User login
Updates on pregnancy outcomes in transgender men
Despite increased societal gains, transgender individuals are still a medically and socially underserved group. The historic rise of antitransgender legislation and the overturning of Roe v. Wade, further compound existing health care disparities, particularly in the realm of contraception and pregnancy. Obstetrician-gynecologists and midwives are typically first-line providers when discussing family planning and fertility options for all patients assigned female at birth. Unfortunately,
Only individuals who are assigned female at birth and have a uterus are capable of pregnancy. This can include both cisgender women and nonbinary/transgender men. However, societal and medical institutions are struggling with this shift in perspective from a traditionally gendered role to a more inclusive one. Obstetrician-gynecologists and midwives can serve to bridge this gap between these patients and societal misconceptions surrounding transgender men who desire and experience pregnancy.
Providers need to remember that many transmasculine individuals will still retain their uterus and are therefore capable of getting pregnant. While testosterone causes amenorrhea, if patients are engaging in penile-vaginal intercourse, conception is still possible. If a patient does not desire pregnancy, all contraceptive options available for cisgender women, which also include combined oral contraceptives, should be offered.
For patients seeking to become pregnant, testosterone must be discontinued. Testosterone is teratogenic; it can cause abnormal urogenital development in the female fetus and should be avoided even prior to conception.1,2 The timing of testosterone discontinuation is debatable. There are no well-established guidelines dictating how early pregnancy can be attempted after cessation of testosterone, but typically if menses has resumed, the teratogenic effects of testosterone are less likely.
For amenorrheic patients on testosterone, menses will occur, on average, 3-6 months after testosterone is stopped. Of note, the longer that testosterone has been suspended, the greater the likelihood of achieving pregnancy.3 In a study by Light et al., 72% of patients conceived within 6 months of attempting pregnancy, 80% resumed menses within 6 months of stopping testosterone, and 20% of individuals conceived while they were amenorrheic from testosterone.4
Psychosocial support is an essential part of pregnancy care in transgender men. For some patients, pregnancy can worsen gender dysphoria, whereas others are empowered by the experience. Insurance companies may also deny obstetric care services to transgender males who have already changed their gender marker from female to male on insurance policies.
Whether transmasculine individuals are at higher risk for pregnancy complications is largely unknown, although emerging research in this field has yielded interesting results. While testosterone can cause vaginal atrophy, it does not seem to increase a patient’s risk of vaginal lacerations or their ability to have a successful vaginal delivery. For transgender men with significant discomfort around their genitalia, an elective cesarean section may be appropriate.5
More recently, Stroumsa et al. conducted an analysis of all deliveries at a Michigan institution from 2014 to 2018. Patients with male gender at the time of delivery or with the diagnostic code of gender dysphoria were identified as transgender.6 The primary outcome of this study was severe parental morbidity (such as amniotic fluid embolism, acute myocardial infarction, eclampsia, etc.), with secondary outcomes investigating rates of cesarean delivery and preterm birth.
During this time period, the researchers identified 256 transgender patients and 1.3 million cisgender patients in their Medicaid database and 1,651 transgender patients and 1.5 million cisgender patients in the commercial database who had experienced a delivery.6 Compared with cisgender patients, transgender patients in the Medicaid database were younger, less likely to be white, and more likely to have a chronic condition.6 Compared with cisgender patients in the commercial database, transgender patients experienced higher rates of anxiety and depression.6 Both transgender and cisgender patients had similar rates of severe parental morbidity. Ironically, rates of cesarean delivery were lower, compared with cisgender patients, in both the Medicaid and commercial databases, with no differences observed between rates of preterm birth.6
While more research is needed on pregnancy in transgender men, this analysis is not only one of the largest to date, but it also challenges many misconceptions providers have regarding pregnancy outcomes. Even though transmasculine patients may require additional medical interventions to achieve pregnancy, such as assisted reproductive technology, or increased psychosocial support during the process, these initial studies are reassuring. Based on current evidence, these patients are not at greater risk for perinatal complications than their cisgender counterparts.
Despite these encouraging findings, there are still several challenges faced by transgender men when it comes to getting pregnant. For instance, they may have difficulty accessing fertility services because of financial constraints or experience a lack of awareness or prejudice from providers; they might also be subject to discrimination or stigma within health care settings. As front-line providers for obstetrical care, we must lead the way towards improving the care for pregnant transmasculine individuals.
Dr. Brandt is an ob.gyn. and fellowship-trained gender-affirming surgeon in West Reading, Pa.
References
1. Light A et al. Family planning and contraception use in transgender men. Contraception. 2018 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2018.06.006.
2. Krempasky C et al. Contraception across the transmasculine spectrum. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Feb. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2019.07.043.
3. Obedin-Maliver J, De Haan G. “Gynecologic care for transgender patients” in Ferrando C, ed., Comprehensive Care of the Transgender Patient. Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2019. 131-51.
4. Light AD et al. Transgender men who experienced pregnancy after female-to-male gender transitioning. Obstet Gynecol. 2014 Dec. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000000540.
5. Brandt JS et al. Transgender men, pregnancy, and the “new” advanced paternal age: A review of the literature. Maturitas. 2019 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2019.07.004.
6. Stroumsa D et al. Pregnancy outcomes in a U.S. cohort of transgender people. JAMA. 2023 Jun 6. doi: 10.1001/jama.2023.7688.
Despite increased societal gains, transgender individuals are still a medically and socially underserved group. The historic rise of antitransgender legislation and the overturning of Roe v. Wade, further compound existing health care disparities, particularly in the realm of contraception and pregnancy. Obstetrician-gynecologists and midwives are typically first-line providers when discussing family planning and fertility options for all patients assigned female at birth. Unfortunately,
Only individuals who are assigned female at birth and have a uterus are capable of pregnancy. This can include both cisgender women and nonbinary/transgender men. However, societal and medical institutions are struggling with this shift in perspective from a traditionally gendered role to a more inclusive one. Obstetrician-gynecologists and midwives can serve to bridge this gap between these patients and societal misconceptions surrounding transgender men who desire and experience pregnancy.
Providers need to remember that many transmasculine individuals will still retain their uterus and are therefore capable of getting pregnant. While testosterone causes amenorrhea, if patients are engaging in penile-vaginal intercourse, conception is still possible. If a patient does not desire pregnancy, all contraceptive options available for cisgender women, which also include combined oral contraceptives, should be offered.
For patients seeking to become pregnant, testosterone must be discontinued. Testosterone is teratogenic; it can cause abnormal urogenital development in the female fetus and should be avoided even prior to conception.1,2 The timing of testosterone discontinuation is debatable. There are no well-established guidelines dictating how early pregnancy can be attempted after cessation of testosterone, but typically if menses has resumed, the teratogenic effects of testosterone are less likely.
For amenorrheic patients on testosterone, menses will occur, on average, 3-6 months after testosterone is stopped. Of note, the longer that testosterone has been suspended, the greater the likelihood of achieving pregnancy.3 In a study by Light et al., 72% of patients conceived within 6 months of attempting pregnancy, 80% resumed menses within 6 months of stopping testosterone, and 20% of individuals conceived while they were amenorrheic from testosterone.4
Psychosocial support is an essential part of pregnancy care in transgender men. For some patients, pregnancy can worsen gender dysphoria, whereas others are empowered by the experience. Insurance companies may also deny obstetric care services to transgender males who have already changed their gender marker from female to male on insurance policies.
Whether transmasculine individuals are at higher risk for pregnancy complications is largely unknown, although emerging research in this field has yielded interesting results. While testosterone can cause vaginal atrophy, it does not seem to increase a patient’s risk of vaginal lacerations or their ability to have a successful vaginal delivery. For transgender men with significant discomfort around their genitalia, an elective cesarean section may be appropriate.5
More recently, Stroumsa et al. conducted an analysis of all deliveries at a Michigan institution from 2014 to 2018. Patients with male gender at the time of delivery or with the diagnostic code of gender dysphoria were identified as transgender.6 The primary outcome of this study was severe parental morbidity (such as amniotic fluid embolism, acute myocardial infarction, eclampsia, etc.), with secondary outcomes investigating rates of cesarean delivery and preterm birth.
During this time period, the researchers identified 256 transgender patients and 1.3 million cisgender patients in their Medicaid database and 1,651 transgender patients and 1.5 million cisgender patients in the commercial database who had experienced a delivery.6 Compared with cisgender patients, transgender patients in the Medicaid database were younger, less likely to be white, and more likely to have a chronic condition.6 Compared with cisgender patients in the commercial database, transgender patients experienced higher rates of anxiety and depression.6 Both transgender and cisgender patients had similar rates of severe parental morbidity. Ironically, rates of cesarean delivery were lower, compared with cisgender patients, in both the Medicaid and commercial databases, with no differences observed between rates of preterm birth.6
While more research is needed on pregnancy in transgender men, this analysis is not only one of the largest to date, but it also challenges many misconceptions providers have regarding pregnancy outcomes. Even though transmasculine patients may require additional medical interventions to achieve pregnancy, such as assisted reproductive technology, or increased psychosocial support during the process, these initial studies are reassuring. Based on current evidence, these patients are not at greater risk for perinatal complications than their cisgender counterparts.
Despite these encouraging findings, there are still several challenges faced by transgender men when it comes to getting pregnant. For instance, they may have difficulty accessing fertility services because of financial constraints or experience a lack of awareness or prejudice from providers; they might also be subject to discrimination or stigma within health care settings. As front-line providers for obstetrical care, we must lead the way towards improving the care for pregnant transmasculine individuals.
Dr. Brandt is an ob.gyn. and fellowship-trained gender-affirming surgeon in West Reading, Pa.
References
1. Light A et al. Family planning and contraception use in transgender men. Contraception. 2018 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2018.06.006.
2. Krempasky C et al. Contraception across the transmasculine spectrum. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Feb. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2019.07.043.
3. Obedin-Maliver J, De Haan G. “Gynecologic care for transgender patients” in Ferrando C, ed., Comprehensive Care of the Transgender Patient. Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2019. 131-51.
4. Light AD et al. Transgender men who experienced pregnancy after female-to-male gender transitioning. Obstet Gynecol. 2014 Dec. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000000540.
5. Brandt JS et al. Transgender men, pregnancy, and the “new” advanced paternal age: A review of the literature. Maturitas. 2019 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2019.07.004.
6. Stroumsa D et al. Pregnancy outcomes in a U.S. cohort of transgender people. JAMA. 2023 Jun 6. doi: 10.1001/jama.2023.7688.
Despite increased societal gains, transgender individuals are still a medically and socially underserved group. The historic rise of antitransgender legislation and the overturning of Roe v. Wade, further compound existing health care disparities, particularly in the realm of contraception and pregnancy. Obstetrician-gynecologists and midwives are typically first-line providers when discussing family planning and fertility options for all patients assigned female at birth. Unfortunately,
Only individuals who are assigned female at birth and have a uterus are capable of pregnancy. This can include both cisgender women and nonbinary/transgender men. However, societal and medical institutions are struggling with this shift in perspective from a traditionally gendered role to a more inclusive one. Obstetrician-gynecologists and midwives can serve to bridge this gap between these patients and societal misconceptions surrounding transgender men who desire and experience pregnancy.
Providers need to remember that many transmasculine individuals will still retain their uterus and are therefore capable of getting pregnant. While testosterone causes amenorrhea, if patients are engaging in penile-vaginal intercourse, conception is still possible. If a patient does not desire pregnancy, all contraceptive options available for cisgender women, which also include combined oral contraceptives, should be offered.
For patients seeking to become pregnant, testosterone must be discontinued. Testosterone is teratogenic; it can cause abnormal urogenital development in the female fetus and should be avoided even prior to conception.1,2 The timing of testosterone discontinuation is debatable. There are no well-established guidelines dictating how early pregnancy can be attempted after cessation of testosterone, but typically if menses has resumed, the teratogenic effects of testosterone are less likely.
For amenorrheic patients on testosterone, menses will occur, on average, 3-6 months after testosterone is stopped. Of note, the longer that testosterone has been suspended, the greater the likelihood of achieving pregnancy.3 In a study by Light et al., 72% of patients conceived within 6 months of attempting pregnancy, 80% resumed menses within 6 months of stopping testosterone, and 20% of individuals conceived while they were amenorrheic from testosterone.4
Psychosocial support is an essential part of pregnancy care in transgender men. For some patients, pregnancy can worsen gender dysphoria, whereas others are empowered by the experience. Insurance companies may also deny obstetric care services to transgender males who have already changed their gender marker from female to male on insurance policies.
Whether transmasculine individuals are at higher risk for pregnancy complications is largely unknown, although emerging research in this field has yielded interesting results. While testosterone can cause vaginal atrophy, it does not seem to increase a patient’s risk of vaginal lacerations or their ability to have a successful vaginal delivery. For transgender men with significant discomfort around their genitalia, an elective cesarean section may be appropriate.5
More recently, Stroumsa et al. conducted an analysis of all deliveries at a Michigan institution from 2014 to 2018. Patients with male gender at the time of delivery or with the diagnostic code of gender dysphoria were identified as transgender.6 The primary outcome of this study was severe parental morbidity (such as amniotic fluid embolism, acute myocardial infarction, eclampsia, etc.), with secondary outcomes investigating rates of cesarean delivery and preterm birth.
During this time period, the researchers identified 256 transgender patients and 1.3 million cisgender patients in their Medicaid database and 1,651 transgender patients and 1.5 million cisgender patients in the commercial database who had experienced a delivery.6 Compared with cisgender patients, transgender patients in the Medicaid database were younger, less likely to be white, and more likely to have a chronic condition.6 Compared with cisgender patients in the commercial database, transgender patients experienced higher rates of anxiety and depression.6 Both transgender and cisgender patients had similar rates of severe parental morbidity. Ironically, rates of cesarean delivery were lower, compared with cisgender patients, in both the Medicaid and commercial databases, with no differences observed between rates of preterm birth.6
While more research is needed on pregnancy in transgender men, this analysis is not only one of the largest to date, but it also challenges many misconceptions providers have regarding pregnancy outcomes. Even though transmasculine patients may require additional medical interventions to achieve pregnancy, such as assisted reproductive technology, or increased psychosocial support during the process, these initial studies are reassuring. Based on current evidence, these patients are not at greater risk for perinatal complications than their cisgender counterparts.
Despite these encouraging findings, there are still several challenges faced by transgender men when it comes to getting pregnant. For instance, they may have difficulty accessing fertility services because of financial constraints or experience a lack of awareness or prejudice from providers; they might also be subject to discrimination or stigma within health care settings. As front-line providers for obstetrical care, we must lead the way towards improving the care for pregnant transmasculine individuals.
Dr. Brandt is an ob.gyn. and fellowship-trained gender-affirming surgeon in West Reading, Pa.
References
1. Light A et al. Family planning and contraception use in transgender men. Contraception. 2018 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2018.06.006.
2. Krempasky C et al. Contraception across the transmasculine spectrum. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Feb. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2019.07.043.
3. Obedin-Maliver J, De Haan G. “Gynecologic care for transgender patients” in Ferrando C, ed., Comprehensive Care of the Transgender Patient. Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2019. 131-51.
4. Light AD et al. Transgender men who experienced pregnancy after female-to-male gender transitioning. Obstet Gynecol. 2014 Dec. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000000540.
5. Brandt JS et al. Transgender men, pregnancy, and the “new” advanced paternal age: A review of the literature. Maturitas. 2019 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2019.07.004.
6. Stroumsa D et al. Pregnancy outcomes in a U.S. cohort of transgender people. JAMA. 2023 Jun 6. doi: 10.1001/jama.2023.7688.
PCOS associated with shorter lifespan
CHICAGO –
In the study, involving nearly 10,000 women with PCOS and matched controls from Finland, women with PCOS died on average a year earlier than their age-matched counterparts, primarily from diseases of the circulatory system, cancer, and diabetes.
PCOS is the most common endocrine disorder of reproductive-age women, of whom about 50%-70% also have obesity.
“I think we need to acknowledge that this is a health burden and not just a reproductive problem. In many cases we deal with the reproductive problem, and then these women are left alone. … So I think the message is we need to look beyond the reproductive outcomes, which are … really good. We can manage that,” said Terhi T. Piltonen, MD, PhD, during a press briefing held June 15 at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
“I think the difficult part is [managing] the lifelong health for these women and supporting them to achieve the best health they can get. We need a multidisciplinary effort and to put more resources into the research,” added Dr. Piltonen, professor in the departments of ob.gyn. and reproductive endocrinology at the University of Oulu, Finland.
Indeed, Punith Kempegowda, MD, PhD, of the University of Birmingham (England) observed: “In our medical schools in the U.K., over 5 years, students get 45 minutes [of education] on PCOS, and they’re expected to learn about it.”
And over the last 20 years, funding for research into the condition has totaled less than a half percent of overall medical funding. “And we’re talking about 10% of all women. …We need to acknowledge it and educate people more. We need more published studies to understand more about it,” he noted.
Asked to comment, Greg Dodell, MD, owner and president of Central Park Endocrinology, New York, said: “PCOS is about a lot more than fertility, and that may not be the goal or on the mind of a woman at the time they start having symptoms of PCOS or get the diagnosis.”
“PCOS is largely a metabolic condition rooted in insulin resistance, and therefore, the potential clinical outcomes, including mortality, are important to recognize.”
Dr. Dodell, who has a special interest in PCOS, advised that, for women with the condition, “focus on reducing insulin resistance with health-promoting behaviors and medications as needed. Data demonstrate that improving fitness, irrespective of a change in weight, can improve metabolic markers.” And, he advised that these women be routinely screened for mental health issues.
He also noted, “PCOS occurs across the size spectrum, but those patients in larger bodies may face weight stigma which has negative health consequences. These patients may avoid going to doctors for routine health screenings, so it is an important issue to continue to address.”
Women with PCOS lose a year of life
The new data come from 9,839 women with PCOS and 70,705 age- and region-matched controls from the Finnish Care Register for Health Care. The group with PCOS had been diagnosed at a mean age of 27 years.
The mean follow-up time was 13.1 years in both groups, during which 1,003 controls and 177 women with PCOS died. The mean age at death was 51.4 years for the PCOS group versus 52.6 years for the control women, a significant difference (P < .001).
Causes of death that were significantly higher among the women with PCOS versus controls after adjustments were cancer (hazard ratio, 1.39), and diseases of the circulatory system (1.68).
In more specific subcategories, after adjustment for education, the women with PCOS had increased mortality from nonischemic diseases, such as hypertensive heart disease, pulmonary embolism, etc. (HR, 2.06), and diabetes (HR, 2.85).
One study limitation was the inability to adjust for body mass index, Dr. Piltonen noted.
Dr. Piltonen, Dr. Kempegowda, and Dr. Dodell have no disclosures.
CHICAGO –
In the study, involving nearly 10,000 women with PCOS and matched controls from Finland, women with PCOS died on average a year earlier than their age-matched counterparts, primarily from diseases of the circulatory system, cancer, and diabetes.
PCOS is the most common endocrine disorder of reproductive-age women, of whom about 50%-70% also have obesity.
“I think we need to acknowledge that this is a health burden and not just a reproductive problem. In many cases we deal with the reproductive problem, and then these women are left alone. … So I think the message is we need to look beyond the reproductive outcomes, which are … really good. We can manage that,” said Terhi T. Piltonen, MD, PhD, during a press briefing held June 15 at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
“I think the difficult part is [managing] the lifelong health for these women and supporting them to achieve the best health they can get. We need a multidisciplinary effort and to put more resources into the research,” added Dr. Piltonen, professor in the departments of ob.gyn. and reproductive endocrinology at the University of Oulu, Finland.
Indeed, Punith Kempegowda, MD, PhD, of the University of Birmingham (England) observed: “In our medical schools in the U.K., over 5 years, students get 45 minutes [of education] on PCOS, and they’re expected to learn about it.”
And over the last 20 years, funding for research into the condition has totaled less than a half percent of overall medical funding. “And we’re talking about 10% of all women. …We need to acknowledge it and educate people more. We need more published studies to understand more about it,” he noted.
Asked to comment, Greg Dodell, MD, owner and president of Central Park Endocrinology, New York, said: “PCOS is about a lot more than fertility, and that may not be the goal or on the mind of a woman at the time they start having symptoms of PCOS or get the diagnosis.”
“PCOS is largely a metabolic condition rooted in insulin resistance, and therefore, the potential clinical outcomes, including mortality, are important to recognize.”
Dr. Dodell, who has a special interest in PCOS, advised that, for women with the condition, “focus on reducing insulin resistance with health-promoting behaviors and medications as needed. Data demonstrate that improving fitness, irrespective of a change in weight, can improve metabolic markers.” And, he advised that these women be routinely screened for mental health issues.
He also noted, “PCOS occurs across the size spectrum, but those patients in larger bodies may face weight stigma which has negative health consequences. These patients may avoid going to doctors for routine health screenings, so it is an important issue to continue to address.”
Women with PCOS lose a year of life
The new data come from 9,839 women with PCOS and 70,705 age- and region-matched controls from the Finnish Care Register for Health Care. The group with PCOS had been diagnosed at a mean age of 27 years.
The mean follow-up time was 13.1 years in both groups, during which 1,003 controls and 177 women with PCOS died. The mean age at death was 51.4 years for the PCOS group versus 52.6 years for the control women, a significant difference (P < .001).
Causes of death that were significantly higher among the women with PCOS versus controls after adjustments were cancer (hazard ratio, 1.39), and diseases of the circulatory system (1.68).
In more specific subcategories, after adjustment for education, the women with PCOS had increased mortality from nonischemic diseases, such as hypertensive heart disease, pulmonary embolism, etc. (HR, 2.06), and diabetes (HR, 2.85).
One study limitation was the inability to adjust for body mass index, Dr. Piltonen noted.
Dr. Piltonen, Dr. Kempegowda, and Dr. Dodell have no disclosures.
CHICAGO –
In the study, involving nearly 10,000 women with PCOS and matched controls from Finland, women with PCOS died on average a year earlier than their age-matched counterparts, primarily from diseases of the circulatory system, cancer, and diabetes.
PCOS is the most common endocrine disorder of reproductive-age women, of whom about 50%-70% also have obesity.
“I think we need to acknowledge that this is a health burden and not just a reproductive problem. In many cases we deal with the reproductive problem, and then these women are left alone. … So I think the message is we need to look beyond the reproductive outcomes, which are … really good. We can manage that,” said Terhi T. Piltonen, MD, PhD, during a press briefing held June 15 at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
“I think the difficult part is [managing] the lifelong health for these women and supporting them to achieve the best health they can get. We need a multidisciplinary effort and to put more resources into the research,” added Dr. Piltonen, professor in the departments of ob.gyn. and reproductive endocrinology at the University of Oulu, Finland.
Indeed, Punith Kempegowda, MD, PhD, of the University of Birmingham (England) observed: “In our medical schools in the U.K., over 5 years, students get 45 minutes [of education] on PCOS, and they’re expected to learn about it.”
And over the last 20 years, funding for research into the condition has totaled less than a half percent of overall medical funding. “And we’re talking about 10% of all women. …We need to acknowledge it and educate people more. We need more published studies to understand more about it,” he noted.
Asked to comment, Greg Dodell, MD, owner and president of Central Park Endocrinology, New York, said: “PCOS is about a lot more than fertility, and that may not be the goal or on the mind of a woman at the time they start having symptoms of PCOS or get the diagnosis.”
“PCOS is largely a metabolic condition rooted in insulin resistance, and therefore, the potential clinical outcomes, including mortality, are important to recognize.”
Dr. Dodell, who has a special interest in PCOS, advised that, for women with the condition, “focus on reducing insulin resistance with health-promoting behaviors and medications as needed. Data demonstrate that improving fitness, irrespective of a change in weight, can improve metabolic markers.” And, he advised that these women be routinely screened for mental health issues.
He also noted, “PCOS occurs across the size spectrum, but those patients in larger bodies may face weight stigma which has negative health consequences. These patients may avoid going to doctors for routine health screenings, so it is an important issue to continue to address.”
Women with PCOS lose a year of life
The new data come from 9,839 women with PCOS and 70,705 age- and region-matched controls from the Finnish Care Register for Health Care. The group with PCOS had been diagnosed at a mean age of 27 years.
The mean follow-up time was 13.1 years in both groups, during which 1,003 controls and 177 women with PCOS died. The mean age at death was 51.4 years for the PCOS group versus 52.6 years for the control women, a significant difference (P < .001).
Causes of death that were significantly higher among the women with PCOS versus controls after adjustments were cancer (hazard ratio, 1.39), and diseases of the circulatory system (1.68).
In more specific subcategories, after adjustment for education, the women with PCOS had increased mortality from nonischemic diseases, such as hypertensive heart disease, pulmonary embolism, etc. (HR, 2.06), and diabetes (HR, 2.85).
One study limitation was the inability to adjust for body mass index, Dr. Piltonen noted.
Dr. Piltonen, Dr. Kempegowda, and Dr. Dodell have no disclosures.
AT ENDO 2023
Vulvodynia: A little-known and treatable condition
Vulvodynia is a little-known condition that, according to some U.S. studies, affects 3%-14% of the female population. It is defined as chronic pain, present for at least 3 months, that generally involves the vulva or some of its specific areas such as the clitoris or vestibule and is not attributable to causes of an infectious, inflammatory, oncologic, or endocrine nature; skin trauma; or damage to nerve fibers.
“There are probably many more women who suffer from it who don’t talk about it out of shame, because they feel ‘wrong,’ ” said gynecologist Pina Belfiore, MD, chair of the Italian Interdisciplinary Society of Vulvology, at the annual conference of the Italian Society of Gender Medicine in Neurosciences. “It is a treatable condition, or at the very least, a patient’s quality of life can be significantly improved with a personalized therapeutic approach.”
The correct diagnosis
The first step for setting the patient on the right course toward recovery is to offer welcome and empathy, recognizing that the suffering, which can have psychological causes, is not imaginary. “We need to explain to patients that their condition has a name, that they are not alone in this situation, and, above all, that there is hope for solving the problem. They can get through it,” said Dr. Belfiore.
First, an accurate history of the pain is needed to correctly diagnose vulvodynia. How long has the pain been going on? Is it continuous or is it triggered by an environmental factor, for example by sexual intercourse or contact with underwear? Is it a burning or stinging sensation? Did it first occur after an infection or after a physical or psychological trauma? Does the patient suffer from other forms of chronic pain such as recurring headaches or fibromyalgia?
“It is then necessary to inspect the vulva to exclude other systematic conditions or injuries that may be responsible for the pain, as well as to locate hypersensitive areas and evaluate the intensity of the symptoms,” said Dr. Belfiore.” A swab test is performed for this purpose, which is carried out by applying light pressure on different points of the vulva with a cotton swab.”
CNS dysfunction
, which confuses signals coming from the peripheral area, interpreting signals of a different nature as painful stimuli.
“The origin of this dysfunction is an individual predisposition. In fact, often the women who suffer from it are also affected by other forms of chronic pain,” said Dr. Belfiore. “Triggers for vulvodynia can be bacterial infections, candidiasis, or traumatic events such as surgically assisted birth or psychological trauma.”
Because inflammatory mechanisms are not involved, anti-inflammatory drugs are not helpful in treating the problem. “Instead, it is necessary to reduce the sensitivity of the CNS. For this purpose, low-dose antidepressant or antiepileptic drugs are used,” said Dr. Belfiore. “Pelvic floor rehabilitation is another treatment that can be beneficial when combined with pharmacologic treatment. This should be conducted by a professional with specific experience in vulvodynia, because an excessive increase in the tone of the levator ani muscle can make the situation worse. Psychotherapy and the adoption of certain hygienic and behavioral measures can also help, such as using lubricant during sexual intercourse, wearing pure cotton underwear, and using gentle intimate body washes.”
“It is important that family doctors who see women with this problem refer them to an experienced specialist,” said Dr. Belfiore.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was translated from Univadis Italy, which is part of the Medscape Professional Network.
Vulvodynia is a little-known condition that, according to some U.S. studies, affects 3%-14% of the female population. It is defined as chronic pain, present for at least 3 months, that generally involves the vulva or some of its specific areas such as the clitoris or vestibule and is not attributable to causes of an infectious, inflammatory, oncologic, or endocrine nature; skin trauma; or damage to nerve fibers.
“There are probably many more women who suffer from it who don’t talk about it out of shame, because they feel ‘wrong,’ ” said gynecologist Pina Belfiore, MD, chair of the Italian Interdisciplinary Society of Vulvology, at the annual conference of the Italian Society of Gender Medicine in Neurosciences. “It is a treatable condition, or at the very least, a patient’s quality of life can be significantly improved with a personalized therapeutic approach.”
The correct diagnosis
The first step for setting the patient on the right course toward recovery is to offer welcome and empathy, recognizing that the suffering, which can have psychological causes, is not imaginary. “We need to explain to patients that their condition has a name, that they are not alone in this situation, and, above all, that there is hope for solving the problem. They can get through it,” said Dr. Belfiore.
First, an accurate history of the pain is needed to correctly diagnose vulvodynia. How long has the pain been going on? Is it continuous or is it triggered by an environmental factor, for example by sexual intercourse or contact with underwear? Is it a burning or stinging sensation? Did it first occur after an infection or after a physical or psychological trauma? Does the patient suffer from other forms of chronic pain such as recurring headaches or fibromyalgia?
“It is then necessary to inspect the vulva to exclude other systematic conditions or injuries that may be responsible for the pain, as well as to locate hypersensitive areas and evaluate the intensity of the symptoms,” said Dr. Belfiore.” A swab test is performed for this purpose, which is carried out by applying light pressure on different points of the vulva with a cotton swab.”
CNS dysfunction
, which confuses signals coming from the peripheral area, interpreting signals of a different nature as painful stimuli.
“The origin of this dysfunction is an individual predisposition. In fact, often the women who suffer from it are also affected by other forms of chronic pain,” said Dr. Belfiore. “Triggers for vulvodynia can be bacterial infections, candidiasis, or traumatic events such as surgically assisted birth or psychological trauma.”
Because inflammatory mechanisms are not involved, anti-inflammatory drugs are not helpful in treating the problem. “Instead, it is necessary to reduce the sensitivity of the CNS. For this purpose, low-dose antidepressant or antiepileptic drugs are used,” said Dr. Belfiore. “Pelvic floor rehabilitation is another treatment that can be beneficial when combined with pharmacologic treatment. This should be conducted by a professional with specific experience in vulvodynia, because an excessive increase in the tone of the levator ani muscle can make the situation worse. Psychotherapy and the adoption of certain hygienic and behavioral measures can also help, such as using lubricant during sexual intercourse, wearing pure cotton underwear, and using gentle intimate body washes.”
“It is important that family doctors who see women with this problem refer them to an experienced specialist,” said Dr. Belfiore.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was translated from Univadis Italy, which is part of the Medscape Professional Network.
Vulvodynia is a little-known condition that, according to some U.S. studies, affects 3%-14% of the female population. It is defined as chronic pain, present for at least 3 months, that generally involves the vulva or some of its specific areas such as the clitoris or vestibule and is not attributable to causes of an infectious, inflammatory, oncologic, or endocrine nature; skin trauma; or damage to nerve fibers.
“There are probably many more women who suffer from it who don’t talk about it out of shame, because they feel ‘wrong,’ ” said gynecologist Pina Belfiore, MD, chair of the Italian Interdisciplinary Society of Vulvology, at the annual conference of the Italian Society of Gender Medicine in Neurosciences. “It is a treatable condition, or at the very least, a patient’s quality of life can be significantly improved with a personalized therapeutic approach.”
The correct diagnosis
The first step for setting the patient on the right course toward recovery is to offer welcome and empathy, recognizing that the suffering, which can have psychological causes, is not imaginary. “We need to explain to patients that their condition has a name, that they are not alone in this situation, and, above all, that there is hope for solving the problem. They can get through it,” said Dr. Belfiore.
First, an accurate history of the pain is needed to correctly diagnose vulvodynia. How long has the pain been going on? Is it continuous or is it triggered by an environmental factor, for example by sexual intercourse or contact with underwear? Is it a burning or stinging sensation? Did it first occur after an infection or after a physical or psychological trauma? Does the patient suffer from other forms of chronic pain such as recurring headaches or fibromyalgia?
“It is then necessary to inspect the vulva to exclude other systematic conditions or injuries that may be responsible for the pain, as well as to locate hypersensitive areas and evaluate the intensity of the symptoms,” said Dr. Belfiore.” A swab test is performed for this purpose, which is carried out by applying light pressure on different points of the vulva with a cotton swab.”
CNS dysfunction
, which confuses signals coming from the peripheral area, interpreting signals of a different nature as painful stimuli.
“The origin of this dysfunction is an individual predisposition. In fact, often the women who suffer from it are also affected by other forms of chronic pain,” said Dr. Belfiore. “Triggers for vulvodynia can be bacterial infections, candidiasis, or traumatic events such as surgically assisted birth or psychological trauma.”
Because inflammatory mechanisms are not involved, anti-inflammatory drugs are not helpful in treating the problem. “Instead, it is necessary to reduce the sensitivity of the CNS. For this purpose, low-dose antidepressant or antiepileptic drugs are used,” said Dr. Belfiore. “Pelvic floor rehabilitation is another treatment that can be beneficial when combined with pharmacologic treatment. This should be conducted by a professional with specific experience in vulvodynia, because an excessive increase in the tone of the levator ani muscle can make the situation worse. Psychotherapy and the adoption of certain hygienic and behavioral measures can also help, such as using lubricant during sexual intercourse, wearing pure cotton underwear, and using gentle intimate body washes.”
“It is important that family doctors who see women with this problem refer them to an experienced specialist,” said Dr. Belfiore.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was translated from Univadis Italy, which is part of the Medscape Professional Network.
Surgical de-escalation passes clinical test in low-risk cervical cancer
CHICAGO –
“Following adequate and rigorous preoperative assessment, and that’s key – very careful [patient selection] – simple hysterectomies can now be considered the new standard of care for patients with low-risk early-stage cervical cancer,” said Marie Plante, MD, during a presentation of the study at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. A simple hysterectomy removes the uterus and cervix, while a radical hysterectomy also removes the parametrium and upper vagina.
Cervical cancer incidence has gone down over the past 2 decades as a result of improved screening, and patients tend to be lower in age and are more likely to have low-risk, early-stage disease, according to Dr. Plante. “Although radical surgery is highly effective for the treatment of low-risk disease, women are at risk of suffering survivorship issues related to long-term surgical side effects including compromised bladder, bowel, and sexual function,” said Dr. Plante, who is a professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Laval University and head of clinical research at l’Hôtel-Dieu de Québec, both in Quebec City.
Retrospective studies found that infiltration of the parametrium is quite rare in low-risk cases, “suggesting that less radical surgery may be a safe option associated with decreased morbidity – what we call surgical de-escalation,” said Dr. Plante.
To test that idea more rigorously, the researchers designed the SHAPE trial, which randomized 700 women to a simple hysterectomy or radical hysterectomy. Patients were carefully selected to be low risk, having squamous cell, adenocarcinoma, or adenosquamous carcinoma, stage IA2 or IB2 tumors, fewer than 10 mm of stromal invasion on loop electrosurgical excision procedure or cone biopsy, less than 50% stromal invasion seen in MRI, and a maximum tumor dimension of 20 mm or less. Tumors were grade I-III or not assessable.
Over a median follow-up of 4.5 years, pelvic recurrence was 2.52% in the simple hysterectomy group and 2.17% in the radical hysterectomy group. The difference between the recurrence rate between the two groups was 0.35%, with an upper 95% confidence limit of 2.32%, below the threshold of 4% which had been predetermined as a benchmark for similar outcomes between the two groups. “Therefore, noninferiority of simple hysterectomy to radical hysterectomy could be concluded,” said Dr. Plante.
There were no statistically significant differences in intraoperative complications or mortality between the groups.
Surgery-related adverse events greater in radical hysterectomy group
There were some differences between the groups with respect to surgery-related adverse events. Within 4 weeks of surgery, there was a greater incidence of any adverse event in the radical hysterectomy group (50.6% vs. 42.6%; P = .04), as well as greater incidences of urinary incontinence (5.5% vs. 2.4%; P = .048) and urinary retention (11.0% vs. 0.6%; P < .0001). In the 4 weeks following surgery, there was a trend toward more surgery-related adverse events in the radical hysterectomy group (60.5% vs. 53.6%; P = .08) and higher incidences of urinary incontinence (11.0% vs. 4.7%; P = .003) and urinary retention (9.9% vs. 0.6%; P < .0001).
“Urinary incontinence and urinary retention are statistically worse in the radical hysterectomy group – both acutely, as well as [during] the following four weeks after surgery, suggesting that the problem persisted over time,” said Dr. Plante.
Dr. Plante also presented the study at a premeeting virtual press conference, during which Kathleen Moore, MD, provided comments on the study. She expressed enthusiasm about the results.
“Amongst those carefully selected tumors, radical hysterectomy can be converted to a simple hysterectomy, including minimally invasive. You still have to do nodes – that’s an important thing to remember – but you can do this without loss of oncologic control. And importantly, with reduction in surgical complications, postop morbidity, specifically neurologic morbidity. The moment this is presented [at the ASCO conference] this will be the new standard of care, and it represents a huge step forward in the care of women with early-stage cervical cancer,” said Dr. Moore, who is a professor of gynecologic oncology at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City.
Also in the press conference, Dr. Plante emphasized the importance of a thorough understanding of the tumor, including size, imaging, and pathology. “The more conservative one wants to be, the more meticulous, the more careful one has to be to make sure that we’re truly dealing with low-risk patients.”
During the question-and-answer session following her presentation at the ASCO session, a moderator asked Dr. Plante if the presence of lymph vascular space invasion (LVSI) should prompt a radical hysterectomy.
Dr. Plante noted that about 13% of both radical and simple hysterectomy groups had LVSI present. “I think the key thing is careful selection, but I’m not sure that we should exclude LVSI [from consideration for simple hysterectomy] de facto,” she said.
Dr. Plante has consulted or advised Merck Serono and has received travel, accommodations, or other expenses from AstraZeneca. Dr. Moore has consulted, advised, and received research funding and travel expenses from numerous pharmaceutical companies.
CHICAGO –
“Following adequate and rigorous preoperative assessment, and that’s key – very careful [patient selection] – simple hysterectomies can now be considered the new standard of care for patients with low-risk early-stage cervical cancer,” said Marie Plante, MD, during a presentation of the study at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. A simple hysterectomy removes the uterus and cervix, while a radical hysterectomy also removes the parametrium and upper vagina.
Cervical cancer incidence has gone down over the past 2 decades as a result of improved screening, and patients tend to be lower in age and are more likely to have low-risk, early-stage disease, according to Dr. Plante. “Although radical surgery is highly effective for the treatment of low-risk disease, women are at risk of suffering survivorship issues related to long-term surgical side effects including compromised bladder, bowel, and sexual function,” said Dr. Plante, who is a professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Laval University and head of clinical research at l’Hôtel-Dieu de Québec, both in Quebec City.
Retrospective studies found that infiltration of the parametrium is quite rare in low-risk cases, “suggesting that less radical surgery may be a safe option associated with decreased morbidity – what we call surgical de-escalation,” said Dr. Plante.
To test that idea more rigorously, the researchers designed the SHAPE trial, which randomized 700 women to a simple hysterectomy or radical hysterectomy. Patients were carefully selected to be low risk, having squamous cell, adenocarcinoma, or adenosquamous carcinoma, stage IA2 or IB2 tumors, fewer than 10 mm of stromal invasion on loop electrosurgical excision procedure or cone biopsy, less than 50% stromal invasion seen in MRI, and a maximum tumor dimension of 20 mm or less. Tumors were grade I-III or not assessable.
Over a median follow-up of 4.5 years, pelvic recurrence was 2.52% in the simple hysterectomy group and 2.17% in the radical hysterectomy group. The difference between the recurrence rate between the two groups was 0.35%, with an upper 95% confidence limit of 2.32%, below the threshold of 4% which had been predetermined as a benchmark for similar outcomes between the two groups. “Therefore, noninferiority of simple hysterectomy to radical hysterectomy could be concluded,” said Dr. Plante.
There were no statistically significant differences in intraoperative complications or mortality between the groups.
Surgery-related adverse events greater in radical hysterectomy group
There were some differences between the groups with respect to surgery-related adverse events. Within 4 weeks of surgery, there was a greater incidence of any adverse event in the radical hysterectomy group (50.6% vs. 42.6%; P = .04), as well as greater incidences of urinary incontinence (5.5% vs. 2.4%; P = .048) and urinary retention (11.0% vs. 0.6%; P < .0001). In the 4 weeks following surgery, there was a trend toward more surgery-related adverse events in the radical hysterectomy group (60.5% vs. 53.6%; P = .08) and higher incidences of urinary incontinence (11.0% vs. 4.7%; P = .003) and urinary retention (9.9% vs. 0.6%; P < .0001).
“Urinary incontinence and urinary retention are statistically worse in the radical hysterectomy group – both acutely, as well as [during] the following four weeks after surgery, suggesting that the problem persisted over time,” said Dr. Plante.
Dr. Plante also presented the study at a premeeting virtual press conference, during which Kathleen Moore, MD, provided comments on the study. She expressed enthusiasm about the results.
“Amongst those carefully selected tumors, radical hysterectomy can be converted to a simple hysterectomy, including minimally invasive. You still have to do nodes – that’s an important thing to remember – but you can do this without loss of oncologic control. And importantly, with reduction in surgical complications, postop morbidity, specifically neurologic morbidity. The moment this is presented [at the ASCO conference] this will be the new standard of care, and it represents a huge step forward in the care of women with early-stage cervical cancer,” said Dr. Moore, who is a professor of gynecologic oncology at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City.
Also in the press conference, Dr. Plante emphasized the importance of a thorough understanding of the tumor, including size, imaging, and pathology. “The more conservative one wants to be, the more meticulous, the more careful one has to be to make sure that we’re truly dealing with low-risk patients.”
During the question-and-answer session following her presentation at the ASCO session, a moderator asked Dr. Plante if the presence of lymph vascular space invasion (LVSI) should prompt a radical hysterectomy.
Dr. Plante noted that about 13% of both radical and simple hysterectomy groups had LVSI present. “I think the key thing is careful selection, but I’m not sure that we should exclude LVSI [from consideration for simple hysterectomy] de facto,” she said.
Dr. Plante has consulted or advised Merck Serono and has received travel, accommodations, or other expenses from AstraZeneca. Dr. Moore has consulted, advised, and received research funding and travel expenses from numerous pharmaceutical companies.
CHICAGO –
“Following adequate and rigorous preoperative assessment, and that’s key – very careful [patient selection] – simple hysterectomies can now be considered the new standard of care for patients with low-risk early-stage cervical cancer,” said Marie Plante, MD, during a presentation of the study at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. A simple hysterectomy removes the uterus and cervix, while a radical hysterectomy also removes the parametrium and upper vagina.
Cervical cancer incidence has gone down over the past 2 decades as a result of improved screening, and patients tend to be lower in age and are more likely to have low-risk, early-stage disease, according to Dr. Plante. “Although radical surgery is highly effective for the treatment of low-risk disease, women are at risk of suffering survivorship issues related to long-term surgical side effects including compromised bladder, bowel, and sexual function,” said Dr. Plante, who is a professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Laval University and head of clinical research at l’Hôtel-Dieu de Québec, both in Quebec City.
Retrospective studies found that infiltration of the parametrium is quite rare in low-risk cases, “suggesting that less radical surgery may be a safe option associated with decreased morbidity – what we call surgical de-escalation,” said Dr. Plante.
To test that idea more rigorously, the researchers designed the SHAPE trial, which randomized 700 women to a simple hysterectomy or radical hysterectomy. Patients were carefully selected to be low risk, having squamous cell, adenocarcinoma, or adenosquamous carcinoma, stage IA2 or IB2 tumors, fewer than 10 mm of stromal invasion on loop electrosurgical excision procedure or cone biopsy, less than 50% stromal invasion seen in MRI, and a maximum tumor dimension of 20 mm or less. Tumors were grade I-III or not assessable.
Over a median follow-up of 4.5 years, pelvic recurrence was 2.52% in the simple hysterectomy group and 2.17% in the radical hysterectomy group. The difference between the recurrence rate between the two groups was 0.35%, with an upper 95% confidence limit of 2.32%, below the threshold of 4% which had been predetermined as a benchmark for similar outcomes between the two groups. “Therefore, noninferiority of simple hysterectomy to radical hysterectomy could be concluded,” said Dr. Plante.
There were no statistically significant differences in intraoperative complications or mortality between the groups.
Surgery-related adverse events greater in radical hysterectomy group
There were some differences between the groups with respect to surgery-related adverse events. Within 4 weeks of surgery, there was a greater incidence of any adverse event in the radical hysterectomy group (50.6% vs. 42.6%; P = .04), as well as greater incidences of urinary incontinence (5.5% vs. 2.4%; P = .048) and urinary retention (11.0% vs. 0.6%; P < .0001). In the 4 weeks following surgery, there was a trend toward more surgery-related adverse events in the radical hysterectomy group (60.5% vs. 53.6%; P = .08) and higher incidences of urinary incontinence (11.0% vs. 4.7%; P = .003) and urinary retention (9.9% vs. 0.6%; P < .0001).
“Urinary incontinence and urinary retention are statistically worse in the radical hysterectomy group – both acutely, as well as [during] the following four weeks after surgery, suggesting that the problem persisted over time,” said Dr. Plante.
Dr. Plante also presented the study at a premeeting virtual press conference, during which Kathleen Moore, MD, provided comments on the study. She expressed enthusiasm about the results.
“Amongst those carefully selected tumors, radical hysterectomy can be converted to a simple hysterectomy, including minimally invasive. You still have to do nodes – that’s an important thing to remember – but you can do this without loss of oncologic control. And importantly, with reduction in surgical complications, postop morbidity, specifically neurologic morbidity. The moment this is presented [at the ASCO conference] this will be the new standard of care, and it represents a huge step forward in the care of women with early-stage cervical cancer,” said Dr. Moore, who is a professor of gynecologic oncology at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City.
Also in the press conference, Dr. Plante emphasized the importance of a thorough understanding of the tumor, including size, imaging, and pathology. “The more conservative one wants to be, the more meticulous, the more careful one has to be to make sure that we’re truly dealing with low-risk patients.”
During the question-and-answer session following her presentation at the ASCO session, a moderator asked Dr. Plante if the presence of lymph vascular space invasion (LVSI) should prompt a radical hysterectomy.
Dr. Plante noted that about 13% of both radical and simple hysterectomy groups had LVSI present. “I think the key thing is careful selection, but I’m not sure that we should exclude LVSI [from consideration for simple hysterectomy] de facto,” she said.
Dr. Plante has consulted or advised Merck Serono and has received travel, accommodations, or other expenses from AstraZeneca. Dr. Moore has consulted, advised, and received research funding and travel expenses from numerous pharmaceutical companies.
AT ASCO 2023
The diagnostic and therapeutic challenges of syringoma
Pain and pruritus are the most common complaints in patients who present to vulvar clinics.1 These symptoms can be related to a variety of conditions, including vulvar lesions. There are both common and uncommon vulvar lesions. Vulvar lesions can be skin colored, yellow, and red. Certain lesions can be diagnosed with history and physical examination alone. Some more common lesions include acrochordons (skin tags), benign growths that are common in patients with diabetes, obesity, and pregnancy.2,3 Other common vulvar lesions are papillomatosis, lichen simplex chronicus, and epidermoid cysts. Other lesions include low- and high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSIL).4 These lesions require biopsy for diagnosis as high-grade lesions require treatment. HSIL of the vulva is considered a premalignancy that necessitates treatment.5 Other lesions that can present with vulvar complaints are molluscum contagiosum, Bartholin gland duct cyst, intradermal melanocytic nevus, and squamous cell carcinoma.
Rarely, other less common conditions can present as vulvar lesions. Syringomas are benign eccrine sweat gland neoplasms. They are more commonly found on the face, neck, or chest.6 On the vulva they are generally small subcutaneous skin-colored papules.7 They may be asymptomatic and noted only on routine examination.
Vulvar syringomas also may present with symptoms. On the vulva, syringomas often present as pruritic papules that can be isolated or multifocal. Often on the labia majora they range in size from 2 to 20 mm.8
They can coalesce to form a larger lesion. They also may be described as painful. When syringomas are pruritic, the overlying skin may appear thickened from rubbing or scratching, and excoriations may be present.
Since vulvar syringomas are rare, there is no standard treatment. Biopsy is necessary for definitive diagnosis. For asymptomatic cases, expectant management is warranted. In symptomatic cases treatment can be considered. Treatment options include cryotherapy, laser ablation, and intralesional electrodissection.8 Intralesional electrodissection and curettage also has been described as treatment.9 Other treatment options include surgical excision of individual lesions or larger excisions if multifocal.
The case study described in "Case letter: Vulvar syringoma" highlights the diagnostic and therapeutic challenges associated with rare lesions of the vulva. Referral to a specialty clinic may be warranted in these challenging cases. ●
- Hansen A, Carr K, Jensen JT. Characteristics and initial diagnoses in women presenting to a referral center for vulvovaginal disorders in 1996–2000. J Reprod Med. 2002; 47: 854-860.
- Boza JC, Trindade EN, Peruzzo J, et al. Skin manifestations of obesity: a comparative study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2012;26:1220-1223.
- Winton GB, Lewis CW. Dermatoses of pregnancy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1982;6:977-998.
- Bornstein J, Bogliatto F, Haefner HK, et al; ISSVD Terminology Committee. The 2015 International Society for the Study of Vulvovaginal Disease (ISSVD) terminology of vulvar squamous intraepithelial lesions. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2016;20:11-14.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Committee opinion no. 675: management of vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia. Obstet Gynecol. 2016;128:e178-e182.
- Heller DS. Benign tumors and tumor-like lesions of the vulva. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2015;58:526-535.
- Shalabi MMK, Homan K, Bicknell L. Vulvar syringomas. Proc (Bayl Univer Med Cent). 2022;35:113-114.
- Ozdemir O, Sari ME, Sen E, et al. Vulvar syringoma in a postmenopausal woman: a case report. J Reprod Med. 2015;60:452-454.
- Stevenson TR, Swanson NA. Syringoma: removal by electrodesiccation and curettage. Ann Plast Surg. 1985;15:151-154.
Pain and pruritus are the most common complaints in patients who present to vulvar clinics.1 These symptoms can be related to a variety of conditions, including vulvar lesions. There are both common and uncommon vulvar lesions. Vulvar lesions can be skin colored, yellow, and red. Certain lesions can be diagnosed with history and physical examination alone. Some more common lesions include acrochordons (skin tags), benign growths that are common in patients with diabetes, obesity, and pregnancy.2,3 Other common vulvar lesions are papillomatosis, lichen simplex chronicus, and epidermoid cysts. Other lesions include low- and high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSIL).4 These lesions require biopsy for diagnosis as high-grade lesions require treatment. HSIL of the vulva is considered a premalignancy that necessitates treatment.5 Other lesions that can present with vulvar complaints are molluscum contagiosum, Bartholin gland duct cyst, intradermal melanocytic nevus, and squamous cell carcinoma.
Rarely, other less common conditions can present as vulvar lesions. Syringomas are benign eccrine sweat gland neoplasms. They are more commonly found on the face, neck, or chest.6 On the vulva they are generally small subcutaneous skin-colored papules.7 They may be asymptomatic and noted only on routine examination.
Vulvar syringomas also may present with symptoms. On the vulva, syringomas often present as pruritic papules that can be isolated or multifocal. Often on the labia majora they range in size from 2 to 20 mm.8
They can coalesce to form a larger lesion. They also may be described as painful. When syringomas are pruritic, the overlying skin may appear thickened from rubbing or scratching, and excoriations may be present.
Since vulvar syringomas are rare, there is no standard treatment. Biopsy is necessary for definitive diagnosis. For asymptomatic cases, expectant management is warranted. In symptomatic cases treatment can be considered. Treatment options include cryotherapy, laser ablation, and intralesional electrodissection.8 Intralesional electrodissection and curettage also has been described as treatment.9 Other treatment options include surgical excision of individual lesions or larger excisions if multifocal.
The case study described in "Case letter: Vulvar syringoma" highlights the diagnostic and therapeutic challenges associated with rare lesions of the vulva. Referral to a specialty clinic may be warranted in these challenging cases. ●
Pain and pruritus are the most common complaints in patients who present to vulvar clinics.1 These symptoms can be related to a variety of conditions, including vulvar lesions. There are both common and uncommon vulvar lesions. Vulvar lesions can be skin colored, yellow, and red. Certain lesions can be diagnosed with history and physical examination alone. Some more common lesions include acrochordons (skin tags), benign growths that are common in patients with diabetes, obesity, and pregnancy.2,3 Other common vulvar lesions are papillomatosis, lichen simplex chronicus, and epidermoid cysts. Other lesions include low- and high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSIL).4 These lesions require biopsy for diagnosis as high-grade lesions require treatment. HSIL of the vulva is considered a premalignancy that necessitates treatment.5 Other lesions that can present with vulvar complaints are molluscum contagiosum, Bartholin gland duct cyst, intradermal melanocytic nevus, and squamous cell carcinoma.
Rarely, other less common conditions can present as vulvar lesions. Syringomas are benign eccrine sweat gland neoplasms. They are more commonly found on the face, neck, or chest.6 On the vulva they are generally small subcutaneous skin-colored papules.7 They may be asymptomatic and noted only on routine examination.
Vulvar syringomas also may present with symptoms. On the vulva, syringomas often present as pruritic papules that can be isolated or multifocal. Often on the labia majora they range in size from 2 to 20 mm.8
They can coalesce to form a larger lesion. They also may be described as painful. When syringomas are pruritic, the overlying skin may appear thickened from rubbing or scratching, and excoriations may be present.
Since vulvar syringomas are rare, there is no standard treatment. Biopsy is necessary for definitive diagnosis. For asymptomatic cases, expectant management is warranted. In symptomatic cases treatment can be considered. Treatment options include cryotherapy, laser ablation, and intralesional electrodissection.8 Intralesional electrodissection and curettage also has been described as treatment.9 Other treatment options include surgical excision of individual lesions or larger excisions if multifocal.
The case study described in "Case letter: Vulvar syringoma" highlights the diagnostic and therapeutic challenges associated with rare lesions of the vulva. Referral to a specialty clinic may be warranted in these challenging cases. ●
- Hansen A, Carr K, Jensen JT. Characteristics and initial diagnoses in women presenting to a referral center for vulvovaginal disorders in 1996–2000. J Reprod Med. 2002; 47: 854-860.
- Boza JC, Trindade EN, Peruzzo J, et al. Skin manifestations of obesity: a comparative study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2012;26:1220-1223.
- Winton GB, Lewis CW. Dermatoses of pregnancy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1982;6:977-998.
- Bornstein J, Bogliatto F, Haefner HK, et al; ISSVD Terminology Committee. The 2015 International Society for the Study of Vulvovaginal Disease (ISSVD) terminology of vulvar squamous intraepithelial lesions. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2016;20:11-14.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Committee opinion no. 675: management of vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia. Obstet Gynecol. 2016;128:e178-e182.
- Heller DS. Benign tumors and tumor-like lesions of the vulva. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2015;58:526-535.
- Shalabi MMK, Homan K, Bicknell L. Vulvar syringomas. Proc (Bayl Univer Med Cent). 2022;35:113-114.
- Ozdemir O, Sari ME, Sen E, et al. Vulvar syringoma in a postmenopausal woman: a case report. J Reprod Med. 2015;60:452-454.
- Stevenson TR, Swanson NA. Syringoma: removal by electrodesiccation and curettage. Ann Plast Surg. 1985;15:151-154.
- Hansen A, Carr K, Jensen JT. Characteristics and initial diagnoses in women presenting to a referral center for vulvovaginal disorders in 1996–2000. J Reprod Med. 2002; 47: 854-860.
- Boza JC, Trindade EN, Peruzzo J, et al. Skin manifestations of obesity: a comparative study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2012;26:1220-1223.
- Winton GB, Lewis CW. Dermatoses of pregnancy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1982;6:977-998.
- Bornstein J, Bogliatto F, Haefner HK, et al; ISSVD Terminology Committee. The 2015 International Society for the Study of Vulvovaginal Disease (ISSVD) terminology of vulvar squamous intraepithelial lesions. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2016;20:11-14.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Committee opinion no. 675: management of vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia. Obstet Gynecol. 2016;128:e178-e182.
- Heller DS. Benign tumors and tumor-like lesions of the vulva. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2015;58:526-535.
- Shalabi MMK, Homan K, Bicknell L. Vulvar syringomas. Proc (Bayl Univer Med Cent). 2022;35:113-114.
- Ozdemir O, Sari ME, Sen E, et al. Vulvar syringoma in a postmenopausal woman: a case report. J Reprod Med. 2015;60:452-454.
- Stevenson TR, Swanson NA. Syringoma: removal by electrodesiccation and curettage. Ann Plast Surg. 1985;15:151-154.
Should you prescribe bioidentical hormones for menopause?
BALTIMORE – according to an expert at the annual clinical and scientific meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG).
Clinicians write an estimated 26 to 33 million prescriptions for compounded bioidentical hormone therapy (cBHT) every year, and almost 41% of menopausal women who need treatment try cBHT during their lives. But these drugs lack the approval for this indication from the Food and Drug Administration.
“There is a public perception that this is natural, safer, and anti-aging,” said Robert Kauffman, MD, a professor of obstetrics and gynecology and assistant dean for research at Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center in Amarillo.
Following the 2002 Women’s Health Initiative report showing a link between hormone therapy (HT) and an increase in the incidence of breast cancer, medical schools have slowed or paused instructing trainees on the traditional treatment, Dr. Kauffman said. The association was later determined to be spurious: HT is not associated with a risk for all-cause mortality or deaths from cardiovascular disease or cancer. However, HT still is largely ignored by younger physicians, Dr. Kauffman said, because of unsubstantiated “dangers” such as heart attack, stroke, and deep vein thrombosis.
The lack of education on HT for medical school students and residents has “opened the door to unsubstantiated marketing claims and practices” for cBHT, Dr. Kauffman said. “Hence, the use of compounded bioidentical hormone therapy has increased” as clinicians look for alternatives.
Groups including ACOG, the North American Menopause Society (NAMS), and the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommend against the use of Non–FDA-approved therapies such as cBHT, except for narrow indications. Dr. Kauffman said that drug manufacturers have not conducted randomized controlled trials or observational studies on cBHT in treating menopause.
He cited studies showing quality problems with the compounding process of these drugs, and wide variations in the amount of actual ingredients from product labels. One 2021 study published in Menopause comparing patients taking cBHT or FDA-approved HT found that side effects were significantly higher in the cBHT group (57.6% vs. 14.8%; P < .0001).
But manufacturers of cBHT claim that their products prevent cardiovascular disease and Alzheimer’s disease and decrease the risk for breast cancer and stroke – assertions that are at best unproven, according to Dr. Kauffman.
The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine in 2020 said that clinicians have a duty to inform patients of the insufficient evidence to support clinical use of cBHT and should prescribe the products only to patients with documented allergies to an active ingredient in an FDA-approved agent or who require an alternative dosage.
Patients may also have to pay much more out of pocket for cBHT products because they often are not covered by insurance. Generic HT products, meanwhile, are relatively inexpensive and typically are covered, he noted.
“We have to be careful to avoid financial harm to patients by prescribing things, which are much more expensive than those which are usually available,” Dr. Kauffman said.
Prescribing any non–FDA-approved product, especially when biosimilars are available, places physicians at legal risk, Dr. Kauffman said. Physicians who recommend cBHT should inform patients that the products are not FDA approved and carefully document this discussion in the patient’s electronic health record. State boards of medicine can sanction physicians for “coercion” for prescribing cBHT products without mentioning alternatives, he added.
JoAnn Pinkerton, MD, professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville, and executive director emeritus of NAMS, who attended the session, praised Dr. Kauffman for providing a balanced and evidence-based overview of the subject.
“There are issues concerning safety, contaminants, and not knowing exactly what dose you’re getting,” with compounded hormones, Dr. Pinkerton said. “They’re being hyped as safer and more effective when in reality, we don’t have any studies that show that information.”
Dr. Pinkerton noted that while a compounded form of physiological testosterone might be relatively reliable, “if you’re using something like a pellet that is super physiologic with incredibly high doses, that you really don’t have any information to stand on that it’s safe or effective ... it might be putting your license at risk.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
BALTIMORE – according to an expert at the annual clinical and scientific meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG).
Clinicians write an estimated 26 to 33 million prescriptions for compounded bioidentical hormone therapy (cBHT) every year, and almost 41% of menopausal women who need treatment try cBHT during their lives. But these drugs lack the approval for this indication from the Food and Drug Administration.
“There is a public perception that this is natural, safer, and anti-aging,” said Robert Kauffman, MD, a professor of obstetrics and gynecology and assistant dean for research at Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center in Amarillo.
Following the 2002 Women’s Health Initiative report showing a link between hormone therapy (HT) and an increase in the incidence of breast cancer, medical schools have slowed or paused instructing trainees on the traditional treatment, Dr. Kauffman said. The association was later determined to be spurious: HT is not associated with a risk for all-cause mortality or deaths from cardiovascular disease or cancer. However, HT still is largely ignored by younger physicians, Dr. Kauffman said, because of unsubstantiated “dangers” such as heart attack, stroke, and deep vein thrombosis.
The lack of education on HT for medical school students and residents has “opened the door to unsubstantiated marketing claims and practices” for cBHT, Dr. Kauffman said. “Hence, the use of compounded bioidentical hormone therapy has increased” as clinicians look for alternatives.
Groups including ACOG, the North American Menopause Society (NAMS), and the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommend against the use of Non–FDA-approved therapies such as cBHT, except for narrow indications. Dr. Kauffman said that drug manufacturers have not conducted randomized controlled trials or observational studies on cBHT in treating menopause.
He cited studies showing quality problems with the compounding process of these drugs, and wide variations in the amount of actual ingredients from product labels. One 2021 study published in Menopause comparing patients taking cBHT or FDA-approved HT found that side effects were significantly higher in the cBHT group (57.6% vs. 14.8%; P < .0001).
But manufacturers of cBHT claim that their products prevent cardiovascular disease and Alzheimer’s disease and decrease the risk for breast cancer and stroke – assertions that are at best unproven, according to Dr. Kauffman.
The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine in 2020 said that clinicians have a duty to inform patients of the insufficient evidence to support clinical use of cBHT and should prescribe the products only to patients with documented allergies to an active ingredient in an FDA-approved agent or who require an alternative dosage.
Patients may also have to pay much more out of pocket for cBHT products because they often are not covered by insurance. Generic HT products, meanwhile, are relatively inexpensive and typically are covered, he noted.
“We have to be careful to avoid financial harm to patients by prescribing things, which are much more expensive than those which are usually available,” Dr. Kauffman said.
Prescribing any non–FDA-approved product, especially when biosimilars are available, places physicians at legal risk, Dr. Kauffman said. Physicians who recommend cBHT should inform patients that the products are not FDA approved and carefully document this discussion in the patient’s electronic health record. State boards of medicine can sanction physicians for “coercion” for prescribing cBHT products without mentioning alternatives, he added.
JoAnn Pinkerton, MD, professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville, and executive director emeritus of NAMS, who attended the session, praised Dr. Kauffman for providing a balanced and evidence-based overview of the subject.
“There are issues concerning safety, contaminants, and not knowing exactly what dose you’re getting,” with compounded hormones, Dr. Pinkerton said. “They’re being hyped as safer and more effective when in reality, we don’t have any studies that show that information.”
Dr. Pinkerton noted that while a compounded form of physiological testosterone might be relatively reliable, “if you’re using something like a pellet that is super physiologic with incredibly high doses, that you really don’t have any information to stand on that it’s safe or effective ... it might be putting your license at risk.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
BALTIMORE – according to an expert at the annual clinical and scientific meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG).
Clinicians write an estimated 26 to 33 million prescriptions for compounded bioidentical hormone therapy (cBHT) every year, and almost 41% of menopausal women who need treatment try cBHT during their lives. But these drugs lack the approval for this indication from the Food and Drug Administration.
“There is a public perception that this is natural, safer, and anti-aging,” said Robert Kauffman, MD, a professor of obstetrics and gynecology and assistant dean for research at Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center in Amarillo.
Following the 2002 Women’s Health Initiative report showing a link between hormone therapy (HT) and an increase in the incidence of breast cancer, medical schools have slowed or paused instructing trainees on the traditional treatment, Dr. Kauffman said. The association was later determined to be spurious: HT is not associated with a risk for all-cause mortality or deaths from cardiovascular disease or cancer. However, HT still is largely ignored by younger physicians, Dr. Kauffman said, because of unsubstantiated “dangers” such as heart attack, stroke, and deep vein thrombosis.
The lack of education on HT for medical school students and residents has “opened the door to unsubstantiated marketing claims and practices” for cBHT, Dr. Kauffman said. “Hence, the use of compounded bioidentical hormone therapy has increased” as clinicians look for alternatives.
Groups including ACOG, the North American Menopause Society (NAMS), and the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommend against the use of Non–FDA-approved therapies such as cBHT, except for narrow indications. Dr. Kauffman said that drug manufacturers have not conducted randomized controlled trials or observational studies on cBHT in treating menopause.
He cited studies showing quality problems with the compounding process of these drugs, and wide variations in the amount of actual ingredients from product labels. One 2021 study published in Menopause comparing patients taking cBHT or FDA-approved HT found that side effects were significantly higher in the cBHT group (57.6% vs. 14.8%; P < .0001).
But manufacturers of cBHT claim that their products prevent cardiovascular disease and Alzheimer’s disease and decrease the risk for breast cancer and stroke – assertions that are at best unproven, according to Dr. Kauffman.
The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine in 2020 said that clinicians have a duty to inform patients of the insufficient evidence to support clinical use of cBHT and should prescribe the products only to patients with documented allergies to an active ingredient in an FDA-approved agent or who require an alternative dosage.
Patients may also have to pay much more out of pocket for cBHT products because they often are not covered by insurance. Generic HT products, meanwhile, are relatively inexpensive and typically are covered, he noted.
“We have to be careful to avoid financial harm to patients by prescribing things, which are much more expensive than those which are usually available,” Dr. Kauffman said.
Prescribing any non–FDA-approved product, especially when biosimilars are available, places physicians at legal risk, Dr. Kauffman said. Physicians who recommend cBHT should inform patients that the products are not FDA approved and carefully document this discussion in the patient’s electronic health record. State boards of medicine can sanction physicians for “coercion” for prescribing cBHT products without mentioning alternatives, he added.
JoAnn Pinkerton, MD, professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville, and executive director emeritus of NAMS, who attended the session, praised Dr. Kauffman for providing a balanced and evidence-based overview of the subject.
“There are issues concerning safety, contaminants, and not knowing exactly what dose you’re getting,” with compounded hormones, Dr. Pinkerton said. “They’re being hyped as safer and more effective when in reality, we don’t have any studies that show that information.”
Dr. Pinkerton noted that while a compounded form of physiological testosterone might be relatively reliable, “if you’re using something like a pellet that is super physiologic with incredibly high doses, that you really don’t have any information to stand on that it’s safe or effective ... it might be putting your license at risk.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ACOG 2023
Female sexual pleasure: Is it in the water?
BALTIMORE – , according to research presented at the annual clinical and scientific meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. In a secondary analysis also presented at the meeting, the lubricants were found not to alter the vaginal microbiome.
Using these types of lubricants during vaginal intercourse at least once a week over a 4-week period resulted in a statistically significant increase of over four points in the 36-point Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI), a self-reported measure of sexual functioning, for participants, said Michael Krychman, MD, executive director of the Southern California Center for Sexual Health and Survivorship Medicine, Newport Beach, the senior author of the study. Statistically significant improvements also were observed in individual areas such as sexual desire and arousal, orgasm, and satisfaction. Results of the study have been published in the Journal of Sexual Medicine.
In the open-label, five-arm, parallel study conducted in Germany, 174 women aged 18-65 years were randomly assigned to use one of five lubricants from three popular brands. After a 4-week run-in period with no use of lubricants, participants were shown how to apply the products and instructed to use the substances during vaginal intercourse at least once a week over a 4-week period.
Participants reported experiencing mild to moderate vaginal dryness and dyspareunia during vaginal intercourse within the previous 3 months.
Statistically significant improvements were seen across all six individual domain scores of the FSFI (desire, arousal, lubrication, orgasm, satisfaction, and pain reduction) from baseline to week 4 with all five lubricants (P < .0001 for lubrication and pain reduction; P < .05 for desire, arousal, orgasm, and satisfaction), according to the researchers.
After 4 weeks, a clinically meaningful improvement in the total FSFI score was observed for four lubricants among premenopausal women and for all lubricants among postmenopausal women. The percentage of participants with sexual function as defined as a score of at least 26.55 on the FSFI was significantly greater after treatment (76.9%) than before treatment (20.8%; P < .0001).
“You would assume if you’re using lubricant it would improve the dryness, but what was very exciting for us is that it improved desire, it improved orgasm, it improved arousal,” Dr. Krychman said in an interview. Like concentric overlapping circles of female sexual function, he said, “if you improve one aspect, you improve the other.”
Nearly 80 nonserious adverse effects occurred in 43 participants, five of which were thought to be possibly attributed to the products, such as vulvovaginal burning, itching, or discomfort. In questionnaires, most women agreed that using the lubricants made sex more enjoyable and provided an overall pleasant experience.
One limitation of the study is that because most participants were Caucasian, the results may not be generalizable to all populations, according to the researchers. Further research is required to fully determine safety and efficacy in patients of all races and ethnicities, they reported, especially given that vaginal dryness has been reported more frequently in non-White ethnic groups.
In a companion presentation, Dr. Krychman discussed another aspect of the study looking at the lubricants’ effects on the vaginal microbiome. Repeated application of the products did not significantly alter the vaginal microbiome for up to 4 weeks, and vaginal pH slightly increased in all treatment groups shortly after use but was restored in most cases after a day.
Water-based lubricants are recommended by the WHO for use with condoms because they do not erode latex, said Karen Adams, MD, professor emeritus of obstetrics and gynecology and founding director of the Menopause and Sexual Medicine Program at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland. Guidelines from the group recommend lubricants should have an osmolality that is as close to normal vaginal secretions as possible to decrease the likelihood of irritation or other side effects, she said. Some available lubricants have four to six times that osmolality, which potentially could dehydrate cells, achieving the opposite of the desired effect.
“The reason this is important is they’re trying to develop lubricants that are more ‘vaginal friendly’ and more in line with the WHO guidelines,” said Dr. Adams, who is joining Stanford (Calif.) University in July to create and lead a new program in menopause and healthy aging. “They came up with four formulas consistent with WHO guidelines to see if these new ones worked at least as well [as commercially available products with higher osmolality], and it turns out they did,” she said. “They worked just fine.”
The study was funded by Reckitt Healthcare. Dr. Krychman is a paid medical consultant for the company. Dr. Adams disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
BALTIMORE – , according to research presented at the annual clinical and scientific meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. In a secondary analysis also presented at the meeting, the lubricants were found not to alter the vaginal microbiome.
Using these types of lubricants during vaginal intercourse at least once a week over a 4-week period resulted in a statistically significant increase of over four points in the 36-point Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI), a self-reported measure of sexual functioning, for participants, said Michael Krychman, MD, executive director of the Southern California Center for Sexual Health and Survivorship Medicine, Newport Beach, the senior author of the study. Statistically significant improvements also were observed in individual areas such as sexual desire and arousal, orgasm, and satisfaction. Results of the study have been published in the Journal of Sexual Medicine.
In the open-label, five-arm, parallel study conducted in Germany, 174 women aged 18-65 years were randomly assigned to use one of five lubricants from three popular brands. After a 4-week run-in period with no use of lubricants, participants were shown how to apply the products and instructed to use the substances during vaginal intercourse at least once a week over a 4-week period.
Participants reported experiencing mild to moderate vaginal dryness and dyspareunia during vaginal intercourse within the previous 3 months.
Statistically significant improvements were seen across all six individual domain scores of the FSFI (desire, arousal, lubrication, orgasm, satisfaction, and pain reduction) from baseline to week 4 with all five lubricants (P < .0001 for lubrication and pain reduction; P < .05 for desire, arousal, orgasm, and satisfaction), according to the researchers.
After 4 weeks, a clinically meaningful improvement in the total FSFI score was observed for four lubricants among premenopausal women and for all lubricants among postmenopausal women. The percentage of participants with sexual function as defined as a score of at least 26.55 on the FSFI was significantly greater after treatment (76.9%) than before treatment (20.8%; P < .0001).
“You would assume if you’re using lubricant it would improve the dryness, but what was very exciting for us is that it improved desire, it improved orgasm, it improved arousal,” Dr. Krychman said in an interview. Like concentric overlapping circles of female sexual function, he said, “if you improve one aspect, you improve the other.”
Nearly 80 nonserious adverse effects occurred in 43 participants, five of which were thought to be possibly attributed to the products, such as vulvovaginal burning, itching, or discomfort. In questionnaires, most women agreed that using the lubricants made sex more enjoyable and provided an overall pleasant experience.
One limitation of the study is that because most participants were Caucasian, the results may not be generalizable to all populations, according to the researchers. Further research is required to fully determine safety and efficacy in patients of all races and ethnicities, they reported, especially given that vaginal dryness has been reported more frequently in non-White ethnic groups.
In a companion presentation, Dr. Krychman discussed another aspect of the study looking at the lubricants’ effects on the vaginal microbiome. Repeated application of the products did not significantly alter the vaginal microbiome for up to 4 weeks, and vaginal pH slightly increased in all treatment groups shortly after use but was restored in most cases after a day.
Water-based lubricants are recommended by the WHO for use with condoms because they do not erode latex, said Karen Adams, MD, professor emeritus of obstetrics and gynecology and founding director of the Menopause and Sexual Medicine Program at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland. Guidelines from the group recommend lubricants should have an osmolality that is as close to normal vaginal secretions as possible to decrease the likelihood of irritation or other side effects, she said. Some available lubricants have four to six times that osmolality, which potentially could dehydrate cells, achieving the opposite of the desired effect.
“The reason this is important is they’re trying to develop lubricants that are more ‘vaginal friendly’ and more in line with the WHO guidelines,” said Dr. Adams, who is joining Stanford (Calif.) University in July to create and lead a new program in menopause and healthy aging. “They came up with four formulas consistent with WHO guidelines to see if these new ones worked at least as well [as commercially available products with higher osmolality], and it turns out they did,” she said. “They worked just fine.”
The study was funded by Reckitt Healthcare. Dr. Krychman is a paid medical consultant for the company. Dr. Adams disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
BALTIMORE – , according to research presented at the annual clinical and scientific meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. In a secondary analysis also presented at the meeting, the lubricants were found not to alter the vaginal microbiome.
Using these types of lubricants during vaginal intercourse at least once a week over a 4-week period resulted in a statistically significant increase of over four points in the 36-point Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI), a self-reported measure of sexual functioning, for participants, said Michael Krychman, MD, executive director of the Southern California Center for Sexual Health and Survivorship Medicine, Newport Beach, the senior author of the study. Statistically significant improvements also were observed in individual areas such as sexual desire and arousal, orgasm, and satisfaction. Results of the study have been published in the Journal of Sexual Medicine.
In the open-label, five-arm, parallel study conducted in Germany, 174 women aged 18-65 years were randomly assigned to use one of five lubricants from three popular brands. After a 4-week run-in period with no use of lubricants, participants were shown how to apply the products and instructed to use the substances during vaginal intercourse at least once a week over a 4-week period.
Participants reported experiencing mild to moderate vaginal dryness and dyspareunia during vaginal intercourse within the previous 3 months.
Statistically significant improvements were seen across all six individual domain scores of the FSFI (desire, arousal, lubrication, orgasm, satisfaction, and pain reduction) from baseline to week 4 with all five lubricants (P < .0001 for lubrication and pain reduction; P < .05 for desire, arousal, orgasm, and satisfaction), according to the researchers.
After 4 weeks, a clinically meaningful improvement in the total FSFI score was observed for four lubricants among premenopausal women and for all lubricants among postmenopausal women. The percentage of participants with sexual function as defined as a score of at least 26.55 on the FSFI was significantly greater after treatment (76.9%) than before treatment (20.8%; P < .0001).
“You would assume if you’re using lubricant it would improve the dryness, but what was very exciting for us is that it improved desire, it improved orgasm, it improved arousal,” Dr. Krychman said in an interview. Like concentric overlapping circles of female sexual function, he said, “if you improve one aspect, you improve the other.”
Nearly 80 nonserious adverse effects occurred in 43 participants, five of which were thought to be possibly attributed to the products, such as vulvovaginal burning, itching, or discomfort. In questionnaires, most women agreed that using the lubricants made sex more enjoyable and provided an overall pleasant experience.
One limitation of the study is that because most participants were Caucasian, the results may not be generalizable to all populations, according to the researchers. Further research is required to fully determine safety and efficacy in patients of all races and ethnicities, they reported, especially given that vaginal dryness has been reported more frequently in non-White ethnic groups.
In a companion presentation, Dr. Krychman discussed another aspect of the study looking at the lubricants’ effects on the vaginal microbiome. Repeated application of the products did not significantly alter the vaginal microbiome for up to 4 weeks, and vaginal pH slightly increased in all treatment groups shortly after use but was restored in most cases after a day.
Water-based lubricants are recommended by the WHO for use with condoms because they do not erode latex, said Karen Adams, MD, professor emeritus of obstetrics and gynecology and founding director of the Menopause and Sexual Medicine Program at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland. Guidelines from the group recommend lubricants should have an osmolality that is as close to normal vaginal secretions as possible to decrease the likelihood of irritation or other side effects, she said. Some available lubricants have four to six times that osmolality, which potentially could dehydrate cells, achieving the opposite of the desired effect.
“The reason this is important is they’re trying to develop lubricants that are more ‘vaginal friendly’ and more in line with the WHO guidelines,” said Dr. Adams, who is joining Stanford (Calif.) University in July to create and lead a new program in menopause and healthy aging. “They came up with four formulas consistent with WHO guidelines to see if these new ones worked at least as well [as commercially available products with higher osmolality], and it turns out they did,” she said. “They worked just fine.”
The study was funded by Reckitt Healthcare. Dr. Krychman is a paid medical consultant for the company. Dr. Adams disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ACOG 2023
Scheduled bleeding may boost tolerability of hormone implants
BALTIMORE – The bleeding causes some women to have the device removed, according to research presented at the annual clinical and scientific meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
In a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial of 51 patients desiring the implants – which suppress ovulation by releasing progestin over a 3-year period – taking norethindrone acetate for 1 week every 4 weeks led to 80% of participants in the treatment group reporting satisfactory bleeding patterns with the etonogestrel implants in place.
Rates of early discontinuation have been variable, according to published literature, ranging from 13% to 21.1%, said Jordan Gray, MD, a fourth-year resident in ob.gyn. at Baylor Scott and White Medical Center, Temple, Tex., who helped conduct the new study. Reasons included bothersome bleeding. Dr. Gray and colleagues found that 24% of women in the placebo group requested removal of the implant, compared with 9% of those in the treatment group. Among these women, none requested removal for bothersome bleeding but rather for reasons such as wanting to get pregnant. One person requested removal because she did not like amenorrhea.
While the results of the study did not achieve statistical significance, owing to its size and noncompliance among some participants, it does indicate that norethindrone acetate may be helpful, Dr. Gray said.
During the study, participants in the treatment group (n = 22) received a monthly treatment regimen of 5 mg of oral norethindrone acetate daily for 7 days each month for the first 6 months after placement of an etonogestrel implant. The placebo group (n = 29) was given inert tablets prescribed in the same regimen. Both groups received products from a mail-order pharmacy.
Participants were women aged 18-48 years who desired an implant or those aged 14 years who had permission from a parent or guardian to receive the contraceptive. The study excluded people with known or suspected pregnancy, those less than 8 weeks’ post partum, those who experienced menarche less than 2 years ago, those with body mass index greater than 40, and those who received depot medroxyprogesterone acetate within the previous 12 weeks. Excessive bleeding was defined as bleeding or spotting on more than 7 consecutive days or a fifth episode of bleeding in 90 days.
Overall, 11 patients (38%) in the placebo group and 10 (45%) in the treatment arm withdrew from the study. Reasons included wanting to get pregnant, mood changes, or noncompliance with study parameters, which included not responding or returning bleeding diaries, Dr. Gray said.
A limitation of the study was that compliance was less than expected. In addition, there were challenges with rates of responses, Dr. Gray said. The study was conducted during the COVID-19 pandemic, when all in-person visits were transitioned to telehealth. Although the investigators offered payment to participants, not all returned text-message surveys. The researchers had intended to enroll 124 participants but curtailed the study early, owing to the limited number of participants.
Given that there is no standard approach to treating prolonged or excessive bleeding with etonogestrel implants, Dr. Gray said, “Our data suggests that this regimen is a simple and acceptable method to treat bothersome bleeding and that predictable bleeding may be more satisfactory than unpredictable bleeding.”
Veronica Maria Pimentel, MD, moderator of the session and a maternal-fetal medicine specialist and director of research for the ob.gyn. residency program at St. Francis Hospital, part of Trinity Health of New England in Hartford, Conn., praised the researchers for a well-designed study.
“However, unfortunately, they were not able to recruit the number of patients that they needed in order to achieve the power to show the difference [between treatment arms], so another study would have to be done to show if there is a difference,” Dr. Pimentel said.
Dr. Pimentel complimented Dr. Gray following her presentation, congratulating her for conducting a randomized, controlled trial: “That’s not easy, as you have shown, but it’s also a good try, so you can actually see how hard it is to obtain quality data from research.”
The study was supported in part by a research grant from the Investigator-Initiated Studies Program of Organon. Dr. Gray is a consultant for Johnson & Johnson. Dr. Pimentel has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
BALTIMORE – The bleeding causes some women to have the device removed, according to research presented at the annual clinical and scientific meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
In a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial of 51 patients desiring the implants – which suppress ovulation by releasing progestin over a 3-year period – taking norethindrone acetate for 1 week every 4 weeks led to 80% of participants in the treatment group reporting satisfactory bleeding patterns with the etonogestrel implants in place.
Rates of early discontinuation have been variable, according to published literature, ranging from 13% to 21.1%, said Jordan Gray, MD, a fourth-year resident in ob.gyn. at Baylor Scott and White Medical Center, Temple, Tex., who helped conduct the new study. Reasons included bothersome bleeding. Dr. Gray and colleagues found that 24% of women in the placebo group requested removal of the implant, compared with 9% of those in the treatment group. Among these women, none requested removal for bothersome bleeding but rather for reasons such as wanting to get pregnant. One person requested removal because she did not like amenorrhea.
While the results of the study did not achieve statistical significance, owing to its size and noncompliance among some participants, it does indicate that norethindrone acetate may be helpful, Dr. Gray said.
During the study, participants in the treatment group (n = 22) received a monthly treatment regimen of 5 mg of oral norethindrone acetate daily for 7 days each month for the first 6 months after placement of an etonogestrel implant. The placebo group (n = 29) was given inert tablets prescribed in the same regimen. Both groups received products from a mail-order pharmacy.
Participants were women aged 18-48 years who desired an implant or those aged 14 years who had permission from a parent or guardian to receive the contraceptive. The study excluded people with known or suspected pregnancy, those less than 8 weeks’ post partum, those who experienced menarche less than 2 years ago, those with body mass index greater than 40, and those who received depot medroxyprogesterone acetate within the previous 12 weeks. Excessive bleeding was defined as bleeding or spotting on more than 7 consecutive days or a fifth episode of bleeding in 90 days.
Overall, 11 patients (38%) in the placebo group and 10 (45%) in the treatment arm withdrew from the study. Reasons included wanting to get pregnant, mood changes, or noncompliance with study parameters, which included not responding or returning bleeding diaries, Dr. Gray said.
A limitation of the study was that compliance was less than expected. In addition, there were challenges with rates of responses, Dr. Gray said. The study was conducted during the COVID-19 pandemic, when all in-person visits were transitioned to telehealth. Although the investigators offered payment to participants, not all returned text-message surveys. The researchers had intended to enroll 124 participants but curtailed the study early, owing to the limited number of participants.
Given that there is no standard approach to treating prolonged or excessive bleeding with etonogestrel implants, Dr. Gray said, “Our data suggests that this regimen is a simple and acceptable method to treat bothersome bleeding and that predictable bleeding may be more satisfactory than unpredictable bleeding.”
Veronica Maria Pimentel, MD, moderator of the session and a maternal-fetal medicine specialist and director of research for the ob.gyn. residency program at St. Francis Hospital, part of Trinity Health of New England in Hartford, Conn., praised the researchers for a well-designed study.
“However, unfortunately, they were not able to recruit the number of patients that they needed in order to achieve the power to show the difference [between treatment arms], so another study would have to be done to show if there is a difference,” Dr. Pimentel said.
Dr. Pimentel complimented Dr. Gray following her presentation, congratulating her for conducting a randomized, controlled trial: “That’s not easy, as you have shown, but it’s also a good try, so you can actually see how hard it is to obtain quality data from research.”
The study was supported in part by a research grant from the Investigator-Initiated Studies Program of Organon. Dr. Gray is a consultant for Johnson & Johnson. Dr. Pimentel has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
BALTIMORE – The bleeding causes some women to have the device removed, according to research presented at the annual clinical and scientific meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
In a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial of 51 patients desiring the implants – which suppress ovulation by releasing progestin over a 3-year period – taking norethindrone acetate for 1 week every 4 weeks led to 80% of participants in the treatment group reporting satisfactory bleeding patterns with the etonogestrel implants in place.
Rates of early discontinuation have been variable, according to published literature, ranging from 13% to 21.1%, said Jordan Gray, MD, a fourth-year resident in ob.gyn. at Baylor Scott and White Medical Center, Temple, Tex., who helped conduct the new study. Reasons included bothersome bleeding. Dr. Gray and colleagues found that 24% of women in the placebo group requested removal of the implant, compared with 9% of those in the treatment group. Among these women, none requested removal for bothersome bleeding but rather for reasons such as wanting to get pregnant. One person requested removal because she did not like amenorrhea.
While the results of the study did not achieve statistical significance, owing to its size and noncompliance among some participants, it does indicate that norethindrone acetate may be helpful, Dr. Gray said.
During the study, participants in the treatment group (n = 22) received a monthly treatment regimen of 5 mg of oral norethindrone acetate daily for 7 days each month for the first 6 months after placement of an etonogestrel implant. The placebo group (n = 29) was given inert tablets prescribed in the same regimen. Both groups received products from a mail-order pharmacy.
Participants were women aged 18-48 years who desired an implant or those aged 14 years who had permission from a parent or guardian to receive the contraceptive. The study excluded people with known or suspected pregnancy, those less than 8 weeks’ post partum, those who experienced menarche less than 2 years ago, those with body mass index greater than 40, and those who received depot medroxyprogesterone acetate within the previous 12 weeks. Excessive bleeding was defined as bleeding or spotting on more than 7 consecutive days or a fifth episode of bleeding in 90 days.
Overall, 11 patients (38%) in the placebo group and 10 (45%) in the treatment arm withdrew from the study. Reasons included wanting to get pregnant, mood changes, or noncompliance with study parameters, which included not responding or returning bleeding diaries, Dr. Gray said.
A limitation of the study was that compliance was less than expected. In addition, there were challenges with rates of responses, Dr. Gray said. The study was conducted during the COVID-19 pandemic, when all in-person visits were transitioned to telehealth. Although the investigators offered payment to participants, not all returned text-message surveys. The researchers had intended to enroll 124 participants but curtailed the study early, owing to the limited number of participants.
Given that there is no standard approach to treating prolonged or excessive bleeding with etonogestrel implants, Dr. Gray said, “Our data suggests that this regimen is a simple and acceptable method to treat bothersome bleeding and that predictable bleeding may be more satisfactory than unpredictable bleeding.”
Veronica Maria Pimentel, MD, moderator of the session and a maternal-fetal medicine specialist and director of research for the ob.gyn. residency program at St. Francis Hospital, part of Trinity Health of New England in Hartford, Conn., praised the researchers for a well-designed study.
“However, unfortunately, they were not able to recruit the number of patients that they needed in order to achieve the power to show the difference [between treatment arms], so another study would have to be done to show if there is a difference,” Dr. Pimentel said.
Dr. Pimentel complimented Dr. Gray following her presentation, congratulating her for conducting a randomized, controlled trial: “That’s not easy, as you have shown, but it’s also a good try, so you can actually see how hard it is to obtain quality data from research.”
The study was supported in part by a research grant from the Investigator-Initiated Studies Program of Organon. Dr. Gray is a consultant for Johnson & Johnson. Dr. Pimentel has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ACOG 2023
Mailed HPV test kits boost cervical cancer screening
The self-sampling kits, which detect human papillomavirus (HPV), are available only for use in clinical trials, but the researchers hope that eventually these kits will be approved for use by the general public.
The researchers, from the University of North Carolina, explored use of these kits in the My Body, My Test-3 study, which was published online in The Lancet Public Health.
In a commentary published with the study, Runzhi Wang, MD, and Jennell Coleman, MD, MPH, both of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said it “provides the required evidence that ... self-collected samples can be an effective strategy for hard-to-reach populations.”
The study involved 665 women (aged 25-64) in North Carolina who were either uninsured or enrolled in Medicaid or Medicare. The patients had low-income backgrounds and lived in urban areas. More than half self-reported as Black or Hispanic (55%), uninsured (78%) or unemployed (57%). None had a Pap smear in at least 4 years or a high-risk HPV test in the last 6 years.
Two-thirds of the women were mailed an HPV self-collection kit and received assistance with scheduling an in-person screening appointment. The kit included a Viba-Brush device, which is inserted into the vagina like a tampon to collect the sample.
The other third of women, the control group, only received scheduling assistance.
The team found that mailing the self-collection tests along with helping women book in-clinic appointments improved screening rates twofold, compared with just assisting patients to schedule an appointment.
Screening success among those who received the at-home collection kit was 72%, compared with 37% in the control group.
Of those who received the kits, 78% returned them. This is “impressive,” said Dr. Wang and Dr. Coleman, as previous studies have reported return rates of only 8%-20%.
About 23% of eligible women are overdue for cervical cancer screening by at least a year, according to the National Cancer Institute. Jennifer Smith, PhD, MPH, professor of epidemiology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and an author of the study, believes every woman deserves equal access to cervical screening.
“I think we really need to make efforts to increase cervical cancer screening among women who are overdue for screening by a year or more from the recommended guidelines,” Dr. Smith said. “We’ve proven along with the wide evidence both in the U.S. and globally that self-collection intervention works well and can motivate screening uptake by breaking down barriers for populations that have less access to care.”
“We’re hoping this research in combination with all of the extensive evidence on the positive performance of HPV self-collection will provide additional information to be considered by the FDA for approval of the kits for primary screening,” Dr. Smith said.
“Government approval of at-home HPV tests would have a huge impact,” said coauthor Noel Brewer, PhD, also of UNC Chapel Hill. “We could better reach those in rural areas where cervical cancer screening is hard to come by.”
Dr. Smith has received research grants, supply donations, and consultancies for Hologic and BD Diagnostics. Dr. Brewer, Dr. Wang, and Dr. Coleman reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The self-sampling kits, which detect human papillomavirus (HPV), are available only for use in clinical trials, but the researchers hope that eventually these kits will be approved for use by the general public.
The researchers, from the University of North Carolina, explored use of these kits in the My Body, My Test-3 study, which was published online in The Lancet Public Health.
In a commentary published with the study, Runzhi Wang, MD, and Jennell Coleman, MD, MPH, both of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said it “provides the required evidence that ... self-collected samples can be an effective strategy for hard-to-reach populations.”
The study involved 665 women (aged 25-64) in North Carolina who were either uninsured or enrolled in Medicaid or Medicare. The patients had low-income backgrounds and lived in urban areas. More than half self-reported as Black or Hispanic (55%), uninsured (78%) or unemployed (57%). None had a Pap smear in at least 4 years or a high-risk HPV test in the last 6 years.
Two-thirds of the women were mailed an HPV self-collection kit and received assistance with scheduling an in-person screening appointment. The kit included a Viba-Brush device, which is inserted into the vagina like a tampon to collect the sample.
The other third of women, the control group, only received scheduling assistance.
The team found that mailing the self-collection tests along with helping women book in-clinic appointments improved screening rates twofold, compared with just assisting patients to schedule an appointment.
Screening success among those who received the at-home collection kit was 72%, compared with 37% in the control group.
Of those who received the kits, 78% returned them. This is “impressive,” said Dr. Wang and Dr. Coleman, as previous studies have reported return rates of only 8%-20%.
About 23% of eligible women are overdue for cervical cancer screening by at least a year, according to the National Cancer Institute. Jennifer Smith, PhD, MPH, professor of epidemiology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and an author of the study, believes every woman deserves equal access to cervical screening.
“I think we really need to make efforts to increase cervical cancer screening among women who are overdue for screening by a year or more from the recommended guidelines,” Dr. Smith said. “We’ve proven along with the wide evidence both in the U.S. and globally that self-collection intervention works well and can motivate screening uptake by breaking down barriers for populations that have less access to care.”
“We’re hoping this research in combination with all of the extensive evidence on the positive performance of HPV self-collection will provide additional information to be considered by the FDA for approval of the kits for primary screening,” Dr. Smith said.
“Government approval of at-home HPV tests would have a huge impact,” said coauthor Noel Brewer, PhD, also of UNC Chapel Hill. “We could better reach those in rural areas where cervical cancer screening is hard to come by.”
Dr. Smith has received research grants, supply donations, and consultancies for Hologic and BD Diagnostics. Dr. Brewer, Dr. Wang, and Dr. Coleman reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The self-sampling kits, which detect human papillomavirus (HPV), are available only for use in clinical trials, but the researchers hope that eventually these kits will be approved for use by the general public.
The researchers, from the University of North Carolina, explored use of these kits in the My Body, My Test-3 study, which was published online in The Lancet Public Health.
In a commentary published with the study, Runzhi Wang, MD, and Jennell Coleman, MD, MPH, both of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said it “provides the required evidence that ... self-collected samples can be an effective strategy for hard-to-reach populations.”
The study involved 665 women (aged 25-64) in North Carolina who were either uninsured or enrolled in Medicaid or Medicare. The patients had low-income backgrounds and lived in urban areas. More than half self-reported as Black or Hispanic (55%), uninsured (78%) or unemployed (57%). None had a Pap smear in at least 4 years or a high-risk HPV test in the last 6 years.
Two-thirds of the women were mailed an HPV self-collection kit and received assistance with scheduling an in-person screening appointment. The kit included a Viba-Brush device, which is inserted into the vagina like a tampon to collect the sample.
The other third of women, the control group, only received scheduling assistance.
The team found that mailing the self-collection tests along with helping women book in-clinic appointments improved screening rates twofold, compared with just assisting patients to schedule an appointment.
Screening success among those who received the at-home collection kit was 72%, compared with 37% in the control group.
Of those who received the kits, 78% returned them. This is “impressive,” said Dr. Wang and Dr. Coleman, as previous studies have reported return rates of only 8%-20%.
About 23% of eligible women are overdue for cervical cancer screening by at least a year, according to the National Cancer Institute. Jennifer Smith, PhD, MPH, professor of epidemiology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and an author of the study, believes every woman deserves equal access to cervical screening.
“I think we really need to make efforts to increase cervical cancer screening among women who are overdue for screening by a year or more from the recommended guidelines,” Dr. Smith said. “We’ve proven along with the wide evidence both in the U.S. and globally that self-collection intervention works well and can motivate screening uptake by breaking down barriers for populations that have less access to care.”
“We’re hoping this research in combination with all of the extensive evidence on the positive performance of HPV self-collection will provide additional information to be considered by the FDA for approval of the kits for primary screening,” Dr. Smith said.
“Government approval of at-home HPV tests would have a huge impact,” said coauthor Noel Brewer, PhD, also of UNC Chapel Hill. “We could better reach those in rural areas where cervical cancer screening is hard to come by.”
Dr. Smith has received research grants, supply donations, and consultancies for Hologic and BD Diagnostics. Dr. Brewer, Dr. Wang, and Dr. Coleman reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM THE LANCET PUBLIC HEALTH
Vulvar syringoma
To the Editor:
Syringomas are common benign tumors of the eccrine sweat glands that usually manifest clinically as multiple flesh-colored papules. They are most commonly seen on the face, neck, and chest of adolescent girls. Syringomas may appear at any site of the body but are rare in the vulva. We present a case of a 51-year-old woman who was referred to the Division of Gynecologic Oncology at the University of Alabama at Birmingham for further management of a tumor carrying a differential diagnosis of vulvar syringoma vs microcystic adnexal carcinoma (MAC).
A 51-year-old woman presented to dermatology (G.G.) and was referred to the Division of Gynecologic Oncology at the University of Alabama at Birmingham for further management of possible vulvar syringoma vs MAC. The patient previously had been evaluated at an outside community practice due to dyspareunia, vulvar discomfort, and vulvar irregularities of 1 month’s duration. At that time, a small biopsy was performed, and the histologic differential diagnosis included syringoma vs an adnexal carcinoma. Consequently, she was referred to gynecologic oncology for further management.
Pelvic examination revealed multilobular nodular areas overlying the clitoral hood that extended down to the labia majora. The nodular processes did not involve the clitoris, labia minora, or perineum. A mobile isolated lymph node measuring 2.0×1.0 cm in the right inguinal area also was noted. The patient’s clinical history was notable for right breast carcinoma treated with a right mastectomy with axillary lymph node dissection that showed metastatic disease. She also underwent adjuvant chemotherapy with paclitaxel and doxorubicin for breast carcinoma.
After discussing the diagnostic differential and treatment options, the patient elected to undergo a bilateral partial radical vulvectomy with reconstruction and resection of the right inguinal lymph node. Gross examination of the vulvectomy specimen showed multiple flesh-colored papules (FIGURE 1). Histologic examination revealed a neoplasm with sweat gland differentiation that was broad and poorly circumscribed but confined to the dermis (FIGURES 2A and 2B). The neoplasm was composed of epithelial cells that formed ductlike structures, lined by 2 layers of cuboidal epithelium within a fibrous stroma (FIGURE 2C). A toluidine blue special stain was performed and demonstrated an increased amount of mast cells in the tissue (FIGURE 3). Immunohistochemical stains for gross cystic disease fluid protein, estrogen receptor (ER), and progesterone receptor (PR) were negative in the tumor cells. The lack of cytologic atypia, perineural invasion, and deep infiltration into the subcutis favored a syringoma. One month later, the case was presented at the Tumor Board Conference at the University of Alabama at Birmingham where a final diagnosis of vulvar syringoma was agreed upon and discussed with the patient. At that time, no recurrence was evident and follow-up was recommended.
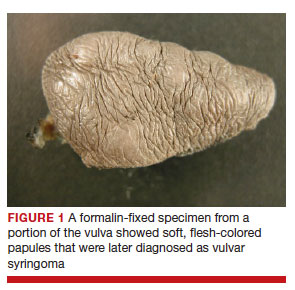
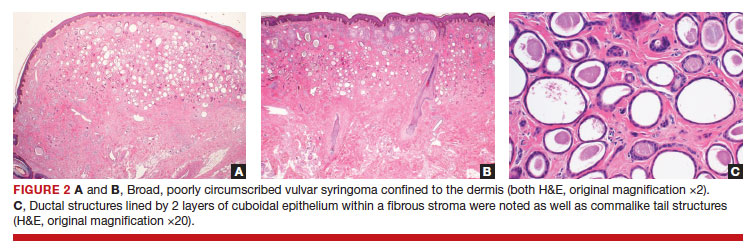
Syringomas are benign tumors of the sweat glands that are fairly common and appear to have a predilection for women. Although most of the literature classifies them as eccrine neoplasms, the term syringoma can be used to describe neoplasms of either apocrine or eccrine lineage.1 To rule out an apocrine lineage of the tumor in our patient, we performed immunohistochemistry for gross cystic disease fluid protein, a marker of apocrine differentiation. This stain highlighted normal apocrine glands that were not involved in the tumor proliferation.
Syringomas may occur at any site on the body but are prone to occur on the periorbital area, especially the eyelids.1 Some of the atypical locations for a syringoma include the anterior neck, chest, abdomen, genitals, axillae, groin, and buttocks.2 Vulvar syringomas were first reported by Carneiro3 in 1971 as usually affecting adolescent girls and middle-aged women. There have been approximately 40 reported cases affecting women aged 8 to 78 years.4,5 Vulvar syringomas classically appear as firm or soft, flesh-colored to transparent, papular lesions. The 2 other clinical variants are miliumlike, whitish, cystic papules as well as lichenoid papules.6 Pérez-Bustillo et al5 reported a case of the lichenoid papule variant on the labia majora of a 78-year-old woman who presented with intermittent vulvar pruritus of 4 years’ duration. Due to this patient’s 9-year history of urinary incontinence, the lesions had been misdiagnosed as irritant dermatitis and associated lichen simplex chronicus (LSC). This case is a reminder to consider vulvar syringoma in patients with LSC who respond poorly to oral antihistamines and topical steroids.5 Rarely, multiple clinical variants may coexist. In a case reported by Dereli et al,7 a 19-year-old woman presented with concurrent classical and miliumlike forms of vulvar syringoma.
Vulvar syringomas usually present as multiple lesions involving both sides of the labia majora; however, Blasdale and McLelland8 reported a single isolated syringoma of the vulva on the anterior right labia minora that measured 1.0×0.5 cm, leading the lesion to be described as a giant syringoma.
Vulvar syringomas usually are asymptomatic and noticed during routine gynecologic examination. Therefore, it is believed that they likely are underdiagnosed.5 When symptomatic, they commonly present with constant9 or intermittent5 pruritus, which may intensify during menstruation, pregnancy, and summertime.6,10-12 Gerdsen et al10 documented a 27-year-old woman who presented with a 2-year history of pruritic vulvar skin lesions that became exacerbated during menstruation, which raised the possibility of cyclical hormonal changes being responsible for periodic exacerbation of vulvar pruritus during menstruation. In addition, patients may experience an increase in size and number of the lesions during pregnancy. Bal et al11 reported a 24-year-old primigravida with vulvar papular lesions that intensified during pregnancy. She had experienced intermittent vulvar pruritus for 12 years but had no change in symptoms during menstruation.11 Few studies have attempted to evaluate the presence of ER and PR in the syringomas. A study of 9 nonvulvar syringomas by Wallace and Smoller13 showed ER positivity in 1 case and PR positivity in 8 cases, lending support to the hormonal theory; however, in another case series of 15 vulvar syringomas, Huang et al6 failed to show ER and PR expression by immunohistochemical staining. A case report published 3 years earlier documented the first case of PR positivity on a vulvar syringoma.14 Our patient also was negative for ER and PR, which suggested that hormonal status is important in some but not all syringomas.
Patients with vulvar syringomas also might have coexisting extragenital syringomas in the neck,4 eyelids,6,7,10 and periorbital area,6 and thorough examination of the body is essential. If an extragenital syringoma is diagnosed, a vulvar syringoma should be considered, especially when the patient presents with unexplained genital symptoms. Although no proven hereditary transmission pattern has been established, family history of syringomas has been established in several cases.15 In a case series reported by Huang et al,6 4 of 18 patients reported a family history of periorbital syringomas. In our case, the patient did not report a family history of syringomas.
The differential diagnosis of vulvar lesions with pruritus is broad and includes Fox-Fordyce disease, lichen planus, LSC, epidermal cysts, senile angiomas, dystrophic calcinosis, xanthomas, steatocytomas, soft fibromas, condyloma acuminatum, and candidiasis. Vulvar syringomas might have a nonspecific appearance, and histologic examination is essential to confirm the diagnosis and rule out any malignant process such as MAC, vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia, extramammary Paget disease, or other glandular neoplasms of the vulva.
Microcystic adnexal carcinoma was first reported in 1982 by Goldstein et al16 as a locally aggressive neoplasm that can be confused with benign adnexal neoplasms, particularly desmoplastic trichoepithelioma, trichoadenoma, and syringoma. Microcystic adnexal carcinomas present as slow-growing, flesh-colored papules that may resemble syringomas and appear in similar body sites. Histologic examination is essential to differentiate between these two entities. Syringomas are tumors confined to the dermis and are composed of multiple small ducts lined by 2 layers of cuboidal epithelium within a dense fibrous stroma. Unlike syringomas, MACs usually infiltrate diffusely into the dermis and subcutis and may extend into the underlying muscle. Although bland cytologic features predominate, perineural invasion frequently is present in MACs. A potential pitfall of misdiagnosis can be caused by a superficial biopsy that may reveal benign histologic appearance, particularly in the upper level of the tumor where it may be confused with a syringoma or a benign follicular neoplasm.17
The initial biopsy performed on our patient was possibly not deep enough to render an unequivocal diagnosis and therefore bilateral partial radical vulvectomy was considered. After surgery, histologic examination of the resection specimen revealed a poorly circumscribed tumor confined to the dermis. The tumor was broad and the lack of deep infiltration into the subcutis and perineural invasion favored a syringoma (FIGURES 2A and 2B). These findings were consistent with case reports that documented syringomas as being more wide than deep on microscopic examination, whereas the opposite pertained to MAC.18 Cases of plaque-type syringomas that initially were misdiagnosed as MACs also have been reported.19 Because misdiagnosis may affect the treatment plan and potentially result in unnecessary surgery, caution should be taken when differentiating between these two entities. When a definitive diagnosis cannot be rendered on a superficial biopsy, a recommendation should be made for a deeper biopsy sampling the subcutis.
For the majority of the patients with vulvar syringomas, treatment is seldom required due to their asymptomatic nature; however, patients who present with symptoms usually report pruritus of variable intensities and patterns. A standardized treatment does not exist for vulvar syringomas, and oral or topical treatment might be used as an initial approach. Commonly prescribed medications with variable results include topical corticosteroids, oral antihistamines, and topical retinoids. In a case reported by Iwao et al,20 vulvar syringomas were successfully treated with tranilast, which has anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects. This medication could have a possible dual action—inhibiting the release of chemical mediators from the mast cells and inhibiting the release of IL-1β from the eccrine duct, which could suppress the proliferation of stromal connective tissue. Our case was stained with toluidine blue and showed an increased number of mast cells in the tissue (FIGURE 3).Patients who are unresponsive to tranilast or have extensive disease resulting in cosmetic disfigurement might benefit from more invasive treatment methods including a variety of lasers, cryotherapy, electrosurgery, and excision. Excisions should include the entire tumor to avoid recurrence. In a case reported by Garman and Metry,21 the lesions were surgically excised using small 2- to 3-mm punches; however, several weeks later the lesions recurred. Our patient presented with a 1-month evolution of dyspareunia, vulvar discomfort, and vulvar irregularities that were probably not treated with oral or topical medications before being referred for surgery.
We report a case of a vulvar syringoma that presented diagnostic challenges in the initial biopsy, which prevented the exclusion of an MAC. After partial radical vulvectomy, histologic examination was more definitive, showing lack of deep infiltration into the subcutis or perineural invasion that are commonly seen in MAC. This case is an example of a notable pitfall in the diagnosis of vulvar syringoma on a limited biopsy leading to overtreatment. Raising awareness of this entity is the only modality to prevent misdiagnosis. We encourage reporting of further cases of syringomas, particularly those with atypical locations or patterns that may cause diagnostic problems. ●
- Ensure adequate depth of biopsy to assist in the histologic diagnosis of syringoma vs microcystic adnexal carcinoma.
- Vulvar syringomas also may contribute to notable pruritus and ultimately be the underlying etiology for secondary skin changes leading to a lichen simplex chronicus–like phenotype
- Bolognia JL, Jorizzo JL, Rapini RP. Dermatology. 2nd ed. Spain: Mosby Elsevier; 2008.
- Weedon D. Skin Pathology. 3rd ed. China: Churchill Livingstone Elsevier; 2010.
- Carneiro SJ, Gardner HL, Knox JM. Syringoma of the vulva. Arch Dermatol. 1971;103:494-496.
- Trager JD, Silvers J, Reed JA, et al. Neck and vulvar papules in an 8-year-old girl. Arch Dermatol. 1999;135:203, 206.
- Pérez-Bustillo A, Ruiz-González I, Delgado S, et al. Vulvar syringoma: a rare cause of vulvar pruritus. Actas DermoSifiliográficas. 2008; 99:580-581.
- Huang YH, Chuang YH, Kuo TT, et al. Vulvar syringoma: a clinicopathologic and immunohistologic study of 18 patients and results of treatment. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;48:735-739.
- Dereli T, Turk BG, Kazandi AC. Syringomas of the vulva. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2007;99:65-66.
- Blasdale C, McLelland J. Solitary giant vulval syringoma. Br J Dermatol. 1999;141:374-375.
- Kavala M, Can B, Zindanci I, et al. Vulvar pruritus caused by syringoma of the vulva. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47:831-832.
- Gerdsen R, Wenzel J, Uerlich M, et al. Periodic genital pruritus caused by syringoma of the vulva. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2002;81:369-370.
- Bal N, Aslan E, Kayaselcuk F, et al. Vulvar syringoma aggravated by pregnancy. Pathol Oncol Res. 2003;9:196-197.
- Turan C, Ugur M, Kutluay L, et al. Vulvar syringoma exacerbated during pregnancy. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 1996;64:141-142.
- Wallace ML, Smoller BR. Progesterone receptor positivity supports hormonal control of syringomas. J Cutan Pathol. 1995; 22:442-445.
- Yorganci A, Kale A, Dunder I, et al. Vulvar syringoma showing progesterone receptor positivity. BJOG. 2000;107:292-294.
- Draznin M. Hereditary syringomas: a case report. Dermatol Online J. 2004;10:19.
- Goldstein DJ, Barr RJ, Santa Cruz DJ. Microcystic adnexal carcinoma: a distinct clinicopathologic entity. Cancer. 1982;50:566-572.
- Hamsch C, Hartschuh W. Microcystic adnexal carcinomaaggressive infiltrative tumor often with innocent clinical appearance. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2010;8:275-278.
- Henner MS, Shapiro PE, Ritter JH, et al. Solitary syringoma. report of five cases and clinicopathologic comparison with microcystic adnexal carcinoma of the skin. Am J Dermatopathol. 1995;17:465-470.
- Suwattee P, McClelland MC, Huiras EE, et al. Plaque-type syringoma: two cases misdiagnosed as microcystic adnexal carcinoma. J Cutan Pathol. 2008;35:570-574.
- Iwao F, Onozuka T, Kawashima T. Vulval syringoma successfully treated with tranilast. Br J Dermatol. 2005;153:1228-1230.
- Garman M, Metry D. Vulvar syringomas in a 9-year-old child with review of the literature. Pediatr Dermatol. 2006;23:369372.
To the Editor:
Syringomas are common benign tumors of the eccrine sweat glands that usually manifest clinically as multiple flesh-colored papules. They are most commonly seen on the face, neck, and chest of adolescent girls. Syringomas may appear at any site of the body but are rare in the vulva. We present a case of a 51-year-old woman who was referred to the Division of Gynecologic Oncology at the University of Alabama at Birmingham for further management of a tumor carrying a differential diagnosis of vulvar syringoma vs microcystic adnexal carcinoma (MAC).
A 51-year-old woman presented to dermatology (G.G.) and was referred to the Division of Gynecologic Oncology at the University of Alabama at Birmingham for further management of possible vulvar syringoma vs MAC. The patient previously had been evaluated at an outside community practice due to dyspareunia, vulvar discomfort, and vulvar irregularities of 1 month’s duration. At that time, a small biopsy was performed, and the histologic differential diagnosis included syringoma vs an adnexal carcinoma. Consequently, she was referred to gynecologic oncology for further management.
Pelvic examination revealed multilobular nodular areas overlying the clitoral hood that extended down to the labia majora. The nodular processes did not involve the clitoris, labia minora, or perineum. A mobile isolated lymph node measuring 2.0×1.0 cm in the right inguinal area also was noted. The patient’s clinical history was notable for right breast carcinoma treated with a right mastectomy with axillary lymph node dissection that showed metastatic disease. She also underwent adjuvant chemotherapy with paclitaxel and doxorubicin for breast carcinoma.
After discussing the diagnostic differential and treatment options, the patient elected to undergo a bilateral partial radical vulvectomy with reconstruction and resection of the right inguinal lymph node. Gross examination of the vulvectomy specimen showed multiple flesh-colored papules (FIGURE 1). Histologic examination revealed a neoplasm with sweat gland differentiation that was broad and poorly circumscribed but confined to the dermis (FIGURES 2A and 2B). The neoplasm was composed of epithelial cells that formed ductlike structures, lined by 2 layers of cuboidal epithelium within a fibrous stroma (FIGURE 2C). A toluidine blue special stain was performed and demonstrated an increased amount of mast cells in the tissue (FIGURE 3). Immunohistochemical stains for gross cystic disease fluid protein, estrogen receptor (ER), and progesterone receptor (PR) were negative in the tumor cells. The lack of cytologic atypia, perineural invasion, and deep infiltration into the subcutis favored a syringoma. One month later, the case was presented at the Tumor Board Conference at the University of Alabama at Birmingham where a final diagnosis of vulvar syringoma was agreed upon and discussed with the patient. At that time, no recurrence was evident and follow-up was recommended.



Syringomas are benign tumors of the sweat glands that are fairly common and appear to have a predilection for women. Although most of the literature classifies them as eccrine neoplasms, the term syringoma can be used to describe neoplasms of either apocrine or eccrine lineage.1 To rule out an apocrine lineage of the tumor in our patient, we performed immunohistochemistry for gross cystic disease fluid protein, a marker of apocrine differentiation. This stain highlighted normal apocrine glands that were not involved in the tumor proliferation.
Syringomas may occur at any site on the body but are prone to occur on the periorbital area, especially the eyelids.1 Some of the atypical locations for a syringoma include the anterior neck, chest, abdomen, genitals, axillae, groin, and buttocks.2 Vulvar syringomas were first reported by Carneiro3 in 1971 as usually affecting adolescent girls and middle-aged women. There have been approximately 40 reported cases affecting women aged 8 to 78 years.4,5 Vulvar syringomas classically appear as firm or soft, flesh-colored to transparent, papular lesions. The 2 other clinical variants are miliumlike, whitish, cystic papules as well as lichenoid papules.6 Pérez-Bustillo et al5 reported a case of the lichenoid papule variant on the labia majora of a 78-year-old woman who presented with intermittent vulvar pruritus of 4 years’ duration. Due to this patient’s 9-year history of urinary incontinence, the lesions had been misdiagnosed as irritant dermatitis and associated lichen simplex chronicus (LSC). This case is a reminder to consider vulvar syringoma in patients with LSC who respond poorly to oral antihistamines and topical steroids.5 Rarely, multiple clinical variants may coexist. In a case reported by Dereli et al,7 a 19-year-old woman presented with concurrent classical and miliumlike forms of vulvar syringoma.
Vulvar syringomas usually present as multiple lesions involving both sides of the labia majora; however, Blasdale and McLelland8 reported a single isolated syringoma of the vulva on the anterior right labia minora that measured 1.0×0.5 cm, leading the lesion to be described as a giant syringoma.
Vulvar syringomas usually are asymptomatic and noticed during routine gynecologic examination. Therefore, it is believed that they likely are underdiagnosed.5 When symptomatic, they commonly present with constant9 or intermittent5 pruritus, which may intensify during menstruation, pregnancy, and summertime.6,10-12 Gerdsen et al10 documented a 27-year-old woman who presented with a 2-year history of pruritic vulvar skin lesions that became exacerbated during menstruation, which raised the possibility of cyclical hormonal changes being responsible for periodic exacerbation of vulvar pruritus during menstruation. In addition, patients may experience an increase in size and number of the lesions during pregnancy. Bal et al11 reported a 24-year-old primigravida with vulvar papular lesions that intensified during pregnancy. She had experienced intermittent vulvar pruritus for 12 years but had no change in symptoms during menstruation.11 Few studies have attempted to evaluate the presence of ER and PR in the syringomas. A study of 9 nonvulvar syringomas by Wallace and Smoller13 showed ER positivity in 1 case and PR positivity in 8 cases, lending support to the hormonal theory; however, in another case series of 15 vulvar syringomas, Huang et al6 failed to show ER and PR expression by immunohistochemical staining. A case report published 3 years earlier documented the first case of PR positivity on a vulvar syringoma.14 Our patient also was negative for ER and PR, which suggested that hormonal status is important in some but not all syringomas.
Patients with vulvar syringomas also might have coexisting extragenital syringomas in the neck,4 eyelids,6,7,10 and periorbital area,6 and thorough examination of the body is essential. If an extragenital syringoma is diagnosed, a vulvar syringoma should be considered, especially when the patient presents with unexplained genital symptoms. Although no proven hereditary transmission pattern has been established, family history of syringomas has been established in several cases.15 In a case series reported by Huang et al,6 4 of 18 patients reported a family history of periorbital syringomas. In our case, the patient did not report a family history of syringomas.
The differential diagnosis of vulvar lesions with pruritus is broad and includes Fox-Fordyce disease, lichen planus, LSC, epidermal cysts, senile angiomas, dystrophic calcinosis, xanthomas, steatocytomas, soft fibromas, condyloma acuminatum, and candidiasis. Vulvar syringomas might have a nonspecific appearance, and histologic examination is essential to confirm the diagnosis and rule out any malignant process such as MAC, vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia, extramammary Paget disease, or other glandular neoplasms of the vulva.
Microcystic adnexal carcinoma was first reported in 1982 by Goldstein et al16 as a locally aggressive neoplasm that can be confused with benign adnexal neoplasms, particularly desmoplastic trichoepithelioma, trichoadenoma, and syringoma. Microcystic adnexal carcinomas present as slow-growing, flesh-colored papules that may resemble syringomas and appear in similar body sites. Histologic examination is essential to differentiate between these two entities. Syringomas are tumors confined to the dermis and are composed of multiple small ducts lined by 2 layers of cuboidal epithelium within a dense fibrous stroma. Unlike syringomas, MACs usually infiltrate diffusely into the dermis and subcutis and may extend into the underlying muscle. Although bland cytologic features predominate, perineural invasion frequently is present in MACs. A potential pitfall of misdiagnosis can be caused by a superficial biopsy that may reveal benign histologic appearance, particularly in the upper level of the tumor where it may be confused with a syringoma or a benign follicular neoplasm.17
The initial biopsy performed on our patient was possibly not deep enough to render an unequivocal diagnosis and therefore bilateral partial radical vulvectomy was considered. After surgery, histologic examination of the resection specimen revealed a poorly circumscribed tumor confined to the dermis. The tumor was broad and the lack of deep infiltration into the subcutis and perineural invasion favored a syringoma (FIGURES 2A and 2B). These findings were consistent with case reports that documented syringomas as being more wide than deep on microscopic examination, whereas the opposite pertained to MAC.18 Cases of plaque-type syringomas that initially were misdiagnosed as MACs also have been reported.19 Because misdiagnosis may affect the treatment plan and potentially result in unnecessary surgery, caution should be taken when differentiating between these two entities. When a definitive diagnosis cannot be rendered on a superficial biopsy, a recommendation should be made for a deeper biopsy sampling the subcutis.
For the majority of the patients with vulvar syringomas, treatment is seldom required due to their asymptomatic nature; however, patients who present with symptoms usually report pruritus of variable intensities and patterns. A standardized treatment does not exist for vulvar syringomas, and oral or topical treatment might be used as an initial approach. Commonly prescribed medications with variable results include topical corticosteroids, oral antihistamines, and topical retinoids. In a case reported by Iwao et al,20 vulvar syringomas were successfully treated with tranilast, which has anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects. This medication could have a possible dual action—inhibiting the release of chemical mediators from the mast cells and inhibiting the release of IL-1β from the eccrine duct, which could suppress the proliferation of stromal connective tissue. Our case was stained with toluidine blue and showed an increased number of mast cells in the tissue (FIGURE 3).Patients who are unresponsive to tranilast or have extensive disease resulting in cosmetic disfigurement might benefit from more invasive treatment methods including a variety of lasers, cryotherapy, electrosurgery, and excision. Excisions should include the entire tumor to avoid recurrence. In a case reported by Garman and Metry,21 the lesions were surgically excised using small 2- to 3-mm punches; however, several weeks later the lesions recurred. Our patient presented with a 1-month evolution of dyspareunia, vulvar discomfort, and vulvar irregularities that were probably not treated with oral or topical medications before being referred for surgery.
We report a case of a vulvar syringoma that presented diagnostic challenges in the initial biopsy, which prevented the exclusion of an MAC. After partial radical vulvectomy, histologic examination was more definitive, showing lack of deep infiltration into the subcutis or perineural invasion that are commonly seen in MAC. This case is an example of a notable pitfall in the diagnosis of vulvar syringoma on a limited biopsy leading to overtreatment. Raising awareness of this entity is the only modality to prevent misdiagnosis. We encourage reporting of further cases of syringomas, particularly those with atypical locations or patterns that may cause diagnostic problems. ●
- Ensure adequate depth of biopsy to assist in the histologic diagnosis of syringoma vs microcystic adnexal carcinoma.
- Vulvar syringomas also may contribute to notable pruritus and ultimately be the underlying etiology for secondary skin changes leading to a lichen simplex chronicus–like phenotype
To the Editor:
Syringomas are common benign tumors of the eccrine sweat glands that usually manifest clinically as multiple flesh-colored papules. They are most commonly seen on the face, neck, and chest of adolescent girls. Syringomas may appear at any site of the body but are rare in the vulva. We present a case of a 51-year-old woman who was referred to the Division of Gynecologic Oncology at the University of Alabama at Birmingham for further management of a tumor carrying a differential diagnosis of vulvar syringoma vs microcystic adnexal carcinoma (MAC).
A 51-year-old woman presented to dermatology (G.G.) and was referred to the Division of Gynecologic Oncology at the University of Alabama at Birmingham for further management of possible vulvar syringoma vs MAC. The patient previously had been evaluated at an outside community practice due to dyspareunia, vulvar discomfort, and vulvar irregularities of 1 month’s duration. At that time, a small biopsy was performed, and the histologic differential diagnosis included syringoma vs an adnexal carcinoma. Consequently, she was referred to gynecologic oncology for further management.
Pelvic examination revealed multilobular nodular areas overlying the clitoral hood that extended down to the labia majora. The nodular processes did not involve the clitoris, labia minora, or perineum. A mobile isolated lymph node measuring 2.0×1.0 cm in the right inguinal area also was noted. The patient’s clinical history was notable for right breast carcinoma treated with a right mastectomy with axillary lymph node dissection that showed metastatic disease. She also underwent adjuvant chemotherapy with paclitaxel and doxorubicin for breast carcinoma.
After discussing the diagnostic differential and treatment options, the patient elected to undergo a bilateral partial radical vulvectomy with reconstruction and resection of the right inguinal lymph node. Gross examination of the vulvectomy specimen showed multiple flesh-colored papules (FIGURE 1). Histologic examination revealed a neoplasm with sweat gland differentiation that was broad and poorly circumscribed but confined to the dermis (FIGURES 2A and 2B). The neoplasm was composed of epithelial cells that formed ductlike structures, lined by 2 layers of cuboidal epithelium within a fibrous stroma (FIGURE 2C). A toluidine blue special stain was performed and demonstrated an increased amount of mast cells in the tissue (FIGURE 3). Immunohistochemical stains for gross cystic disease fluid protein, estrogen receptor (ER), and progesterone receptor (PR) were negative in the tumor cells. The lack of cytologic atypia, perineural invasion, and deep infiltration into the subcutis favored a syringoma. One month later, the case was presented at the Tumor Board Conference at the University of Alabama at Birmingham where a final diagnosis of vulvar syringoma was agreed upon and discussed with the patient. At that time, no recurrence was evident and follow-up was recommended.



Syringomas are benign tumors of the sweat glands that are fairly common and appear to have a predilection for women. Although most of the literature classifies them as eccrine neoplasms, the term syringoma can be used to describe neoplasms of either apocrine or eccrine lineage.1 To rule out an apocrine lineage of the tumor in our patient, we performed immunohistochemistry for gross cystic disease fluid protein, a marker of apocrine differentiation. This stain highlighted normal apocrine glands that were not involved in the tumor proliferation.
Syringomas may occur at any site on the body but are prone to occur on the periorbital area, especially the eyelids.1 Some of the atypical locations for a syringoma include the anterior neck, chest, abdomen, genitals, axillae, groin, and buttocks.2 Vulvar syringomas were first reported by Carneiro3 in 1971 as usually affecting adolescent girls and middle-aged women. There have been approximately 40 reported cases affecting women aged 8 to 78 years.4,5 Vulvar syringomas classically appear as firm or soft, flesh-colored to transparent, papular lesions. The 2 other clinical variants are miliumlike, whitish, cystic papules as well as lichenoid papules.6 Pérez-Bustillo et al5 reported a case of the lichenoid papule variant on the labia majora of a 78-year-old woman who presented with intermittent vulvar pruritus of 4 years’ duration. Due to this patient’s 9-year history of urinary incontinence, the lesions had been misdiagnosed as irritant dermatitis and associated lichen simplex chronicus (LSC). This case is a reminder to consider vulvar syringoma in patients with LSC who respond poorly to oral antihistamines and topical steroids.5 Rarely, multiple clinical variants may coexist. In a case reported by Dereli et al,7 a 19-year-old woman presented with concurrent classical and miliumlike forms of vulvar syringoma.
Vulvar syringomas usually present as multiple lesions involving both sides of the labia majora; however, Blasdale and McLelland8 reported a single isolated syringoma of the vulva on the anterior right labia minora that measured 1.0×0.5 cm, leading the lesion to be described as a giant syringoma.
Vulvar syringomas usually are asymptomatic and noticed during routine gynecologic examination. Therefore, it is believed that they likely are underdiagnosed.5 When symptomatic, they commonly present with constant9 or intermittent5 pruritus, which may intensify during menstruation, pregnancy, and summertime.6,10-12 Gerdsen et al10 documented a 27-year-old woman who presented with a 2-year history of pruritic vulvar skin lesions that became exacerbated during menstruation, which raised the possibility of cyclical hormonal changes being responsible for periodic exacerbation of vulvar pruritus during menstruation. In addition, patients may experience an increase in size and number of the lesions during pregnancy. Bal et al11 reported a 24-year-old primigravida with vulvar papular lesions that intensified during pregnancy. She had experienced intermittent vulvar pruritus for 12 years but had no change in symptoms during menstruation.11 Few studies have attempted to evaluate the presence of ER and PR in the syringomas. A study of 9 nonvulvar syringomas by Wallace and Smoller13 showed ER positivity in 1 case and PR positivity in 8 cases, lending support to the hormonal theory; however, in another case series of 15 vulvar syringomas, Huang et al6 failed to show ER and PR expression by immunohistochemical staining. A case report published 3 years earlier documented the first case of PR positivity on a vulvar syringoma.14 Our patient also was negative for ER and PR, which suggested that hormonal status is important in some but not all syringomas.
Patients with vulvar syringomas also might have coexisting extragenital syringomas in the neck,4 eyelids,6,7,10 and periorbital area,6 and thorough examination of the body is essential. If an extragenital syringoma is diagnosed, a vulvar syringoma should be considered, especially when the patient presents with unexplained genital symptoms. Although no proven hereditary transmission pattern has been established, family history of syringomas has been established in several cases.15 In a case series reported by Huang et al,6 4 of 18 patients reported a family history of periorbital syringomas. In our case, the patient did not report a family history of syringomas.
The differential diagnosis of vulvar lesions with pruritus is broad and includes Fox-Fordyce disease, lichen planus, LSC, epidermal cysts, senile angiomas, dystrophic calcinosis, xanthomas, steatocytomas, soft fibromas, condyloma acuminatum, and candidiasis. Vulvar syringomas might have a nonspecific appearance, and histologic examination is essential to confirm the diagnosis and rule out any malignant process such as MAC, vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia, extramammary Paget disease, or other glandular neoplasms of the vulva.
Microcystic adnexal carcinoma was first reported in 1982 by Goldstein et al16 as a locally aggressive neoplasm that can be confused with benign adnexal neoplasms, particularly desmoplastic trichoepithelioma, trichoadenoma, and syringoma. Microcystic adnexal carcinomas present as slow-growing, flesh-colored papules that may resemble syringomas and appear in similar body sites. Histologic examination is essential to differentiate between these two entities. Syringomas are tumors confined to the dermis and are composed of multiple small ducts lined by 2 layers of cuboidal epithelium within a dense fibrous stroma. Unlike syringomas, MACs usually infiltrate diffusely into the dermis and subcutis and may extend into the underlying muscle. Although bland cytologic features predominate, perineural invasion frequently is present in MACs. A potential pitfall of misdiagnosis can be caused by a superficial biopsy that may reveal benign histologic appearance, particularly in the upper level of the tumor where it may be confused with a syringoma or a benign follicular neoplasm.17
The initial biopsy performed on our patient was possibly not deep enough to render an unequivocal diagnosis and therefore bilateral partial radical vulvectomy was considered. After surgery, histologic examination of the resection specimen revealed a poorly circumscribed tumor confined to the dermis. The tumor was broad and the lack of deep infiltration into the subcutis and perineural invasion favored a syringoma (FIGURES 2A and 2B). These findings were consistent with case reports that documented syringomas as being more wide than deep on microscopic examination, whereas the opposite pertained to MAC.18 Cases of plaque-type syringomas that initially were misdiagnosed as MACs also have been reported.19 Because misdiagnosis may affect the treatment plan and potentially result in unnecessary surgery, caution should be taken when differentiating between these two entities. When a definitive diagnosis cannot be rendered on a superficial biopsy, a recommendation should be made for a deeper biopsy sampling the subcutis.
For the majority of the patients with vulvar syringomas, treatment is seldom required due to their asymptomatic nature; however, patients who present with symptoms usually report pruritus of variable intensities and patterns. A standardized treatment does not exist for vulvar syringomas, and oral or topical treatment might be used as an initial approach. Commonly prescribed medications with variable results include topical corticosteroids, oral antihistamines, and topical retinoids. In a case reported by Iwao et al,20 vulvar syringomas were successfully treated with tranilast, which has anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects. This medication could have a possible dual action—inhibiting the release of chemical mediators from the mast cells and inhibiting the release of IL-1β from the eccrine duct, which could suppress the proliferation of stromal connective tissue. Our case was stained with toluidine blue and showed an increased number of mast cells in the tissue (FIGURE 3).Patients who are unresponsive to tranilast or have extensive disease resulting in cosmetic disfigurement might benefit from more invasive treatment methods including a variety of lasers, cryotherapy, electrosurgery, and excision. Excisions should include the entire tumor to avoid recurrence. In a case reported by Garman and Metry,21 the lesions were surgically excised using small 2- to 3-mm punches; however, several weeks later the lesions recurred. Our patient presented with a 1-month evolution of dyspareunia, vulvar discomfort, and vulvar irregularities that were probably not treated with oral or topical medications before being referred for surgery.
We report a case of a vulvar syringoma that presented diagnostic challenges in the initial biopsy, which prevented the exclusion of an MAC. After partial radical vulvectomy, histologic examination was more definitive, showing lack of deep infiltration into the subcutis or perineural invasion that are commonly seen in MAC. This case is an example of a notable pitfall in the diagnosis of vulvar syringoma on a limited biopsy leading to overtreatment. Raising awareness of this entity is the only modality to prevent misdiagnosis. We encourage reporting of further cases of syringomas, particularly those with atypical locations or patterns that may cause diagnostic problems. ●
- Ensure adequate depth of biopsy to assist in the histologic diagnosis of syringoma vs microcystic adnexal carcinoma.
- Vulvar syringomas also may contribute to notable pruritus and ultimately be the underlying etiology for secondary skin changes leading to a lichen simplex chronicus–like phenotype
- Bolognia JL, Jorizzo JL, Rapini RP. Dermatology. 2nd ed. Spain: Mosby Elsevier; 2008.
- Weedon D. Skin Pathology. 3rd ed. China: Churchill Livingstone Elsevier; 2010.
- Carneiro SJ, Gardner HL, Knox JM. Syringoma of the vulva. Arch Dermatol. 1971;103:494-496.
- Trager JD, Silvers J, Reed JA, et al. Neck and vulvar papules in an 8-year-old girl. Arch Dermatol. 1999;135:203, 206.
- Pérez-Bustillo A, Ruiz-González I, Delgado S, et al. Vulvar syringoma: a rare cause of vulvar pruritus. Actas DermoSifiliográficas. 2008; 99:580-581.
- Huang YH, Chuang YH, Kuo TT, et al. Vulvar syringoma: a clinicopathologic and immunohistologic study of 18 patients and results of treatment. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;48:735-739.
- Dereli T, Turk BG, Kazandi AC. Syringomas of the vulva. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2007;99:65-66.
- Blasdale C, McLelland J. Solitary giant vulval syringoma. Br J Dermatol. 1999;141:374-375.
- Kavala M, Can B, Zindanci I, et al. Vulvar pruritus caused by syringoma of the vulva. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47:831-832.
- Gerdsen R, Wenzel J, Uerlich M, et al. Periodic genital pruritus caused by syringoma of the vulva. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2002;81:369-370.
- Bal N, Aslan E, Kayaselcuk F, et al. Vulvar syringoma aggravated by pregnancy. Pathol Oncol Res. 2003;9:196-197.
- Turan C, Ugur M, Kutluay L, et al. Vulvar syringoma exacerbated during pregnancy. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 1996;64:141-142.
- Wallace ML, Smoller BR. Progesterone receptor positivity supports hormonal control of syringomas. J Cutan Pathol. 1995; 22:442-445.
- Yorganci A, Kale A, Dunder I, et al. Vulvar syringoma showing progesterone receptor positivity. BJOG. 2000;107:292-294.
- Draznin M. Hereditary syringomas: a case report. Dermatol Online J. 2004;10:19.
- Goldstein DJ, Barr RJ, Santa Cruz DJ. Microcystic adnexal carcinoma: a distinct clinicopathologic entity. Cancer. 1982;50:566-572.
- Hamsch C, Hartschuh W. Microcystic adnexal carcinomaaggressive infiltrative tumor often with innocent clinical appearance. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2010;8:275-278.
- Henner MS, Shapiro PE, Ritter JH, et al. Solitary syringoma. report of five cases and clinicopathologic comparison with microcystic adnexal carcinoma of the skin. Am J Dermatopathol. 1995;17:465-470.
- Suwattee P, McClelland MC, Huiras EE, et al. Plaque-type syringoma: two cases misdiagnosed as microcystic adnexal carcinoma. J Cutan Pathol. 2008;35:570-574.
- Iwao F, Onozuka T, Kawashima T. Vulval syringoma successfully treated with tranilast. Br J Dermatol. 2005;153:1228-1230.
- Garman M, Metry D. Vulvar syringomas in a 9-year-old child with review of the literature. Pediatr Dermatol. 2006;23:369372.
- Bolognia JL, Jorizzo JL, Rapini RP. Dermatology. 2nd ed. Spain: Mosby Elsevier; 2008.
- Weedon D. Skin Pathology. 3rd ed. China: Churchill Livingstone Elsevier; 2010.
- Carneiro SJ, Gardner HL, Knox JM. Syringoma of the vulva. Arch Dermatol. 1971;103:494-496.
- Trager JD, Silvers J, Reed JA, et al. Neck and vulvar papules in an 8-year-old girl. Arch Dermatol. 1999;135:203, 206.
- Pérez-Bustillo A, Ruiz-González I, Delgado S, et al. Vulvar syringoma: a rare cause of vulvar pruritus. Actas DermoSifiliográficas. 2008; 99:580-581.
- Huang YH, Chuang YH, Kuo TT, et al. Vulvar syringoma: a clinicopathologic and immunohistologic study of 18 patients and results of treatment. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;48:735-739.
- Dereli T, Turk BG, Kazandi AC. Syringomas of the vulva. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2007;99:65-66.
- Blasdale C, McLelland J. Solitary giant vulval syringoma. Br J Dermatol. 1999;141:374-375.
- Kavala M, Can B, Zindanci I, et al. Vulvar pruritus caused by syringoma of the vulva. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47:831-832.
- Gerdsen R, Wenzel J, Uerlich M, et al. Periodic genital pruritus caused by syringoma of the vulva. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2002;81:369-370.
- Bal N, Aslan E, Kayaselcuk F, et al. Vulvar syringoma aggravated by pregnancy. Pathol Oncol Res. 2003;9:196-197.
- Turan C, Ugur M, Kutluay L, et al. Vulvar syringoma exacerbated during pregnancy. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 1996;64:141-142.
- Wallace ML, Smoller BR. Progesterone receptor positivity supports hormonal control of syringomas. J Cutan Pathol. 1995; 22:442-445.
- Yorganci A, Kale A, Dunder I, et al. Vulvar syringoma showing progesterone receptor positivity. BJOG. 2000;107:292-294.
- Draznin M. Hereditary syringomas: a case report. Dermatol Online J. 2004;10:19.
- Goldstein DJ, Barr RJ, Santa Cruz DJ. Microcystic adnexal carcinoma: a distinct clinicopathologic entity. Cancer. 1982;50:566-572.
- Hamsch C, Hartschuh W. Microcystic adnexal carcinomaaggressive infiltrative tumor often with innocent clinical appearance. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2010;8:275-278.
- Henner MS, Shapiro PE, Ritter JH, et al. Solitary syringoma. report of five cases and clinicopathologic comparison with microcystic adnexal carcinoma of the skin. Am J Dermatopathol. 1995;17:465-470.
- Suwattee P, McClelland MC, Huiras EE, et al. Plaque-type syringoma: two cases misdiagnosed as microcystic adnexal carcinoma. J Cutan Pathol. 2008;35:570-574.
- Iwao F, Onozuka T, Kawashima T. Vulval syringoma successfully treated with tranilast. Br J Dermatol. 2005;153:1228-1230.
- Garman M, Metry D. Vulvar syringomas in a 9-year-old child with review of the literature. Pediatr Dermatol. 2006;23:369372.










