearance, demographic distribution, and associated histopathologic findings. The differential diagnosis of FP includes pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE), anetoderma, scleromyxedema, and lichen amyloidosis.
Pseudoxanthoma elasticum is a hereditary or acquired multisystem disease characterized by fragmentation and calcification of elastic fibers in the mid dermis.1,4 Its clinical presentation resembles that of FP, appearing as small, asymptomatic, yellowish or flesh-colored papules in a reticular pattern that progressively coalesce into larger plaques with a cobblestonelike appearance.1 Like FP, PXE commonly affects the flexural creases in women but in contrast may manifest earlier (ie, second or third decades of life). Additionally, the pathogenesis of PXE is not related to UV radiation exposure. The hereditary form develops due to a gene variation, whereas the acquired form may be due to conditions associated with physiologic and/or mechanical stress.1
Anetoderma, also known as macular atrophy, is another condition that demonstrates elastic tissue loss in the dermis on histopathology.1 Anetoderma commonly is seen in younger patients and can be differentiated from FP by the antecedent presence of an inflammatory process. Anetoderma is classified as primary or secondary. Primary anetoderma is associated with prothrombotic abnormalities, while secondary anetoderma is associated with systemic disease including but not limited to sarcoidosis, systemic lupus erythematous, and Graves disease.1
Neither lichen myxedematosus (LM) nor lichen amyloidosis (LA) are true elastolytic conditions. Lichen myxedematosus is considered in the differential diagnosis of FP due to the associated loss of elastin observed with disease progression. An idiopathic cutaneous mucinosis, LM is a localized form of scleromyxedema, which is characterized by small, firm, waxy papules; mucin deposition in the skin; fibroblast proliferation; and fibrosis. On histologic analysis, typical findings of LM include irregularly arranged fibroblasts, diffuse mucin deposition within the upper and mid reticular dermis, increased collagen deposition, and a decrease in elastin fibers.5
Lichen amyloidosis is a subtype of primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis, a rare condition characterized by the extracellular deposition of amyloid proteins in the skin and a lack of systemic involvement. Although it is not an elastolytic condition, LA is clinically similar to FP, often manifesting as multiple localized, pruritic, hyperpigmented papules that can coalesce into larger plaques; it tends to develop on the shins, calves, ankles, and thighs.6,7 The condition commonly manifests in the fifth and sixth decades of life; however, in contrast to FP, LA is more prevalent in men and individuals from Central and South American as well as Middle Eastern and non-Chinese Asian populations.8 Lichen amyloidosis is a keratin-derived amyloidosis with cytokeratin-based amyloid precursors that only deposit in the dermis.6 Histopathology reveals colloid bodies due to the presence of apoptotic basal keratinocytes. The etiology of LA is unknown, but on rare occasions it has been associated with multiple endocrine neoplasia 2A rearranged during transfection mutations.6
In summary, FP is an uncommonly diagnosed elastolytic condition that often is asymptomatic or associated with mild pruritus. Biopsy is warranted to help differentiate it from mimicker conditions that may be associated with systemic disease. Currently, there is no established therapy that provides successful treatment. Research suggests unsatisfactory results with the use of topical tretinoin or topical antioxidants.3 More recently, nonablative fractional resurfacing lasers have been evaluated as a possible therapeutic strategy of promise for elastic disorders.9
The Diagnosis: Fibroelastolytic Papulosis
Histopathology demonstrated decreased density and fragmentation of elastic fibers in the superficial reticular and papillary dermis consistent with an elastolytic disease process (Figure). Of note, elastolysis typically is visualized with Verhoeff-van Gieson stain but cannot be visualized well with standard hematoxylin and eosin staining. Additional staining with Congo red was negative for amyloid, and colloidal iron did not show any increase in dermal mucin, ruling out amyloidosis and scleromyxedema, respectively. Based on the histopathologic findings and the clinical history, a diagnosis of fibroelastolytic papulosis (FP) was made. Given the benign nature of the condition, the patient was prescribed a topical steroid (clobetasol 0.05%) for symptomatic relief.

Cutaneous conditions can arise from abnormalities in the elastin composition of connective tissue due to abnormal elastin formation or degradation (elastolysis).1 Fibroelastolytic papulosis is a distinct elastolytic disorder diagnosed histologically by a notable loss of elastic fibers localized to the papillary dermis.2 Fibroelastolytic papulosis is an acquired condition linked to exposure to UV radiation, abnormal elastogenesis, and hormonal factors that commonly involves the neck, supraclavicular area, and upper back.1-3 Predominantly affecting elderly women, FP is characterized by soft white papules that often coalesce into a cobblestonelike plaque.2 Because the condition rarely is seen in men, there is speculation that it may involve genetic, hereditary, and hormonal factors that have yet to be identified.1
Fibroelastolytic papulosis can be classified as either pseudoxanthoma elasticum–like papillary dermal elastolysis or white fibrous papulosis.2,3 White fibrous papulosis manifests with haphazardly arranged collagen fibers in the reticular and deep dermis with papillary dermal elastolysis and most commonly develops on the neck.3 Although our patient’s lesion was on the neck, the absence of thickened collagen bands on histology supported classification as the pseudoxanthoma elasticum– like papillary dermal elastolysis subtype.
Fibroelastolytic papulosis can be distinguished from other elastic abnormalities by its characteristic clinical appearance, demographic distribution, and associated histopathologic findings. The differential diagnosis of FP includes pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE), anetoderma, scleromyxedema, and lichen amyloidosis.
Pseudoxanthoma elasticum is a hereditary or acquired multisystem disease characterized by fragmentation and calcification of elastic fibers in the mid dermis.1,4 Its clinical presentation resembles that of FP, appearing as small, asymptomatic, yellowish or flesh-colored papules in a reticular pattern that progressively coalesce into larger plaques with a cobblestonelike appearance.1 Like FP, PXE commonly affects the flexural creases in women but in contrast may manifest earlier (ie, second or third decades of life). Additionally, the pathogenesis of PXE is not related to UV radiation exposure. The hereditary form develops due to a gene variation, whereas the acquired form may be due to conditions associated with physiologic and/or mechanical stress.1
Anetoderma, also known as macular atrophy, is another condition that demonstrates elastic tissue loss in the dermis on histopathology.1 Anetoderma commonly is seen in younger patients and can be differentiated from FP by the antecedent presence of an inflammatory process. Anetoderma is classified as primary or secondary. Primary anetoderma is associated with prothrombotic abnormalities, while secondary anetoderma is associated with systemic disease including but not limited to sarcoidosis, systemic lupus erythematous, and Graves disease.1
Neither lichen myxedematosus (LM) nor lichen amyloidosis (LA) are true elastolytic conditions. Lichen myxedematosus is considered in the differential diagnosis of FP due to the associated loss of elastin observed with disease progression. An idiopathic cutaneous mucinosis, LM is a localized form of scleromyxedema, which is characterized by small, firm, waxy papules; mucin deposition in the skin; fibroblast proliferation; and fibrosis. On histologic analysis, typical findings of LM include irregularly arranged fibroblasts, diffuse mucin deposition within the upper and mid reticular dermis, increased collagen deposition, and a decrease in elastin fibers.5
Lichen amyloidosis is a subtype of primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis, a rare condition characterized by the extracellular deposition of amyloid proteins in the skin and a lack of systemic involvement. Although it is not an elastolytic condition, LA is clinically similar to FP, often manifesting as multiple localized, pruritic, hyperpigmented papules that can coalesce into larger plaques; it tends to develop on the shins, calves, ankles, and thighs.6,7 The condition commonly manifests in the fifth and sixth decades of life; however, in contrast to FP, LA is more prevalent in men and individuals from Central and South American as well as Middle Eastern and non-Chinese Asian populations.8 Lichen amyloidosis is a keratin-derived amyloidosis with cytokeratin-based amyloid precursors that only deposit in the dermis.6 Histopathology reveals colloid bodies due to the presence of apoptotic basal keratinocytes. The etiology of LA is unknown, but on rare occasions it has been associated with multiple endocrine neoplasia 2A rearranged during transfection mutations.6
In summary, FP is an uncommonly diagnosed elastolytic condition that often is asymptomatic or associated with mild pruritus. Biopsy is warranted to help differentiate it from mimicker conditions that may be associated with systemic disease. Currently, there is no established therapy that provides successful treatment. Research suggests unsatisfactory results with the use of topical tretinoin or topical antioxidants.3 More recently, nonablative fractional resurfacing lasers have been evaluated as a possible therapeutic strategy of promise for elastic disorders.9
- Andrés-Ramos I, Alegría-Landa V, Gimeno I, et al. Cutaneous elastic tissue anomalies. Am J Dermatopathol. 2019;41:85-117. doi:10.1097/DAD.0000000000001275
- Valbuena V, Assaad D, Yeung J. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum-like papillary dermal elastolysis: a single case report. J Cutan Med Surg. 2017;21:345-347. doi:10.1177/1203475417699407
- Dokic Y, Tschen J. White fibrous papulosis of the axillae and neck. Cureus. 2020;12:E7635. doi:10.7759/cureus.7635
- Recio-Monescillo M, Torre-Castro J, Manzanas C, et al. Papillary dermal elastolysis histopathology mimicking folliculotropic mycosis fungoides. J Cutan Pathol. 2023;50:430-433. doi:10.1111/cup.14402
- Cokonis Georgakis CD, Falasca G, Georgakis A, et al. Scleromyxedema. Clin Dermatol. 2006;24:493-497. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2006.07.011
- Weidner T, Illing T, Elsner P. Primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis: a systematic treatment review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2017;18:629-642. doi:10.1007/s40257-017-0278-9
- Ladizinski B, Lee KC. Lichen amyloidosis. CMAJ. 2014;186:532. doi:10.1503/cmaj.130698
- Chen JF, Chen YF. Answer: can you identify this condition? Can Fam Physician. 2012;58:1234-1235.
- Foering K, Torbeck RL, Frank MP, et al. Treatment of pseudoxanthoma elasticum-like papillary dermal elastolysis with nonablative fractional resurfacing laser resulting in clinical and histologic improvement in elastin and collagen. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2018;20:382-384. doi:10.1080/14764172.2017.1358457
- Andrés-Ramos I, Alegría-Landa V, Gimeno I, et al. Cutaneous elastic tissue anomalies. Am J Dermatopathol. 2019;41:85-117. doi:10.1097/DAD.0000000000001275
- Valbuena V, Assaad D, Yeung J. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum-like papillary dermal elastolysis: a single case report. J Cutan Med Surg. 2017;21:345-347. doi:10.1177/1203475417699407
- Dokic Y, Tschen J. White fibrous papulosis of the axillae and neck. Cureus. 2020;12:E7635. doi:10.7759/cureus.7635
- Recio-Monescillo M, Torre-Castro J, Manzanas C, et al. Papillary dermal elastolysis histopathology mimicking folliculotropic mycosis fungoides. J Cutan Pathol. 2023;50:430-433. doi:10.1111/cup.14402
- Cokonis Georgakis CD, Falasca G, Georgakis A, et al. Scleromyxedema. Clin Dermatol. 2006;24:493-497. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2006.07.011
- Weidner T, Illing T, Elsner P. Primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis: a systematic treatment review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2017;18:629-642. doi:10.1007/s40257-017-0278-9
- Ladizinski B, Lee KC. Lichen amyloidosis. CMAJ. 2014;186:532. doi:10.1503/cmaj.130698
- Chen JF, Chen YF. Answer: can you identify this condition? Can Fam Physician. 2012;58:1234-1235.
- Foering K, Torbeck RL, Frank MP, et al. Treatment of pseudoxanthoma elasticum-like papillary dermal elastolysis with nonablative fractional resurfacing laser resulting in clinical and histologic improvement in elastin and collagen. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2018;20:382-384. doi:10.1080/14764172.2017.1358457
A 76-year-old woman presented to the dermatology clinic for evaluation of a pruritic rash on the posterior lateral neck of several years’ duration. The rash had been slowly worsening and was intermittently symptomatic. Physical examination revealed monomorphous flesh-colored papules coalescing on the neck, yielding a cobblestonelike texture. The patient had been treated previously by dermatology with topical steroids, but symptoms persisted. A punch biopsy of the left lateral neck was performed.
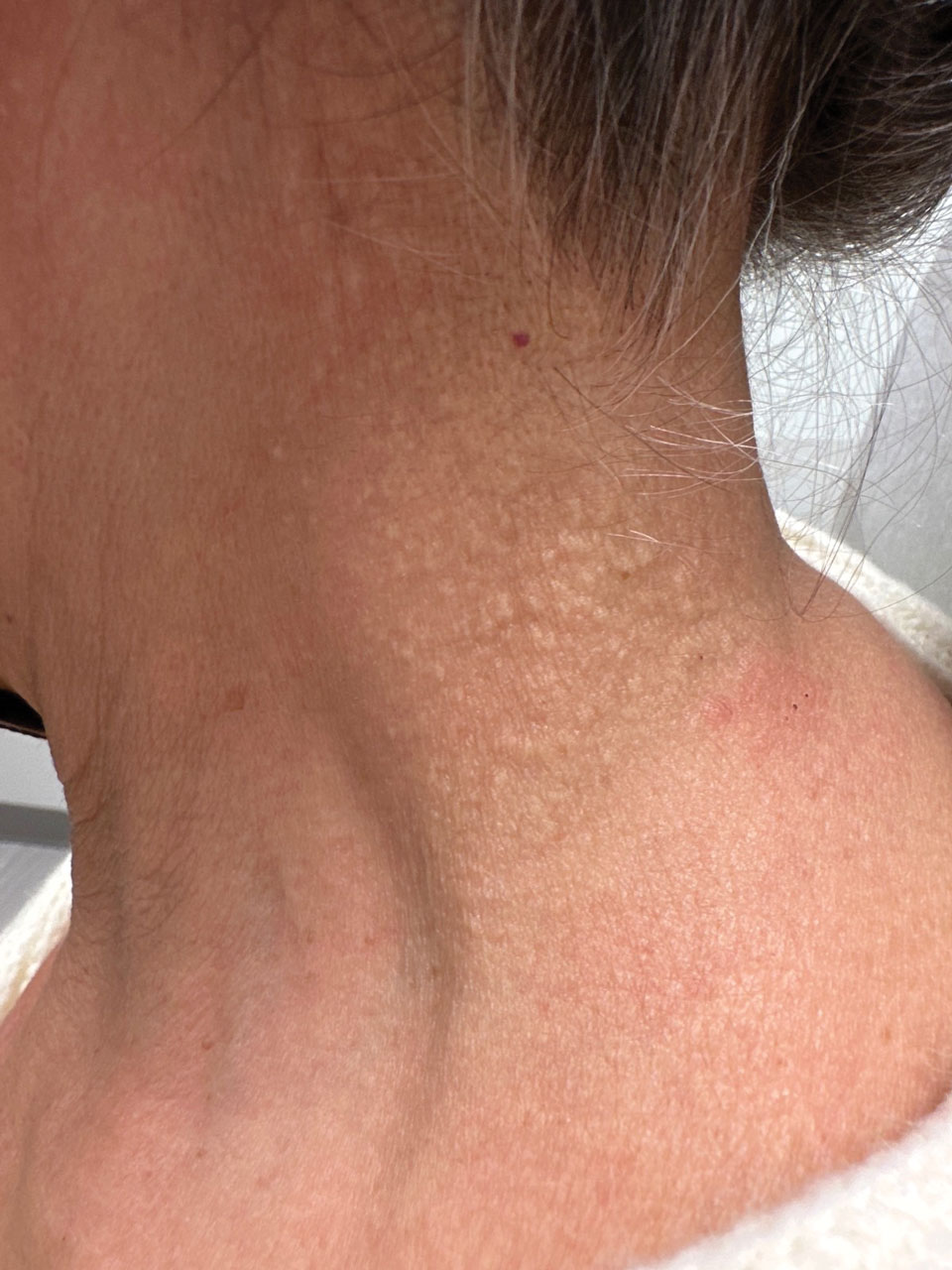
Alopecia and Pruritic Rash on the Forehead and Scalp
Alopecia and Pruritic Rash on the Forehead and Scalp
THE DIAGNOSIS: Folliculitis Decalvans
Biopsy results revealed a brisk perifollicular and intrafollicular mixed inflammatory infiltrate comprising lymphocytes, neutrophils, and plasma cells filling the upper dermis and encircling dilated hair follicles. Elastic stain (Verhoeff-van Gieson) demonstrated loss of elastic fibers in areas of scarring. Periodic acid–Schiff with diastase staining was negative for fungal elements, while Gram staining revealed colonies of bacterial cocci in the stratum corneum and within the hair follicles. Immunofluorescence was unremarkable, and culture revealed methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus, leading to a diagnosis of folliculitis decalvans (FD). The patient was treated with doxycycline 100 mg twice daily and received intralesional triamcinolone 2.5 mg/mL (total volume, 2 mL) every 6 weeks with considerable improvement in pustules, erythema, and scaling (Figure). While not yet in complete remission, our patient demonstrated short regrowing hairs in areas of incomplete scarring and focal remaining perifollicular erythema and scale along the midline frontal scalp 5 months after initial presentation.
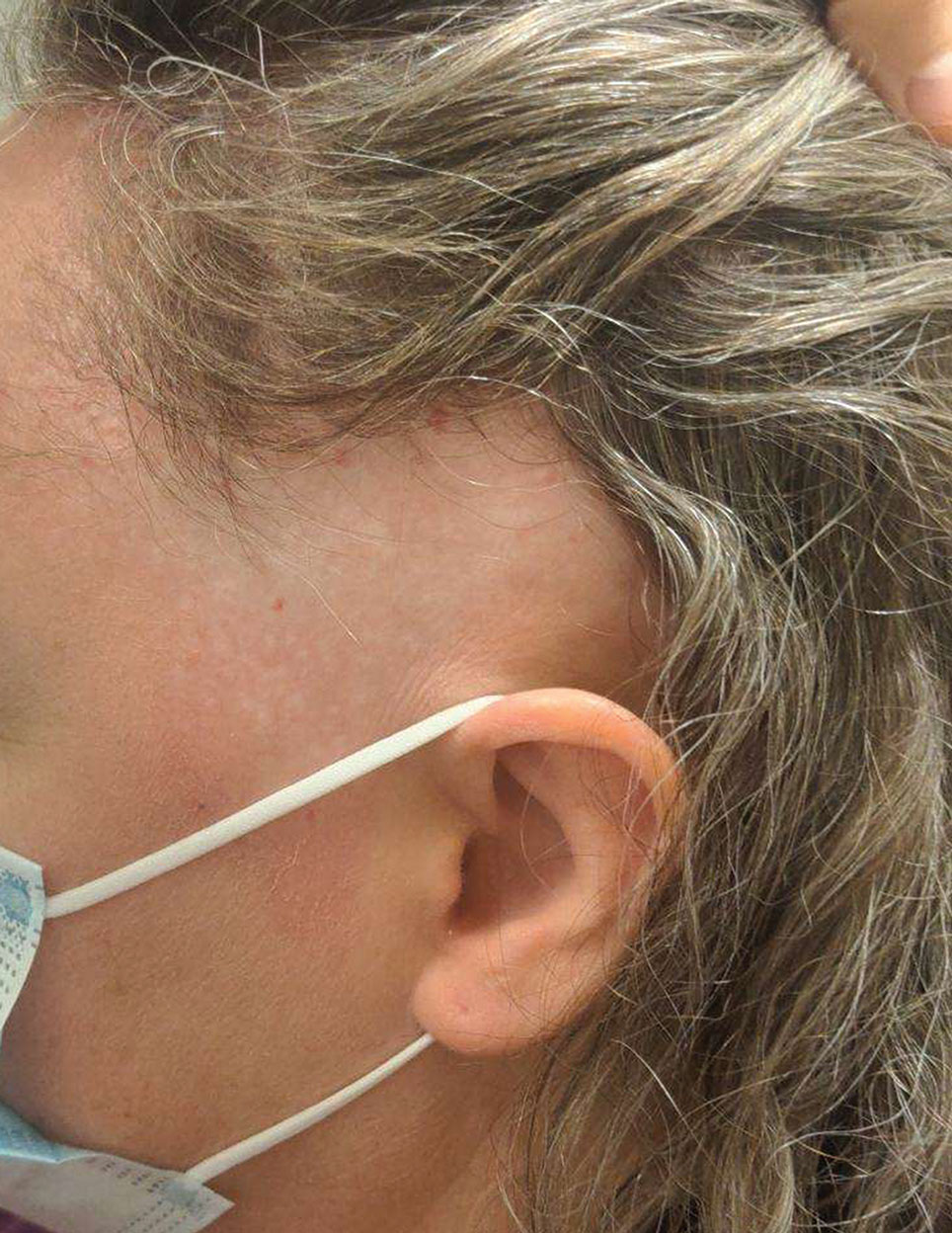
Folliculitis decalvans is an uncommon subtype of cicatricial alopecia that may mimic other forms of alopecia. Cicatricial alopecia often is difficult to diagnose due to its overlapping clinical characteristics, but early diagnosis is essential for appropriate management and prevention of further permanent hair loss. Traditionally classified as a primary neutrophilic cicatricial alopecia, lymphocyte-predominant variants of FD now are recognized.1
Patients with FD typically present with patchy scarring alopecia at the vertex scalp that gradually expands and may demonstrate secondary features of follicular tufting and pustules.1-3 While the epidemiology of FD is poorly characterized, Vañó-Galván et al4 reported that FD accounted for 2.8% of all alopecia cases and 10.5% of cicatricial alopecia cases in a multicenter study of 2835 patients. The pathophysiology of FD still is under investigation but is thought to result from a dysregulated immune response to a chronic bacterial infection (eg, S aureus), with resulting neutrophilpredominant inflammation in early stages.1-3 Vañó-Galván et al4 reported that, among 35 patients with FD cultured for bacteria, 74% (26/35) returned positive results, 96% (25/26) of which grew S aureus.5
A systematic review of 20 studies that included 263 patients found rifampin and clindamycin to be the most common treatments for FD; however, there is insufficient evidence to determine if this treatment is the most effective.6 In our patient, clindamycin was avoided due to its propensity to negatively alter the gut microbiome long term.7 Other therapies such as oral tetracyclines, high-potency topical steroids, and intralesional triamcinolone also can be used to achieve disease remission.5,6 Other treatments such as isotretinoin, red-light photodynamic therapy, tacrolimus, and external beam radiation have been reported in the literature but vary in efficacy.6 Our patient improved on a regimen of topical benzoyl peroxide wash, oral doxycycline, and intralesional triamcinolone.
Notably, FD may share clinical features with other causes of cicatricial alopecia. In our patient, FD mimicked other entities including discoid lupus erythematosus, frontal fibrosing alopecia, dissecting cellulitis, and erosive pustular dermatosis (Table).1-14 Discoid lupus erythematosus manifests as round hypopigmented and hyperpigmented plaques with associated atrophy, perifollicular erythema, and follicular plugging. Frontal fibrosing alopecia is a primary lymphocytic scarring alopecia that manifests in a bandlike linear distribution over the frontal scalp and may involve the temporal scalp, posterior hairline, and/or eyebrows. Isolated hairs (known as lonely hairs) often are seen. Dissecting cellulitis is characterized by boggy nodules associated with alopecia on the scalp without notable epidermal change, although pustules and sinus tracts may develop.9 Erosive pustular dermatosis is a diagnosis of exclusion but often is seen in older adults with chronic sun damage and clinically manifests with eroded plaques with adherent crusts.10
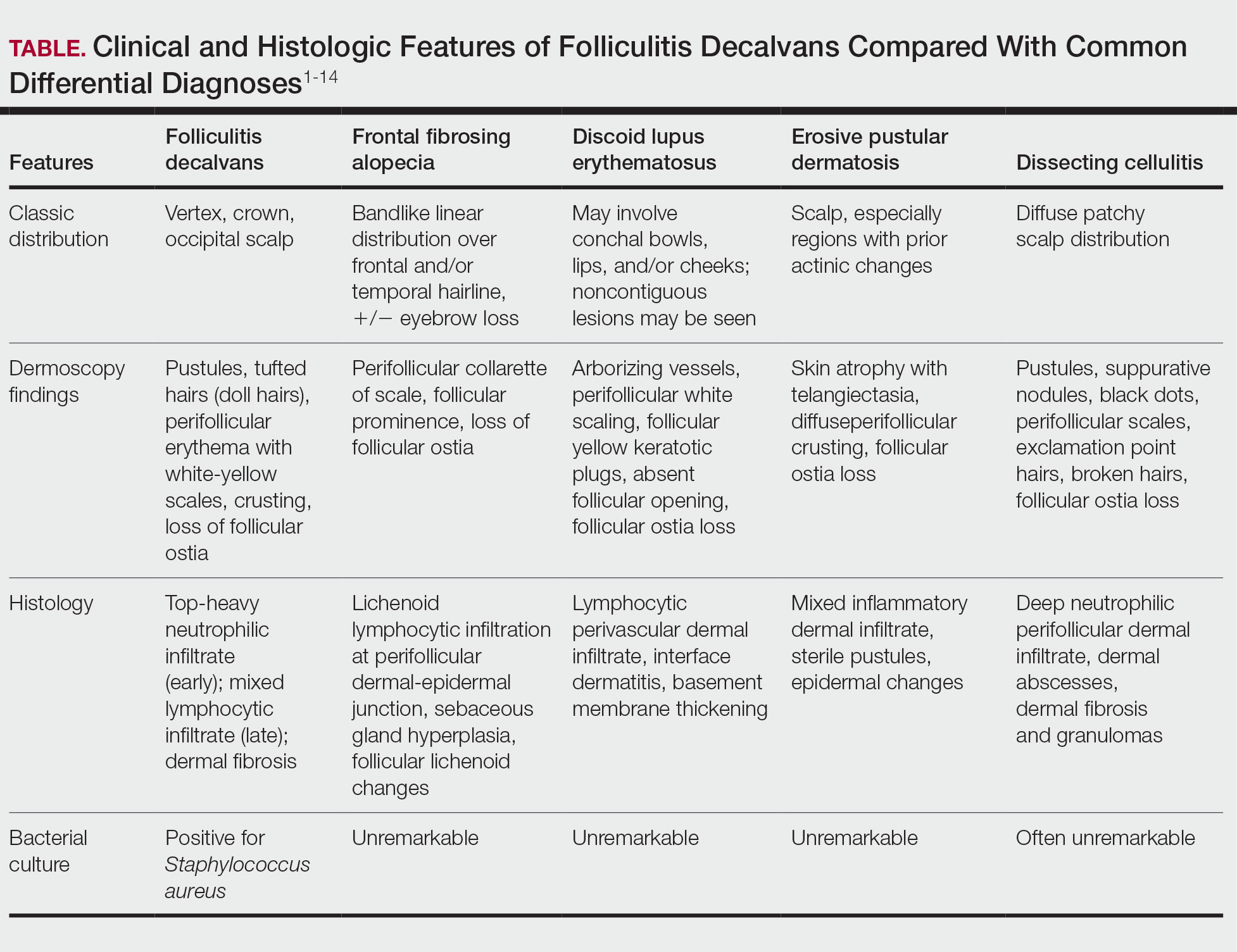
While our patient presented with several overlapping clinical features, including progressive hair loss along the frontal scalp in a bandlike pattern suspicious for frontal fibrosing alopecia as well as atrophic depigmented plaques with adherent peripheral scaling suspicious for discoid lupus erythematosus, the presence of pustules was an important clue. The biopsy demonstrating a mixed infiltrate inclusive of neutrophils confirmed the diagnosis of FD.
- Olsen EA, Bergfeld WF, Cotsarelis G, et al. Summary of North American Hair Research Society (NAHRS)-sponsored Workshop on Cicatricial Alopecia, Duke University Medical Center, February 10 and 11, 2001. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;48:103-110. doi:10.1067/mjd.2003.68
- Filbrandt R, Rufaut N, Jones L. Primary cicatricial alopecia: diagnosis and treatment. CMAJ. 2013;185:1579-1585. doi:10.1503/cmaj.111570
- Otberg N, Kang H, Alzolibani AA, et al. Folliculitis decalvans. Dermatol Ther. 2008;21:238-244. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8019.2008.00204.x
- Vañó-Galván S, Saceda-Corralo D, Blume-Peytavi U, et al. Frequency of the types of alopecia at twenty-two specialist hair clinics: a multicenter study. Skin Appendage Disord. 2019;5:309-315. doi:10.1159/000496708
- Vañó-Galván S, Molina-Ruiz AM, Fernández-Crehuet P, et al. Folliculitis decalvans: a multicentre review of 82 patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:1750-1757. doi:10.1111/jdv.12993
- Rambhia PH, Conic RRZ, Murad A, et al. Updates in therapeutics for folliculitis decalvans: a systematic review with evidence-based analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:794-801. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.07.050
- Zimmermann P, Curtis N. The effect of antibiotics on the composition of the intestinal microbiota - a systematic review. J Infect. 2019;79:471-489. doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2019.10.008
- Kanti V, Röwert-Huber J, Vogt A, et al. Cicatricial alopecia. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2018;16:435-461. doi:10.1111/ddg.13498
- Melo DF, Slaibi EB, Siqueira TMFM, et al. Trichoscopy findings in dissecting cellulitis. An Bras Dermatol. 2019;94:608-611. doi:10.1016/j.abd.2019.09.006
- Anzai A, Pirmez R, Vincenzi C, et al. Trichoscopy findings of frontal fibrosing alopecia on the eyebrows: a study of 151 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:1130-1134. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.12.023
- Starace M, Loi C, Bruni F, et al. Erosive pustular dermatosis of the scalp: clinical, trichoscopic, and histopathologic features of 20 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:1109-1114. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2016.12.016
- Rongioletti F, Christana K. Cicatricial (scarring) alopecias: an overview of pathogenesis, classification, diagnosis, and treatment. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2012;13:247-260. doi:10.2165/11596960-000000000-00000
- Badaoui A, Reygagne P, Cavelier-Balloy B, et al. Dissecting cellulitis of the scalp: a retrospective study of 51 patients and review of literature. Br J Dermatol. 2016;174:421-423. doi:10.1111/bjd.13999
- Michelerio A, Vassallo C, Fiandrino G, et al. Erosive pustular dermatosis of the scalp: a clinicopathologic study of fifty cases. Dermatopathology (Basel). 2021;8:450-462. doi:10.3390/dermatopathology8040048
THE DIAGNOSIS: Folliculitis Decalvans
Biopsy results revealed a brisk perifollicular and intrafollicular mixed inflammatory infiltrate comprising lymphocytes, neutrophils, and plasma cells filling the upper dermis and encircling dilated hair follicles. Elastic stain (Verhoeff-van Gieson) demonstrated loss of elastic fibers in areas of scarring. Periodic acid–Schiff with diastase staining was negative for fungal elements, while Gram staining revealed colonies of bacterial cocci in the stratum corneum and within the hair follicles. Immunofluorescence was unremarkable, and culture revealed methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus, leading to a diagnosis of folliculitis decalvans (FD). The patient was treated with doxycycline 100 mg twice daily and received intralesional triamcinolone 2.5 mg/mL (total volume, 2 mL) every 6 weeks with considerable improvement in pustules, erythema, and scaling (Figure). While not yet in complete remission, our patient demonstrated short regrowing hairs in areas of incomplete scarring and focal remaining perifollicular erythema and scale along the midline frontal scalp 5 months after initial presentation.

Folliculitis decalvans is an uncommon subtype of cicatricial alopecia that may mimic other forms of alopecia. Cicatricial alopecia often is difficult to diagnose due to its overlapping clinical characteristics, but early diagnosis is essential for appropriate management and prevention of further permanent hair loss. Traditionally classified as a primary neutrophilic cicatricial alopecia, lymphocyte-predominant variants of FD now are recognized.1
Patients with FD typically present with patchy scarring alopecia at the vertex scalp that gradually expands and may demonstrate secondary features of follicular tufting and pustules.1-3 While the epidemiology of FD is poorly characterized, Vañó-Galván et al4 reported that FD accounted for 2.8% of all alopecia cases and 10.5% of cicatricial alopecia cases in a multicenter study of 2835 patients. The pathophysiology of FD still is under investigation but is thought to result from a dysregulated immune response to a chronic bacterial infection (eg, S aureus), with resulting neutrophilpredominant inflammation in early stages.1-3 Vañó-Galván et al4 reported that, among 35 patients with FD cultured for bacteria, 74% (26/35) returned positive results, 96% (25/26) of which grew S aureus.5
A systematic review of 20 studies that included 263 patients found rifampin and clindamycin to be the most common treatments for FD; however, there is insufficient evidence to determine if this treatment is the most effective.6 In our patient, clindamycin was avoided due to its propensity to negatively alter the gut microbiome long term.7 Other therapies such as oral tetracyclines, high-potency topical steroids, and intralesional triamcinolone also can be used to achieve disease remission.5,6 Other treatments such as isotretinoin, red-light photodynamic therapy, tacrolimus, and external beam radiation have been reported in the literature but vary in efficacy.6 Our patient improved on a regimen of topical benzoyl peroxide wash, oral doxycycline, and intralesional triamcinolone.
Notably, FD may share clinical features with other causes of cicatricial alopecia. In our patient, FD mimicked other entities including discoid lupus erythematosus, frontal fibrosing alopecia, dissecting cellulitis, and erosive pustular dermatosis (Table).1-14 Discoid lupus erythematosus manifests as round hypopigmented and hyperpigmented plaques with associated atrophy, perifollicular erythema, and follicular plugging. Frontal fibrosing alopecia is a primary lymphocytic scarring alopecia that manifests in a bandlike linear distribution over the frontal scalp and may involve the temporal scalp, posterior hairline, and/or eyebrows. Isolated hairs (known as lonely hairs) often are seen. Dissecting cellulitis is characterized by boggy nodules associated with alopecia on the scalp without notable epidermal change, although pustules and sinus tracts may develop.9 Erosive pustular dermatosis is a diagnosis of exclusion but often is seen in older adults with chronic sun damage and clinically manifests with eroded plaques with adherent crusts.10

While our patient presented with several overlapping clinical features, including progressive hair loss along the frontal scalp in a bandlike pattern suspicious for frontal fibrosing alopecia as well as atrophic depigmented plaques with adherent peripheral scaling suspicious for discoid lupus erythematosus, the presence of pustules was an important clue. The biopsy demonstrating a mixed infiltrate inclusive of neutrophils confirmed the diagnosis of FD.
THE DIAGNOSIS: Folliculitis Decalvans
Biopsy results revealed a brisk perifollicular and intrafollicular mixed inflammatory infiltrate comprising lymphocytes, neutrophils, and plasma cells filling the upper dermis and encircling dilated hair follicles. Elastic stain (Verhoeff-van Gieson) demonstrated loss of elastic fibers in areas of scarring. Periodic acid–Schiff with diastase staining was negative for fungal elements, while Gram staining revealed colonies of bacterial cocci in the stratum corneum and within the hair follicles. Immunofluorescence was unremarkable, and culture revealed methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus, leading to a diagnosis of folliculitis decalvans (FD). The patient was treated with doxycycline 100 mg twice daily and received intralesional triamcinolone 2.5 mg/mL (total volume, 2 mL) every 6 weeks with considerable improvement in pustules, erythema, and scaling (Figure). While not yet in complete remission, our patient demonstrated short regrowing hairs in areas of incomplete scarring and focal remaining perifollicular erythema and scale along the midline frontal scalp 5 months after initial presentation.

Folliculitis decalvans is an uncommon subtype of cicatricial alopecia that may mimic other forms of alopecia. Cicatricial alopecia often is difficult to diagnose due to its overlapping clinical characteristics, but early diagnosis is essential for appropriate management and prevention of further permanent hair loss. Traditionally classified as a primary neutrophilic cicatricial alopecia, lymphocyte-predominant variants of FD now are recognized.1
Patients with FD typically present with patchy scarring alopecia at the vertex scalp that gradually expands and may demonstrate secondary features of follicular tufting and pustules.1-3 While the epidemiology of FD is poorly characterized, Vañó-Galván et al4 reported that FD accounted for 2.8% of all alopecia cases and 10.5% of cicatricial alopecia cases in a multicenter study of 2835 patients. The pathophysiology of FD still is under investigation but is thought to result from a dysregulated immune response to a chronic bacterial infection (eg, S aureus), with resulting neutrophilpredominant inflammation in early stages.1-3 Vañó-Galván et al4 reported that, among 35 patients with FD cultured for bacteria, 74% (26/35) returned positive results, 96% (25/26) of which grew S aureus.5
A systematic review of 20 studies that included 263 patients found rifampin and clindamycin to be the most common treatments for FD; however, there is insufficient evidence to determine if this treatment is the most effective.6 In our patient, clindamycin was avoided due to its propensity to negatively alter the gut microbiome long term.7 Other therapies such as oral tetracyclines, high-potency topical steroids, and intralesional triamcinolone also can be used to achieve disease remission.5,6 Other treatments such as isotretinoin, red-light photodynamic therapy, tacrolimus, and external beam radiation have been reported in the literature but vary in efficacy.6 Our patient improved on a regimen of topical benzoyl peroxide wash, oral doxycycline, and intralesional triamcinolone.
Notably, FD may share clinical features with other causes of cicatricial alopecia. In our patient, FD mimicked other entities including discoid lupus erythematosus, frontal fibrosing alopecia, dissecting cellulitis, and erosive pustular dermatosis (Table).1-14 Discoid lupus erythematosus manifests as round hypopigmented and hyperpigmented plaques with associated atrophy, perifollicular erythema, and follicular plugging. Frontal fibrosing alopecia is a primary lymphocytic scarring alopecia that manifests in a bandlike linear distribution over the frontal scalp and may involve the temporal scalp, posterior hairline, and/or eyebrows. Isolated hairs (known as lonely hairs) often are seen. Dissecting cellulitis is characterized by boggy nodules associated with alopecia on the scalp without notable epidermal change, although pustules and sinus tracts may develop.9 Erosive pustular dermatosis is a diagnosis of exclusion but often is seen in older adults with chronic sun damage and clinically manifests with eroded plaques with adherent crusts.10

While our patient presented with several overlapping clinical features, including progressive hair loss along the frontal scalp in a bandlike pattern suspicious for frontal fibrosing alopecia as well as atrophic depigmented plaques with adherent peripheral scaling suspicious for discoid lupus erythematosus, the presence of pustules was an important clue. The biopsy demonstrating a mixed infiltrate inclusive of neutrophils confirmed the diagnosis of FD.
- Olsen EA, Bergfeld WF, Cotsarelis G, et al. Summary of North American Hair Research Society (NAHRS)-sponsored Workshop on Cicatricial Alopecia, Duke University Medical Center, February 10 and 11, 2001. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;48:103-110. doi:10.1067/mjd.2003.68
- Filbrandt R, Rufaut N, Jones L. Primary cicatricial alopecia: diagnosis and treatment. CMAJ. 2013;185:1579-1585. doi:10.1503/cmaj.111570
- Otberg N, Kang H, Alzolibani AA, et al. Folliculitis decalvans. Dermatol Ther. 2008;21:238-244. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8019.2008.00204.x
- Vañó-Galván S, Saceda-Corralo D, Blume-Peytavi U, et al. Frequency of the types of alopecia at twenty-two specialist hair clinics: a multicenter study. Skin Appendage Disord. 2019;5:309-315. doi:10.1159/000496708
- Vañó-Galván S, Molina-Ruiz AM, Fernández-Crehuet P, et al. Folliculitis decalvans: a multicentre review of 82 patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:1750-1757. doi:10.1111/jdv.12993
- Rambhia PH, Conic RRZ, Murad A, et al. Updates in therapeutics for folliculitis decalvans: a systematic review with evidence-based analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:794-801. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.07.050
- Zimmermann P, Curtis N. The effect of antibiotics on the composition of the intestinal microbiota - a systematic review. J Infect. 2019;79:471-489. doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2019.10.008
- Kanti V, Röwert-Huber J, Vogt A, et al. Cicatricial alopecia. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2018;16:435-461. doi:10.1111/ddg.13498
- Melo DF, Slaibi EB, Siqueira TMFM, et al. Trichoscopy findings in dissecting cellulitis. An Bras Dermatol. 2019;94:608-611. doi:10.1016/j.abd.2019.09.006
- Anzai A, Pirmez R, Vincenzi C, et al. Trichoscopy findings of frontal fibrosing alopecia on the eyebrows: a study of 151 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:1130-1134. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.12.023
- Starace M, Loi C, Bruni F, et al. Erosive pustular dermatosis of the scalp: clinical, trichoscopic, and histopathologic features of 20 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:1109-1114. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2016.12.016
- Rongioletti F, Christana K. Cicatricial (scarring) alopecias: an overview of pathogenesis, classification, diagnosis, and treatment. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2012;13:247-260. doi:10.2165/11596960-000000000-00000
- Badaoui A, Reygagne P, Cavelier-Balloy B, et al. Dissecting cellulitis of the scalp: a retrospective study of 51 patients and review of literature. Br J Dermatol. 2016;174:421-423. doi:10.1111/bjd.13999
- Michelerio A, Vassallo C, Fiandrino G, et al. Erosive pustular dermatosis of the scalp: a clinicopathologic study of fifty cases. Dermatopathology (Basel). 2021;8:450-462. doi:10.3390/dermatopathology8040048
- Olsen EA, Bergfeld WF, Cotsarelis G, et al. Summary of North American Hair Research Society (NAHRS)-sponsored Workshop on Cicatricial Alopecia, Duke University Medical Center, February 10 and 11, 2001. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;48:103-110. doi:10.1067/mjd.2003.68
- Filbrandt R, Rufaut N, Jones L. Primary cicatricial alopecia: diagnosis and treatment. CMAJ. 2013;185:1579-1585. doi:10.1503/cmaj.111570
- Otberg N, Kang H, Alzolibani AA, et al. Folliculitis decalvans. Dermatol Ther. 2008;21:238-244. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8019.2008.00204.x
- Vañó-Galván S, Saceda-Corralo D, Blume-Peytavi U, et al. Frequency of the types of alopecia at twenty-two specialist hair clinics: a multicenter study. Skin Appendage Disord. 2019;5:309-315. doi:10.1159/000496708
- Vañó-Galván S, Molina-Ruiz AM, Fernández-Crehuet P, et al. Folliculitis decalvans: a multicentre review of 82 patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:1750-1757. doi:10.1111/jdv.12993
- Rambhia PH, Conic RRZ, Murad A, et al. Updates in therapeutics for folliculitis decalvans: a systematic review with evidence-based analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:794-801. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.07.050
- Zimmermann P, Curtis N. The effect of antibiotics on the composition of the intestinal microbiota - a systematic review. J Infect. 2019;79:471-489. doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2019.10.008
- Kanti V, Röwert-Huber J, Vogt A, et al. Cicatricial alopecia. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2018;16:435-461. doi:10.1111/ddg.13498
- Melo DF, Slaibi EB, Siqueira TMFM, et al. Trichoscopy findings in dissecting cellulitis. An Bras Dermatol. 2019;94:608-611. doi:10.1016/j.abd.2019.09.006
- Anzai A, Pirmez R, Vincenzi C, et al. Trichoscopy findings of frontal fibrosing alopecia on the eyebrows: a study of 151 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:1130-1134. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.12.023
- Starace M, Loi C, Bruni F, et al. Erosive pustular dermatosis of the scalp: clinical, trichoscopic, and histopathologic features of 20 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:1109-1114. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2016.12.016
- Rongioletti F, Christana K. Cicatricial (scarring) alopecias: an overview of pathogenesis, classification, diagnosis, and treatment. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2012;13:247-260. doi:10.2165/11596960-000000000-00000
- Badaoui A, Reygagne P, Cavelier-Balloy B, et al. Dissecting cellulitis of the scalp: a retrospective study of 51 patients and review of literature. Br J Dermatol. 2016;174:421-423. doi:10.1111/bjd.13999
- Michelerio A, Vassallo C, Fiandrino G, et al. Erosive pustular dermatosis of the scalp: a clinicopathologic study of fifty cases. Dermatopathology (Basel). 2021;8:450-462. doi:10.3390/dermatopathology8040048
Alopecia and Pruritic Rash on the Forehead and Scalp
Alopecia and Pruritic Rash on the Forehead and Scalp
A 52-year-old woman presented to the dermatology department with an intermittently pruritic rash in a bandlike distribution on the left upper forehead and the frontal and temporal scalp of 4 years’ duration. The rash initially was diagnosed as psoriasis at an outside facility. Treatment over the year prior to presentation included tildrakizumab-asmn; topical crisaborole 2%; and excimer laser, which was complicated by blistering. The patient reported no history of topical or injected steroid use in the involved areas. Physical examination at the current presentation revealed arcuate erythematous plaques with follicular prominence, perifollicular scaling, pustules, and lone hairs. There also were porcelain-white atrophic plaques with loss of follicular ostia that were most prominent over the temporal scalp. A biopsy of the left lateral forehead was performed.
Interview Tips for Dermatology Applicants From Dr. Scott Worswick
What qualities are dermatology programs looking for that may be different from 5 years ago?
DR. WORSWICK: Every dermatology residency program is different, and as a result, each program is looking for different qualities in its applicants. Overall, I don’t think there has been a huge change in what programs are generally looking for, though. While each program may have a particular trait it values more than another, in general, programs are looking to find residents who will be competent and caring doctors, who work well in teams, and who could be future leaders in our field.
What are common mistakes you see in dermatology residency interviews, and how can applicants avoid them?
DR. WORSWICK: Most dermatology applicants are highly accomplished and empathic soon-to-be physicians, so I haven’t found a lot of “mistakes” from this incredible group of people that we have the privilege of interviewing. From time to time, an applicant will lie in an interview, usually out of a desire to appear to be a certain way, and occasionally, they may be nervous and stumble over their words. The former is a really big problem when it happens, and I would recommend that applicants be honest in all their encounters. The latter is not a major problem, and in some cases, might be avoided by lots of practice in advance.
What types of questions do you recommend applicants ask their interviewers to demonstrate genuine interest in the program?
DR. WORSWICK: Because of the signaling system, I think that programs assume interest at baseline once an applicant has sent the signal. So, “demonstrating interest” is generally not something I would recommend to applicants during the interview day. It is important for applicants to determine on interview day if a program is a fit for them, so applicants should showcase their unique strengths and skills and find out about what makes any given program different from another. The match generally works well and gets applicants into a program that closely aligns with their strengths and interests. So, think of interview day as your time to figure out how good a fit a program is for you, and not the other way around.
How can applicants who feel they don't have standout research or leadership credentials differentiate themselves in the interview?
DR. WORSWICK: While leadership, and less so research experience, is a trait valued highly by most if not all dermatology programs, it is only a part of what an applicant can offer a program. Most programs employ holistic review and consider several factors, probably most commonly grades in medical school, leadership experience, mentorship, teaching, volunteering, Step 2 scores, and letters of recommendation. Any given applicant does not need to excel in all of these. If an applicant has not done a lot of research, they may not match into a research-heavy program, but it doesn’t mean they won’t match. They should determine in which areas they shine and signal the programs that align with those interests/strengths.
How should applicants discuss nontraditional experiences in a way that adds value rather than raising red flags?
DR. WORSWICK: In general, my recommendation would be to explain what happened leading up to the change or challenge so that someone reading the application clearly understands the circumstances of the experience, then add value to the description by explaining what was learned and how this might relate to the applicant being a dermatology resident. For example, if a resident took time off for financial reasons and had to work as a medical assitant for a year, a concise description that explains the need for the leave (financial) as well as what value was gained (a year of hands-on patient care experience that validated their choice of going into medicine) could be very helpful.
What qualities are dermatology programs looking for that may be different from 5 years ago?
DR. WORSWICK: Every dermatology residency program is different, and as a result, each program is looking for different qualities in its applicants. Overall, I don’t think there has been a huge change in what programs are generally looking for, though. While each program may have a particular trait it values more than another, in general, programs are looking to find residents who will be competent and caring doctors, who work well in teams, and who could be future leaders in our field.
What are common mistakes you see in dermatology residency interviews, and how can applicants avoid them?
DR. WORSWICK: Most dermatology applicants are highly accomplished and empathic soon-to-be physicians, so I haven’t found a lot of “mistakes” from this incredible group of people that we have the privilege of interviewing. From time to time, an applicant will lie in an interview, usually out of a desire to appear to be a certain way, and occasionally, they may be nervous and stumble over their words. The former is a really big problem when it happens, and I would recommend that applicants be honest in all their encounters. The latter is not a major problem, and in some cases, might be avoided by lots of practice in advance.
What types of questions do you recommend applicants ask their interviewers to demonstrate genuine interest in the program?
DR. WORSWICK: Because of the signaling system, I think that programs assume interest at baseline once an applicant has sent the signal. So, “demonstrating interest” is generally not something I would recommend to applicants during the interview day. It is important for applicants to determine on interview day if a program is a fit for them, so applicants should showcase their unique strengths and skills and find out about what makes any given program different from another. The match generally works well and gets applicants into a program that closely aligns with their strengths and interests. So, think of interview day as your time to figure out how good a fit a program is for you, and not the other way around.
How can applicants who feel they don't have standout research or leadership credentials differentiate themselves in the interview?
DR. WORSWICK: While leadership, and less so research experience, is a trait valued highly by most if not all dermatology programs, it is only a part of what an applicant can offer a program. Most programs employ holistic review and consider several factors, probably most commonly grades in medical school, leadership experience, mentorship, teaching, volunteering, Step 2 scores, and letters of recommendation. Any given applicant does not need to excel in all of these. If an applicant has not done a lot of research, they may not match into a research-heavy program, but it doesn’t mean they won’t match. They should determine in which areas they shine and signal the programs that align with those interests/strengths.
How should applicants discuss nontraditional experiences in a way that adds value rather than raising red flags?
DR. WORSWICK: In general, my recommendation would be to explain what happened leading up to the change or challenge so that someone reading the application clearly understands the circumstances of the experience, then add value to the description by explaining what was learned and how this might relate to the applicant being a dermatology resident. For example, if a resident took time off for financial reasons and had to work as a medical assitant for a year, a concise description that explains the need for the leave (financial) as well as what value was gained (a year of hands-on patient care experience that validated their choice of going into medicine) could be very helpful.
What qualities are dermatology programs looking for that may be different from 5 years ago?
DR. WORSWICK: Every dermatology residency program is different, and as a result, each program is looking for different qualities in its applicants. Overall, I don’t think there has been a huge change in what programs are generally looking for, though. While each program may have a particular trait it values more than another, in general, programs are looking to find residents who will be competent and caring doctors, who work well in teams, and who could be future leaders in our field.
What are common mistakes you see in dermatology residency interviews, and how can applicants avoid them?
DR. WORSWICK: Most dermatology applicants are highly accomplished and empathic soon-to-be physicians, so I haven’t found a lot of “mistakes” from this incredible group of people that we have the privilege of interviewing. From time to time, an applicant will lie in an interview, usually out of a desire to appear to be a certain way, and occasionally, they may be nervous and stumble over their words. The former is a really big problem when it happens, and I would recommend that applicants be honest in all their encounters. The latter is not a major problem, and in some cases, might be avoided by lots of practice in advance.
What types of questions do you recommend applicants ask their interviewers to demonstrate genuine interest in the program?
DR. WORSWICK: Because of the signaling system, I think that programs assume interest at baseline once an applicant has sent the signal. So, “demonstrating interest” is generally not something I would recommend to applicants during the interview day. It is important for applicants to determine on interview day if a program is a fit for them, so applicants should showcase their unique strengths and skills and find out about what makes any given program different from another. The match generally works well and gets applicants into a program that closely aligns with their strengths and interests. So, think of interview day as your time to figure out how good a fit a program is for you, and not the other way around.
How can applicants who feel they don't have standout research or leadership credentials differentiate themselves in the interview?
DR. WORSWICK: While leadership, and less so research experience, is a trait valued highly by most if not all dermatology programs, it is only a part of what an applicant can offer a program. Most programs employ holistic review and consider several factors, probably most commonly grades in medical school, leadership experience, mentorship, teaching, volunteering, Step 2 scores, and letters of recommendation. Any given applicant does not need to excel in all of these. If an applicant has not done a lot of research, they may not match into a research-heavy program, but it doesn’t mean they won’t match. They should determine in which areas they shine and signal the programs that align with those interests/strengths.
How should applicants discuss nontraditional experiences in a way that adds value rather than raising red flags?
DR. WORSWICK: In general, my recommendation would be to explain what happened leading up to the change or challenge so that someone reading the application clearly understands the circumstances of the experience, then add value to the description by explaining what was learned and how this might relate to the applicant being a dermatology resident. For example, if a resident took time off for financial reasons and had to work as a medical assitant for a year, a concise description that explains the need for the leave (financial) as well as what value was gained (a year of hands-on patient care experience that validated their choice of going into medicine) could be very helpful.