User login
Durable Tocilizumab Responses Seen in Trial Extensions of Polyarticular and Systemic JIA Subtypes
TOPLINE:
Subcutaneous tocilizumab provides durable disease control rates in patients with polyarticular and systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (pJIA and sJIA, respectively).
METHODOLOGY:
- This long-term extension (LTE) study included 44 patients with pJIA and 38 patients with sJIA, according to the International League of Associations for Rheumatology criteria, from two 52-week phase 1b trials (NCT01904292 and NCT01904279).
- In the core trials, the dosing frequency of subcutaneous tocilizumab was determined by weight: Every 3 weeks for those < 30 kg in pJIA and every 2 weeks for those ≥ 30 kg; in sJIA, initially every 10 days for those < 30 kg, transitioning to every 2 weeks, and weekly for those ≥ 30 kg.
- Patients who had adequate disease control with subcutaneous tocilizumab, comparable with the use of intravenous tocilizumab in the core trials, continued to receive subcutaneous tocilizumab.
- The study outcome was the change in Juvenile Arthritis Disease Activity Score on 71 joints (JADAS-71, range 0-101).
TAKEAWAY:
- Disease control remained stable in both groups, with sustained improvements in median JADAS-71 scores in pJIA (−0.2 with lower frequency dosing to −0.5 with higher frequency) and sJIA (−0.1 at both dosing frequencies).
- In the pJIA group, 90% and 53% of patients weighing < 30 kg and ≥ 30 kg achieved inactive disease, respectively, whereas in the sJIA group, the respective rates were 91% and 92%.
- A total of five of 15 patients with pJIA weighing ≥ 30 kg who received subcutaneous tocilizumab every 2 weeks achieved clinical remission, whereas in other groups, the clinical remission rates ranged from 74% to 92%.
- Six patients with pJIA reported seven serious adverse events (SAEs), while five patients with sJIA experienced six SAEs. Five patients with pJIA and one patient with sJIA reported serious infections.
IN PRACTICE:
The authors concluded that subcutaneous tocilizumab treatment provided long-term disease control in patients with pJIA or sJIA, with a safety profile consistent with past studies of tocilizumab.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Hermine I. Brunner, MD, director of the Division of Rheumatology at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. It was published online in Rheumatology (Oxford).
LIMITATIONS:
The open-label design and lack of a control group limited the analysis. Only a few patients continued the treatment for 5 years.
DISCLOSURES:
This work was supported by F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. Eight authors reported receiving honoraria and consulting or speaker fees from various pharma sources. The remaining authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Subcutaneous tocilizumab provides durable disease control rates in patients with polyarticular and systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (pJIA and sJIA, respectively).
METHODOLOGY:
- This long-term extension (LTE) study included 44 patients with pJIA and 38 patients with sJIA, according to the International League of Associations for Rheumatology criteria, from two 52-week phase 1b trials (NCT01904292 and NCT01904279).
- In the core trials, the dosing frequency of subcutaneous tocilizumab was determined by weight: Every 3 weeks for those < 30 kg in pJIA and every 2 weeks for those ≥ 30 kg; in sJIA, initially every 10 days for those < 30 kg, transitioning to every 2 weeks, and weekly for those ≥ 30 kg.
- Patients who had adequate disease control with subcutaneous tocilizumab, comparable with the use of intravenous tocilizumab in the core trials, continued to receive subcutaneous tocilizumab.
- The study outcome was the change in Juvenile Arthritis Disease Activity Score on 71 joints (JADAS-71, range 0-101).
TAKEAWAY:
- Disease control remained stable in both groups, with sustained improvements in median JADAS-71 scores in pJIA (−0.2 with lower frequency dosing to −0.5 with higher frequency) and sJIA (−0.1 at both dosing frequencies).
- In the pJIA group, 90% and 53% of patients weighing < 30 kg and ≥ 30 kg achieved inactive disease, respectively, whereas in the sJIA group, the respective rates were 91% and 92%.
- A total of five of 15 patients with pJIA weighing ≥ 30 kg who received subcutaneous tocilizumab every 2 weeks achieved clinical remission, whereas in other groups, the clinical remission rates ranged from 74% to 92%.
- Six patients with pJIA reported seven serious adverse events (SAEs), while five patients with sJIA experienced six SAEs. Five patients with pJIA and one patient with sJIA reported serious infections.
IN PRACTICE:
The authors concluded that subcutaneous tocilizumab treatment provided long-term disease control in patients with pJIA or sJIA, with a safety profile consistent with past studies of tocilizumab.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Hermine I. Brunner, MD, director of the Division of Rheumatology at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. It was published online in Rheumatology (Oxford).
LIMITATIONS:
The open-label design and lack of a control group limited the analysis. Only a few patients continued the treatment for 5 years.
DISCLOSURES:
This work was supported by F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. Eight authors reported receiving honoraria and consulting or speaker fees from various pharma sources. The remaining authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Subcutaneous tocilizumab provides durable disease control rates in patients with polyarticular and systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (pJIA and sJIA, respectively).
METHODOLOGY:
- This long-term extension (LTE) study included 44 patients with pJIA and 38 patients with sJIA, according to the International League of Associations for Rheumatology criteria, from two 52-week phase 1b trials (NCT01904292 and NCT01904279).
- In the core trials, the dosing frequency of subcutaneous tocilizumab was determined by weight: Every 3 weeks for those < 30 kg in pJIA and every 2 weeks for those ≥ 30 kg; in sJIA, initially every 10 days for those < 30 kg, transitioning to every 2 weeks, and weekly for those ≥ 30 kg.
- Patients who had adequate disease control with subcutaneous tocilizumab, comparable with the use of intravenous tocilizumab in the core trials, continued to receive subcutaneous tocilizumab.
- The study outcome was the change in Juvenile Arthritis Disease Activity Score on 71 joints (JADAS-71, range 0-101).
TAKEAWAY:
- Disease control remained stable in both groups, with sustained improvements in median JADAS-71 scores in pJIA (−0.2 with lower frequency dosing to −0.5 with higher frequency) and sJIA (−0.1 at both dosing frequencies).
- In the pJIA group, 90% and 53% of patients weighing < 30 kg and ≥ 30 kg achieved inactive disease, respectively, whereas in the sJIA group, the respective rates were 91% and 92%.
- A total of five of 15 patients with pJIA weighing ≥ 30 kg who received subcutaneous tocilizumab every 2 weeks achieved clinical remission, whereas in other groups, the clinical remission rates ranged from 74% to 92%.
- Six patients with pJIA reported seven serious adverse events (SAEs), while five patients with sJIA experienced six SAEs. Five patients with pJIA and one patient with sJIA reported serious infections.
IN PRACTICE:
The authors concluded that subcutaneous tocilizumab treatment provided long-term disease control in patients with pJIA or sJIA, with a safety profile consistent with past studies of tocilizumab.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Hermine I. Brunner, MD, director of the Division of Rheumatology at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. It was published online in Rheumatology (Oxford).
LIMITATIONS:
The open-label design and lack of a control group limited the analysis. Only a few patients continued the treatment for 5 years.
DISCLOSURES:
This work was supported by F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. Eight authors reported receiving honoraria and consulting or speaker fees from various pharma sources. The remaining authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Body Fat Levels Affect Physical Function in Biologic-Treated Axial Spondyloarthritis
TOPLINE:
Higher levels of body fat and visceral adipose tissue are associated with increased functional disability and reduced spinal mobility in patients with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) receiving biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs).
METHODOLOGY:
- Research showed that patients with axSpA respond poorly to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors if they have a high body mass index (BMI) or obesity; however, studies delving into the association between biologic therapy and body composition are limited.
- Researchers investigated the association between body composition evaluated by bioimpedance analysis and disease activity, physical function, and mobility in 74 patients with axSpA (mean age, 36.5; 71.6% men) at 6 months and 1 year after initiating bDMARDs.
- These participants from the German Spondyloarthritis Inception Cohort presented with high disease activity despite previous treatment with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and initiated bDMARD therapy between 2015 and 2019.
- Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index and Axial Spondyloarthritis Disease Activity Score were used to measure disease activity, while Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index and Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Mobility Index assessed physical function and spinal mobility, respectively.
- BMI, fat mass, fat mass index, and visceral adipose tissue (VAT) were used to determine body composition along with other parameters.
TAKEAWAY:
- Higher BMI (parameter estimates [β], 0.081; 95% CI, 0.016-0.145), fat mass (β, 0.037; 95% CI, 0.004-0.070), and fat mass index (β, 0.125; 95% CI, 0.031-0.219) were associated with worse physical function in the overall population.
- VAT was positively associated with reduced spinal mobility (β, 0.201; 95% CI, 0.071-0.332), particularly in men.
- In women, an increase in VAT was linked to worse disease activity and functional disability.
- Treatment with bDMARDs reduced all disease activity parameters but led to an increase in BMI and fat-related parameters, indicating that lifestyle modifications are also necessary to achieve the desired outcomes with bDMARD therapy.
IN PRACTICE:
“Overall, our findings highlight the importance of maintaining a healthy body weight and body composition — characterized by adequate lean mass and reduced FM [fat mass] — to improve physical function and quality of life in patients with SpA,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Valeria Rios Rodriguez, MD, department of gastroenterology, infectiology and rheumatology, Charité Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Germany. It was published online March 20, 2024, in Rheumatology (Oxford).
LIMITATIONS:
This study lacked a control group of patients with axSpA who did not receive biologics. It also did not include dietary habits and comorbidities such as hypertension or diabetes. Additionally, bioimpedance analysis was chosen as the method to assess body composition instead of dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research and the Berlin Institute of Health. Some of the authors declared receiving personal fees, grants, and consulting fees from various pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Higher levels of body fat and visceral adipose tissue are associated with increased functional disability and reduced spinal mobility in patients with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) receiving biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs).
METHODOLOGY:
- Research showed that patients with axSpA respond poorly to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors if they have a high body mass index (BMI) or obesity; however, studies delving into the association between biologic therapy and body composition are limited.
- Researchers investigated the association between body composition evaluated by bioimpedance analysis and disease activity, physical function, and mobility in 74 patients with axSpA (mean age, 36.5; 71.6% men) at 6 months and 1 year after initiating bDMARDs.
- These participants from the German Spondyloarthritis Inception Cohort presented with high disease activity despite previous treatment with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and initiated bDMARD therapy between 2015 and 2019.
- Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index and Axial Spondyloarthritis Disease Activity Score were used to measure disease activity, while Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index and Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Mobility Index assessed physical function and spinal mobility, respectively.
- BMI, fat mass, fat mass index, and visceral adipose tissue (VAT) were used to determine body composition along with other parameters.
TAKEAWAY:
- Higher BMI (parameter estimates [β], 0.081; 95% CI, 0.016-0.145), fat mass (β, 0.037; 95% CI, 0.004-0.070), and fat mass index (β, 0.125; 95% CI, 0.031-0.219) were associated with worse physical function in the overall population.
- VAT was positively associated with reduced spinal mobility (β, 0.201; 95% CI, 0.071-0.332), particularly in men.
- In women, an increase in VAT was linked to worse disease activity and functional disability.
- Treatment with bDMARDs reduced all disease activity parameters but led to an increase in BMI and fat-related parameters, indicating that lifestyle modifications are also necessary to achieve the desired outcomes with bDMARD therapy.
IN PRACTICE:
“Overall, our findings highlight the importance of maintaining a healthy body weight and body composition — characterized by adequate lean mass and reduced FM [fat mass] — to improve physical function and quality of life in patients with SpA,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Valeria Rios Rodriguez, MD, department of gastroenterology, infectiology and rheumatology, Charité Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Germany. It was published online March 20, 2024, in Rheumatology (Oxford).
LIMITATIONS:
This study lacked a control group of patients with axSpA who did not receive biologics. It also did not include dietary habits and comorbidities such as hypertension or diabetes. Additionally, bioimpedance analysis was chosen as the method to assess body composition instead of dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research and the Berlin Institute of Health. Some of the authors declared receiving personal fees, grants, and consulting fees from various pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Higher levels of body fat and visceral adipose tissue are associated with increased functional disability and reduced spinal mobility in patients with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) receiving biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs).
METHODOLOGY:
- Research showed that patients with axSpA respond poorly to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors if they have a high body mass index (BMI) or obesity; however, studies delving into the association between biologic therapy and body composition are limited.
- Researchers investigated the association between body composition evaluated by bioimpedance analysis and disease activity, physical function, and mobility in 74 patients with axSpA (mean age, 36.5; 71.6% men) at 6 months and 1 year after initiating bDMARDs.
- These participants from the German Spondyloarthritis Inception Cohort presented with high disease activity despite previous treatment with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and initiated bDMARD therapy between 2015 and 2019.
- Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index and Axial Spondyloarthritis Disease Activity Score were used to measure disease activity, while Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index and Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Mobility Index assessed physical function and spinal mobility, respectively.
- BMI, fat mass, fat mass index, and visceral adipose tissue (VAT) were used to determine body composition along with other parameters.
TAKEAWAY:
- Higher BMI (parameter estimates [β], 0.081; 95% CI, 0.016-0.145), fat mass (β, 0.037; 95% CI, 0.004-0.070), and fat mass index (β, 0.125; 95% CI, 0.031-0.219) were associated with worse physical function in the overall population.
- VAT was positively associated with reduced spinal mobility (β, 0.201; 95% CI, 0.071-0.332), particularly in men.
- In women, an increase in VAT was linked to worse disease activity and functional disability.
- Treatment with bDMARDs reduced all disease activity parameters but led to an increase in BMI and fat-related parameters, indicating that lifestyle modifications are also necessary to achieve the desired outcomes with bDMARD therapy.
IN PRACTICE:
“Overall, our findings highlight the importance of maintaining a healthy body weight and body composition — characterized by adequate lean mass and reduced FM [fat mass] — to improve physical function and quality of life in patients with SpA,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Valeria Rios Rodriguez, MD, department of gastroenterology, infectiology and rheumatology, Charité Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Germany. It was published online March 20, 2024, in Rheumatology (Oxford).
LIMITATIONS:
This study lacked a control group of patients with axSpA who did not receive biologics. It also did not include dietary habits and comorbidities such as hypertension or diabetes. Additionally, bioimpedance analysis was chosen as the method to assess body composition instead of dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research and the Berlin Institute of Health. Some of the authors declared receiving personal fees, grants, and consulting fees from various pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Worldwide Prevalence of Psoriatic Arthritis More Precisely Determined
TOPLINE:
According to this meta-analysis, psoriatic arthritis (PsA) affects 112 out of every 100,000 adults globally, with higher rates observed in Europe and North America than in Asia and South America, according to an analysis of 30 studies.
METHODOLOGY:
- Many previous epidemiological studies have estimated the global prevalence of PsA but have reported marked variations, which could be explained by differences in methodology and inclusion criteria.
- This meta-analysis used data from 30 studies conducted between 1982 and 2020 to estimate the worldwide prevalence of PsA in the general adult population, giving particular attention to methodological differences among the included studies.
- The included studies were either population-based (n = 13) or based on health administrative records (n = 17) and covered over 180 million adults across 24 countries.
- Overall, 15 studies were from Europe, seven from Asia, six from North America, and two from South America.
TAKEAWAY:
- The global prevalence of PsA was estimated at 113 (95% CI, 64-198) and 109 (75-158) cases per 100,000 based on population-based studies and health administrative data studies, respectively.
- The pooled global prevalence of PsA (combining the population-based and health administrative studies) was 112 cases per 100,000 (95% CI, 83-151).
- Combining both study designs, the global prevalence rates of PsA were 188 (95% CI, 128-289) cases per 100,000 for Europe, 48 (95% CI, 20-115) for Asia, 133 (95% CI, 93-191) for North America, and 17 (95% CI, 4-70) for South America.
IN PRACTICE:
“Robust estimates of prevalence are crucial for healthcare planning and resource allocation,” wrote the authors.
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by Stephanie Lembke, MSc, and colleagues from the Aberdeen Centre for Arthritis and Musculoskeletal Health, University of Aberdeen, Scotland. It was published online in Rheumatology (Oxford).
LIMITATIONS:
The meta-analysis had high levels of uncertainty and high heterogeneity between studies. In countries with unequal healthcare access, using data from statutory or private insurance databases to calculate PsA prevalence may systematically exclude uninsured individuals or those covered by private insurers. Moreover, the data were insufficient for a statistically meaningful subgroup analysis.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not receive any specific funding from any public, commercial, or nonprofit sectors to carry out this work. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
According to this meta-analysis, psoriatic arthritis (PsA) affects 112 out of every 100,000 adults globally, with higher rates observed in Europe and North America than in Asia and South America, according to an analysis of 30 studies.
METHODOLOGY:
- Many previous epidemiological studies have estimated the global prevalence of PsA but have reported marked variations, which could be explained by differences in methodology and inclusion criteria.
- This meta-analysis used data from 30 studies conducted between 1982 and 2020 to estimate the worldwide prevalence of PsA in the general adult population, giving particular attention to methodological differences among the included studies.
- The included studies were either population-based (n = 13) or based on health administrative records (n = 17) and covered over 180 million adults across 24 countries.
- Overall, 15 studies were from Europe, seven from Asia, six from North America, and two from South America.
TAKEAWAY:
- The global prevalence of PsA was estimated at 113 (95% CI, 64-198) and 109 (75-158) cases per 100,000 based on population-based studies and health administrative data studies, respectively.
- The pooled global prevalence of PsA (combining the population-based and health administrative studies) was 112 cases per 100,000 (95% CI, 83-151).
- Combining both study designs, the global prevalence rates of PsA were 188 (95% CI, 128-289) cases per 100,000 for Europe, 48 (95% CI, 20-115) for Asia, 133 (95% CI, 93-191) for North America, and 17 (95% CI, 4-70) for South America.
IN PRACTICE:
“Robust estimates of prevalence are crucial for healthcare planning and resource allocation,” wrote the authors.
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by Stephanie Lembke, MSc, and colleagues from the Aberdeen Centre for Arthritis and Musculoskeletal Health, University of Aberdeen, Scotland. It was published online in Rheumatology (Oxford).
LIMITATIONS:
The meta-analysis had high levels of uncertainty and high heterogeneity between studies. In countries with unequal healthcare access, using data from statutory or private insurance databases to calculate PsA prevalence may systematically exclude uninsured individuals or those covered by private insurers. Moreover, the data were insufficient for a statistically meaningful subgroup analysis.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not receive any specific funding from any public, commercial, or nonprofit sectors to carry out this work. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
According to this meta-analysis, psoriatic arthritis (PsA) affects 112 out of every 100,000 adults globally, with higher rates observed in Europe and North America than in Asia and South America, according to an analysis of 30 studies.
METHODOLOGY:
- Many previous epidemiological studies have estimated the global prevalence of PsA but have reported marked variations, which could be explained by differences in methodology and inclusion criteria.
- This meta-analysis used data from 30 studies conducted between 1982 and 2020 to estimate the worldwide prevalence of PsA in the general adult population, giving particular attention to methodological differences among the included studies.
- The included studies were either population-based (n = 13) or based on health administrative records (n = 17) and covered over 180 million adults across 24 countries.
- Overall, 15 studies were from Europe, seven from Asia, six from North America, and two from South America.
TAKEAWAY:
- The global prevalence of PsA was estimated at 113 (95% CI, 64-198) and 109 (75-158) cases per 100,000 based on population-based studies and health administrative data studies, respectively.
- The pooled global prevalence of PsA (combining the population-based and health administrative studies) was 112 cases per 100,000 (95% CI, 83-151).
- Combining both study designs, the global prevalence rates of PsA were 188 (95% CI, 128-289) cases per 100,000 for Europe, 48 (95% CI, 20-115) for Asia, 133 (95% CI, 93-191) for North America, and 17 (95% CI, 4-70) for South America.
IN PRACTICE:
“Robust estimates of prevalence are crucial for healthcare planning and resource allocation,” wrote the authors.
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by Stephanie Lembke, MSc, and colleagues from the Aberdeen Centre for Arthritis and Musculoskeletal Health, University of Aberdeen, Scotland. It was published online in Rheumatology (Oxford).
LIMITATIONS:
The meta-analysis had high levels of uncertainty and high heterogeneity between studies. In countries with unequal healthcare access, using data from statutory or private insurance databases to calculate PsA prevalence may systematically exclude uninsured individuals or those covered by private insurers. Moreover, the data were insufficient for a statistically meaningful subgroup analysis.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not receive any specific funding from any public, commercial, or nonprofit sectors to carry out this work. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
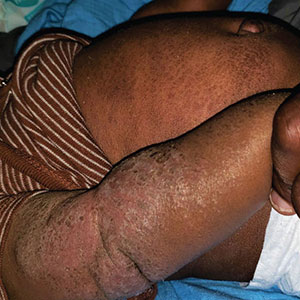
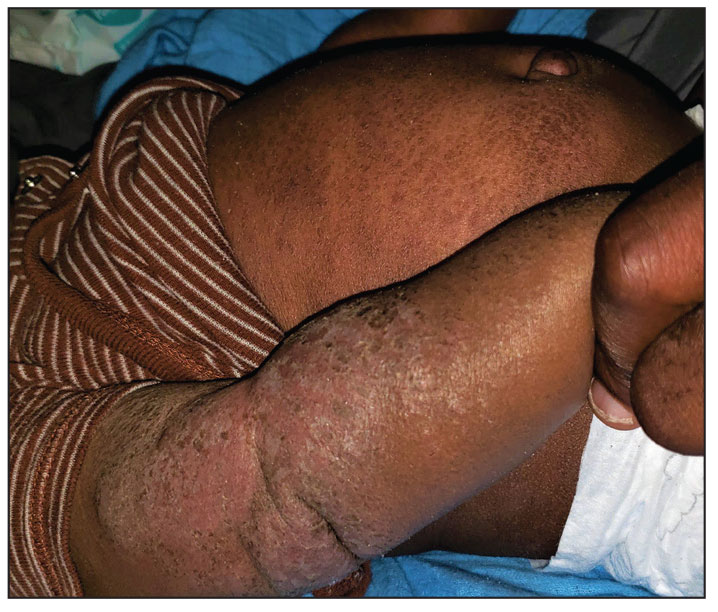
Progressively Worsening Scaly Patches and Plaques in an Infant
The Diagnosis: Erythrodermic Allergic Contact Dermatitis
The worsening symptoms in our patient prompted intervention rather than observation and reassurance. Contact allergy to lanolin was suspected given the worsening presentation after the addition of Minerin, which was immediately discontinued. The patient’s family applied betamethasone cream 0.1% twice daily to severe plaques, pimecrolimus cream 1% to the face, and triamcinolone cream 0.1% to the rest of the body. At follow-up 1 week later, he experienced complete resolution of symptoms, which supported the diagnosis of erythrodermic allergic contact dermatitis (ACD).
The prevalence of ACD caused by lanolin varies among the general population from 1.2% to 6.9%.1 Lanolin recently was named Allergen of the Year in 2023 by the American Contact Dermatitis Society.2 It can be found in various commercial products, including creams, soaps, and ointments. Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a common pediatric inflammatory skin disorder that typically is treated with these products.3 In a study analyzing 533 products, up to 6% of skin care products for babies and children contained lanolin.4 Therefore, exposure to lanolin-containing products may be fairly common in the pediatric population.
Lanolin is a fatlike substance derived from sheep sebaceous gland secretions and extracted from sheep’s wool. Its composition varies by sheep breed, location, and extraction and purification methods. The most common allergens involve the alcoholic fraction produced by hydrolysis of lanolin.4 In 1996, Wolf5 described the “lanolin paradox,” which argued the difficulty with identifying lanolin as an allergen (similar to Fisher’s “paraben paradox”) based on 4 principles: (1) lanolin-containing topical medicaments tend to be more sensitizing than lanolin-containing cosmetics; (2) patients with ACD after applying lanolin-containing topical medicaments to damaged or ulcerated skin often can apply lanolin-containing cosmetics to normal or unaffected skin without a reaction; (3) false-negative patch test results often occur in lanolin-sensitive patients; and (4) patch testing with a single lanolin-containing agent (lanolin alcohol [30% in petrolatum]) is an unreliable and inadequate method of detecting lanolin allergy.6,7 This theory elucidates the challenge of diagnosing contact allergies, particularly lanolin contact allergies.
Clinical features of acute ACD vary by skin type. Lighter skin types may have well-demarcated, pruritic, eczematous patches and plaques affecting the flexor surfaces. Asian patients may present with psoriasiform plaques with more well-demarcated borders and increased scaling and lichenification. In patients with darker skin types, dermatitis may manifest as papulation, lichenification, and color changes (violet, gray, or darker brown) along extensor surfaces.8 Chronic dermatitis manifests as lichenified scaly plaques. Given the diversity in dermatitis manifestation and the challenges of identifying erythema, especially in skin of color, clinicians may misidentify disease severity. These features aid in diagnosing and treating patients presenting with diffuse erythroderma and worsening eczematous patches and plaques despite use of typical topical treatments.
The differential diagnosis includes irritant contact dermatitis, AD, seborrheic dermatitis, and chronic plaque psoriasis. Negative patch testing suggests contact dermatitis based on exposure to a product. A thorough medication and personal history helps distinguish ACD from AD. Atopic dermatitis classically appears on the flexural areas, face, eyelids, and hands of patients with a personal or family history of atopy. Greasy scaly plaques on the central part of the face, eyelids, and scalp commonly are found in seborrheic dermatitis. In chronic plaque psoriasis, lesions typically are described as welldemarcated, inflamed plaques with notable scale located primarily in the scalp and diaper area in newborns and children until the age of 2 years. Our patient presented with scaly plaques throughout most of the body. The history of Minerin use over the course of 3 to 5 months and worsening skin eruptions involving a majority of the skin surface suggested continued exposure.
Patch testing assists in the diagnosis of ACD, with varying results due to manufacturing and processing inconsistencies in the composition of various substances used in the standard test sets, often making it difficult to diagnose lanolin as an allergen. According to Lee and Warshaw,6 the lack of uniformity within testing of lanolin-containing products may cause false-positive results, poor patch-test reproducibility, and loss of allergic contact response. A 2019 study utilized a combination of Amerchol L101 and lanolin alcohol to improve the diagnosis of lanolin allergy, as standard testing may not identify patients with lanolin sensitivities.1 A study with the North American Contact Dermatitis Group from 2005 to 2012 demonstrated that positive patch testing among children was the most consistent method for diagnosing ACD, and results were clinically relevant.9 However, the different lanolin-containing products are not standardized in patch testing, which often causes mixed reactions and does not definitely demonstrate classic positive results, even with the use of repeated open application tests.2 Although there has been an emphasis on refining the standardization of the lanolin used for patch testing, lanolin contact allergy remains a predominantly clinical diagnosis.
Both AD and ACD are common pediatric skin findings, and mixed positive and neutral associations between AD and allergy to lanolin have been described in a few studies.1,3,9,10 A history of atopy is more notable in a pediatric patient vs an adult, as sensitivities tend to subside into adulthood.9 Further studies and more precise testing are needed to investigate the relationship between AD and ACD.
- Knijp J, Bruynzeel DP, Rustemeyer T. Diagnosing lanolin contact allergy with lanolin alcohol and Amerchol L101. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;80:298-303. doi:10.1111/cod.13210
- Jenkins BA, Belsito DV. Lanolin. Dermatitis. 2023;34:4-12. doi:10.1089 /derm.2022.0002
- Jacob SE, McGowan M, Silverberg NB, et al. Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Registry data on contact allergy in children with atopic dermatitis. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:765-770. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol .2016.6136
- Bonchak JG, Prouty ME, de la Feld SF. Prevalence of contact allergens in personal care products for babies and children. Dermatitis. 2018; 29:81-84. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000348
- Wolf R. The lanolin paradox. Dermatology. 1996;192:198-202. doi:10.1159/000246365
- Lee B, Warshaw E. Lanolin allergy: history, epidemiology, responsible allergens, and management. Dermatitis. 2008;19:63-72.
- Miest RY, Yiannias JA, Chang YH, et al. Diagnosis and prevalence of lanolin allergy. Dermatitis. 2013;24:119-123. doi:10.1097 /DER.0b013e3182937aa4
- Sangha AM. Dermatological conditions in SKIN OF COLOR-: managing atopic dermatitis. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2021;14(3 Suppl 1):S20-S22.
- Zug KA, Pham AK, Belsito DV, et al. Patch testing in children from 2005 to 2012: results from the North American contact dermatitis group. Dermatitis. 2014;25:345-355. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000083
- Wakelin SH, Smith H, White IR, et al. A retrospective analysis of contact allergy to lanolin. Br J Dermatol. 2001;145:28-31. doi:10.1046 /j.1365-2133.2001.04277.x
The Diagnosis: Erythrodermic Allergic Contact Dermatitis
The worsening symptoms in our patient prompted intervention rather than observation and reassurance. Contact allergy to lanolin was suspected given the worsening presentation after the addition of Minerin, which was immediately discontinued. The patient’s family applied betamethasone cream 0.1% twice daily to severe plaques, pimecrolimus cream 1% to the face, and triamcinolone cream 0.1% to the rest of the body. At follow-up 1 week later, he experienced complete resolution of symptoms, which supported the diagnosis of erythrodermic allergic contact dermatitis (ACD).
The prevalence of ACD caused by lanolin varies among the general population from 1.2% to 6.9%.1 Lanolin recently was named Allergen of the Year in 2023 by the American Contact Dermatitis Society.2 It can be found in various commercial products, including creams, soaps, and ointments. Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a common pediatric inflammatory skin disorder that typically is treated with these products.3 In a study analyzing 533 products, up to 6% of skin care products for babies and children contained lanolin.4 Therefore, exposure to lanolin-containing products may be fairly common in the pediatric population.
Lanolin is a fatlike substance derived from sheep sebaceous gland secretions and extracted from sheep’s wool. Its composition varies by sheep breed, location, and extraction and purification methods. The most common allergens involve the alcoholic fraction produced by hydrolysis of lanolin.4 In 1996, Wolf5 described the “lanolin paradox,” which argued the difficulty with identifying lanolin as an allergen (similar to Fisher’s “paraben paradox”) based on 4 principles: (1) lanolin-containing topical medicaments tend to be more sensitizing than lanolin-containing cosmetics; (2) patients with ACD after applying lanolin-containing topical medicaments to damaged or ulcerated skin often can apply lanolin-containing cosmetics to normal or unaffected skin without a reaction; (3) false-negative patch test results often occur in lanolin-sensitive patients; and (4) patch testing with a single lanolin-containing agent (lanolin alcohol [30% in petrolatum]) is an unreliable and inadequate method of detecting lanolin allergy.6,7 This theory elucidates the challenge of diagnosing contact allergies, particularly lanolin contact allergies.
Clinical features of acute ACD vary by skin type. Lighter skin types may have well-demarcated, pruritic, eczematous patches and plaques affecting the flexor surfaces. Asian patients may present with psoriasiform plaques with more well-demarcated borders and increased scaling and lichenification. In patients with darker skin types, dermatitis may manifest as papulation, lichenification, and color changes (violet, gray, or darker brown) along extensor surfaces.8 Chronic dermatitis manifests as lichenified scaly plaques. Given the diversity in dermatitis manifestation and the challenges of identifying erythema, especially in skin of color, clinicians may misidentify disease severity. These features aid in diagnosing and treating patients presenting with diffuse erythroderma and worsening eczematous patches and plaques despite use of typical topical treatments.
The differential diagnosis includes irritant contact dermatitis, AD, seborrheic dermatitis, and chronic plaque psoriasis. Negative patch testing suggests contact dermatitis based on exposure to a product. A thorough medication and personal history helps distinguish ACD from AD. Atopic dermatitis classically appears on the flexural areas, face, eyelids, and hands of patients with a personal or family history of atopy. Greasy scaly plaques on the central part of the face, eyelids, and scalp commonly are found in seborrheic dermatitis. In chronic plaque psoriasis, lesions typically are described as welldemarcated, inflamed plaques with notable scale located primarily in the scalp and diaper area in newborns and children until the age of 2 years. Our patient presented with scaly plaques throughout most of the body. The history of Minerin use over the course of 3 to 5 months and worsening skin eruptions involving a majority of the skin surface suggested continued exposure.
Patch testing assists in the diagnosis of ACD, with varying results due to manufacturing and processing inconsistencies in the composition of various substances used in the standard test sets, often making it difficult to diagnose lanolin as an allergen. According to Lee and Warshaw,6 the lack of uniformity within testing of lanolin-containing products may cause false-positive results, poor patch-test reproducibility, and loss of allergic contact response. A 2019 study utilized a combination of Amerchol L101 and lanolin alcohol to improve the diagnosis of lanolin allergy, as standard testing may not identify patients with lanolin sensitivities.1 A study with the North American Contact Dermatitis Group from 2005 to 2012 demonstrated that positive patch testing among children was the most consistent method for diagnosing ACD, and results were clinically relevant.9 However, the different lanolin-containing products are not standardized in patch testing, which often causes mixed reactions and does not definitely demonstrate classic positive results, even with the use of repeated open application tests.2 Although there has been an emphasis on refining the standardization of the lanolin used for patch testing, lanolin contact allergy remains a predominantly clinical diagnosis.
Both AD and ACD are common pediatric skin findings, and mixed positive and neutral associations between AD and allergy to lanolin have been described in a few studies.1,3,9,10 A history of atopy is more notable in a pediatric patient vs an adult, as sensitivities tend to subside into adulthood.9 Further studies and more precise testing are needed to investigate the relationship between AD and ACD.
The Diagnosis: Erythrodermic Allergic Contact Dermatitis
The worsening symptoms in our patient prompted intervention rather than observation and reassurance. Contact allergy to lanolin was suspected given the worsening presentation after the addition of Minerin, which was immediately discontinued. The patient’s family applied betamethasone cream 0.1% twice daily to severe plaques, pimecrolimus cream 1% to the face, and triamcinolone cream 0.1% to the rest of the body. At follow-up 1 week later, he experienced complete resolution of symptoms, which supported the diagnosis of erythrodermic allergic contact dermatitis (ACD).
The prevalence of ACD caused by lanolin varies among the general population from 1.2% to 6.9%.1 Lanolin recently was named Allergen of the Year in 2023 by the American Contact Dermatitis Society.2 It can be found in various commercial products, including creams, soaps, and ointments. Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a common pediatric inflammatory skin disorder that typically is treated with these products.3 In a study analyzing 533 products, up to 6% of skin care products for babies and children contained lanolin.4 Therefore, exposure to lanolin-containing products may be fairly common in the pediatric population.
Lanolin is a fatlike substance derived from sheep sebaceous gland secretions and extracted from sheep’s wool. Its composition varies by sheep breed, location, and extraction and purification methods. The most common allergens involve the alcoholic fraction produced by hydrolysis of lanolin.4 In 1996, Wolf5 described the “lanolin paradox,” which argued the difficulty with identifying lanolin as an allergen (similar to Fisher’s “paraben paradox”) based on 4 principles: (1) lanolin-containing topical medicaments tend to be more sensitizing than lanolin-containing cosmetics; (2) patients with ACD after applying lanolin-containing topical medicaments to damaged or ulcerated skin often can apply lanolin-containing cosmetics to normal or unaffected skin without a reaction; (3) false-negative patch test results often occur in lanolin-sensitive patients; and (4) patch testing with a single lanolin-containing agent (lanolin alcohol [30% in petrolatum]) is an unreliable and inadequate method of detecting lanolin allergy.6,7 This theory elucidates the challenge of diagnosing contact allergies, particularly lanolin contact allergies.
Clinical features of acute ACD vary by skin type. Lighter skin types may have well-demarcated, pruritic, eczematous patches and plaques affecting the flexor surfaces. Asian patients may present with psoriasiform plaques with more well-demarcated borders and increased scaling and lichenification. In patients with darker skin types, dermatitis may manifest as papulation, lichenification, and color changes (violet, gray, or darker brown) along extensor surfaces.8 Chronic dermatitis manifests as lichenified scaly plaques. Given the diversity in dermatitis manifestation and the challenges of identifying erythema, especially in skin of color, clinicians may misidentify disease severity. These features aid in diagnosing and treating patients presenting with diffuse erythroderma and worsening eczematous patches and plaques despite use of typical topical treatments.
The differential diagnosis includes irritant contact dermatitis, AD, seborrheic dermatitis, and chronic plaque psoriasis. Negative patch testing suggests contact dermatitis based on exposure to a product. A thorough medication and personal history helps distinguish ACD from AD. Atopic dermatitis classically appears on the flexural areas, face, eyelids, and hands of patients with a personal or family history of atopy. Greasy scaly plaques on the central part of the face, eyelids, and scalp commonly are found in seborrheic dermatitis. In chronic plaque psoriasis, lesions typically are described as welldemarcated, inflamed plaques with notable scale located primarily in the scalp and diaper area in newborns and children until the age of 2 years. Our patient presented with scaly plaques throughout most of the body. The history of Minerin use over the course of 3 to 5 months and worsening skin eruptions involving a majority of the skin surface suggested continued exposure.
Patch testing assists in the diagnosis of ACD, with varying results due to manufacturing and processing inconsistencies in the composition of various substances used in the standard test sets, often making it difficult to diagnose lanolin as an allergen. According to Lee and Warshaw,6 the lack of uniformity within testing of lanolin-containing products may cause false-positive results, poor patch-test reproducibility, and loss of allergic contact response. A 2019 study utilized a combination of Amerchol L101 and lanolin alcohol to improve the diagnosis of lanolin allergy, as standard testing may not identify patients with lanolin sensitivities.1 A study with the North American Contact Dermatitis Group from 2005 to 2012 demonstrated that positive patch testing among children was the most consistent method for diagnosing ACD, and results were clinically relevant.9 However, the different lanolin-containing products are not standardized in patch testing, which often causes mixed reactions and does not definitely demonstrate classic positive results, even with the use of repeated open application tests.2 Although there has been an emphasis on refining the standardization of the lanolin used for patch testing, lanolin contact allergy remains a predominantly clinical diagnosis.
Both AD and ACD are common pediatric skin findings, and mixed positive and neutral associations between AD and allergy to lanolin have been described in a few studies.1,3,9,10 A history of atopy is more notable in a pediatric patient vs an adult, as sensitivities tend to subside into adulthood.9 Further studies and more precise testing are needed to investigate the relationship between AD and ACD.
- Knijp J, Bruynzeel DP, Rustemeyer T. Diagnosing lanolin contact allergy with lanolin alcohol and Amerchol L101. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;80:298-303. doi:10.1111/cod.13210
- Jenkins BA, Belsito DV. Lanolin. Dermatitis. 2023;34:4-12. doi:10.1089 /derm.2022.0002
- Jacob SE, McGowan M, Silverberg NB, et al. Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Registry data on contact allergy in children with atopic dermatitis. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:765-770. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol .2016.6136
- Bonchak JG, Prouty ME, de la Feld SF. Prevalence of contact allergens in personal care products for babies and children. Dermatitis. 2018; 29:81-84. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000348
- Wolf R. The lanolin paradox. Dermatology. 1996;192:198-202. doi:10.1159/000246365
- Lee B, Warshaw E. Lanolin allergy: history, epidemiology, responsible allergens, and management. Dermatitis. 2008;19:63-72.
- Miest RY, Yiannias JA, Chang YH, et al. Diagnosis and prevalence of lanolin allergy. Dermatitis. 2013;24:119-123. doi:10.1097 /DER.0b013e3182937aa4
- Sangha AM. Dermatological conditions in SKIN OF COLOR-: managing atopic dermatitis. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2021;14(3 Suppl 1):S20-S22.
- Zug KA, Pham AK, Belsito DV, et al. Patch testing in children from 2005 to 2012: results from the North American contact dermatitis group. Dermatitis. 2014;25:345-355. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000083
- Wakelin SH, Smith H, White IR, et al. A retrospective analysis of contact allergy to lanolin. Br J Dermatol. 2001;145:28-31. doi:10.1046 /j.1365-2133.2001.04277.x
- Knijp J, Bruynzeel DP, Rustemeyer T. Diagnosing lanolin contact allergy with lanolin alcohol and Amerchol L101. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;80:298-303. doi:10.1111/cod.13210
- Jenkins BA, Belsito DV. Lanolin. Dermatitis. 2023;34:4-12. doi:10.1089 /derm.2022.0002
- Jacob SE, McGowan M, Silverberg NB, et al. Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Registry data on contact allergy in children with atopic dermatitis. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:765-770. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol .2016.6136
- Bonchak JG, Prouty ME, de la Feld SF. Prevalence of contact allergens in personal care products for babies and children. Dermatitis. 2018; 29:81-84. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000348
- Wolf R. The lanolin paradox. Dermatology. 1996;192:198-202. doi:10.1159/000246365
- Lee B, Warshaw E. Lanolin allergy: history, epidemiology, responsible allergens, and management. Dermatitis. 2008;19:63-72.
- Miest RY, Yiannias JA, Chang YH, et al. Diagnosis and prevalence of lanolin allergy. Dermatitis. 2013;24:119-123. doi:10.1097 /DER.0b013e3182937aa4
- Sangha AM. Dermatological conditions in SKIN OF COLOR-: managing atopic dermatitis. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2021;14(3 Suppl 1):S20-S22.
- Zug KA, Pham AK, Belsito DV, et al. Patch testing in children from 2005 to 2012: results from the North American contact dermatitis group. Dermatitis. 2014;25:345-355. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000083
- Wakelin SH, Smith H, White IR, et al. A retrospective analysis of contact allergy to lanolin. Br J Dermatol. 2001;145:28-31. doi:10.1046 /j.1365-2133.2001.04277.x
A 5-month-old male with moderately brown skin that rarely burns and tans profusely presented to the emergency department with a worsening red rash of more than 4 months’ duration. The patient had diffuse erythroderma and eczematous patches and plaques covering 95% of the total body surface area, including lichenified plaques on the arms and elbows, with no signs of infection. He initially presented for his 1-month appointment at the pediatric clinic with scaly patches and plaques on the face and trunk as well as diffuse xerosis. He was prescribed daily oatmeal baths and topical Minerin (Major Pharmaceuticals)—containing water, petrolatum, mineral oil, mineral wax, lanolin alcohol, methylchloroisothiazolinone, and methylisothiazolinone—to be applied to the whole body twice daily. At the patient’s 2-month well visit, symptoms persisted. The patient’s pediatrician increased application of Minerin to 2 to 3 times daily, and hydrocortisone cream 2.5% application 2 to 3 times daily was added.
New Trial Deepens Debate Over Late-Preterm Steroids
The early cancellation of a trial in southern India suggests that the use of antenatal steroids to prevent respiratory complications after late-preterm birth — a recommended practice in the United States — may not be effective in the developing world.
As reported in Obstetrics & Gynecology, researchers led by Hilda Yenuberi, MD, of Christian Medical College, Vellore, Tamil Nadu, India, stopped the randomized, triple-blinded, placebo-controlled CLAP (Corticosteroids in Late Pregnancy) study at 70% enrollment. An interim analysis found no benefit from prescribing betamethasone vs placebo to women at risk of late-preterm delivery between 34 and 36 and 6/7 weeks of gestation (primary outcome of respiratory distress: 4.9% vs 4.8%, respectively, relative risk [RR], 1.03; 95% CI, 0.57-1.84; number needed to treat = 786).
“These findings may suggest differing efficacy of antenatal corticosteroids in developing countries compared with developed countries ... that should be considered when late-preterm antenatal corticosteroids are administered,” the researchers wrote.
The use of steroids in patients at risk of delivery before 34 weeks is widely accepted as a way to prevent neonatal respiratory distress, a common and potentially deadly condition in premature infants whose lungs are not fully developed. However, there’s debate over steroid treatment in women who are expected to deliver later than 34 weeks but still preterm.
As the study notes, “the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends a single course of betamethasone for pregnant individuals at risk of delivering between 34 and 36 6/7 weeks of gestation on the basis of the ALPS (Antenatal Late Preterm Steroid) trial.”
But other randomized trials have reached different conclusions, and steroids are not without risks. Studies have linked prenatal steroids to neurosensory disorders in babies, meaning they’re more likely to need hearing aids and eyeglasses, said Kellie Murphy, MD, MSc, professor of obstetrics and gynecology, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, in an interview. Dr. Murphy, who was not involved in the new trial, added that there are links between steroids and greater likelihood of poorer performance in school,
For the new study, conducted from 2020 to 2022 at Christian Medical College and Hospital in Vellore, India, researchers randomly assigned 423 patients to betamethasone (410 in the interim analysis; average age, 26.8 years) and 424 to placebo (415 in the interim analysis; average age, 26.2 years).
The average age of participants was 26.8 years. All were between 34 and 36 6/7 weeks of gestation and expected to give birth within the next week. A quarter of participants delivered at term, which the authors wrote “may have influenced the primary outcome.” The total number of neonates was 883, including 58 twin pregnancies.
There was no significant difference in respiratory distress between groups, “defined as need for oxygen or continuous positive airway pressure or mechanical ventilation for at least 2 hours in the first 72 hours of life.” There also were no significant differences in maternal outcomes such as chorioamnionitis or length of hospitalization or neonatal secondary outcomes such as transient tachypnea of the newborn, respiratory distress syndrome, necrotizing enterocolitis, sepsis, hyperbilirubinemia, stillbirth, and early neonatal death.
Serious adverse events occurred in four neonates but none were linked to the intervention.
The study doesn’t discuss cost, but a 2019 report suggests that use of betamethasone to prevent neonatal respiratory distress is cost-effective.
“Our findings are contradictory to those of a systematic review, the major contributor of which was the ALPS trial,” the authors of the new study reported. “The primary outcome of the ALPS trial, the composite of neonatal treatment in the first 72 hours, was significantly less in the group who received betamethasone (11.6%), compared with the placebo group (14.4%; relative risk [RR], 0.80; 95% CI, 0.66-0.97).”
The study authors, who didn’t respond to requests for comment, noted that their trial included twin pregnancies and patients with gestational diabetes; the ALPS trial did not.
Perinatologist Cynthia Gyamfi-Bannerman, MD, MS, chair and professor of Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Reproductive Sciences at the University of California,San Diego, and principal investigator of the ALPS study, said in an interview that the inclusion of twins in the new trial is “a fundamental flaw.”
“Because antenatal corticosteroids have not been shown to be useful in twins at any gestational age, it is not surprising that including twins likely moved the findings to the null in this study,” she said. “Twins were purposefully excluded from the ALPS trial for this reason.”
According to the new study, “the primary outcome among singleton neonates occurred in 4.8% (18/374) who received betamethasone and 5.1% (20/393) who received placebo (RR, 0.94; 95% CI, 0.51-1.75)
What should clinicians take from the study findings? In an accompanying commentary, Blair J. Wylie, MD, MPH, of Columbia University Medical Center, New York, NY, and Syed Asad Ali, MBBS, MPH, of Aga Khan University, Karachi, Pakistan, wrote that, “in settings similar to the US-based ALPS trial, the practice of administering a course of late-preterm antenatal corticosteroids should be continued, as espoused by our professional organizations.”
However, the new study suggests that “research in high-resource environments may not be generalizable to low-resource settings,” they write.
Neonatologist Elizabeth Asztalos, MD, MSc, an associate scientist with Sunnybrook Health Sciences Center in Toronto, Canada, said in an interview that she doesn’t worry about pregnant mothers not getting steroids later than 34 weeks. “We have tools in our armamentarium in the NICU setting to help babies if they need it,” said Dr. Asztalos, who didn’t take part in the new trial. “We can put them on CPAP if they have wet lung. If they have an element of respiratory distress, we can give them surfactants. These bigger babies have more ability to recover from all this compared to a baby who was born at 24, 25, 26 weeks.”
For her part, the University of Toronto’s Dr. Murphy said decision-making about late-preterm steroids is complicated. “You don’t want to miss the opportunity to give to provide benefits for the patients” via steroids, she said. “But on the flip side, it’s a double-edged sword. It’s not easy. It’s not straightforward.”
In the big picture, she said, “people need to be really clear why they’re giving an intervention and what they hope to achieve.”
Christian Medical College supported the study. The authors, Dr. Murphy, Dr. Asztalos, and commentary co-author Dr. Ali have no disclosures. Dr. Gyamfi-Bannerman discloses being principal investigator of the ALPS trial. Commentary co-author Dr. Wylie serves on the ultrasound quality assurance committee of a trial discussed in the commentary.
The early cancellation of a trial in southern India suggests that the use of antenatal steroids to prevent respiratory complications after late-preterm birth — a recommended practice in the United States — may not be effective in the developing world.
As reported in Obstetrics & Gynecology, researchers led by Hilda Yenuberi, MD, of Christian Medical College, Vellore, Tamil Nadu, India, stopped the randomized, triple-blinded, placebo-controlled CLAP (Corticosteroids in Late Pregnancy) study at 70% enrollment. An interim analysis found no benefit from prescribing betamethasone vs placebo to women at risk of late-preterm delivery between 34 and 36 and 6/7 weeks of gestation (primary outcome of respiratory distress: 4.9% vs 4.8%, respectively, relative risk [RR], 1.03; 95% CI, 0.57-1.84; number needed to treat = 786).
“These findings may suggest differing efficacy of antenatal corticosteroids in developing countries compared with developed countries ... that should be considered when late-preterm antenatal corticosteroids are administered,” the researchers wrote.
The use of steroids in patients at risk of delivery before 34 weeks is widely accepted as a way to prevent neonatal respiratory distress, a common and potentially deadly condition in premature infants whose lungs are not fully developed. However, there’s debate over steroid treatment in women who are expected to deliver later than 34 weeks but still preterm.
As the study notes, “the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends a single course of betamethasone for pregnant individuals at risk of delivering between 34 and 36 6/7 weeks of gestation on the basis of the ALPS (Antenatal Late Preterm Steroid) trial.”
But other randomized trials have reached different conclusions, and steroids are not without risks. Studies have linked prenatal steroids to neurosensory disorders in babies, meaning they’re more likely to need hearing aids and eyeglasses, said Kellie Murphy, MD, MSc, professor of obstetrics and gynecology, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, in an interview. Dr. Murphy, who was not involved in the new trial, added that there are links between steroids and greater likelihood of poorer performance in school,
For the new study, conducted from 2020 to 2022 at Christian Medical College and Hospital in Vellore, India, researchers randomly assigned 423 patients to betamethasone (410 in the interim analysis; average age, 26.8 years) and 424 to placebo (415 in the interim analysis; average age, 26.2 years).
The average age of participants was 26.8 years. All were between 34 and 36 6/7 weeks of gestation and expected to give birth within the next week. A quarter of participants delivered at term, which the authors wrote “may have influenced the primary outcome.” The total number of neonates was 883, including 58 twin pregnancies.
There was no significant difference in respiratory distress between groups, “defined as need for oxygen or continuous positive airway pressure or mechanical ventilation for at least 2 hours in the first 72 hours of life.” There also were no significant differences in maternal outcomes such as chorioamnionitis or length of hospitalization or neonatal secondary outcomes such as transient tachypnea of the newborn, respiratory distress syndrome, necrotizing enterocolitis, sepsis, hyperbilirubinemia, stillbirth, and early neonatal death.
Serious adverse events occurred in four neonates but none were linked to the intervention.
The study doesn’t discuss cost, but a 2019 report suggests that use of betamethasone to prevent neonatal respiratory distress is cost-effective.
“Our findings are contradictory to those of a systematic review, the major contributor of which was the ALPS trial,” the authors of the new study reported. “The primary outcome of the ALPS trial, the composite of neonatal treatment in the first 72 hours, was significantly less in the group who received betamethasone (11.6%), compared with the placebo group (14.4%; relative risk [RR], 0.80; 95% CI, 0.66-0.97).”
The study authors, who didn’t respond to requests for comment, noted that their trial included twin pregnancies and patients with gestational diabetes; the ALPS trial did not.
Perinatologist Cynthia Gyamfi-Bannerman, MD, MS, chair and professor of Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Reproductive Sciences at the University of California,San Diego, and principal investigator of the ALPS study, said in an interview that the inclusion of twins in the new trial is “a fundamental flaw.”
“Because antenatal corticosteroids have not been shown to be useful in twins at any gestational age, it is not surprising that including twins likely moved the findings to the null in this study,” she said. “Twins were purposefully excluded from the ALPS trial for this reason.”
According to the new study, “the primary outcome among singleton neonates occurred in 4.8% (18/374) who received betamethasone and 5.1% (20/393) who received placebo (RR, 0.94; 95% CI, 0.51-1.75)
What should clinicians take from the study findings? In an accompanying commentary, Blair J. Wylie, MD, MPH, of Columbia University Medical Center, New York, NY, and Syed Asad Ali, MBBS, MPH, of Aga Khan University, Karachi, Pakistan, wrote that, “in settings similar to the US-based ALPS trial, the practice of administering a course of late-preterm antenatal corticosteroids should be continued, as espoused by our professional organizations.”
However, the new study suggests that “research in high-resource environments may not be generalizable to low-resource settings,” they write.
Neonatologist Elizabeth Asztalos, MD, MSc, an associate scientist with Sunnybrook Health Sciences Center in Toronto, Canada, said in an interview that she doesn’t worry about pregnant mothers not getting steroids later than 34 weeks. “We have tools in our armamentarium in the NICU setting to help babies if they need it,” said Dr. Asztalos, who didn’t take part in the new trial. “We can put them on CPAP if they have wet lung. If they have an element of respiratory distress, we can give them surfactants. These bigger babies have more ability to recover from all this compared to a baby who was born at 24, 25, 26 weeks.”
For her part, the University of Toronto’s Dr. Murphy said decision-making about late-preterm steroids is complicated. “You don’t want to miss the opportunity to give to provide benefits for the patients” via steroids, she said. “But on the flip side, it’s a double-edged sword. It’s not easy. It’s not straightforward.”
In the big picture, she said, “people need to be really clear why they’re giving an intervention and what they hope to achieve.”
Christian Medical College supported the study. The authors, Dr. Murphy, Dr. Asztalos, and commentary co-author Dr. Ali have no disclosures. Dr. Gyamfi-Bannerman discloses being principal investigator of the ALPS trial. Commentary co-author Dr. Wylie serves on the ultrasound quality assurance committee of a trial discussed in the commentary.
The early cancellation of a trial in southern India suggests that the use of antenatal steroids to prevent respiratory complications after late-preterm birth — a recommended practice in the United States — may not be effective in the developing world.
As reported in Obstetrics & Gynecology, researchers led by Hilda Yenuberi, MD, of Christian Medical College, Vellore, Tamil Nadu, India, stopped the randomized, triple-blinded, placebo-controlled CLAP (Corticosteroids in Late Pregnancy) study at 70% enrollment. An interim analysis found no benefit from prescribing betamethasone vs placebo to women at risk of late-preterm delivery between 34 and 36 and 6/7 weeks of gestation (primary outcome of respiratory distress: 4.9% vs 4.8%, respectively, relative risk [RR], 1.03; 95% CI, 0.57-1.84; number needed to treat = 786).
“These findings may suggest differing efficacy of antenatal corticosteroids in developing countries compared with developed countries ... that should be considered when late-preterm antenatal corticosteroids are administered,” the researchers wrote.
The use of steroids in patients at risk of delivery before 34 weeks is widely accepted as a way to prevent neonatal respiratory distress, a common and potentially deadly condition in premature infants whose lungs are not fully developed. However, there’s debate over steroid treatment in women who are expected to deliver later than 34 weeks but still preterm.
As the study notes, “the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends a single course of betamethasone for pregnant individuals at risk of delivering between 34 and 36 6/7 weeks of gestation on the basis of the ALPS (Antenatal Late Preterm Steroid) trial.”
But other randomized trials have reached different conclusions, and steroids are not without risks. Studies have linked prenatal steroids to neurosensory disorders in babies, meaning they’re more likely to need hearing aids and eyeglasses, said Kellie Murphy, MD, MSc, professor of obstetrics and gynecology, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, in an interview. Dr. Murphy, who was not involved in the new trial, added that there are links between steroids and greater likelihood of poorer performance in school,
For the new study, conducted from 2020 to 2022 at Christian Medical College and Hospital in Vellore, India, researchers randomly assigned 423 patients to betamethasone (410 in the interim analysis; average age, 26.8 years) and 424 to placebo (415 in the interim analysis; average age, 26.2 years).
The average age of participants was 26.8 years. All were between 34 and 36 6/7 weeks of gestation and expected to give birth within the next week. A quarter of participants delivered at term, which the authors wrote “may have influenced the primary outcome.” The total number of neonates was 883, including 58 twin pregnancies.
There was no significant difference in respiratory distress between groups, “defined as need for oxygen or continuous positive airway pressure or mechanical ventilation for at least 2 hours in the first 72 hours of life.” There also were no significant differences in maternal outcomes such as chorioamnionitis or length of hospitalization or neonatal secondary outcomes such as transient tachypnea of the newborn, respiratory distress syndrome, necrotizing enterocolitis, sepsis, hyperbilirubinemia, stillbirth, and early neonatal death.
Serious adverse events occurred in four neonates but none were linked to the intervention.
The study doesn’t discuss cost, but a 2019 report suggests that use of betamethasone to prevent neonatal respiratory distress is cost-effective.
“Our findings are contradictory to those of a systematic review, the major contributor of which was the ALPS trial,” the authors of the new study reported. “The primary outcome of the ALPS trial, the composite of neonatal treatment in the first 72 hours, was significantly less in the group who received betamethasone (11.6%), compared with the placebo group (14.4%; relative risk [RR], 0.80; 95% CI, 0.66-0.97).”
The study authors, who didn’t respond to requests for comment, noted that their trial included twin pregnancies and patients with gestational diabetes; the ALPS trial did not.
Perinatologist Cynthia Gyamfi-Bannerman, MD, MS, chair and professor of Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Reproductive Sciences at the University of California,San Diego, and principal investigator of the ALPS study, said in an interview that the inclusion of twins in the new trial is “a fundamental flaw.”
“Because antenatal corticosteroids have not been shown to be useful in twins at any gestational age, it is not surprising that including twins likely moved the findings to the null in this study,” she said. “Twins were purposefully excluded from the ALPS trial for this reason.”
According to the new study, “the primary outcome among singleton neonates occurred in 4.8% (18/374) who received betamethasone and 5.1% (20/393) who received placebo (RR, 0.94; 95% CI, 0.51-1.75)
What should clinicians take from the study findings? In an accompanying commentary, Blair J. Wylie, MD, MPH, of Columbia University Medical Center, New York, NY, and Syed Asad Ali, MBBS, MPH, of Aga Khan University, Karachi, Pakistan, wrote that, “in settings similar to the US-based ALPS trial, the practice of administering a course of late-preterm antenatal corticosteroids should be continued, as espoused by our professional organizations.”
However, the new study suggests that “research in high-resource environments may not be generalizable to low-resource settings,” they write.
Neonatologist Elizabeth Asztalos, MD, MSc, an associate scientist with Sunnybrook Health Sciences Center in Toronto, Canada, said in an interview that she doesn’t worry about pregnant mothers not getting steroids later than 34 weeks. “We have tools in our armamentarium in the NICU setting to help babies if they need it,” said Dr. Asztalos, who didn’t take part in the new trial. “We can put them on CPAP if they have wet lung. If they have an element of respiratory distress, we can give them surfactants. These bigger babies have more ability to recover from all this compared to a baby who was born at 24, 25, 26 weeks.”
For her part, the University of Toronto’s Dr. Murphy said decision-making about late-preterm steroids is complicated. “You don’t want to miss the opportunity to give to provide benefits for the patients” via steroids, she said. “But on the flip side, it’s a double-edged sword. It’s not easy. It’s not straightforward.”
In the big picture, she said, “people need to be really clear why they’re giving an intervention and what they hope to achieve.”
Christian Medical College supported the study. The authors, Dr. Murphy, Dr. Asztalos, and commentary co-author Dr. Ali have no disclosures. Dr. Gyamfi-Bannerman discloses being principal investigator of the ALPS trial. Commentary co-author Dr. Wylie serves on the ultrasound quality assurance committee of a trial discussed in the commentary.
FROM OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY
Antibiotics of Little Benefit in Lower Respiratory Tract Infection
Antibiotics had no measurable effect on the severity or duration of coughs due to acute lower respiratory tract infection (LRTI, or acute bronchitis), a large prospective study found.
In fact, those receiving an antibiotic in the primary- and urgent-care setting had a small but significant increase in overall length of illness (17.5 vs 15.9 days; P = .05) — largely because patients with longer illness before the index visit were more likely to receive these drugs. The study adds further support for reducing the prescription of antibiotics for LRTIs.
“Importantly, the pathogen data demonstrated that the length of time until illness resolution for those with bacterial infection was the same as for those not receiving an antibiotic versus those receiving one (17.3 vs 17.4 days),” researchers led by Daniel J. Merenstein, MD, a professor and director of research programs, family medicine, at Georgetown University Medical Center in Washington, wrote in the Journal of General Internal Medicine (doi: 10.1007/s11606-024-08758-y).
Patients believed an antibiotic would shorten their illness by an average of about 4 days, from 13.4 days to 9.7 days, whereas the average duration of all coughs was more than 2 weeks regardless of pathogen type or receipt of an antibiotic.
“Patients had unrealistic expectations regarding the duration of LRTI and the effect of antibiotics, which should be the target of antibiotic stewardship efforts,” the group wrote.
LRTIs can, however, be dangerous, with 3%-5% progressing to pneumonia, “but not everyone has easy access at an initial visit to an x-ray, which may be the reason clinicians still give antibiotics without any other evidence of a bacterial infection,” Dr. Merenstein said in a news release. “Patients have come to expect antibiotics for a cough, even if it doesn’t help. Basic symptom-relieving medications plus time bring a resolution to most people’s infections.”
The authors noted that cough is the most common reason for an ambulatory care visit, accounting for 2.7 million outpatient visits and more than 4 million emergency department visits annually.
Risks
Overuse of antibiotics can result in dizziness, nausea, diarrhea, and rash, along with a roughly 4% chance of serious adverse effects including anaphylaxis; Stevens-Johnson syndrome, a serious skin and mucous membrane disorder; and Clostridioides difficile-associated diarrhea.
An estimated half of all antibiotic prescriptions for acute respiratory conditions are unnecessary. Before the COVID-19 pandemic, antibiotics were prescribed about 70% of the time for a diagnosis of uncomplicated cough and LRTI. The viral pandemic did not change this practice according to a meta-analysis of 130 studies showing that 78% of COVID-19 patients were prescribed an antibiotic.
The study
The study looked at a cohort of 718 patients, with a mean age of 38.9 years, 65.3% female, of whom 207 received an antibiotic and 511 did not. Of those with baseline data, 29% had an antibiotic prescribed at baseline, the most common (in 85%) being amoxicillin-clavulanate, azithromycin, doxycycline, and amoxicillin. Antibiotics had no effect on the duration or overall severity of cough in viral, bacterial, or mixed infections. Receipt of an antibiotic did, however, reduce the likelihood of a follow-up visit: 14.1% vs 8.2% (adjusted odds ratio, 0.47; 95% confidence interval, 0.26-0.84) — perhaps because it removed the motivation for seeking another consultation. Antibiotic recipients were more likely to receive a systemic corticosteroid (31.9% vs 4.5%, P <.001) and were also more likely to receive an albuterol inhaler (22.7% vs 7.6%, P <.001).
Jeffrey A. Linder, MD, MPH, a primary care physician and chief of internal medicine and geriatrics at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine in Chicago, agrees that in the vast majority of LRTIs — usually acute bronchitis — antibiotics do not speed the healing process. “Forty years of research show that antibiotics do not make acute bronchitis go away any faster,” Dr. Linder, who was not involved in the current study, said in an interview. “There’s even growing evidence that a lot of pneumonia is viral as well, and 10 or 20 years from now we may often not be giving antibiotics for pneumonia because we’ll be able to see better if it’s caused by a virus.”
A large 2018 review by Dr. Linder and associates reported that 46% of antibiotics were prescribed without any infection-related diagnosis code and 20% without an office visit.
Dr. Linder routinely informs patients requesting an antibiotic about the risks of putting an ineffective chemical into their body. “I stress that it can cause rash and other allergic reactions, and even promote C diff infection,” he said. “And I also say it messes with the good bacteria in the microbiome, and they usually come around.”
Patients need to know, Dr. Linder added, that the normal course of healing the respiratory tract after acute bronchitis takes weeks. While a wet cough with sputum or phlegm will last a few days, it’s replaced with a dry annoying cough that persists for up to 3 weeks. “As long as they’re feeling generally better, that cough is normal,” he said. “A virus has run roughshod over their airways and they need a long time to heal and the cough is part of the healing process. Think how long it takes to heal a cut on a finger.”
In an era of escalating antimicrobial resistance fueled by antibiotic overuse, it’s become increasingly important to reserve antibiotics for necessary cases. According to a recent World Health Organization call to action, “Uncontrolled antimicrobial resistance is expected to lower life expectancy and lead to unprecedented health expenditure and economic losses.”
That said, there is important clinical work to be done to determine if there is a limited role for antibiotics in patients with cough, perhaps based on age and baseline severity. “Serious cough symptoms and how to treat them properly needs to be studied more, perhaps in a randomized clinical trial as this study was observational and there haven’t been any randomized trials looking at this issue since about 2012,” Dr. Merenstein said.
This research was funded by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. Dr. Linder reported stock ownership in pharmaceutical companies but none that make antibiotics or other infectious disease drugs.
Antibiotics had no measurable effect on the severity or duration of coughs due to acute lower respiratory tract infection (LRTI, or acute bronchitis), a large prospective study found.
In fact, those receiving an antibiotic in the primary- and urgent-care setting had a small but significant increase in overall length of illness (17.5 vs 15.9 days; P = .05) — largely because patients with longer illness before the index visit were more likely to receive these drugs. The study adds further support for reducing the prescription of antibiotics for LRTIs.
“Importantly, the pathogen data demonstrated that the length of time until illness resolution for those with bacterial infection was the same as for those not receiving an antibiotic versus those receiving one (17.3 vs 17.4 days),” researchers led by Daniel J. Merenstein, MD, a professor and director of research programs, family medicine, at Georgetown University Medical Center in Washington, wrote in the Journal of General Internal Medicine (doi: 10.1007/s11606-024-08758-y).
Patients believed an antibiotic would shorten their illness by an average of about 4 days, from 13.4 days to 9.7 days, whereas the average duration of all coughs was more than 2 weeks regardless of pathogen type or receipt of an antibiotic.
“Patients had unrealistic expectations regarding the duration of LRTI and the effect of antibiotics, which should be the target of antibiotic stewardship efforts,” the group wrote.
LRTIs can, however, be dangerous, with 3%-5% progressing to pneumonia, “but not everyone has easy access at an initial visit to an x-ray, which may be the reason clinicians still give antibiotics without any other evidence of a bacterial infection,” Dr. Merenstein said in a news release. “Patients have come to expect antibiotics for a cough, even if it doesn’t help. Basic symptom-relieving medications plus time bring a resolution to most people’s infections.”
The authors noted that cough is the most common reason for an ambulatory care visit, accounting for 2.7 million outpatient visits and more than 4 million emergency department visits annually.
Risks
Overuse of antibiotics can result in dizziness, nausea, diarrhea, and rash, along with a roughly 4% chance of serious adverse effects including anaphylaxis; Stevens-Johnson syndrome, a serious skin and mucous membrane disorder; and Clostridioides difficile-associated diarrhea.
An estimated half of all antibiotic prescriptions for acute respiratory conditions are unnecessary. Before the COVID-19 pandemic, antibiotics were prescribed about 70% of the time for a diagnosis of uncomplicated cough and LRTI. The viral pandemic did not change this practice according to a meta-analysis of 130 studies showing that 78% of COVID-19 patients were prescribed an antibiotic.
The study
The study looked at a cohort of 718 patients, with a mean age of 38.9 years, 65.3% female, of whom 207 received an antibiotic and 511 did not. Of those with baseline data, 29% had an antibiotic prescribed at baseline, the most common (in 85%) being amoxicillin-clavulanate, azithromycin, doxycycline, and amoxicillin. Antibiotics had no effect on the duration or overall severity of cough in viral, bacterial, or mixed infections. Receipt of an antibiotic did, however, reduce the likelihood of a follow-up visit: 14.1% vs 8.2% (adjusted odds ratio, 0.47; 95% confidence interval, 0.26-0.84) — perhaps because it removed the motivation for seeking another consultation. Antibiotic recipients were more likely to receive a systemic corticosteroid (31.9% vs 4.5%, P <.001) and were also more likely to receive an albuterol inhaler (22.7% vs 7.6%, P <.001).
Jeffrey A. Linder, MD, MPH, a primary care physician and chief of internal medicine and geriatrics at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine in Chicago, agrees that in the vast majority of LRTIs — usually acute bronchitis — antibiotics do not speed the healing process. “Forty years of research show that antibiotics do not make acute bronchitis go away any faster,” Dr. Linder, who was not involved in the current study, said in an interview. “There’s even growing evidence that a lot of pneumonia is viral as well, and 10 or 20 years from now we may often not be giving antibiotics for pneumonia because we’ll be able to see better if it’s caused by a virus.”
A large 2018 review by Dr. Linder and associates reported that 46% of antibiotics were prescribed without any infection-related diagnosis code and 20% without an office visit.
Dr. Linder routinely informs patients requesting an antibiotic about the risks of putting an ineffective chemical into their body. “I stress that it can cause rash and other allergic reactions, and even promote C diff infection,” he said. “And I also say it messes with the good bacteria in the microbiome, and they usually come around.”
Patients need to know, Dr. Linder added, that the normal course of healing the respiratory tract after acute bronchitis takes weeks. While a wet cough with sputum or phlegm will last a few days, it’s replaced with a dry annoying cough that persists for up to 3 weeks. “As long as they’re feeling generally better, that cough is normal,” he said. “A virus has run roughshod over their airways and they need a long time to heal and the cough is part of the healing process. Think how long it takes to heal a cut on a finger.”
In an era of escalating antimicrobial resistance fueled by antibiotic overuse, it’s become increasingly important to reserve antibiotics for necessary cases. According to a recent World Health Organization call to action, “Uncontrolled antimicrobial resistance is expected to lower life expectancy and lead to unprecedented health expenditure and economic losses.”
That said, there is important clinical work to be done to determine if there is a limited role for antibiotics in patients with cough, perhaps based on age and baseline severity. “Serious cough symptoms and how to treat them properly needs to be studied more, perhaps in a randomized clinical trial as this study was observational and there haven’t been any randomized trials looking at this issue since about 2012,” Dr. Merenstein said.
This research was funded by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. Dr. Linder reported stock ownership in pharmaceutical companies but none that make antibiotics or other infectious disease drugs.
Antibiotics had no measurable effect on the severity or duration of coughs due to acute lower respiratory tract infection (LRTI, or acute bronchitis), a large prospective study found.
In fact, those receiving an antibiotic in the primary- and urgent-care setting had a small but significant increase in overall length of illness (17.5 vs 15.9 days; P = .05) — largely because patients with longer illness before the index visit were more likely to receive these drugs. The study adds further support for reducing the prescription of antibiotics for LRTIs.
“Importantly, the pathogen data demonstrated that the length of time until illness resolution for those with bacterial infection was the same as for those not receiving an antibiotic versus those receiving one (17.3 vs 17.4 days),” researchers led by Daniel J. Merenstein, MD, a professor and director of research programs, family medicine, at Georgetown University Medical Center in Washington, wrote in the Journal of General Internal Medicine (doi: 10.1007/s11606-024-08758-y).
Patients believed an antibiotic would shorten their illness by an average of about 4 days, from 13.4 days to 9.7 days, whereas the average duration of all coughs was more than 2 weeks regardless of pathogen type or receipt of an antibiotic.
“Patients had unrealistic expectations regarding the duration of LRTI and the effect of antibiotics, which should be the target of antibiotic stewardship efforts,” the group wrote.
LRTIs can, however, be dangerous, with 3%-5% progressing to pneumonia, “but not everyone has easy access at an initial visit to an x-ray, which may be the reason clinicians still give antibiotics without any other evidence of a bacterial infection,” Dr. Merenstein said in a news release. “Patients have come to expect antibiotics for a cough, even if it doesn’t help. Basic symptom-relieving medications plus time bring a resolution to most people’s infections.”
The authors noted that cough is the most common reason for an ambulatory care visit, accounting for 2.7 million outpatient visits and more than 4 million emergency department visits annually.
Risks
Overuse of antibiotics can result in dizziness, nausea, diarrhea, and rash, along with a roughly 4% chance of serious adverse effects including anaphylaxis; Stevens-Johnson syndrome, a serious skin and mucous membrane disorder; and Clostridioides difficile-associated diarrhea.
An estimated half of all antibiotic prescriptions for acute respiratory conditions are unnecessary. Before the COVID-19 pandemic, antibiotics were prescribed about 70% of the time for a diagnosis of uncomplicated cough and LRTI. The viral pandemic did not change this practice according to a meta-analysis of 130 studies showing that 78% of COVID-19 patients were prescribed an antibiotic.
The study
The study looked at a cohort of 718 patients, with a mean age of 38.9 years, 65.3% female, of whom 207 received an antibiotic and 511 did not. Of those with baseline data, 29% had an antibiotic prescribed at baseline, the most common (in 85%) being amoxicillin-clavulanate, azithromycin, doxycycline, and amoxicillin. Antibiotics had no effect on the duration or overall severity of cough in viral, bacterial, or mixed infections. Receipt of an antibiotic did, however, reduce the likelihood of a follow-up visit: 14.1% vs 8.2% (adjusted odds ratio, 0.47; 95% confidence interval, 0.26-0.84) — perhaps because it removed the motivation for seeking another consultation. Antibiotic recipients were more likely to receive a systemic corticosteroid (31.9% vs 4.5%, P <.001) and were also more likely to receive an albuterol inhaler (22.7% vs 7.6%, P <.001).
Jeffrey A. Linder, MD, MPH, a primary care physician and chief of internal medicine and geriatrics at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine in Chicago, agrees that in the vast majority of LRTIs — usually acute bronchitis — antibiotics do not speed the healing process. “Forty years of research show that antibiotics do not make acute bronchitis go away any faster,” Dr. Linder, who was not involved in the current study, said in an interview. “There’s even growing evidence that a lot of pneumonia is viral as well, and 10 or 20 years from now we may often not be giving antibiotics for pneumonia because we’ll be able to see better if it’s caused by a virus.”
A large 2018 review by Dr. Linder and associates reported that 46% of antibiotics were prescribed without any infection-related diagnosis code and 20% without an office visit.
Dr. Linder routinely informs patients requesting an antibiotic about the risks of putting an ineffective chemical into their body. “I stress that it can cause rash and other allergic reactions, and even promote C diff infection,” he said. “And I also say it messes with the good bacteria in the microbiome, and they usually come around.”
Patients need to know, Dr. Linder added, that the normal course of healing the respiratory tract after acute bronchitis takes weeks. While a wet cough with sputum or phlegm will last a few days, it’s replaced with a dry annoying cough that persists for up to 3 weeks. “As long as they’re feeling generally better, that cough is normal,” he said. “A virus has run roughshod over their airways and they need a long time to heal and the cough is part of the healing process. Think how long it takes to heal a cut on a finger.”
In an era of escalating antimicrobial resistance fueled by antibiotic overuse, it’s become increasingly important to reserve antibiotics for necessary cases. According to a recent World Health Organization call to action, “Uncontrolled antimicrobial resistance is expected to lower life expectancy and lead to unprecedented health expenditure and economic losses.”
That said, there is important clinical work to be done to determine if there is a limited role for antibiotics in patients with cough, perhaps based on age and baseline severity. “Serious cough symptoms and how to treat them properly needs to be studied more, perhaps in a randomized clinical trial as this study was observational and there haven’t been any randomized trials looking at this issue since about 2012,” Dr. Merenstein said.
This research was funded by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. Dr. Linder reported stock ownership in pharmaceutical companies but none that make antibiotics or other infectious disease drugs.
FROM JOURNAL OF GENERAL INTERNAL MEDICINE
How New ICI Combos Change Bladder Cancer Management
according to Thomas W. Flaig, MD, vice chancellor for research at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Aurora.
Combination therapies involving enfortumab and nivolumab are demonstrating success in recent studies and have been incorporated into the latest guidelines, Dr. Flaig said in a presentation at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) annual conference.
What's New in The Updated Guidelines?
Advances in the treatment options for metastatic urothelial carcinoma in the last decade have been dramatic, with ongoing developments and new emerging treatment options, Dr. Flaig told the audience of his session.
This has led to the identification of new and effective immune checkpoint inhibitor combinations. Consequently, immune checkpoint inhibitors are currently included in all preferred/other recommended first-line treatment regimens, he said.
“Enfortumab vedotin plus pembrolizumab is now the sole preferred first-line regimen for locally advanced or metastatic disease.” Based on the recent research, the mindset regarding cisplatin-eligible patient selection may be changing, he added.
“We have used cisplatin eligibility as a key factor in determining first-line therapy for years, and that paradigm is now shifting with the emergence of enfortumab plus pembrolizumab, a new non–cisplatin containing regimen” Dr. Flaig noted.
Although the optimal choice for second- or third-line therapy after immune checkpoint inhibitors is not well-defined, options include platinum regimens, antibody-drug conjugate, and erdafitinib in eligible patients, he said.
Other Current Strategies for Localized Bladder Cancer Management
The incidence of bladder cancer has been stable for decades, with minimal therapeutic developments until the approval of immune checkpoint inhibitors in the last decade, Dr. Flaig said.
Bladder cancer is more common in older adults, with an average onset age of 73 years, and most patients (75%) are male, he said. Comorbid disease is common in these patients, and many have a history of smoking, Dr. Flaig added.
The traditional medical approach to treating bladder cancer has been based on combination therapies including cisplatin. This has also reflected the approach used in the treatment of lung cancer, historically, Dr. Flaig said.
Cisplatin, while effective, is a challenging therapy to administer and is not an option for all bladder cancer patients because of potential adverse effects, he noted. Antibody drug conjugates and immune checkpoint inhibitors are new alternatives for some who are not able to receive cisplatin.
What are the New Options for Treating Metastatic Urothelial Bladder Cancer?
The approval of antibody drug conjugates offers new treatment with a “specific target and therapeutic payload,” said Dr. Flaig in his presentation. Two antibody drug conjugates, enfortumab vedotin and sacituzumab govitecan, have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), he said. Enforumab vedotin was approved by the FDA in 2021 for adults with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial cancer for subsequent line therapy in select patients. In a 2021 study published in The New England Journal of Medicine, the primary outcome of overall response rate was significantly greater in patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma who were treated with enfortumab vedotin than in those treated with standard chemotherapy (overall response rate [ORR] 40.6% vs 17.9%, respectively).
Side effects associated with enfortumab vedotin “are intrinsic to the payload toxicity and the target distribution. Ideally, the target would be present on all of the cancer cells and none of the normal tissue,” said Dr. Flaig. With enfortumab, specific toxicities included neuropathy, skin reactions, and blood glucose elevation/diabetic ketoacidosis, he said.
A second agent, sacituzumab govitecan, was approved by the FDA for metastatic urothelial cancer patients in 2021, based on data from the TROPHY-U-O1 phase 2 open-label study of 113 individuals. In that study, the ORR was 27% at a median follow-up of 9.1 months. Adverse events included neutropenia, leukopenia, and diarrhea.
What Do the Latest Studies of Combination Therapy Show?
Immune checkpoint inhibitor combinations are significantly changing the landscape of bladder cancer treatment, Dr. Flaig explained.
A recent phase 3 study published in 2024 in The New England Journal of Medicine comparing enfortumab vedotin plus pembrolizumab to platinum-based combination chemotherapy showed an overall response rate of 67.7% vs 44.4% in favor of enfortumab/pembrolizumab, said Dr. Flaig. In addition, the risk of disease progression or death was approximately 55% lower in the enfortumab vedotin-pembrolizumab group vs the chemotherapy group (hazard ratio [HR], 0.45; P less than .001) and the median progression-free survival was approximately doubled (12.5 months vs 6.3 months).
Dr. Flaig described this study as “very notable”because “the enfortumab plus pembrolizumab arm was clearly more effective than the long-standing chemotherapy arm, now becoming the preferred, first-line treatment in the NCCN guidelines. Based on preliminary results of the study, this combination was approved by the FDA in 2023 for locally advanced or metastatic urothelial cancer patients regardless of their eligibility for cisplatin.
Another promising combination, nivolumab plus gemcitabine-cisplatin, was associated with significantly longer overall and progression-free survival in patients with previously untreated unresectable or metastatic urothelial carcinoma, Dr. Flaig said. The therapy was approved by the FDA in March 2024 for first-line therapy.
In a study of 608 patients published in The New England Journal of Medicine, median overall survival was 21.7 months for the nivolumab group vs 18.9 months for the gemcitabine-cisplatin alone group. The overall response rates were 57.6% in the nivolumab group vs 43.1% in the gemcitabine-cisplatin–alone group, and complete response rates were 21.7% and 11.8%, respectively. Serious adverse events (grade 3 or higher) were similar between the groups (61.8% and 51.7%, respectively).
What About Targeted Therapy?
Erdafitinib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor of FGFR1–4, was approved by the FDA in January 2024 for adults with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma who had susceptible FGFR3 genetic alterations, said Dr. Flaig, during his presentation. The limitation of this treatment to only those patients with an FGFR3 mutation is a recent update in its use, he noted.
“Up to 20% of patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma have FGFR alterations,” he said. In an open-label phase 2 study of 99 individuals with unresectable or metastatic urothelial carcinoma, past chemotherapy, and FGFR alterations, confirmed response to erdafitinib was 40% with a median overall survival of 13.8 months.
Dr. Flaig disclosed grant/research support from Agensys; Astellas Pharma US; AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LP; Bristol Myers Squibb; Genentech, Inc.; Janssen Pharmaceutica Products, LP; Merck & Co.; Sanofi-Aventis U.S.; and SeaGen. He also disclosed equity interest/stock options and intellectual property rights in Aurora Oncology, and serving as a consultant or scientific advisor for Janssen Pharmaceutica Product, LP, and Criterium, Inc.
according to Thomas W. Flaig, MD, vice chancellor for research at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Aurora.
Combination therapies involving enfortumab and nivolumab are demonstrating success in recent studies and have been incorporated into the latest guidelines, Dr. Flaig said in a presentation at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) annual conference.
What's New in The Updated Guidelines?
Advances in the treatment options for metastatic urothelial carcinoma in the last decade have been dramatic, with ongoing developments and new emerging treatment options, Dr. Flaig told the audience of his session.
This has led to the identification of new and effective immune checkpoint inhibitor combinations. Consequently, immune checkpoint inhibitors are currently included in all preferred/other recommended first-line treatment regimens, he said.
“Enfortumab vedotin plus pembrolizumab is now the sole preferred first-line regimen for locally advanced or metastatic disease.” Based on the recent research, the mindset regarding cisplatin-eligible patient selection may be changing, he added.
“We have used cisplatin eligibility as a key factor in determining first-line therapy for years, and that paradigm is now shifting with the emergence of enfortumab plus pembrolizumab, a new non–cisplatin containing regimen” Dr. Flaig noted.
Although the optimal choice for second- or third-line therapy after immune checkpoint inhibitors is not well-defined, options include platinum regimens, antibody-drug conjugate, and erdafitinib in eligible patients, he said.
Other Current Strategies for Localized Bladder Cancer Management
The incidence of bladder cancer has been stable for decades, with minimal therapeutic developments until the approval of immune checkpoint inhibitors in the last decade, Dr. Flaig said.
Bladder cancer is more common in older adults, with an average onset age of 73 years, and most patients (75%) are male, he said. Comorbid disease is common in these patients, and many have a history of smoking, Dr. Flaig added.
The traditional medical approach to treating bladder cancer has been based on combination therapies including cisplatin. This has also reflected the approach used in the treatment of lung cancer, historically, Dr. Flaig said.
Cisplatin, while effective, is a challenging therapy to administer and is not an option for all bladder cancer patients because of potential adverse effects, he noted. Antibody drug conjugates and immune checkpoint inhibitors are new alternatives for some who are not able to receive cisplatin.
What are the New Options for Treating Metastatic Urothelial Bladder Cancer?
The approval of antibody drug conjugates offers new treatment with a “specific target and therapeutic payload,” said Dr. Flaig in his presentation. Two antibody drug conjugates, enfortumab vedotin and sacituzumab govitecan, have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), he said. Enforumab vedotin was approved by the FDA in 2021 for adults with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial cancer for subsequent line therapy in select patients. In a 2021 study published in The New England Journal of Medicine, the primary outcome of overall response rate was significantly greater in patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma who were treated with enfortumab vedotin than in those treated with standard chemotherapy (overall response rate [ORR] 40.6% vs 17.9%, respectively).
Side effects associated with enfortumab vedotin “are intrinsic to the payload toxicity and the target distribution. Ideally, the target would be present on all of the cancer cells and none of the normal tissue,” said Dr. Flaig. With enfortumab, specific toxicities included neuropathy, skin reactions, and blood glucose elevation/diabetic ketoacidosis, he said.
A second agent, sacituzumab govitecan, was approved by the FDA for metastatic urothelial cancer patients in 2021, based on data from the TROPHY-U-O1 phase 2 open-label study of 113 individuals. In that study, the ORR was 27% at a median follow-up of 9.1 months. Adverse events included neutropenia, leukopenia, and diarrhea.
What Do the Latest Studies of Combination Therapy Show?
Immune checkpoint inhibitor combinations are significantly changing the landscape of bladder cancer treatment, Dr. Flaig explained.
A recent phase 3 study published in 2024 in The New England Journal of Medicine comparing enfortumab vedotin plus pembrolizumab to platinum-based combination chemotherapy showed an overall response rate of 67.7% vs 44.4% in favor of enfortumab/pembrolizumab, said Dr. Flaig. In addition, the risk of disease progression or death was approximately 55% lower in the enfortumab vedotin-pembrolizumab group vs the chemotherapy group (hazard ratio [HR], 0.45; P less than .001) and the median progression-free survival was approximately doubled (12.5 months vs 6.3 months).
Dr. Flaig described this study as “very notable”because “the enfortumab plus pembrolizumab arm was clearly more effective than the long-standing chemotherapy arm, now becoming the preferred, first-line treatment in the NCCN guidelines. Based on preliminary results of the study, this combination was approved by the FDA in 2023 for locally advanced or metastatic urothelial cancer patients regardless of their eligibility for cisplatin.
Another promising combination, nivolumab plus gemcitabine-cisplatin, was associated with significantly longer overall and progression-free survival in patients with previously untreated unresectable or metastatic urothelial carcinoma, Dr. Flaig said. The therapy was approved by the FDA in March 2024 for first-line therapy.
In a study of 608 patients published in The New England Journal of Medicine, median overall survival was 21.7 months for the nivolumab group vs 18.9 months for the gemcitabine-cisplatin alone group. The overall response rates were 57.6% in the nivolumab group vs 43.1% in the gemcitabine-cisplatin–alone group, and complete response rates were 21.7% and 11.8%, respectively. Serious adverse events (grade 3 or higher) were similar between the groups (61.8% and 51.7%, respectively).
What About Targeted Therapy?
Erdafitinib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor of FGFR1–4, was approved by the FDA in January 2024 for adults with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma who had susceptible FGFR3 genetic alterations, said Dr. Flaig, during his presentation. The limitation of this treatment to only those patients with an FGFR3 mutation is a recent update in its use, he noted.
“Up to 20% of patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma have FGFR alterations,” he said. In an open-label phase 2 study of 99 individuals with unresectable or metastatic urothelial carcinoma, past chemotherapy, and FGFR alterations, confirmed response to erdafitinib was 40% with a median overall survival of 13.8 months.
Dr. Flaig disclosed grant/research support from Agensys; Astellas Pharma US; AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LP; Bristol Myers Squibb; Genentech, Inc.; Janssen Pharmaceutica Products, LP; Merck & Co.; Sanofi-Aventis U.S.; and SeaGen. He also disclosed equity interest/stock options and intellectual property rights in Aurora Oncology, and serving as a consultant or scientific advisor for Janssen Pharmaceutica Product, LP, and Criterium, Inc.
according to Thomas W. Flaig, MD, vice chancellor for research at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Aurora.
Combination therapies involving enfortumab and nivolumab are demonstrating success in recent studies and have been incorporated into the latest guidelines, Dr. Flaig said in a presentation at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) annual conference.
What's New in The Updated Guidelines?
Advances in the treatment options for metastatic urothelial carcinoma in the last decade have been dramatic, with ongoing developments and new emerging treatment options, Dr. Flaig told the audience of his session.
This has led to the identification of new and effective immune checkpoint inhibitor combinations. Consequently, immune checkpoint inhibitors are currently included in all preferred/other recommended first-line treatment regimens, he said.
“Enfortumab vedotin plus pembrolizumab is now the sole preferred first-line regimen for locally advanced or metastatic disease.” Based on the recent research, the mindset regarding cisplatin-eligible patient selection may be changing, he added.
“We have used cisplatin eligibility as a key factor in determining first-line therapy for years, and that paradigm is now shifting with the emergence of enfortumab plus pembrolizumab, a new non–cisplatin containing regimen” Dr. Flaig noted.
Although the optimal choice for second- or third-line therapy after immune checkpoint inhibitors is not well-defined, options include platinum regimens, antibody-drug conjugate, and erdafitinib in eligible patients, he said.
Other Current Strategies for Localized Bladder Cancer Management
The incidence of bladder cancer has been stable for decades, with minimal therapeutic developments until the approval of immune checkpoint inhibitors in the last decade, Dr. Flaig said.
Bladder cancer is more common in older adults, with an average onset age of 73 years, and most patients (75%) are male, he said. Comorbid disease is common in these patients, and many have a history of smoking, Dr. Flaig added.
The traditional medical approach to treating bladder cancer has been based on combination therapies including cisplatin. This has also reflected the approach used in the treatment of lung cancer, historically, Dr. Flaig said.
Cisplatin, while effective, is a challenging therapy to administer and is not an option for all bladder cancer patients because of potential adverse effects, he noted. Antibody drug conjugates and immune checkpoint inhibitors are new alternatives for some who are not able to receive cisplatin.
What are the New Options for Treating Metastatic Urothelial Bladder Cancer?
The approval of antibody drug conjugates offers new treatment with a “specific target and therapeutic payload,” said Dr. Flaig in his presentation. Two antibody drug conjugates, enfortumab vedotin and sacituzumab govitecan, have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), he said. Enforumab vedotin was approved by the FDA in 2021 for adults with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial cancer for subsequent line therapy in select patients. In a 2021 study published in The New England Journal of Medicine, the primary outcome of overall response rate was significantly greater in patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma who were treated with enfortumab vedotin than in those treated with standard chemotherapy (overall response rate [ORR] 40.6% vs 17.9%, respectively).
Side effects associated with enfortumab vedotin “are intrinsic to the payload toxicity and the target distribution. Ideally, the target would be present on all of the cancer cells and none of the normal tissue,” said Dr. Flaig. With enfortumab, specific toxicities included neuropathy, skin reactions, and blood glucose elevation/diabetic ketoacidosis, he said.
A second agent, sacituzumab govitecan, was approved by the FDA for metastatic urothelial cancer patients in 2021, based on data from the TROPHY-U-O1 phase 2 open-label study of 113 individuals. In that study, the ORR was 27% at a median follow-up of 9.1 months. Adverse events included neutropenia, leukopenia, and diarrhea.
What Do the Latest Studies of Combination Therapy Show?
Immune checkpoint inhibitor combinations are significantly changing the landscape of bladder cancer treatment, Dr. Flaig explained.
A recent phase 3 study published in 2024 in The New England Journal of Medicine comparing enfortumab vedotin plus pembrolizumab to platinum-based combination chemotherapy showed an overall response rate of 67.7% vs 44.4% in favor of enfortumab/pembrolizumab, said Dr. Flaig. In addition, the risk of disease progression or death was approximately 55% lower in the enfortumab vedotin-pembrolizumab group vs the chemotherapy group (hazard ratio [HR], 0.45; P less than .001) and the median progression-free survival was approximately doubled (12.5 months vs 6.3 months).
Dr. Flaig described this study as “very notable”because “the enfortumab plus pembrolizumab arm was clearly more effective than the long-standing chemotherapy arm, now becoming the preferred, first-line treatment in the NCCN guidelines. Based on preliminary results of the study, this combination was approved by the FDA in 2023 for locally advanced or metastatic urothelial cancer patients regardless of their eligibility for cisplatin.
Another promising combination, nivolumab plus gemcitabine-cisplatin, was associated with significantly longer overall and progression-free survival in patients with previously untreated unresectable or metastatic urothelial carcinoma, Dr. Flaig said. The therapy was approved by the FDA in March 2024 for first-line therapy.
In a study of 608 patients published in The New England Journal of Medicine, median overall survival was 21.7 months for the nivolumab group vs 18.9 months for the gemcitabine-cisplatin alone group. The overall response rates were 57.6% in the nivolumab group vs 43.1% in the gemcitabine-cisplatin–alone group, and complete response rates were 21.7% and 11.8%, respectively. Serious adverse events (grade 3 or higher) were similar between the groups (61.8% and 51.7%, respectively).
What About Targeted Therapy?
Erdafitinib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor of FGFR1–4, was approved by the FDA in January 2024 for adults with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma who had susceptible FGFR3 genetic alterations, said Dr. Flaig, during his presentation. The limitation of this treatment to only those patients with an FGFR3 mutation is a recent update in its use, he noted.
“Up to 20% of patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma have FGFR alterations,” he said. In an open-label phase 2 study of 99 individuals with unresectable or metastatic urothelial carcinoma, past chemotherapy, and FGFR alterations, confirmed response to erdafitinib was 40% with a median overall survival of 13.8 months.
Dr. Flaig disclosed grant/research support from Agensys; Astellas Pharma US; AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LP; Bristol Myers Squibb; Genentech, Inc.; Janssen Pharmaceutica Products, LP; Merck & Co.; Sanofi-Aventis U.S.; and SeaGen. He also disclosed equity interest/stock options and intellectual property rights in Aurora Oncology, and serving as a consultant or scientific advisor for Janssen Pharmaceutica Product, LP, and Criterium, Inc.
FROM NCCN 2024
Panel: MRD Tests May Speed Myeloma Tx Approvals
The Oncologic Drugs Advisory Committee (ODAC) of the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) voted 12-0 on April 12 on the following question: Does the evidence support the use of MRD as an accelerated approval endpoint in multiple myeloma clinical trials?
The FDA is not bound to accept the recommendations of its panels, but often does so.
ODAC panelists said they felt comfortable in this recommendation because they expected the FDA to mandate confirmatory studies of any drugs to be given accelerated approval based on MRD data.
There’s a risk that MRD results might mislead regulators into clearing a drug later found to lack benefit, said Christopher Hourigan, DM, DPhil, an ODAC panelist and a physician-scientist at Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, Virginia, who treats people with blood cancer. Further tests would ultimately show if drugs cleared based on MRD data actually delivered benefits such as extending progression-free survival (PFS).
“That’s why we’re talking about accelerated approval,” Dr. Hourigan said. “There is harm to inaction. We’re not currently curing people in multiple myeloma. I’m not willing to make patients wait on principle for a theoretical perfect that may never come.”
“Our responsibility is to accept the world as messy and be agile enough to adapt and iterate that the evidence develops rather than create barriers to the work of discovering effective new therapies for these patients,” he added.
Advances in testing now allow for detection of the presence of malignant cells at orders of magnitude below previous assessments. MRD assays used in tracking what’s happening with myeloma generally have a sensitivity level of 10-5, or a detection capacity of one cell of 100,000, said Ola Landgren, MD, PhD, of the University of Miami, Miami, Florida, during a presentation at the meeting.
The April 12 meeting was somewhat unusual for ODAC.
Instead of reviewing the benefits and risks of a specific drug, the panel reviewed results from two separate major research efforts done to see how MRD could be used in development of drugs.
These were Dr. Landgren’s EVIDENCE (Evaluating minimal residual disease as an intermediate clinical endpoint for multiple myeloma) meta-analysis, and the similar work of the i2TEAMM group, affiliated with the International Myeloma Foundation.
In its review, the FDA staff noted differences in the approaches of the two groups. In its analysis, the i2TEAMM removed information about patients with missing MRD data, while the University of Miami team retained information about these kinds of patients in the analyses and assigned their status to be MRD positive.
The FDA staff also noted in their review and presentations weaknesses in the case for MRD. For example, the FDA staff noted that the treatment effect on MRD negativity was not statistically significant in 4 of the 8 treatment comparisons in the work from Dr. Landgren and colleagues.
The FDA staff looked at what these analyses suggested at both an individual level and trial level. The data from these two research projects taken as a whole showed “strong individual-level” associations between negative MRD findings and later positive outcomes for patients, although trial-level associations were “weak to moderate” in some cases, the staff wrote.
The FDA staff concluded that the research appeared to support arguments in favor of the “prognostic value,” even with outstanding questions about how best to use this test.
In the briefing document for the meeting, the FDA also emphasized the need for new treatments.
Multiple myeloma remains an incurable disease with a 5-year relative survival rate of 59.8%, even after significant recent progress in treatment, the agency said. In the past decade, the FDA has approved 15 new drugs and greater than 20 new indications have been approved for the treatment of patients with multiple myeloma.
The FDA has been working with drugmakers and academic researchers for several years to address the potential of MRD in development of blood cancers. The agency in 2020 issued a guidance document on this issue.
Several ODAC members praised the i2TEAMM and Dr. Landgren’s EVIDENCE teams for their work, which took place across several nations and extended over many years.
“This was a herculean effort. It really changes the playbook for how we think about biomarkers across all cancer types,” said ODAC panelist Neil Vasan, MD, PhD, of Columbia University, New York, NY. “To me, the important word was reasonable. Is this a reasonable surrogate endpoint? Is this a reasonable intermediate endpoint? I think it is more than reasonable.”
Still, ODAC panelist Jorge Nieva, MD, raised a point of concern about how use of MRD as an endpoint could change the design of studies. He urged caution among researchers about potential ramping up of collection of MRD tests in search of more robust data, which could lead to more testing for patients.
“I have this tremendous fear that this is going to mean every myeloma protocol has a marrow biopsy every six weeks on the patients forever,” said Dr. Nieva of the Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern California, Los Angeles. “I just don’t want to see that happen. So I think we need to balance these two things.”
The Oncologic Drugs Advisory Committee (ODAC) of the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) voted 12-0 on April 12 on the following question: Does the evidence support the use of MRD as an accelerated approval endpoint in multiple myeloma clinical trials?
The FDA is not bound to accept the recommendations of its panels, but often does so.
ODAC panelists said they felt comfortable in this recommendation because they expected the FDA to mandate confirmatory studies of any drugs to be given accelerated approval based on MRD data.
There’s a risk that MRD results might mislead regulators into clearing a drug later found to lack benefit, said Christopher Hourigan, DM, DPhil, an ODAC panelist and a physician-scientist at Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, Virginia, who treats people with blood cancer. Further tests would ultimately show if drugs cleared based on MRD data actually delivered benefits such as extending progression-free survival (PFS).
“That’s why we’re talking about accelerated approval,” Dr. Hourigan said. “There is harm to inaction. We’re not currently curing people in multiple myeloma. I’m not willing to make patients wait on principle for a theoretical perfect that may never come.”
“Our responsibility is to accept the world as messy and be agile enough to adapt and iterate that the evidence develops rather than create barriers to the work of discovering effective new therapies for these patients,” he added.
Advances in testing now allow for detection of the presence of malignant cells at orders of magnitude below previous assessments. MRD assays used in tracking what’s happening with myeloma generally have a sensitivity level of 10-5, or a detection capacity of one cell of 100,000, said Ola Landgren, MD, PhD, of the University of Miami, Miami, Florida, during a presentation at the meeting.
The April 12 meeting was somewhat unusual for ODAC.
Instead of reviewing the benefits and risks of a specific drug, the panel reviewed results from two separate major research efforts done to see how MRD could be used in development of drugs.
These were Dr. Landgren’s EVIDENCE (Evaluating minimal residual disease as an intermediate clinical endpoint for multiple myeloma) meta-analysis, and the similar work of the i2TEAMM group, affiliated with the International Myeloma Foundation.
In its review, the FDA staff noted differences in the approaches of the two groups. In its analysis, the i2TEAMM removed information about patients with missing MRD data, while the University of Miami team retained information about these kinds of patients in the analyses and assigned their status to be MRD positive.
The FDA staff also noted in their review and presentations weaknesses in the case for MRD. For example, the FDA staff noted that the treatment effect on MRD negativity was not statistically significant in 4 of the 8 treatment comparisons in the work from Dr. Landgren and colleagues.
The FDA staff looked at what these analyses suggested at both an individual level and trial level. The data from these two research projects taken as a whole showed “strong individual-level” associations between negative MRD findings and later positive outcomes for patients, although trial-level associations were “weak to moderate” in some cases, the staff wrote.
The FDA staff concluded that the research appeared to support arguments in favor of the “prognostic value,” even with outstanding questions about how best to use this test.
In the briefing document for the meeting, the FDA also emphasized the need for new treatments.
Multiple myeloma remains an incurable disease with a 5-year relative survival rate of 59.8%, even after significant recent progress in treatment, the agency said. In the past decade, the FDA has approved 15 new drugs and greater than 20 new indications have been approved for the treatment of patients with multiple myeloma.
The FDA has been working with drugmakers and academic researchers for several years to address the potential of MRD in development of blood cancers. The agency in 2020 issued a guidance document on this issue.
Several ODAC members praised the i2TEAMM and Dr. Landgren’s EVIDENCE teams for their work, which took place across several nations and extended over many years.
“This was a herculean effort. It really changes the playbook for how we think about biomarkers across all cancer types,” said ODAC panelist Neil Vasan, MD, PhD, of Columbia University, New York, NY. “To me, the important word was reasonable. Is this a reasonable surrogate endpoint? Is this a reasonable intermediate endpoint? I think it is more than reasonable.”
Still, ODAC panelist Jorge Nieva, MD, raised a point of concern about how use of MRD as an endpoint could change the design of studies. He urged caution among researchers about potential ramping up of collection of MRD tests in search of more robust data, which could lead to more testing for patients.
“I have this tremendous fear that this is going to mean every myeloma protocol has a marrow biopsy every six weeks on the patients forever,” said Dr. Nieva of the Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern California, Los Angeles. “I just don’t want to see that happen. So I think we need to balance these two things.”
The Oncologic Drugs Advisory Committee (ODAC) of the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) voted 12-0 on April 12 on the following question: Does the evidence support the use of MRD as an accelerated approval endpoint in multiple myeloma clinical trials?
The FDA is not bound to accept the recommendations of its panels, but often does so.
ODAC panelists said they felt comfortable in this recommendation because they expected the FDA to mandate confirmatory studies of any drugs to be given accelerated approval based on MRD data.
There’s a risk that MRD results might mislead regulators into clearing a drug later found to lack benefit, said Christopher Hourigan, DM, DPhil, an ODAC panelist and a physician-scientist at Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, Virginia, who treats people with blood cancer. Further tests would ultimately show if drugs cleared based on MRD data actually delivered benefits such as extending progression-free survival (PFS).
“That’s why we’re talking about accelerated approval,” Dr. Hourigan said. “There is harm to inaction. We’re not currently curing people in multiple myeloma. I’m not willing to make patients wait on principle for a theoretical perfect that may never come.”
“Our responsibility is to accept the world as messy and be agile enough to adapt and iterate that the evidence develops rather than create barriers to the work of discovering effective new therapies for these patients,” he added.
Advances in testing now allow for detection of the presence of malignant cells at orders of magnitude below previous assessments. MRD assays used in tracking what’s happening with myeloma generally have a sensitivity level of 10-5, or a detection capacity of one cell of 100,000, said Ola Landgren, MD, PhD, of the University of Miami, Miami, Florida, during a presentation at the meeting.
The April 12 meeting was somewhat unusual for ODAC.
Instead of reviewing the benefits and risks of a specific drug, the panel reviewed results from two separate major research efforts done to see how MRD could be used in development of drugs.
These were Dr. Landgren’s EVIDENCE (Evaluating minimal residual disease as an intermediate clinical endpoint for multiple myeloma) meta-analysis, and the similar work of the i2TEAMM group, affiliated with the International Myeloma Foundation.
In its review, the FDA staff noted differences in the approaches of the two groups. In its analysis, the i2TEAMM removed information about patients with missing MRD data, while the University of Miami team retained information about these kinds of patients in the analyses and assigned their status to be MRD positive.
The FDA staff also noted in their review and presentations weaknesses in the case for MRD. For example, the FDA staff noted that the treatment effect on MRD negativity was not statistically significant in 4 of the 8 treatment comparisons in the work from Dr. Landgren and colleagues.
The FDA staff looked at what these analyses suggested at both an individual level and trial level. The data from these two research projects taken as a whole showed “strong individual-level” associations between negative MRD findings and later positive outcomes for patients, although trial-level associations were “weak to moderate” in some cases, the staff wrote.
The FDA staff concluded that the research appeared to support arguments in favor of the “prognostic value,” even with outstanding questions about how best to use this test.
In the briefing document for the meeting, the FDA also emphasized the need for new treatments.
Multiple myeloma remains an incurable disease with a 5-year relative survival rate of 59.8%, even after significant recent progress in treatment, the agency said. In the past decade, the FDA has approved 15 new drugs and greater than 20 new indications have been approved for the treatment of patients with multiple myeloma.
The FDA has been working with drugmakers and academic researchers for several years to address the potential of MRD in development of blood cancers. The agency in 2020 issued a guidance document on this issue.
Several ODAC members praised the i2TEAMM and Dr. Landgren’s EVIDENCE teams for their work, which took place across several nations and extended over many years.
“This was a herculean effort. It really changes the playbook for how we think about biomarkers across all cancer types,” said ODAC panelist Neil Vasan, MD, PhD, of Columbia University, New York, NY. “To me, the important word was reasonable. Is this a reasonable surrogate endpoint? Is this a reasonable intermediate endpoint? I think it is more than reasonable.”
Still, ODAC panelist Jorge Nieva, MD, raised a point of concern about how use of MRD as an endpoint could change the design of studies. He urged caution among researchers about potential ramping up of collection of MRD tests in search of more robust data, which could lead to more testing for patients.
“I have this tremendous fear that this is going to mean every myeloma protocol has a marrow biopsy every six weeks on the patients forever,” said Dr. Nieva of the Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern California, Los Angeles. “I just don’t want to see that happen. So I think we need to balance these two things.”
Antidiabetic Drugs That Lower Stroke Risk Do So By Unclear Mechanisms
DENVER —
In patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), the evidence is strong that “they are not working through glycemic control per se,” according to Larry B. Goldstein, MD, chair of neurology, University of Kentucky School of Medicine, Louisville. “But it is not yet clear what the mechanism of benefit is.”
In the past, several large randomized studies, such as the ACCORD trial, provided compelling evidence that tighter glycemic control does not translate into meaningful protection across stroke. Performed before many of the modern therapies were available, this lack of protection was observed with essentially “no heterogeneity across specific drugs,” according to Dr. Goldstein.
In long-term results from ACCORD, published in 2011, the odds ratio for a fatal or nonfatal stroke was a nonsignificant 0.97 in favor of tight glycemic control relative to standard control. The wide confidence intervals ruled out any hint of statistical significance (95% CI, 0.77-1.33; P = .85). Dr. Goldstein provided data from numerous other studies and meta-analyses that drew the same conclusion.
Stroke Prevention With Antidiabetic Drugs
“What has changed is that we have new ways of glycemic control, and some of these do show protection against stroke,” Dr. Goldstein said. Yet, the newer drugs do not do a better job at sustained reductions of HbA1c or other measures of reaching lower blood glucose reductions when adherence is similar.
“The level of glucose control with the newer agents is really about the same,” Dr. Goldstein said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology, where he led a symposium called Controversies in Stroke Treatment and Prevention.
The newer agents, such as sodium glucose co-transport-2 inhibitors (SGLT-2i) and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RA), have been associated with significant and clinically meaningful reductions in cardiovascular events. However, it is not clear that even these two medications perform similarly for stroke prevention specifically.
Of these two drug classes, Dr. Goldstein said the evidence most strongly supports GLP-1 receptor agonists. He cited one meta-analysis of eight randomized studies that calculated a risk reduction of about 15% whether calculated for fatal or nonfatal strokes. For each the protection was highly statistically significant (P = .0002 and P < .001, respectively).
In contrast, the effect of SGLT-2 inhibitors is weaker. In a study that distilled data from large cardiovascular trials with GLP-1RA, SGLT2i, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors (DPP4i), and pioglitazone, a thiazolidinedione, only GLP-1RA drugs were associated with a highly significant (P < .001) reduction in risk of stroke. The risk reduction for pioglitazone reached significance (P = .025), but there was no signal of risk reduction for SGLT2i (P = .88) or for DPP4i (P = .5).
Weight Loss Is Potential Mechanism
Looking to explain the protection from stroke associated with some of the newer antidiabetic therapies, Gordon Kelley, MD, who leads the stroke program for AdventHealth Medical Group, Shawnee Mission, Kansas, suggested that weight loss is probably important.
“In our group, we work as a team to manage stroke risk in patients with diabetes, so I am not much involved in the choice of antidiabetic therapies, but it does seem that SGLT2 inhibitors and the GLP-1 receptor agonists share weight loss as an effect beyond glucose control,” he said.
Dr. Goldstein agreed that weight loss is a potential contributor to the cardiovascular benefits of GLP-1RA and SGLT2i, but he indicated that it might not help explain the reduction in stroke, an effect demonstrated repeatedly with GLP-1RA but inconsistently with SGLT2i.
The argument against weight loss as the critical mechanism of stroke prevention from newer antidiabetic drugs is strengthened by studies that suggest weight loss with SGLT2i appears to be even better than on GLP-1RA. In a study published in a pharmacy journal, weight loss was about twice as great among T2DM patients after 6 months of treatment managed with SGLT2i relative to those on a GLP-1RA (-2.8 vs 1.15 kg; P = .014).
Newer Antidiabetic Agents Guideline Recommended
In the 2019 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association guidelines on the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease, stroke reduction is not discussed as an isolated risk, but these guidelines do recommend GLP-1RA or SGLT2i after metformin for glycemic control in T2DM patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk factors. This is based on evidence that drugs of both classes reduce risk for ASCVD events. The risk reduction has been particularly strong for heart failure.
For the risk of stroke specifically in patients with T2DM, Dr. Goldstein recommended calculating the ASCVD risk with the simple but well validated ACC risk calculator that is available online and is quickly completed when values for patient risk factors are readily available. For those with greater than 10% risk of an event in the next 10 years, he thinks GLP-1RA are a reasonable choice for prevention of stroke and other ASCVD events.
“GLP-1RA is mentioned in the guidelines, so this is supported,” said Dr. Goldstein, although adding that his choice of this class over SGLT2i is a personal if informed recommendation. He believes that the data favor GLP-1RA even if the exact mechanism of this protection is yet to be identified.
Dr. Goldstein and Dr. Kelley report no potential conflicts of interest.
DENVER —
In patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), the evidence is strong that “they are not working through glycemic control per se,” according to Larry B. Goldstein, MD, chair of neurology, University of Kentucky School of Medicine, Louisville. “But it is not yet clear what the mechanism of benefit is.”
In the past, several large randomized studies, such as the ACCORD trial, provided compelling evidence that tighter glycemic control does not translate into meaningful protection across stroke. Performed before many of the modern therapies were available, this lack of protection was observed with essentially “no heterogeneity across specific drugs,” according to Dr. Goldstein.
In long-term results from ACCORD, published in 2011, the odds ratio for a fatal or nonfatal stroke was a nonsignificant 0.97 in favor of tight glycemic control relative to standard control. The wide confidence intervals ruled out any hint of statistical significance (95% CI, 0.77-1.33; P = .85). Dr. Goldstein provided data from numerous other studies and meta-analyses that drew the same conclusion.
Stroke Prevention With Antidiabetic Drugs
“What has changed is that we have new ways of glycemic control, and some of these do show protection against stroke,” Dr. Goldstein said. Yet, the newer drugs do not do a better job at sustained reductions of HbA1c or other measures of reaching lower blood glucose reductions when adherence is similar.
“The level of glucose control with the newer agents is really about the same,” Dr. Goldstein said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology, where he led a symposium called Controversies in Stroke Treatment and Prevention.
The newer agents, such as sodium glucose co-transport-2 inhibitors (SGLT-2i) and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RA), have been associated with significant and clinically meaningful reductions in cardiovascular events. However, it is not clear that even these two medications perform similarly for stroke prevention specifically.
Of these two drug classes, Dr. Goldstein said the evidence most strongly supports GLP-1 receptor agonists. He cited one meta-analysis of eight randomized studies that calculated a risk reduction of about 15% whether calculated for fatal or nonfatal strokes. For each the protection was highly statistically significant (P = .0002 and P < .001, respectively).
In contrast, the effect of SGLT-2 inhibitors is weaker. In a study that distilled data from large cardiovascular trials with GLP-1RA, SGLT2i, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors (DPP4i), and pioglitazone, a thiazolidinedione, only GLP-1RA drugs were associated with a highly significant (P < .001) reduction in risk of stroke. The risk reduction for pioglitazone reached significance (P = .025), but there was no signal of risk reduction for SGLT2i (P = .88) or for DPP4i (P = .5).
Weight Loss Is Potential Mechanism
Looking to explain the protection from stroke associated with some of the newer antidiabetic therapies, Gordon Kelley, MD, who leads the stroke program for AdventHealth Medical Group, Shawnee Mission, Kansas, suggested that weight loss is probably important.
“In our group, we work as a team to manage stroke risk in patients with diabetes, so I am not much involved in the choice of antidiabetic therapies, but it does seem that SGLT2 inhibitors and the GLP-1 receptor agonists share weight loss as an effect beyond glucose control,” he said.
Dr. Goldstein agreed that weight loss is a potential contributor to the cardiovascular benefits of GLP-1RA and SGLT2i, but he indicated that it might not help explain the reduction in stroke, an effect demonstrated repeatedly with GLP-1RA but inconsistently with SGLT2i.
The argument against weight loss as the critical mechanism of stroke prevention from newer antidiabetic drugs is strengthened by studies that suggest weight loss with SGLT2i appears to be even better than on GLP-1RA. In a study published in a pharmacy journal, weight loss was about twice as great among T2DM patients after 6 months of treatment managed with SGLT2i relative to those on a GLP-1RA (-2.8 vs 1.15 kg; P = .014).
Newer Antidiabetic Agents Guideline Recommended
In the 2019 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association guidelines on the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease, stroke reduction is not discussed as an isolated risk, but these guidelines do recommend GLP-1RA or SGLT2i after metformin for glycemic control in T2DM patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk factors. This is based on evidence that drugs of both classes reduce risk for ASCVD events. The risk reduction has been particularly strong for heart failure.
For the risk of stroke specifically in patients with T2DM, Dr. Goldstein recommended calculating the ASCVD risk with the simple but well validated ACC risk calculator that is available online and is quickly completed when values for patient risk factors are readily available. For those with greater than 10% risk of an event in the next 10 years, he thinks GLP-1RA are a reasonable choice for prevention of stroke and other ASCVD events.
“GLP-1RA is mentioned in the guidelines, so this is supported,” said Dr. Goldstein, although adding that his choice of this class over SGLT2i is a personal if informed recommendation. He believes that the data favor GLP-1RA even if the exact mechanism of this protection is yet to be identified.
Dr. Goldstein and Dr. Kelley report no potential conflicts of interest.
DENVER —
In patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), the evidence is strong that “they are not working through glycemic control per se,” according to Larry B. Goldstein, MD, chair of neurology, University of Kentucky School of Medicine, Louisville. “But it is not yet clear what the mechanism of benefit is.”
In the past, several large randomized studies, such as the ACCORD trial, provided compelling evidence that tighter glycemic control does not translate into meaningful protection across stroke. Performed before many of the modern therapies were available, this lack of protection was observed with essentially “no heterogeneity across specific drugs,” according to Dr. Goldstein.
In long-term results from ACCORD, published in 2011, the odds ratio for a fatal or nonfatal stroke was a nonsignificant 0.97 in favor of tight glycemic control relative to standard control. The wide confidence intervals ruled out any hint of statistical significance (95% CI, 0.77-1.33; P = .85). Dr. Goldstein provided data from numerous other studies and meta-analyses that drew the same conclusion.
Stroke Prevention With Antidiabetic Drugs
“What has changed is that we have new ways of glycemic control, and some of these do show protection against stroke,” Dr. Goldstein said. Yet, the newer drugs do not do a better job at sustained reductions of HbA1c or other measures of reaching lower blood glucose reductions when adherence is similar.
“The level of glucose control with the newer agents is really about the same,” Dr. Goldstein said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology, where he led a symposium called Controversies in Stroke Treatment and Prevention.
The newer agents, such as sodium glucose co-transport-2 inhibitors (SGLT-2i) and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RA), have been associated with significant and clinically meaningful reductions in cardiovascular events. However, it is not clear that even these two medications perform similarly for stroke prevention specifically.
Of these two drug classes, Dr. Goldstein said the evidence most strongly supports GLP-1 receptor agonists. He cited one meta-analysis of eight randomized studies that calculated a risk reduction of about 15% whether calculated for fatal or nonfatal strokes. For each the protection was highly statistically significant (P = .0002 and P < .001, respectively).
In contrast, the effect of SGLT-2 inhibitors is weaker. In a study that distilled data from large cardiovascular trials with GLP-1RA, SGLT2i, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors (DPP4i), and pioglitazone, a thiazolidinedione, only GLP-1RA drugs were associated with a highly significant (P < .001) reduction in risk of stroke. The risk reduction for pioglitazone reached significance (P = .025), but there was no signal of risk reduction for SGLT2i (P = .88) or for DPP4i (P = .5).
Weight Loss Is Potential Mechanism
Looking to explain the protection from stroke associated with some of the newer antidiabetic therapies, Gordon Kelley, MD, who leads the stroke program for AdventHealth Medical Group, Shawnee Mission, Kansas, suggested that weight loss is probably important.
“In our group, we work as a team to manage stroke risk in patients with diabetes, so I am not much involved in the choice of antidiabetic therapies, but it does seem that SGLT2 inhibitors and the GLP-1 receptor agonists share weight loss as an effect beyond glucose control,” he said.
Dr. Goldstein agreed that weight loss is a potential contributor to the cardiovascular benefits of GLP-1RA and SGLT2i, but he indicated that it might not help explain the reduction in stroke, an effect demonstrated repeatedly with GLP-1RA but inconsistently with SGLT2i.
The argument against weight loss as the critical mechanism of stroke prevention from newer antidiabetic drugs is strengthened by studies that suggest weight loss with SGLT2i appears to be even better than on GLP-1RA. In a study published in a pharmacy journal, weight loss was about twice as great among T2DM patients after 6 months of treatment managed with SGLT2i relative to those on a GLP-1RA (-2.8 vs 1.15 kg; P = .014).
Newer Antidiabetic Agents Guideline Recommended
In the 2019 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association guidelines on the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease, stroke reduction is not discussed as an isolated risk, but these guidelines do recommend GLP-1RA or SGLT2i after metformin for glycemic control in T2DM patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk factors. This is based on evidence that drugs of both classes reduce risk for ASCVD events. The risk reduction has been particularly strong for heart failure.
For the risk of stroke specifically in patients with T2DM, Dr. Goldstein recommended calculating the ASCVD risk with the simple but well validated ACC risk calculator that is available online and is quickly completed when values for patient risk factors are readily available. For those with greater than 10% risk of an event in the next 10 years, he thinks GLP-1RA are a reasonable choice for prevention of stroke and other ASCVD events.
“GLP-1RA is mentioned in the guidelines, so this is supported,” said Dr. Goldstein, although adding that his choice of this class over SGLT2i is a personal if informed recommendation. He believes that the data favor GLP-1RA even if the exact mechanism of this protection is yet to be identified.
Dr. Goldstein and Dr. Kelley report no potential conflicts of interest.
FROM AAN 2024
Barcelona’s Best: Vasculitis Treatment Studies on Stopping Steroids, Abatacept, Plasma Exchange, Vaccination
Some of the best clinical trials of patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody–associated vasculitis (AAV) that were presented at the 21st International Vasculitis Workshop in Barcelona, Spain, included studies addressing relapse after stopping steroids, preventing relapse with abatacept, improving kidney function with plasma exchange, and vaccinating rituximab-treated patients.
Stopping Steroids After Remission in GPA
In the randomized, open-label TAPIR (The Assessment of Prednisone In Remission Trial) study of 159 adults with GPA in remission who had tapered to a prednisone dose of 5 mg/day, those who remained at that dosage had a significantly lower rate of relapse after 6 months than those who tapered to 0 mg/day (4.2% vs 15.5%; P = .227), according to results reported at the meeting.
However, use of a higher dose of prednisone for disease relapse by 6 months was similar for patients who used rituximab at baseline (8.8% with 0 mg/day vs 6.1% with 5 mg/day; P = .667), and the difference in this primary outcome was more pronounced among patients who did not take rituximab at baseline (20.0% with 0 mg/day vs 2.6% with 5 mg/day; P = .023).
A higher percentage of patients taking prednisone 0 mg/day had disease relapses that were considered minor (14.1% and 4.2%; P = .0391). Major relapses occurred in none of the patients taking 5 mg/day and in 1.4% receiving 0 mg/day. About 90% of patients in either treatment arm completed the trial.
The study, funded by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskelatal and Skin Diseases and the National Heart Lung and Blood Institute, was unique in that half of patients randomized in the study were enrolled at community clinics and half were enrolled at Vasculitis Clinical Research Consortium clinical centers.
Abatacept Falls Short for Preventing Relapse in GPA
Adding abatacept to glucocorticoids failed to reduce risk of relapse, worsening disease, or failure to reach remission in adults with relapsing, nonsevere GPA, based on data from a randomized trial of 65 individuals.
In the 20-site, randomized, double-blind ABROGATE (Abatacept for the Treatment of Relapsing, Non-Severe, Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis) study, 34 patients received 125 mg subcutaneous abatacept once a week or a placebo in addition to 30 mg/day of prednisone that was tapered and discontinued after 12 weeks. Patients who were receiving methotrexate, azathioprine, mycophenolate, or leflunomide at baseline continued the medication at a stable dose.
The primary outcome of disease worsening or relapse occurred in 62% of the abatacept group and 68% of the placebo group, and no significant difference in treatment failure rate appeared between the groups. In addition, key secondary endpoints of time to full remission, duration of glucocorticoid-free remission, relapse severity, prevention of damage, and patient-reported quality of life outcomes were not significantly different between the groups.
A total of 112 adverse events occurred, with similar type and severity between the groups, including incidence of infections.
The findings were limited by the relatively small sample size, but the results suggest a need for further research to determine mechanisms of disease and explore additional novel treatments for this rare patient population, the researchers wrote in their abstract.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health and Bristol-Myers Squibb.
Plasma Exchange Improves Kidney Function in AAV
Use of therapeutic plasma exchange (PLEX) as an adjunct treatment improved early kidney function in adults with AAV and glomerulonephritis but did not extend beyond 8 weeks, and recovery of kidney function was no different between patients receiving a regular glucocorticoid regimen versus a reduced course, based on a post-hoc analysis of 691 individuals in the international randomized controlled trial called PEXIVAS.
The primary outcomes of change in kidney function based on estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) from baseline over 1 year and the percentage of patients with improvement in eGFR of at least 15 mL/min/1.73 m2 at weeks 12, 26, and 52.
The rate of improved eGFR was significantly greater in the PLEX group, compared with controls, at 2, 4, and 8 weeks. At 4 weeks, significantly more patients in the PLEX group had an increase in eGFR by at least 15 mL/min/1.73 m2, compared with the control group (relative risk [RR], 1.41; P = .008). In addition, improved kidney function within 4 weeks was significantly associated with lower risk of kidney failure within 1 year, regardless of treatment group.
The original PEXIVAS trial was supported by various government institutes and agencies from multiple countries.
Reinforced Vaccine Strategy with Rituximab Improved Antibody Response in AAV
A vaccine strategy consisting of a double dose of 13-valent antipneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13) at day 0 and day 7 followed by a single dose of 23-valent unconjugated pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPV23) at 5 months significantly improved antibody responses against Streptococcus pneumoniae in patients with AAV, compared with standard treatment, based on data from 95 individuals in the multicenter, open-label study called PNEUMOVAS.
Adults with newly diagnosed AAV were randomly assigned to one of three treatment arms: a standard regimen of one dose of PCV13 at day 0 and one dose of PPV23 at month 5 (arm 1); a double dose of PCV13 at day 0 and day 7 with a dose of PPV23 at month 5 (arm 2); or four doses of PCV13 at day 0 and one dose of PPV23 at month 5 (arm 3). These patients received PCV13 within 2 days before or after their first infusion of rituximab.
The primary endpoint was positive antibody response against 12 pneumococcal subtypes common to the PCV13 and PCV23 vaccines at 6 months. At 6 months, the immune response to 0-3, 4-6, 7-9, or 10-12 serotypes was 83.3%, 13.3%, 3.3%, and 0%, respectively, in arm 1; 56.3%, 28.1%, 15.6%, and 0% in arm 2; and 60.6%, 33.3%, 6.1%, and 0% in arm 3.
No severe adverse events related to vaccination were observed in any of the groups; a total of eight AAV flares occurred in six patients (one in arm 1, two in arm 2, and three in arm 3). Local and systemic reactions occurred more frequently with the reinforced dose regimens, but these were mostly grade 1 or 2 local reactions.
The study was supported by the French Ministry of Health.
Some of the best clinical trials of patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody–associated vasculitis (AAV) that were presented at the 21st International Vasculitis Workshop in Barcelona, Spain, included studies addressing relapse after stopping steroids, preventing relapse with abatacept, improving kidney function with plasma exchange, and vaccinating rituximab-treated patients.
Stopping Steroids After Remission in GPA
In the randomized, open-label TAPIR (The Assessment of Prednisone In Remission Trial) study of 159 adults with GPA in remission who had tapered to a prednisone dose of 5 mg/day, those who remained at that dosage had a significantly lower rate of relapse after 6 months than those who tapered to 0 mg/day (4.2% vs 15.5%; P = .227), according to results reported at the meeting.
However, use of a higher dose of prednisone for disease relapse by 6 months was similar for patients who used rituximab at baseline (8.8% with 0 mg/day vs 6.1% with 5 mg/day; P = .667), and the difference in this primary outcome was more pronounced among patients who did not take rituximab at baseline (20.0% with 0 mg/day vs 2.6% with 5 mg/day; P = .023).
A higher percentage of patients taking prednisone 0 mg/day had disease relapses that were considered minor (14.1% and 4.2%; P = .0391). Major relapses occurred in none of the patients taking 5 mg/day and in 1.4% receiving 0 mg/day. About 90% of patients in either treatment arm completed the trial.
The study, funded by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskelatal and Skin Diseases and the National Heart Lung and Blood Institute, was unique in that half of patients randomized in the study were enrolled at community clinics and half were enrolled at Vasculitis Clinical Research Consortium clinical centers.
Abatacept Falls Short for Preventing Relapse in GPA
Adding abatacept to glucocorticoids failed to reduce risk of relapse, worsening disease, or failure to reach remission in adults with relapsing, nonsevere GPA, based on data from a randomized trial of 65 individuals.
In the 20-site, randomized, double-blind ABROGATE (Abatacept for the Treatment of Relapsing, Non-Severe, Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis) study, 34 patients received 125 mg subcutaneous abatacept once a week or a placebo in addition to 30 mg/day of prednisone that was tapered and discontinued after 12 weeks. Patients who were receiving methotrexate, azathioprine, mycophenolate, or leflunomide at baseline continued the medication at a stable dose.
The primary outcome of disease worsening or relapse occurred in 62% of the abatacept group and 68% of the placebo group, and no significant difference in treatment failure rate appeared between the groups. In addition, key secondary endpoints of time to full remission, duration of glucocorticoid-free remission, relapse severity, prevention of damage, and patient-reported quality of life outcomes were not significantly different between the groups.
A total of 112 adverse events occurred, with similar type and severity between the groups, including incidence of infections.
The findings were limited by the relatively small sample size, but the results suggest a need for further research to determine mechanisms of disease and explore additional novel treatments for this rare patient population, the researchers wrote in their abstract.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health and Bristol-Myers Squibb.
Plasma Exchange Improves Kidney Function in AAV
Use of therapeutic plasma exchange (PLEX) as an adjunct treatment improved early kidney function in adults with AAV and glomerulonephritis but did not extend beyond 8 weeks, and recovery of kidney function was no different between patients receiving a regular glucocorticoid regimen versus a reduced course, based on a post-hoc analysis of 691 individuals in the international randomized controlled trial called PEXIVAS.
The primary outcomes of change in kidney function based on estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) from baseline over 1 year and the percentage of patients with improvement in eGFR of at least 15 mL/min/1.73 m2 at weeks 12, 26, and 52.
The rate of improved eGFR was significantly greater in the PLEX group, compared with controls, at 2, 4, and 8 weeks. At 4 weeks, significantly more patients in the PLEX group had an increase in eGFR by at least 15 mL/min/1.73 m2, compared with the control group (relative risk [RR], 1.41; P = .008). In addition, improved kidney function within 4 weeks was significantly associated with lower risk of kidney failure within 1 year, regardless of treatment group.
The original PEXIVAS trial was supported by various government institutes and agencies from multiple countries.
Reinforced Vaccine Strategy with Rituximab Improved Antibody Response in AAV
A vaccine strategy consisting of a double dose of 13-valent antipneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13) at day 0 and day 7 followed by a single dose of 23-valent unconjugated pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPV23) at 5 months significantly improved antibody responses against Streptococcus pneumoniae in patients with AAV, compared with standard treatment, based on data from 95 individuals in the multicenter, open-label study called PNEUMOVAS.
Adults with newly diagnosed AAV were randomly assigned to one of three treatment arms: a standard regimen of one dose of PCV13 at day 0 and one dose of PPV23 at month 5 (arm 1); a double dose of PCV13 at day 0 and day 7 with a dose of PPV23 at month 5 (arm 2); or four doses of PCV13 at day 0 and one dose of PPV23 at month 5 (arm 3). These patients received PCV13 within 2 days before or after their first infusion of rituximab.
The primary endpoint was positive antibody response against 12 pneumococcal subtypes common to the PCV13 and PCV23 vaccines at 6 months. At 6 months, the immune response to 0-3, 4-6, 7-9, or 10-12 serotypes was 83.3%, 13.3%, 3.3%, and 0%, respectively, in arm 1; 56.3%, 28.1%, 15.6%, and 0% in arm 2; and 60.6%, 33.3%, 6.1%, and 0% in arm 3.
No severe adverse events related to vaccination were observed in any of the groups; a total of eight AAV flares occurred in six patients (one in arm 1, two in arm 2, and three in arm 3). Local and systemic reactions occurred more frequently with the reinforced dose regimens, but these were mostly grade 1 or 2 local reactions.
The study was supported by the French Ministry of Health.
Some of the best clinical trials of patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody–associated vasculitis (AAV) that were presented at the 21st International Vasculitis Workshop in Barcelona, Spain, included studies addressing relapse after stopping steroids, preventing relapse with abatacept, improving kidney function with plasma exchange, and vaccinating rituximab-treated patients.
Stopping Steroids After Remission in GPA
In the randomized, open-label TAPIR (The Assessment of Prednisone In Remission Trial) study of 159 adults with GPA in remission who had tapered to a prednisone dose of 5 mg/day, those who remained at that dosage had a significantly lower rate of relapse after 6 months than those who tapered to 0 mg/day (4.2% vs 15.5%; P = .227), according to results reported at the meeting.
However, use of a higher dose of prednisone for disease relapse by 6 months was similar for patients who used rituximab at baseline (8.8% with 0 mg/day vs 6.1% with 5 mg/day; P = .667), and the difference in this primary outcome was more pronounced among patients who did not take rituximab at baseline (20.0% with 0 mg/day vs 2.6% with 5 mg/day; P = .023).
A higher percentage of patients taking prednisone 0 mg/day had disease relapses that were considered minor (14.1% and 4.2%; P = .0391). Major relapses occurred in none of the patients taking 5 mg/day and in 1.4% receiving 0 mg/day. About 90% of patients in either treatment arm completed the trial.
The study, funded by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskelatal and Skin Diseases and the National Heart Lung and Blood Institute, was unique in that half of patients randomized in the study were enrolled at community clinics and half were enrolled at Vasculitis Clinical Research Consortium clinical centers.
Abatacept Falls Short for Preventing Relapse in GPA
Adding abatacept to glucocorticoids failed to reduce risk of relapse, worsening disease, or failure to reach remission in adults with relapsing, nonsevere GPA, based on data from a randomized trial of 65 individuals.
In the 20-site, randomized, double-blind ABROGATE (Abatacept for the Treatment of Relapsing, Non-Severe, Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis) study, 34 patients received 125 mg subcutaneous abatacept once a week or a placebo in addition to 30 mg/day of prednisone that was tapered and discontinued after 12 weeks. Patients who were receiving methotrexate, azathioprine, mycophenolate, or leflunomide at baseline continued the medication at a stable dose.
The primary outcome of disease worsening or relapse occurred in 62% of the abatacept group and 68% of the placebo group, and no significant difference in treatment failure rate appeared between the groups. In addition, key secondary endpoints of time to full remission, duration of glucocorticoid-free remission, relapse severity, prevention of damage, and patient-reported quality of life outcomes were not significantly different between the groups.
A total of 112 adverse events occurred, with similar type and severity between the groups, including incidence of infections.
The findings were limited by the relatively small sample size, but the results suggest a need for further research to determine mechanisms of disease and explore additional novel treatments for this rare patient population, the researchers wrote in their abstract.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health and Bristol-Myers Squibb.
Plasma Exchange Improves Kidney Function in AAV
Use of therapeutic plasma exchange (PLEX) as an adjunct treatment improved early kidney function in adults with AAV and glomerulonephritis but did not extend beyond 8 weeks, and recovery of kidney function was no different between patients receiving a regular glucocorticoid regimen versus a reduced course, based on a post-hoc analysis of 691 individuals in the international randomized controlled trial called PEXIVAS.
The primary outcomes of change in kidney function based on estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) from baseline over 1 year and the percentage of patients with improvement in eGFR of at least 15 mL/min/1.73 m2 at weeks 12, 26, and 52.
The rate of improved eGFR was significantly greater in the PLEX group, compared with controls, at 2, 4, and 8 weeks. At 4 weeks, significantly more patients in the PLEX group had an increase in eGFR by at least 15 mL/min/1.73 m2, compared with the control group (relative risk [RR], 1.41; P = .008). In addition, improved kidney function within 4 weeks was significantly associated with lower risk of kidney failure within 1 year, regardless of treatment group.
The original PEXIVAS trial was supported by various government institutes and agencies from multiple countries.
Reinforced Vaccine Strategy with Rituximab Improved Antibody Response in AAV
A vaccine strategy consisting of a double dose of 13-valent antipneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13) at day 0 and day 7 followed by a single dose of 23-valent unconjugated pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPV23) at 5 months significantly improved antibody responses against Streptococcus pneumoniae in patients with AAV, compared with standard treatment, based on data from 95 individuals in the multicenter, open-label study called PNEUMOVAS.
Adults with newly diagnosed AAV were randomly assigned to one of three treatment arms: a standard regimen of one dose of PCV13 at day 0 and one dose of PPV23 at month 5 (arm 1); a double dose of PCV13 at day 0 and day 7 with a dose of PPV23 at month 5 (arm 2); or four doses of PCV13 at day 0 and one dose of PPV23 at month 5 (arm 3). These patients received PCV13 within 2 days before or after their first infusion of rituximab.
The primary endpoint was positive antibody response against 12 pneumococcal subtypes common to the PCV13 and PCV23 vaccines at 6 months. At 6 months, the immune response to 0-3, 4-6, 7-9, or 10-12 serotypes was 83.3%, 13.3%, 3.3%, and 0%, respectively, in arm 1; 56.3%, 28.1%, 15.6%, and 0% in arm 2; and 60.6%, 33.3%, 6.1%, and 0% in arm 3.
No severe adverse events related to vaccination were observed in any of the groups; a total of eight AAV flares occurred in six patients (one in arm 1, two in arm 2, and three in arm 3). Local and systemic reactions occurred more frequently with the reinforced dose regimens, but these were mostly grade 1 or 2 local reactions.
The study was supported by the French Ministry of Health.