User login
ADHD Tied to Risk for Lewy Body Disease, Dementia, MCI
, results of a new study showed.
“Determining whether there is an association between ADHD and subsequent conversion to a specific type of dementia is important. This information could generate opportunities for prevention and early treatment, as well as initiate research into the pathophysiological processes involved in understanding the process of cognitive decline,” the researchers, led by Ángel Golimstok, MD, of Hospital Italiano, Buenos Aires, Argentina, wrote.
The findings were published online in The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry.
Seeking Confirmation
The researchers first identified a link between DLB and ADHD in 2011. Since then, there have been eight additional studies from other groups also showing a possible link between ADHD and DLB.
To confirm the relationship, the researchers recruited 270 individuals between the ages of 45 and 70 years between 2007 and 2012. Of these, 161 had ADHD, and 109 were healthy controls.
Participants with ADHD met the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition, text revision criteria for a diagnosis in the past and had a chronic course of ADHD symptoms from adolescence to adulthood that caused mild to severe impairment.
Investigators excluded participants who had been taking ADHD medications for 6 months or more, those with MCI at study initiation, and those with other comorbid psychiatric disorders.
At baseline, all participants received a physical exam, an MRI, and a neuropsychological exam to test for any type of dementia-related impairment.
Study participants were followed for an average of 12 years. A total of 27 individuals with ADHD developed dementia versus four patients in the control group (17% vs 4%, respectively), and 19 of those also had DLB (P = .002 for both).
Of those who developed any type of dementia, 87% were from the ADHD group. The most frequent type of dementia was DLB, 95% of which occurred in the ADHD group. Overall, DLB represented 70% of the dementia cases among participants with ADHD.
A total of 108 participants with ADHD were subsequently diagnosed with naMCI versus 19 healthy controls (67% vs 17%; P < .001).
“Although this pattern of deficits is reasonably expected in early DLB, these results should be interpreted with caution because they may be related to the overlap of symptoms and cognitive deficits between ADHD and naMCI, which may lead to an overestimation of the degenerative phenomenon. Thus, our cases of naMCI could correspond to the natural aging of ADHD patients and not to pathological deterioration,” the authors wrote.
The researchers pointed out that the sample of patients with ADHD originally sought evaluation because of a cognitive complaint or their own motivation. Therefore, the study results are not generalizable to all patients with ADHD. Another limitation was the relatively small number of patients included in the sample.
There was no reported source of funding, and there were no relevant disclosures reported.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, results of a new study showed.
“Determining whether there is an association between ADHD and subsequent conversion to a specific type of dementia is important. This information could generate opportunities for prevention and early treatment, as well as initiate research into the pathophysiological processes involved in understanding the process of cognitive decline,” the researchers, led by Ángel Golimstok, MD, of Hospital Italiano, Buenos Aires, Argentina, wrote.
The findings were published online in The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry.
Seeking Confirmation
The researchers first identified a link between DLB and ADHD in 2011. Since then, there have been eight additional studies from other groups also showing a possible link between ADHD and DLB.
To confirm the relationship, the researchers recruited 270 individuals between the ages of 45 and 70 years between 2007 and 2012. Of these, 161 had ADHD, and 109 were healthy controls.
Participants with ADHD met the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition, text revision criteria for a diagnosis in the past and had a chronic course of ADHD symptoms from adolescence to adulthood that caused mild to severe impairment.
Investigators excluded participants who had been taking ADHD medications for 6 months or more, those with MCI at study initiation, and those with other comorbid psychiatric disorders.
At baseline, all participants received a physical exam, an MRI, and a neuropsychological exam to test for any type of dementia-related impairment.
Study participants were followed for an average of 12 years. A total of 27 individuals with ADHD developed dementia versus four patients in the control group (17% vs 4%, respectively), and 19 of those also had DLB (P = .002 for both).
Of those who developed any type of dementia, 87% were from the ADHD group. The most frequent type of dementia was DLB, 95% of which occurred in the ADHD group. Overall, DLB represented 70% of the dementia cases among participants with ADHD.
A total of 108 participants with ADHD were subsequently diagnosed with naMCI versus 19 healthy controls (67% vs 17%; P < .001).
“Although this pattern of deficits is reasonably expected in early DLB, these results should be interpreted with caution because they may be related to the overlap of symptoms and cognitive deficits between ADHD and naMCI, which may lead to an overestimation of the degenerative phenomenon. Thus, our cases of naMCI could correspond to the natural aging of ADHD patients and not to pathological deterioration,” the authors wrote.
The researchers pointed out that the sample of patients with ADHD originally sought evaluation because of a cognitive complaint or their own motivation. Therefore, the study results are not generalizable to all patients with ADHD. Another limitation was the relatively small number of patients included in the sample.
There was no reported source of funding, and there were no relevant disclosures reported.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, results of a new study showed.
“Determining whether there is an association between ADHD and subsequent conversion to a specific type of dementia is important. This information could generate opportunities for prevention and early treatment, as well as initiate research into the pathophysiological processes involved in understanding the process of cognitive decline,” the researchers, led by Ángel Golimstok, MD, of Hospital Italiano, Buenos Aires, Argentina, wrote.
The findings were published online in The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry.
Seeking Confirmation
The researchers first identified a link between DLB and ADHD in 2011. Since then, there have been eight additional studies from other groups also showing a possible link between ADHD and DLB.
To confirm the relationship, the researchers recruited 270 individuals between the ages of 45 and 70 years between 2007 and 2012. Of these, 161 had ADHD, and 109 were healthy controls.
Participants with ADHD met the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition, text revision criteria for a diagnosis in the past and had a chronic course of ADHD symptoms from adolescence to adulthood that caused mild to severe impairment.
Investigators excluded participants who had been taking ADHD medications for 6 months or more, those with MCI at study initiation, and those with other comorbid psychiatric disorders.
At baseline, all participants received a physical exam, an MRI, and a neuropsychological exam to test for any type of dementia-related impairment.
Study participants were followed for an average of 12 years. A total of 27 individuals with ADHD developed dementia versus four patients in the control group (17% vs 4%, respectively), and 19 of those also had DLB (P = .002 for both).
Of those who developed any type of dementia, 87% were from the ADHD group. The most frequent type of dementia was DLB, 95% of which occurred in the ADHD group. Overall, DLB represented 70% of the dementia cases among participants with ADHD.
A total of 108 participants with ADHD were subsequently diagnosed with naMCI versus 19 healthy controls (67% vs 17%; P < .001).
“Although this pattern of deficits is reasonably expected in early DLB, these results should be interpreted with caution because they may be related to the overlap of symptoms and cognitive deficits between ADHD and naMCI, which may lead to an overestimation of the degenerative phenomenon. Thus, our cases of naMCI could correspond to the natural aging of ADHD patients and not to pathological deterioration,” the authors wrote.
The researchers pointed out that the sample of patients with ADHD originally sought evaluation because of a cognitive complaint or their own motivation. Therefore, the study results are not generalizable to all patients with ADHD. Another limitation was the relatively small number of patients included in the sample.
There was no reported source of funding, and there were no relevant disclosures reported.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF GERIATRIC PSYCHIATRY
Proton Pump Inhibitors Tied to Migraine, Other Severe Headache Types
, new research showed.
Using data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), investigators conducted a cross-sectional analysis and found all types of acid-suppression therapy were associated with an increased risk for severe headache including migraine but that PPIs conferred the greatest risk.
“It’s important to note that many people do need acid-reducing medications to manage acid reflux or other conditions, and people with migraine or severe headache who are taking these drugs or supplements should talk with their doctors about whether they should continue,” lead author Margaret Slavin, PhD, of the University of Maryland in College Park, said in a press release.
The findings were published online in Neurology Clinical Practice.
New Look at Old Data
Previous research has shown that headache is listed among the most common adverse reactions in adults taking PPIs and histamine receptor agonists (H2RAs), which include cimetidine, famotidine, and nizatidine.
Other large studies of health databases have shown increased headache risk within a week of PPI exposure.
To compare the risk from PPIs versus H2RAs and other generics, researchers analyzed data from the NHANES for those who used PPIs, H2RAs, and generic antacids to learn more about the potential link between acid-suppression therapy and headache.
They used survey data from 1999 to 2004, the only years the NHANES included a question about migraine and other headache during the past 3 months.
Investigators analyzed data for 11,800 participants aged 20 years or older who used prescription drugs, over-the-counter medications, and nutritional supplements during the past month.
Participants who used acid-suppressing medications had an increased risk for migraine or severe headache versus those who did not use these agents. Investigators found PPIs were tied to a 70% increased risk, while H2RAs and antacids were associated with 40% and 30% higher risks, respectively. Use of any type of acid-suppression therapy was tied to a 47% increased risk for severe headache.
Magnesium a Risk Factor?
While magnesium supplements are sometimes prescribed as a “natural” headache prevention therapy to prevent migraine and other headache types, the investigators noted they were surprised to find individuals taking H2RAs who met the dietary reference intake for magnesium had a nearly threefold increased risk for migraine or severe headache (odds ratio, 2.80; 95% CI, 1.02-1.45; P = .025).
However, there was no association between magnesium and the other acid-reducing medications.
The study’s limitations included the use of a single question to identify migraine or severe headache, which may have resulted in some misclassification of the outcome. The authors also pointed out that dietary and drug-intake data may be subject to recall bias.
“These results suggest that there is a need for more intentionally designed prospective work to inform the extent to which associations between migraine and acid-suppression therapy are merely detecting comorbidities or to what extent migraine is an adverse event associated with the medications,” the authors wrote.
There was no targeted funding. Disclosures are noted in the original article.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research showed.
Using data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), investigators conducted a cross-sectional analysis and found all types of acid-suppression therapy were associated with an increased risk for severe headache including migraine but that PPIs conferred the greatest risk.
“It’s important to note that many people do need acid-reducing medications to manage acid reflux or other conditions, and people with migraine or severe headache who are taking these drugs or supplements should talk with their doctors about whether they should continue,” lead author Margaret Slavin, PhD, of the University of Maryland in College Park, said in a press release.
The findings were published online in Neurology Clinical Practice.
New Look at Old Data
Previous research has shown that headache is listed among the most common adverse reactions in adults taking PPIs and histamine receptor agonists (H2RAs), which include cimetidine, famotidine, and nizatidine.
Other large studies of health databases have shown increased headache risk within a week of PPI exposure.
To compare the risk from PPIs versus H2RAs and other generics, researchers analyzed data from the NHANES for those who used PPIs, H2RAs, and generic antacids to learn more about the potential link between acid-suppression therapy and headache.
They used survey data from 1999 to 2004, the only years the NHANES included a question about migraine and other headache during the past 3 months.
Investigators analyzed data for 11,800 participants aged 20 years or older who used prescription drugs, over-the-counter medications, and nutritional supplements during the past month.
Participants who used acid-suppressing medications had an increased risk for migraine or severe headache versus those who did not use these agents. Investigators found PPIs were tied to a 70% increased risk, while H2RAs and antacids were associated with 40% and 30% higher risks, respectively. Use of any type of acid-suppression therapy was tied to a 47% increased risk for severe headache.
Magnesium a Risk Factor?
While magnesium supplements are sometimes prescribed as a “natural” headache prevention therapy to prevent migraine and other headache types, the investigators noted they were surprised to find individuals taking H2RAs who met the dietary reference intake for magnesium had a nearly threefold increased risk for migraine or severe headache (odds ratio, 2.80; 95% CI, 1.02-1.45; P = .025).
However, there was no association between magnesium and the other acid-reducing medications.
The study’s limitations included the use of a single question to identify migraine or severe headache, which may have resulted in some misclassification of the outcome. The authors also pointed out that dietary and drug-intake data may be subject to recall bias.
“These results suggest that there is a need for more intentionally designed prospective work to inform the extent to which associations between migraine and acid-suppression therapy are merely detecting comorbidities or to what extent migraine is an adverse event associated with the medications,” the authors wrote.
There was no targeted funding. Disclosures are noted in the original article.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research showed.
Using data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), investigators conducted a cross-sectional analysis and found all types of acid-suppression therapy were associated with an increased risk for severe headache including migraine but that PPIs conferred the greatest risk.
“It’s important to note that many people do need acid-reducing medications to manage acid reflux or other conditions, and people with migraine or severe headache who are taking these drugs or supplements should talk with their doctors about whether they should continue,” lead author Margaret Slavin, PhD, of the University of Maryland in College Park, said in a press release.
The findings were published online in Neurology Clinical Practice.
New Look at Old Data
Previous research has shown that headache is listed among the most common adverse reactions in adults taking PPIs and histamine receptor agonists (H2RAs), which include cimetidine, famotidine, and nizatidine.
Other large studies of health databases have shown increased headache risk within a week of PPI exposure.
To compare the risk from PPIs versus H2RAs and other generics, researchers analyzed data from the NHANES for those who used PPIs, H2RAs, and generic antacids to learn more about the potential link between acid-suppression therapy and headache.
They used survey data from 1999 to 2004, the only years the NHANES included a question about migraine and other headache during the past 3 months.
Investigators analyzed data for 11,800 participants aged 20 years or older who used prescription drugs, over-the-counter medications, and nutritional supplements during the past month.
Participants who used acid-suppressing medications had an increased risk for migraine or severe headache versus those who did not use these agents. Investigators found PPIs were tied to a 70% increased risk, while H2RAs and antacids were associated with 40% and 30% higher risks, respectively. Use of any type of acid-suppression therapy was tied to a 47% increased risk for severe headache.
Magnesium a Risk Factor?
While magnesium supplements are sometimes prescribed as a “natural” headache prevention therapy to prevent migraine and other headache types, the investigators noted they were surprised to find individuals taking H2RAs who met the dietary reference intake for magnesium had a nearly threefold increased risk for migraine or severe headache (odds ratio, 2.80; 95% CI, 1.02-1.45; P = .025).
However, there was no association between magnesium and the other acid-reducing medications.
The study’s limitations included the use of a single question to identify migraine or severe headache, which may have resulted in some misclassification of the outcome. The authors also pointed out that dietary and drug-intake data may be subject to recall bias.
“These results suggest that there is a need for more intentionally designed prospective work to inform the extent to which associations between migraine and acid-suppression therapy are merely detecting comorbidities or to what extent migraine is an adverse event associated with the medications,” the authors wrote.
There was no targeted funding. Disclosures are noted in the original article.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NEUROLOGY CLINICAL PRACTICE
New HIV Infections After Vampire Facials at Unlicensed Spa
At least three clients of an unlicensed spa in New Mexico contracted HIV after receiving platelet-rich plasma (PRP) microneedling facials, according to an investigation by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
The investigation, spanning 5 years with parts of it still ongoing, has resulted in the closure of the spa and is raising questions about public safety in cosmetic clinics.
Though transmission of HIV by unsterile injection practices is a known risk, this is the first time it has been linked to cosmetic injection services, said Anna Stadelman-Behar, PhD, MPH, of the CDC’s Epidemic Intelligence Service.
Sometimes called a vampire facial, the PRP treatment involves taking a patient’s own blood and separating it in a centrifuge. The portion containing a high concentration of platelets is then reinjected with a syringe or microneedling device.
“The idea is that when you inject this concentrated amount of platelets, the growth factors that the platelets release help to stimulate the regenerative nature of that area,” said Anthony Rossi, MD, professor of dermatology at Weill Cornell Medical College in New York, and attending dermatologist at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center.
The infections under investigation first came to light when a woman was diagnosed with HIV with no known risk factors for the disease other than exposure to microneedling facials at a cosmetic spa.
The New Mexico Department of Health and the CDC launched an investigation of the spa and discovered a litany of “gross violations of infection control practices,” said Dr. Stadelman-Behar.
Infection-Control Violations
At the spa in New Mexico, investigators found:
- On a kitchen counter, a centrifuge, a heating dry bath, and a rack of unlabeled tubes containing blood
- In a refrigerator, unlabeled tubes of blood and medical injectables including botox and lidocaine stored along with food
- Unwrapped syringes in drawers, on counters, and discarded in regular trash cans
- No autoclave for steam sterilization on the premises
- Only surface cleaning for procedure equipment with ammonium chloride disinfecting spray and benzalkonium chloride disinfecting wipes after each client visit
- Disposable electric desiccator tips cleaned only by alcohol immersion to be reused
The spa’s owner operated without appropriate licenses at multiple locations and did not have an appointment scheduling system that stored client contact information.
Investigators contacted as many people as they could find and launched a large-scale community outreach effort to find more.
In total, four clients and one intimate partner of a client were diagnosed with HIV during the investigation, but one client and her partner were determined to likely have been infected before the spa visit.
It is not clear whether the infections were due to unlabeled contaminated blood products being given to the wrong client or contamination on shared needles. Investigators did not have the authority to collect specimens during their site visit that would have allowed them to study that.
“We can’t definitively say what the route of contamination was,” noted Dr. Stadelman-Behar.
Anne Chapas, MD, a board-certified dermatologist, and instructor at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York, added that just because a procedure is cosmetic, that doesn’t mean it is not medical. “Personally, I feel it should only be done by medical practitioners who understand the risks.”
A Medical Procedure
PRP microneedling has been used extensively in orthopedic surgery to promote joint regeneration. For the past 10 years, it has also been used in dermatology to treat hair loss from alopecia, to augment wound healing, and cosmetically to reduce facial wrinkles.
It is generally done in a doctor’s office or medical spa, and the procedure takes about half an hour.
Dr. Stadelman-Behar said that this ongoing investigation highlights the importance of front-line healthcare workers using their clinical expertise to help identify potential new routes of transmission for infections. “It was provider-led intuition that sparked this investigation, so it’s important to let the department of health know if there is something amiss with any of the exposures that the patient might have had,” she said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
At least three clients of an unlicensed spa in New Mexico contracted HIV after receiving platelet-rich plasma (PRP) microneedling facials, according to an investigation by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
The investigation, spanning 5 years with parts of it still ongoing, has resulted in the closure of the spa and is raising questions about public safety in cosmetic clinics.
Though transmission of HIV by unsterile injection practices is a known risk, this is the first time it has been linked to cosmetic injection services, said Anna Stadelman-Behar, PhD, MPH, of the CDC’s Epidemic Intelligence Service.
Sometimes called a vampire facial, the PRP treatment involves taking a patient’s own blood and separating it in a centrifuge. The portion containing a high concentration of platelets is then reinjected with a syringe or microneedling device.
“The idea is that when you inject this concentrated amount of platelets, the growth factors that the platelets release help to stimulate the regenerative nature of that area,” said Anthony Rossi, MD, professor of dermatology at Weill Cornell Medical College in New York, and attending dermatologist at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center.
The infections under investigation first came to light when a woman was diagnosed with HIV with no known risk factors for the disease other than exposure to microneedling facials at a cosmetic spa.
The New Mexico Department of Health and the CDC launched an investigation of the spa and discovered a litany of “gross violations of infection control practices,” said Dr. Stadelman-Behar.
Infection-Control Violations
At the spa in New Mexico, investigators found:
- On a kitchen counter, a centrifuge, a heating dry bath, and a rack of unlabeled tubes containing blood
- In a refrigerator, unlabeled tubes of blood and medical injectables including botox and lidocaine stored along with food
- Unwrapped syringes in drawers, on counters, and discarded in regular trash cans
- No autoclave for steam sterilization on the premises
- Only surface cleaning for procedure equipment with ammonium chloride disinfecting spray and benzalkonium chloride disinfecting wipes after each client visit
- Disposable electric desiccator tips cleaned only by alcohol immersion to be reused
The spa’s owner operated without appropriate licenses at multiple locations and did not have an appointment scheduling system that stored client contact information.
Investigators contacted as many people as they could find and launched a large-scale community outreach effort to find more.
In total, four clients and one intimate partner of a client were diagnosed with HIV during the investigation, but one client and her partner were determined to likely have been infected before the spa visit.
It is not clear whether the infections were due to unlabeled contaminated blood products being given to the wrong client or contamination on shared needles. Investigators did not have the authority to collect specimens during their site visit that would have allowed them to study that.
“We can’t definitively say what the route of contamination was,” noted Dr. Stadelman-Behar.
Anne Chapas, MD, a board-certified dermatologist, and instructor at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York, added that just because a procedure is cosmetic, that doesn’t mean it is not medical. “Personally, I feel it should only be done by medical practitioners who understand the risks.”
A Medical Procedure
PRP microneedling has been used extensively in orthopedic surgery to promote joint regeneration. For the past 10 years, it has also been used in dermatology to treat hair loss from alopecia, to augment wound healing, and cosmetically to reduce facial wrinkles.
It is generally done in a doctor’s office or medical spa, and the procedure takes about half an hour.
Dr. Stadelman-Behar said that this ongoing investigation highlights the importance of front-line healthcare workers using their clinical expertise to help identify potential new routes of transmission for infections. “It was provider-led intuition that sparked this investigation, so it’s important to let the department of health know if there is something amiss with any of the exposures that the patient might have had,” she said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
At least three clients of an unlicensed spa in New Mexico contracted HIV after receiving platelet-rich plasma (PRP) microneedling facials, according to an investigation by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
The investigation, spanning 5 years with parts of it still ongoing, has resulted in the closure of the spa and is raising questions about public safety in cosmetic clinics.
Though transmission of HIV by unsterile injection practices is a known risk, this is the first time it has been linked to cosmetic injection services, said Anna Stadelman-Behar, PhD, MPH, of the CDC’s Epidemic Intelligence Service.
Sometimes called a vampire facial, the PRP treatment involves taking a patient’s own blood and separating it in a centrifuge. The portion containing a high concentration of platelets is then reinjected with a syringe or microneedling device.
“The idea is that when you inject this concentrated amount of platelets, the growth factors that the platelets release help to stimulate the regenerative nature of that area,” said Anthony Rossi, MD, professor of dermatology at Weill Cornell Medical College in New York, and attending dermatologist at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center.
The infections under investigation first came to light when a woman was diagnosed with HIV with no known risk factors for the disease other than exposure to microneedling facials at a cosmetic spa.
The New Mexico Department of Health and the CDC launched an investigation of the spa and discovered a litany of “gross violations of infection control practices,” said Dr. Stadelman-Behar.
Infection-Control Violations
At the spa in New Mexico, investigators found:
- On a kitchen counter, a centrifuge, a heating dry bath, and a rack of unlabeled tubes containing blood
- In a refrigerator, unlabeled tubes of blood and medical injectables including botox and lidocaine stored along with food
- Unwrapped syringes in drawers, on counters, and discarded in regular trash cans
- No autoclave for steam sterilization on the premises
- Only surface cleaning for procedure equipment with ammonium chloride disinfecting spray and benzalkonium chloride disinfecting wipes after each client visit
- Disposable electric desiccator tips cleaned only by alcohol immersion to be reused
The spa’s owner operated without appropriate licenses at multiple locations and did not have an appointment scheduling system that stored client contact information.
Investigators contacted as many people as they could find and launched a large-scale community outreach effort to find more.
In total, four clients and one intimate partner of a client were diagnosed with HIV during the investigation, but one client and her partner were determined to likely have been infected before the spa visit.
It is not clear whether the infections were due to unlabeled contaminated blood products being given to the wrong client or contamination on shared needles. Investigators did not have the authority to collect specimens during their site visit that would have allowed them to study that.
“We can’t definitively say what the route of contamination was,” noted Dr. Stadelman-Behar.
Anne Chapas, MD, a board-certified dermatologist, and instructor at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York, added that just because a procedure is cosmetic, that doesn’t mean it is not medical. “Personally, I feel it should only be done by medical practitioners who understand the risks.”
A Medical Procedure
PRP microneedling has been used extensively in orthopedic surgery to promote joint regeneration. For the past 10 years, it has also been used in dermatology to treat hair loss from alopecia, to augment wound healing, and cosmetically to reduce facial wrinkles.
It is generally done in a doctor’s office or medical spa, and the procedure takes about half an hour.
Dr. Stadelman-Behar said that this ongoing investigation highlights the importance of front-line healthcare workers using their clinical expertise to help identify potential new routes of transmission for infections. “It was provider-led intuition that sparked this investigation, so it’s important to let the department of health know if there is something amiss with any of the exposures that the patient might have had,” she said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Terminal Cancer: What Matters to Patients and Caregivers
New research found that patients and caregivers both tend to prioritize symptom control over life extension but often preferring a balance. Patients and caregivers, however, are less aligned on decisions about cost containment, with patients more likely to prioritize cost containment.
“Our research has revealed that patients and caregivers generally share similar end-of-life goals,” with a “notable exception” when it comes to costs, first author Semra Ozdemir, PhD, with the Lien Centre for Palliative Care, Duke-NUS Medical School, Singapore, told this news organization.
However, when patients and caregivers have a better understanding of the patient’s prognosis, both may be more inclined to avoid costly life-extending treatments and prioritize symptom management.
In other words, the survey suggests that “knowing the prognosis helps patients and their families set realistic expectations for care and adequately prepare for end-of-life decisions,” said Dr. Ozdemir.
This study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Patients with advanced cancer often face difficult decisions: Do they opt for treatments that may — or may not — extend life or do they focus more on symptom control?
Family caregivers, who also play an important role in this decision-making process, may have different care goals. Some research suggests that caregivers tend to prioritize treatments that could extend life, whereas patients prioritize symptom management, but it’s less clear how these priorities may change over time and how patients and caregivers may influence each other.
In the current study, the researchers examined goals of care among patients with stage IV solid tumors and caregivers during the last 2 years of life, focusing on life extension vs symptom management and cost containment, as well as how these goals changed over time.
The survey included 210 patient-caregiver pairs, recruited from outpatient clinics at two major cancer centers in Singapore. Patients had a mean age of 63 years, and about half were men. The caregivers had a mean age of 49 years, and almost two third (63%) were women.
Overall, 34% patients and 29% caregivers prioritized symptom management over life extension, whereas 24% patients and 19% caregivers prioritized life extension. Most patients and caregivers preferred balancing the two, with 34%-47% patients and 37%-69% caregivers supporting this approach.
When balancing cost and treatment decisions, however, patients were more likely to prioritize containing costs — 28% vs 17% for caregivers — over extending life — 26% of patients vs 35% of caregivers.
Cost containment tended to be more of a priority for older patients, those with a higher symptom burden, and those with less family caregiver support. For caregivers, cost containment was more of a priority for those who reported that caregiving had a big impact on their finances, those with worse self-esteem related to their caregiving abilities, as well as those caring for older patients.
To better align cost containment priorities between patients and caregivers, it’s essential for families to engage in open and thorough discussions about the allocation of resources, Dr. Ozdemir said.
Although “patients, families, and physicians often avoid discussions about prognosis,” such conversations are essential for setting realistic expectations for care and adequately preparing for end-of-life decisions, Dr. Ozdemir told this news organization.
“These conversations should aim to balance competing interests and create care plans that are mutually acceptable to both patients and caregivers,” she said, adding that “this approach will help in minimizing any potential conflicts and ensure that both parties feel respected and understood in their decision-making process.”
Managing Unrealistic Expectations
As patients approached the end of life, neither patients nor caregivers shifted their priorities from life extension to symptom management.
This finding raises concerns because it suggests that many patients hold unrealistic expectations regarding their care and “underscores the need for continuous dialogue and reassessment of care goals throughout the progression of illness,” Dr. Ozdemir said.
“This stability in preferences over time suggests that initial care decisions are deeply ingrained or that there may be a lack of ongoing communication about evolving care needs and possibilities as conditions change,” Ozdemir said.
Yet, it can be hard to define what unrealistic expectations mean, said Olivia Seecof, MD, who wasn’t involved in the study.
“I think people are hopeful that a devastating diagnosis won’t lead to the end of their life and that there will be a treatment or something that will change [their prognosis], and they’ll get better,” said Dr. Seecof, palliative care expert with the Supportive Oncology Program at NYU Langone Health’s Perlmutter Cancer Center in New York City.
Giving patients and caregivers a realistic understanding of the prognosis is important, but “there’s more to it than just telling the patient their diagnosis,” she said.
“We have to plan for end of life, what it can look like,” said Dr. Seecof, adding that “often we don’t do a very good job of talking about that early on in an illness course.”
Overall, though, Dr. Seecof stressed that no two patients or situations are the same, and it’s important to understand what’s important in each scenario. End-of-life care requires “an individual approach because every patient is different, even if they have the same diagnosis as someone else,” she said.
This work was supported by funding from the Singapore Millennium Foundation and the Lien Centre for Palliative Care. Dr. Ozdemir and Dr. Seecof had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
New research found that patients and caregivers both tend to prioritize symptom control over life extension but often preferring a balance. Patients and caregivers, however, are less aligned on decisions about cost containment, with patients more likely to prioritize cost containment.
“Our research has revealed that patients and caregivers generally share similar end-of-life goals,” with a “notable exception” when it comes to costs, first author Semra Ozdemir, PhD, with the Lien Centre for Palliative Care, Duke-NUS Medical School, Singapore, told this news organization.
However, when patients and caregivers have a better understanding of the patient’s prognosis, both may be more inclined to avoid costly life-extending treatments and prioritize symptom management.
In other words, the survey suggests that “knowing the prognosis helps patients and their families set realistic expectations for care and adequately prepare for end-of-life decisions,” said Dr. Ozdemir.
This study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Patients with advanced cancer often face difficult decisions: Do they opt for treatments that may — or may not — extend life or do they focus more on symptom control?
Family caregivers, who also play an important role in this decision-making process, may have different care goals. Some research suggests that caregivers tend to prioritize treatments that could extend life, whereas patients prioritize symptom management, but it’s less clear how these priorities may change over time and how patients and caregivers may influence each other.
In the current study, the researchers examined goals of care among patients with stage IV solid tumors and caregivers during the last 2 years of life, focusing on life extension vs symptom management and cost containment, as well as how these goals changed over time.
The survey included 210 patient-caregiver pairs, recruited from outpatient clinics at two major cancer centers in Singapore. Patients had a mean age of 63 years, and about half were men. The caregivers had a mean age of 49 years, and almost two third (63%) were women.
Overall, 34% patients and 29% caregivers prioritized symptom management over life extension, whereas 24% patients and 19% caregivers prioritized life extension. Most patients and caregivers preferred balancing the two, with 34%-47% patients and 37%-69% caregivers supporting this approach.
When balancing cost and treatment decisions, however, patients were more likely to prioritize containing costs — 28% vs 17% for caregivers — over extending life — 26% of patients vs 35% of caregivers.
Cost containment tended to be more of a priority for older patients, those with a higher symptom burden, and those with less family caregiver support. For caregivers, cost containment was more of a priority for those who reported that caregiving had a big impact on their finances, those with worse self-esteem related to their caregiving abilities, as well as those caring for older patients.
To better align cost containment priorities between patients and caregivers, it’s essential for families to engage in open and thorough discussions about the allocation of resources, Dr. Ozdemir said.
Although “patients, families, and physicians often avoid discussions about prognosis,” such conversations are essential for setting realistic expectations for care and adequately preparing for end-of-life decisions, Dr. Ozdemir told this news organization.
“These conversations should aim to balance competing interests and create care plans that are mutually acceptable to both patients and caregivers,” she said, adding that “this approach will help in minimizing any potential conflicts and ensure that both parties feel respected and understood in their decision-making process.”
Managing Unrealistic Expectations
As patients approached the end of life, neither patients nor caregivers shifted their priorities from life extension to symptom management.
This finding raises concerns because it suggests that many patients hold unrealistic expectations regarding their care and “underscores the need for continuous dialogue and reassessment of care goals throughout the progression of illness,” Dr. Ozdemir said.
“This stability in preferences over time suggests that initial care decisions are deeply ingrained or that there may be a lack of ongoing communication about evolving care needs and possibilities as conditions change,” Ozdemir said.
Yet, it can be hard to define what unrealistic expectations mean, said Olivia Seecof, MD, who wasn’t involved in the study.
“I think people are hopeful that a devastating diagnosis won’t lead to the end of their life and that there will be a treatment or something that will change [their prognosis], and they’ll get better,” said Dr. Seecof, palliative care expert with the Supportive Oncology Program at NYU Langone Health’s Perlmutter Cancer Center in New York City.
Giving patients and caregivers a realistic understanding of the prognosis is important, but “there’s more to it than just telling the patient their diagnosis,” she said.
“We have to plan for end of life, what it can look like,” said Dr. Seecof, adding that “often we don’t do a very good job of talking about that early on in an illness course.”
Overall, though, Dr. Seecof stressed that no two patients or situations are the same, and it’s important to understand what’s important in each scenario. End-of-life care requires “an individual approach because every patient is different, even if they have the same diagnosis as someone else,” she said.
This work was supported by funding from the Singapore Millennium Foundation and the Lien Centre for Palliative Care. Dr. Ozdemir and Dr. Seecof had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
New research found that patients and caregivers both tend to prioritize symptom control over life extension but often preferring a balance. Patients and caregivers, however, are less aligned on decisions about cost containment, with patients more likely to prioritize cost containment.
“Our research has revealed that patients and caregivers generally share similar end-of-life goals,” with a “notable exception” when it comes to costs, first author Semra Ozdemir, PhD, with the Lien Centre for Palliative Care, Duke-NUS Medical School, Singapore, told this news organization.
However, when patients and caregivers have a better understanding of the patient’s prognosis, both may be more inclined to avoid costly life-extending treatments and prioritize symptom management.
In other words, the survey suggests that “knowing the prognosis helps patients and their families set realistic expectations for care and adequately prepare for end-of-life decisions,” said Dr. Ozdemir.
This study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Patients with advanced cancer often face difficult decisions: Do they opt for treatments that may — or may not — extend life or do they focus more on symptom control?
Family caregivers, who also play an important role in this decision-making process, may have different care goals. Some research suggests that caregivers tend to prioritize treatments that could extend life, whereas patients prioritize symptom management, but it’s less clear how these priorities may change over time and how patients and caregivers may influence each other.
In the current study, the researchers examined goals of care among patients with stage IV solid tumors and caregivers during the last 2 years of life, focusing on life extension vs symptom management and cost containment, as well as how these goals changed over time.
The survey included 210 patient-caregiver pairs, recruited from outpatient clinics at two major cancer centers in Singapore. Patients had a mean age of 63 years, and about half were men. The caregivers had a mean age of 49 years, and almost two third (63%) were women.
Overall, 34% patients and 29% caregivers prioritized symptom management over life extension, whereas 24% patients and 19% caregivers prioritized life extension. Most patients and caregivers preferred balancing the two, with 34%-47% patients and 37%-69% caregivers supporting this approach.
When balancing cost and treatment decisions, however, patients were more likely to prioritize containing costs — 28% vs 17% for caregivers — over extending life — 26% of patients vs 35% of caregivers.
Cost containment tended to be more of a priority for older patients, those with a higher symptom burden, and those with less family caregiver support. For caregivers, cost containment was more of a priority for those who reported that caregiving had a big impact on their finances, those with worse self-esteem related to their caregiving abilities, as well as those caring for older patients.
To better align cost containment priorities between patients and caregivers, it’s essential for families to engage in open and thorough discussions about the allocation of resources, Dr. Ozdemir said.
Although “patients, families, and physicians often avoid discussions about prognosis,” such conversations are essential for setting realistic expectations for care and adequately preparing for end-of-life decisions, Dr. Ozdemir told this news organization.
“These conversations should aim to balance competing interests and create care plans that are mutually acceptable to both patients and caregivers,” she said, adding that “this approach will help in minimizing any potential conflicts and ensure that both parties feel respected and understood in their decision-making process.”
Managing Unrealistic Expectations
As patients approached the end of life, neither patients nor caregivers shifted their priorities from life extension to symptom management.
This finding raises concerns because it suggests that many patients hold unrealistic expectations regarding their care and “underscores the need for continuous dialogue and reassessment of care goals throughout the progression of illness,” Dr. Ozdemir said.
“This stability in preferences over time suggests that initial care decisions are deeply ingrained or that there may be a lack of ongoing communication about evolving care needs and possibilities as conditions change,” Ozdemir said.
Yet, it can be hard to define what unrealistic expectations mean, said Olivia Seecof, MD, who wasn’t involved in the study.
“I think people are hopeful that a devastating diagnosis won’t lead to the end of their life and that there will be a treatment or something that will change [their prognosis], and they’ll get better,” said Dr. Seecof, palliative care expert with the Supportive Oncology Program at NYU Langone Health’s Perlmutter Cancer Center in New York City.
Giving patients and caregivers a realistic understanding of the prognosis is important, but “there’s more to it than just telling the patient their diagnosis,” she said.
“We have to plan for end of life, what it can look like,” said Dr. Seecof, adding that “often we don’t do a very good job of talking about that early on in an illness course.”
Overall, though, Dr. Seecof stressed that no two patients or situations are the same, and it’s important to understand what’s important in each scenario. End-of-life care requires “an individual approach because every patient is different, even if they have the same diagnosis as someone else,” she said.
This work was supported by funding from the Singapore Millennium Foundation and the Lien Centre for Palliative Care. Dr. Ozdemir and Dr. Seecof had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Home ventilation consult
Specialist input on a sudden shift in device availability
Philips Respironics released a public statement on January 25, 2024, that would dramatically change the landscape of home mechanical ventilation and sleep-disordered breathing management in the United States. The company announced that, effective immediately in the US and US territories, Philips Respironics would stop production and sale of all hospital and home mechanical ventilation products, home and hospital ventilation devices, and oxygen concentrators.
There are many unknowns and uncertainties about how to proceed with care for patients requiring these devices. So we gathered an expert panel of clinicians from CHEST’s Home-Based Mechanical Ventilation and Neuromuscular Section within the Sleep Medicine Network to explain the current situation and offer suggestions on moving forward in caring for these patients.
Why is this happening?
John M. Coleman III, MD, FCCP: To understand the current Philips Respironics announcement, we must go back to June 2021. At that time, Philips recalled certain home mechanical ventilators, CPAP machines, and BiPAP machines due to potential health risks related to breakdown of the polyester-based polyurethane (PE-PUR) foam placed in these devices for noise reduction. Small and microscopic particles of this foam were at risk for being inhaled or ingested by patients using these devices. It was suspected that inhalation of these particles could potentially result in temporary or permanent injury. Machines in hot temperatures or using ozone cleaning were at increased risk. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued a class 1 recall, defined as “a situation in which there is reasonable probability that the use of or exposure to a violative product will cause serious adverse health consequences or death.”
In the months following the initial recall, there were additional recalls of both in-hospital and home ventilators related to the potential of these foam particles to move and block the air path, reducing airflow and causing the device to alarm.
Over the next few years, tens of thousands of medical device reports were filed about PE-PUR foam-related injuries, with some cases resulting in death. At this time, the Department of Justice began collaborating with the FDA on a consent decree. There were ongoing recalls of the CoughAssist T70 device, as well as the newest generation of Philips Respironics home ventilators, the Trilogy EVO.
Ultimately, after years of ongoing recalls and reports of numerous deaths and injuries, with multiple class action lawsuits, the consent decree was finalized. Philips Respironics agreed to stop production of all respiratory-related products in the US and US territories.
What devices does this apply to?
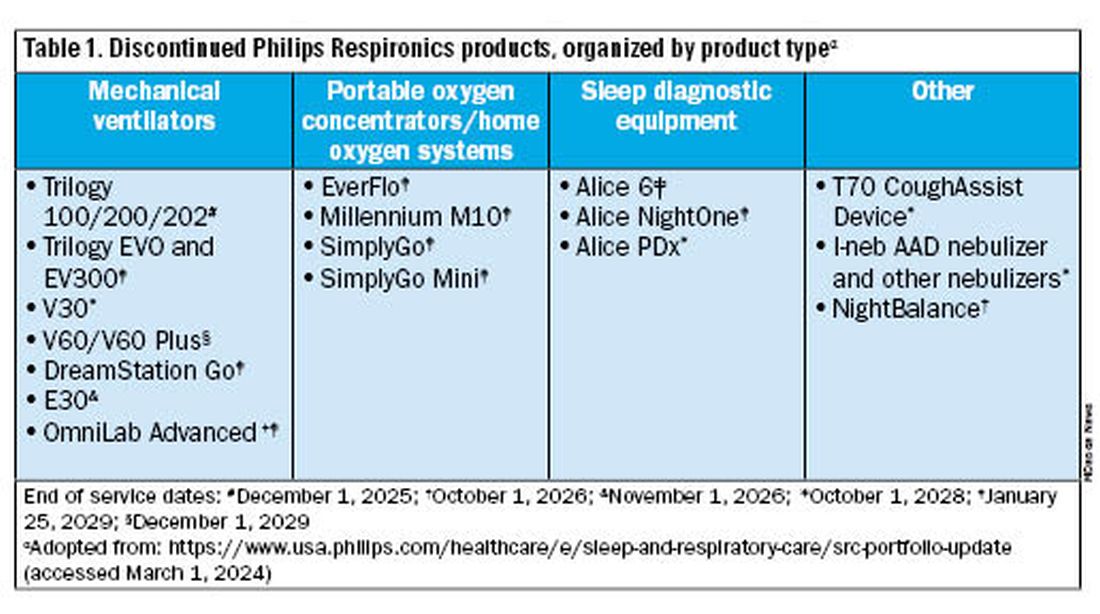
Jason Ackrivo, MD: This notice affects the devices shown in Table 1. All sales and device shipments have been discontinued as of January 25, 2024. Philips Respironics will continue to service the devices, subject to part availability, up to 5 years after sales discontinuation. However, Philips Respironics will continue to sell consumables and accessories, including masks.
What are my options for home mechanical ventilators?
Bethany L. Lussier, MD, FCCP: In the US, alternative approved home mechanical ventilator (HMV) devices include Astral by ResMed, Vivo 45 and Vivo 65 by Breas, and VOCSN by Ventec. Additional options made available through emergency use authorization by the FDA between 2020 and 2022 included Luisa by Löwenstein Medical, the V+ by Ventec, and Life2000 by Baxter. Many of us expedite disposition from the hospital by prescribing HMVs rather than respiratory assist devices (RADs) because it is easier to meet qualifying criteria for insurance. In efforts to promote just allocation of resources, now might be the ideal time to reconsider higher utilization of RADs over HMVs. Reasonable RAD candidates are those who do not need autotitration of EPAP, dual mode therapy, or invasive ventilation. In these cases, the qualifying criteria and patient needs may be met with a RAD capable of VAPS or BPAP-ST mode.
How are these alternative devices similar to and different from the Trilogy EVO?
Dr. Ackrivo:All these devices are portable ventilators that can deliver noninvasive or invasive ventilation. They have internal batteries for enabling portability. They offer multiple programmable presets and mouthpiece ventilation, and some offer both oxygenation and CO2 monitoring (both TcCO2 and EtCO2).
All alternative portable ventilators include a proprietary ventilation mode analogous to the Trilogy AVAPS algorithm (Table 2). The ResMed Astral has a safety tidal volume feature that targets a minimum tidal volume in PS, S/T, or P(A)C modes. The ResMed iVAPS algorithm adjusts inspiratory pressure and respiratory rate to target an alveolar ventilation based on patient-entered height. The Breas Vivo can target a tidal volume (TgV) in either PSV or PCV mode.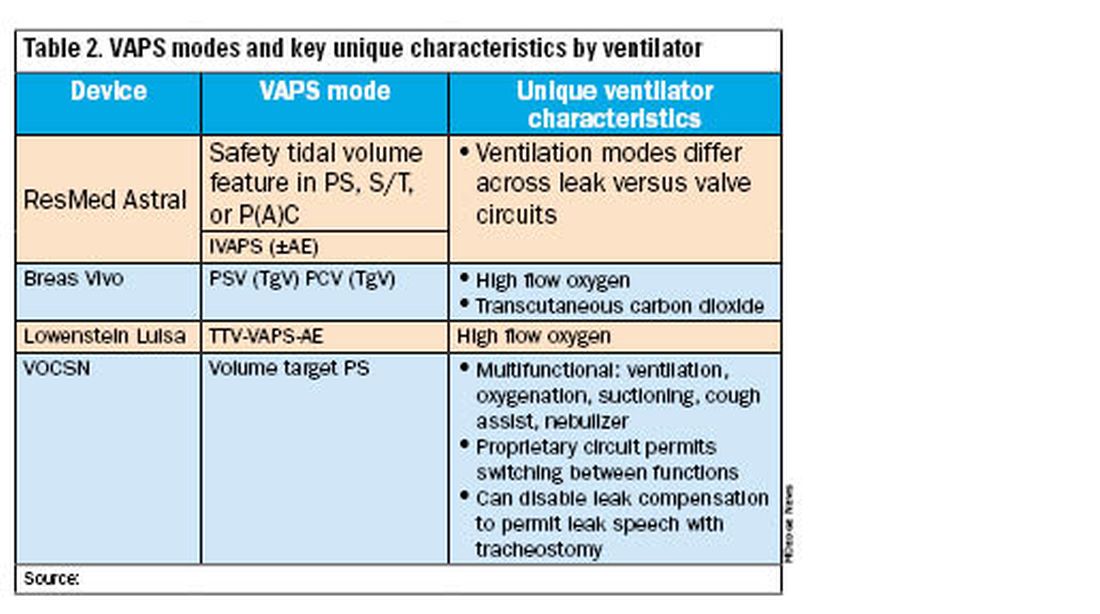
Unique ventilator characteristics are shown in Table 2. ResMed Astral mode options will differ between leak (passive) or valve (active) circuits. Both the Breas Vivo and Löwenstein Luisa enable high-flow oxygen delivery. Only the Breas Vivo enables connecting to a transcutaneous carbon dioxide monitor. The VOCSN name is an acronym for its multifunctional capabilities: ventilation, oxygenation, cough assist, suction, and nebulizer treatments. Lastly, the VOCSN can disable leak compensation, which may be advantageous for enabling leak speech with a tracheostomy.
I just provided my patient with a Trilogy EVO. Do I need to change this immediately?
Dr. Coleman: No, but you should start conversations with your patient/caregiving support and with your durable medical equipment (DME) provider about alternative options. The ripple effects of the Philips Respironics recall will be ongoing for years. The silver lining of this situation is that there are numerous HMV options on the market currently. It is important to review the differences between these new devices and consider what will work best for your patient and your practice. In addition, it is critical that your DME provider is familiar with these new devices, both for support and education, and is taking steps to make alternate devices available. We anticipate a push in coming months to switch patients off Trilogy EVO, so it important to get this process started.
For patients not interested in switching just yet, Philips Respironics will continue to service and offer supplies for these devices for up to 5 years, depending on part availability (Table 1). Refer to the Philips Respironics Sleep & Respiratory Product Portfolio Changes website for the most up-to-date information.
I have a patient on AVAPS, and I must change to iVAPS. What now?
Dr. Lussier: As mentioned previously by Dr. Ackrivo, the ResMed iVAPS algorithm adjusts inspiratory pressure and respiratory rate to target an alveolar ventilation based on patient-entered height. A download from a current VAPS setting can be helpful in defining target ventilation and pressure ranges for a tailored prescription. ResMed has an online iVAPS calculator (resmed.com) to assist in making this switch. Close clinical monitoring with data downloads is recommended to assure desired targets are still achieved.
What will happen to Philips Respironics’ cloud patient data?
Dr. Lussier: Representatives have reported that both providers and DME companies will have continued access to Care Orchestrator going forward. Currently, the logistics of data maintenance and ownership remain unclear, which poses additional questions about global access to patients’ data downloads.
----------
The recent discontinuation of Philips Respironics ventilation devices will induce a dramatic shift in home ventilation options in the US. Clinicians and DME companies should begin familiarizing themselves with alternative ventilators and their unique features. While significant uncertainty exists, we encourage a proactive approach to education and communication to ensure a smooth transition for patients on home ventilation.
John M. Coleman III, MD, FCCP, is Associate Professor, Division of Pulmonary & Critical Care Medicine, Department of Neurology, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine. Bethany L. Lussier, MD, FCCP, is in the Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Pulmonary & Critical Care Medicine, Department of Neurology, Division of Neurocritical Care, UT Southwestern Medical Center. Jason Ackrivo, MD, is Assistant Professor of Medicine and Neurology, and Associate Director, Jay and Randy Fishman Program for Home Assisted Ventilation, Pulmonary, Allergy, and Critical Care Division, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania.
Specialist input on a sudden shift in device availability
Specialist input on a sudden shift in device availability
Philips Respironics released a public statement on January 25, 2024, that would dramatically change the landscape of home mechanical ventilation and sleep-disordered breathing management in the United States. The company announced that, effective immediately in the US and US territories, Philips Respironics would stop production and sale of all hospital and home mechanical ventilation products, home and hospital ventilation devices, and oxygen concentrators.
There are many unknowns and uncertainties about how to proceed with care for patients requiring these devices. So we gathered an expert panel of clinicians from CHEST’s Home-Based Mechanical Ventilation and Neuromuscular Section within the Sleep Medicine Network to explain the current situation and offer suggestions on moving forward in caring for these patients.
Why is this happening?
John M. Coleman III, MD, FCCP: To understand the current Philips Respironics announcement, we must go back to June 2021. At that time, Philips recalled certain home mechanical ventilators, CPAP machines, and BiPAP machines due to potential health risks related to breakdown of the polyester-based polyurethane (PE-PUR) foam placed in these devices for noise reduction. Small and microscopic particles of this foam were at risk for being inhaled or ingested by patients using these devices. It was suspected that inhalation of these particles could potentially result in temporary or permanent injury. Machines in hot temperatures or using ozone cleaning were at increased risk. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued a class 1 recall, defined as “a situation in which there is reasonable probability that the use of or exposure to a violative product will cause serious adverse health consequences or death.”
In the months following the initial recall, there were additional recalls of both in-hospital and home ventilators related to the potential of these foam particles to move and block the air path, reducing airflow and causing the device to alarm.
Over the next few years, tens of thousands of medical device reports were filed about PE-PUR foam-related injuries, with some cases resulting in death. At this time, the Department of Justice began collaborating with the FDA on a consent decree. There were ongoing recalls of the CoughAssist T70 device, as well as the newest generation of Philips Respironics home ventilators, the Trilogy EVO.
Ultimately, after years of ongoing recalls and reports of numerous deaths and injuries, with multiple class action lawsuits, the consent decree was finalized. Philips Respironics agreed to stop production of all respiratory-related products in the US and US territories.
What devices does this apply to?
Jason Ackrivo, MD: This notice affects the devices shown in Table 1. All sales and device shipments have been discontinued as of January 25, 2024. Philips Respironics will continue to service the devices, subject to part availability, up to 5 years after sales discontinuation. However, Philips Respironics will continue to sell consumables and accessories, including masks.

What are my options for home mechanical ventilators?
Bethany L. Lussier, MD, FCCP: In the US, alternative approved home mechanical ventilator (HMV) devices include Astral by ResMed, Vivo 45 and Vivo 65 by Breas, and VOCSN by Ventec. Additional options made available through emergency use authorization by the FDA between 2020 and 2022 included Luisa by Löwenstein Medical, the V+ by Ventec, and Life2000 by Baxter. Many of us expedite disposition from the hospital by prescribing HMVs rather than respiratory assist devices (RADs) because it is easier to meet qualifying criteria for insurance. In efforts to promote just allocation of resources, now might be the ideal time to reconsider higher utilization of RADs over HMVs. Reasonable RAD candidates are those who do not need autotitration of EPAP, dual mode therapy, or invasive ventilation. In these cases, the qualifying criteria and patient needs may be met with a RAD capable of VAPS or BPAP-ST mode.
How are these alternative devices similar to and different from the Trilogy EVO?
Dr. Ackrivo:All these devices are portable ventilators that can deliver noninvasive or invasive ventilation. They have internal batteries for enabling portability. They offer multiple programmable presets and mouthpiece ventilation, and some offer both oxygenation and CO2 monitoring (both TcCO2 and EtCO2).
All alternative portable ventilators include a proprietary ventilation mode analogous to the Trilogy AVAPS algorithm (Table 2). The ResMed Astral has a safety tidal volume feature that targets a minimum tidal volume in PS, S/T, or P(A)C modes. The ResMed iVAPS algorithm adjusts inspiratory pressure and respiratory rate to target an alveolar ventilation based on patient-entered height. The Breas Vivo can target a tidal volume (TgV) in either PSV or PCV mode.
Unique ventilator characteristics are shown in Table 2. ResMed Astral mode options will differ between leak (passive) or valve (active) circuits. Both the Breas Vivo and Löwenstein Luisa enable high-flow oxygen delivery. Only the Breas Vivo enables connecting to a transcutaneous carbon dioxide monitor. The VOCSN name is an acronym for its multifunctional capabilities: ventilation, oxygenation, cough assist, suction, and nebulizer treatments. Lastly, the VOCSN can disable leak compensation, which may be advantageous for enabling leak speech with a tracheostomy.
I just provided my patient with a Trilogy EVO. Do I need to change this immediately?
Dr. Coleman: No, but you should start conversations with your patient/caregiving support and with your durable medical equipment (DME) provider about alternative options. The ripple effects of the Philips Respironics recall will be ongoing for years. The silver lining of this situation is that there are numerous HMV options on the market currently. It is important to review the differences between these new devices and consider what will work best for your patient and your practice. In addition, it is critical that your DME provider is familiar with these new devices, both for support and education, and is taking steps to make alternate devices available. We anticipate a push in coming months to switch patients off Trilogy EVO, so it important to get this process started.
For patients not interested in switching just yet, Philips Respironics will continue to service and offer supplies for these devices for up to 5 years, depending on part availability (Table 1). Refer to the Philips Respironics Sleep & Respiratory Product Portfolio Changes website for the most up-to-date information.
I have a patient on AVAPS, and I must change to iVAPS. What now?
Dr. Lussier: As mentioned previously by Dr. Ackrivo, the ResMed iVAPS algorithm adjusts inspiratory pressure and respiratory rate to target an alveolar ventilation based on patient-entered height. A download from a current VAPS setting can be helpful in defining target ventilation and pressure ranges for a tailored prescription. ResMed has an online iVAPS calculator (resmed.com) to assist in making this switch. Close clinical monitoring with data downloads is recommended to assure desired targets are still achieved.
What will happen to Philips Respironics’ cloud patient data?
Dr. Lussier: Representatives have reported that both providers and DME companies will have continued access to Care Orchestrator going forward. Currently, the logistics of data maintenance and ownership remain unclear, which poses additional questions about global access to patients’ data downloads.
----------
The recent discontinuation of Philips Respironics ventilation devices will induce a dramatic shift in home ventilation options in the US. Clinicians and DME companies should begin familiarizing themselves with alternative ventilators and their unique features. While significant uncertainty exists, we encourage a proactive approach to education and communication to ensure a smooth transition for patients on home ventilation.
John M. Coleman III, MD, FCCP, is Associate Professor, Division of Pulmonary & Critical Care Medicine, Department of Neurology, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine. Bethany L. Lussier, MD, FCCP, is in the Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Pulmonary & Critical Care Medicine, Department of Neurology, Division of Neurocritical Care, UT Southwestern Medical Center. Jason Ackrivo, MD, is Assistant Professor of Medicine and Neurology, and Associate Director, Jay and Randy Fishman Program for Home Assisted Ventilation, Pulmonary, Allergy, and Critical Care Division, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania.
Philips Respironics released a public statement on January 25, 2024, that would dramatically change the landscape of home mechanical ventilation and sleep-disordered breathing management in the United States. The company announced that, effective immediately in the US and US territories, Philips Respironics would stop production and sale of all hospital and home mechanical ventilation products, home and hospital ventilation devices, and oxygen concentrators.
There are many unknowns and uncertainties about how to proceed with care for patients requiring these devices. So we gathered an expert panel of clinicians from CHEST’s Home-Based Mechanical Ventilation and Neuromuscular Section within the Sleep Medicine Network to explain the current situation and offer suggestions on moving forward in caring for these patients.
Why is this happening?
John M. Coleman III, MD, FCCP: To understand the current Philips Respironics announcement, we must go back to June 2021. At that time, Philips recalled certain home mechanical ventilators, CPAP machines, and BiPAP machines due to potential health risks related to breakdown of the polyester-based polyurethane (PE-PUR) foam placed in these devices for noise reduction. Small and microscopic particles of this foam were at risk for being inhaled or ingested by patients using these devices. It was suspected that inhalation of these particles could potentially result in temporary or permanent injury. Machines in hot temperatures or using ozone cleaning were at increased risk. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued a class 1 recall, defined as “a situation in which there is reasonable probability that the use of or exposure to a violative product will cause serious adverse health consequences or death.”
In the months following the initial recall, there were additional recalls of both in-hospital and home ventilators related to the potential of these foam particles to move and block the air path, reducing airflow and causing the device to alarm.
Over the next few years, tens of thousands of medical device reports were filed about PE-PUR foam-related injuries, with some cases resulting in death. At this time, the Department of Justice began collaborating with the FDA on a consent decree. There were ongoing recalls of the CoughAssist T70 device, as well as the newest generation of Philips Respironics home ventilators, the Trilogy EVO.
Ultimately, after years of ongoing recalls and reports of numerous deaths and injuries, with multiple class action lawsuits, the consent decree was finalized. Philips Respironics agreed to stop production of all respiratory-related products in the US and US territories.
What devices does this apply to?
Jason Ackrivo, MD: This notice affects the devices shown in Table 1. All sales and device shipments have been discontinued as of January 25, 2024. Philips Respironics will continue to service the devices, subject to part availability, up to 5 years after sales discontinuation. However, Philips Respironics will continue to sell consumables and accessories, including masks.

What are my options for home mechanical ventilators?
Bethany L. Lussier, MD, FCCP: In the US, alternative approved home mechanical ventilator (HMV) devices include Astral by ResMed, Vivo 45 and Vivo 65 by Breas, and VOCSN by Ventec. Additional options made available through emergency use authorization by the FDA between 2020 and 2022 included Luisa by Löwenstein Medical, the V+ by Ventec, and Life2000 by Baxter. Many of us expedite disposition from the hospital by prescribing HMVs rather than respiratory assist devices (RADs) because it is easier to meet qualifying criteria for insurance. In efforts to promote just allocation of resources, now might be the ideal time to reconsider higher utilization of RADs over HMVs. Reasonable RAD candidates are those who do not need autotitration of EPAP, dual mode therapy, or invasive ventilation. In these cases, the qualifying criteria and patient needs may be met with a RAD capable of VAPS or BPAP-ST mode.
How are these alternative devices similar to and different from the Trilogy EVO?
Dr. Ackrivo:All these devices are portable ventilators that can deliver noninvasive or invasive ventilation. They have internal batteries for enabling portability. They offer multiple programmable presets and mouthpiece ventilation, and some offer both oxygenation and CO2 monitoring (both TcCO2 and EtCO2).
All alternative portable ventilators include a proprietary ventilation mode analogous to the Trilogy AVAPS algorithm (Table 2). The ResMed Astral has a safety tidal volume feature that targets a minimum tidal volume in PS, S/T, or P(A)C modes. The ResMed iVAPS algorithm adjusts inspiratory pressure and respiratory rate to target an alveolar ventilation based on patient-entered height. The Breas Vivo can target a tidal volume (TgV) in either PSV or PCV mode.
Unique ventilator characteristics are shown in Table 2. ResMed Astral mode options will differ between leak (passive) or valve (active) circuits. Both the Breas Vivo and Löwenstein Luisa enable high-flow oxygen delivery. Only the Breas Vivo enables connecting to a transcutaneous carbon dioxide monitor. The VOCSN name is an acronym for its multifunctional capabilities: ventilation, oxygenation, cough assist, suction, and nebulizer treatments. Lastly, the VOCSN can disable leak compensation, which may be advantageous for enabling leak speech with a tracheostomy.
I just provided my patient with a Trilogy EVO. Do I need to change this immediately?
Dr. Coleman: No, but you should start conversations with your patient/caregiving support and with your durable medical equipment (DME) provider about alternative options. The ripple effects of the Philips Respironics recall will be ongoing for years. The silver lining of this situation is that there are numerous HMV options on the market currently. It is important to review the differences between these new devices and consider what will work best for your patient and your practice. In addition, it is critical that your DME provider is familiar with these new devices, both for support and education, and is taking steps to make alternate devices available. We anticipate a push in coming months to switch patients off Trilogy EVO, so it important to get this process started.
For patients not interested in switching just yet, Philips Respironics will continue to service and offer supplies for these devices for up to 5 years, depending on part availability (Table 1). Refer to the Philips Respironics Sleep & Respiratory Product Portfolio Changes website for the most up-to-date information.
I have a patient on AVAPS, and I must change to iVAPS. What now?
Dr. Lussier: As mentioned previously by Dr. Ackrivo, the ResMed iVAPS algorithm adjusts inspiratory pressure and respiratory rate to target an alveolar ventilation based on patient-entered height. A download from a current VAPS setting can be helpful in defining target ventilation and pressure ranges for a tailored prescription. ResMed has an online iVAPS calculator (resmed.com) to assist in making this switch. Close clinical monitoring with data downloads is recommended to assure desired targets are still achieved.
What will happen to Philips Respironics’ cloud patient data?
Dr. Lussier: Representatives have reported that both providers and DME companies will have continued access to Care Orchestrator going forward. Currently, the logistics of data maintenance and ownership remain unclear, which poses additional questions about global access to patients’ data downloads.
----------
The recent discontinuation of Philips Respironics ventilation devices will induce a dramatic shift in home ventilation options in the US. Clinicians and DME companies should begin familiarizing themselves with alternative ventilators and their unique features. While significant uncertainty exists, we encourage a proactive approach to education and communication to ensure a smooth transition for patients on home ventilation.
John M. Coleman III, MD, FCCP, is Associate Professor, Division of Pulmonary & Critical Care Medicine, Department of Neurology, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine. Bethany L. Lussier, MD, FCCP, is in the Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Pulmonary & Critical Care Medicine, Department of Neurology, Division of Neurocritical Care, UT Southwestern Medical Center. Jason Ackrivo, MD, is Assistant Professor of Medicine and Neurology, and Associate Director, Jay and Randy Fishman Program for Home Assisted Ventilation, Pulmonary, Allergy, and Critical Care Division, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania.
Making invisible problems visible
How Erika Mosesón, MD, educates on the effects of air pollution and encourages community-level advocacy
For Erika Mosesón, MD, a pulmonologist and ICU doctor, advocacy for clean air and climate action started small: signing petitions and writing letters.
Even as she attended conferences and learned about the health impacts of air pollution, her impression was that experts were handling it. “I didn’t really think my voice was worth highlighting,” Dr. Mosesón said.
But her concerns grew with the repeal of the Clean Power Plan in 2019 and rolled-back federal protections around particulate matter and other environmental guidelines.
In response, Dr. Mosesón moved from writing letters to educating people in her home state of Oregon on the lung-related effects of pollution. She spoke at organization meetings and town halls and met with legislators. One way or another, she knew she needed to get the word out.
After all, problem-causing particulates are teeny-tiny; too small to be seen. “It’s literally invisible,” Dr. Mosesón said. But the impact on patients is not.
That’s how the Air Health Our Health podcast was born.
The podcast has a straightforward tagline — ”Clean air saves lives” — and a blunt recommendation: “If you do nothing else, don’t light things on fire and breathe them into your lungs.”
Giving a voice to the voiceless
In early 2017, the Oregon legislature was considering bills aimed at transitioning from diesel-fueled engines to cleaner alternatives. At the time, Dr. Mosesón was on the executive committee for the Oregon Thoracic Society, and, in partnership with the American Lung Association, she was tapped to speak to legislators about clean air and the health impacts of air pollution.
This role made it clear to her that lawmakers don’t hear diverse perspectives. A trucking company may budget for full-time lobbyists, whereas parents of kids with asthma aren’t in the room.
So there’s an asymmetry to who is and is not heard from, Dr. Mosesón said. That’s why in her conversations and presentations, she advocates for those who might not otherwise be represented in the rooms where big decisions are made.
Automating advocacy
Over time, Dr. Mosesón found her schedule was filling up with meetings and presentations.
“I’m a full-time clinician,” Dr. Mosesón noted. She’s also a parent to three kids. When she was asked to attend a hearing, sometimes her schedule required her to decline. And so, early in the pandemic, the Air Health Our Health podcast and the accompanying website were born.
“The podcast and website were honestly a way to automate advocacy,” Dr. Mosesón said.
In many ways, the pandemic was an ideal time to launch the podcast. For one thing, the idea of podcasting from your closet or living room (as opposed to a professional audio studio) became commonplace. Plus, for a pulmonologist, these years were full of relevant topics like how climate change and particulate matter interacted with COVID-19 , Dr. Mosesón noted.
Then, in 2020, the Labor Day fires led to Oregon’s having the worst air quality in the world. That same year, there were George Floyd protests around the country, including in Portland, which led to rampant use of tear gas and prompted Dr. Mosesón to dig into studies about these chemicals.
Given just how much air pollution affects health — and the continued extreme weather events (such as Oregon’s heat dome in summer 2021) — there was no shortage of topics for the podcast.
Next steps to empower physicians
Confronting climate change is daunting, and it is made more challenging by a partisan environment, distrust of experts, and disinformation. On her podcast, Dr. Mosesón aims to make it easier.
In each episode, she shares information and interviews experts. She shares how a patient might be affected by particular issues — radon, wildfires, and so on. The goal is to provide clinicians with a foundation on everyday issues.
“Every single doctor feels like they can talk to a patient about smoking, even if they don’t know all the deep nitty-gritty studies about it,” Dr. Mosesón said. The exact effects of smoking — cancer, heart disease, and lung disease — occur due to air pollution. “When I give talks, I tell people, if you can talk about smoking, you can talk about air pollution.”
Each podcast also features an array of action items.
Some steps are practical, such as creating a plan for heat events or encouraging radon testing. The solution could also be as simple as asking the right questions.
For example, at a doctor’s visit for asthma, common recommendations are to use a HEPA filter or place a sheet protector on the bed, Dr. Mosesón said. It won’t typically come up that a patient’s asthma may be caused or exacerbated by living beside a highway.
Dr. Mosesón also encourages advocacy. “There are all these different levels [of response],” she said. Next steps might involve writing a letter, contacting a councilperson, or advocating for a program (like retiring gas-powered leaf blowers).
For many patients, their doctor is the only person they routinely interact with who has advanced scientific training. Rather than presenting dry data, Dr. Mosesón recommends framing changes and recommendations in ways that are meaningful to neighbors.
“Each physician or clinician is going to know the values of their community,” Dr. Mosesón said. If you’re in a military town, advocating for electric cars may be easier if framed around decreasing dependence on foreign oil. If the region recently experienced back-to-back heat events, advocating for a cooling center might be galvanizing.
What is Dr. Mosesón’s ultimate goal? Inform others so well that she can retire her podcasting equipment.
“I would love,” Dr. Mosesón said, “for every physician in their local community to be a clean air and climate advocate.”
------
Be sure to check out a special episode of the Air Health Our Health podcast, where Dr. Mosesón and CHEST Advocates Editor in Chief, Drew Harris, MD, FCCP, discuss the serious health issues impacting coal miners. They take a deep dive into black lung disease and silica dust, highlighting the science and research, prevention efforts and challenges to implementation, and the importance of advocacy work.
LISTEN NOW »
This article was adapted from the Winter 2024 online issue of CHEST Advocates. For the full article — and to engage with the other content from this issue — visit chestnet.org/chest-advocates.
How Erika Mosesón, MD, educates on the effects of air pollution and encourages community-level advocacy
How Erika Mosesón, MD, educates on the effects of air pollution and encourages community-level advocacy
For Erika Mosesón, MD, a pulmonologist and ICU doctor, advocacy for clean air and climate action started small: signing petitions and writing letters.
Even as she attended conferences and learned about the health impacts of air pollution, her impression was that experts were handling it. “I didn’t really think my voice was worth highlighting,” Dr. Mosesón said.
But her concerns grew with the repeal of the Clean Power Plan in 2019 and rolled-back federal protections around particulate matter and other environmental guidelines.
In response, Dr. Mosesón moved from writing letters to educating people in her home state of Oregon on the lung-related effects of pollution. She spoke at organization meetings and town halls and met with legislators. One way or another, she knew she needed to get the word out.
After all, problem-causing particulates are teeny-tiny; too small to be seen. “It’s literally invisible,” Dr. Mosesón said. But the impact on patients is not.
That’s how the Air Health Our Health podcast was born.
The podcast has a straightforward tagline — ”Clean air saves lives” — and a blunt recommendation: “If you do nothing else, don’t light things on fire and breathe them into your lungs.”
Giving a voice to the voiceless
In early 2017, the Oregon legislature was considering bills aimed at transitioning from diesel-fueled engines to cleaner alternatives. At the time, Dr. Mosesón was on the executive committee for the Oregon Thoracic Society, and, in partnership with the American Lung Association, she was tapped to speak to legislators about clean air and the health impacts of air pollution.
This role made it clear to her that lawmakers don’t hear diverse perspectives. A trucking company may budget for full-time lobbyists, whereas parents of kids with asthma aren’t in the room.
So there’s an asymmetry to who is and is not heard from, Dr. Mosesón said. That’s why in her conversations and presentations, she advocates for those who might not otherwise be represented in the rooms where big decisions are made.
Automating advocacy
Over time, Dr. Mosesón found her schedule was filling up with meetings and presentations.
“I’m a full-time clinician,” Dr. Mosesón noted. She’s also a parent to three kids. When she was asked to attend a hearing, sometimes her schedule required her to decline. And so, early in the pandemic, the Air Health Our Health podcast and the accompanying website were born.
“The podcast and website were honestly a way to automate advocacy,” Dr. Mosesón said.
In many ways, the pandemic was an ideal time to launch the podcast. For one thing, the idea of podcasting from your closet or living room (as opposed to a professional audio studio) became commonplace. Plus, for a pulmonologist, these years were full of relevant topics like how climate change and particulate matter interacted with COVID-19 , Dr. Mosesón noted.
Then, in 2020, the Labor Day fires led to Oregon’s having the worst air quality in the world. That same year, there were George Floyd protests around the country, including in Portland, which led to rampant use of tear gas and prompted Dr. Mosesón to dig into studies about these chemicals.
Given just how much air pollution affects health — and the continued extreme weather events (such as Oregon’s heat dome in summer 2021) — there was no shortage of topics for the podcast.
Next steps to empower physicians
Confronting climate change is daunting, and it is made more challenging by a partisan environment, distrust of experts, and disinformation. On her podcast, Dr. Mosesón aims to make it easier.
In each episode, she shares information and interviews experts. She shares how a patient might be affected by particular issues — radon, wildfires, and so on. The goal is to provide clinicians with a foundation on everyday issues.
“Every single doctor feels like they can talk to a patient about smoking, even if they don’t know all the deep nitty-gritty studies about it,” Dr. Mosesón said. The exact effects of smoking — cancer, heart disease, and lung disease — occur due to air pollution. “When I give talks, I tell people, if you can talk about smoking, you can talk about air pollution.”
Each podcast also features an array of action items.
Some steps are practical, such as creating a plan for heat events or encouraging radon testing. The solution could also be as simple as asking the right questions.
For example, at a doctor’s visit for asthma, common recommendations are to use a HEPA filter or place a sheet protector on the bed, Dr. Mosesón said. It won’t typically come up that a patient’s asthma may be caused or exacerbated by living beside a highway.
Dr. Mosesón also encourages advocacy. “There are all these different levels [of response],” she said. Next steps might involve writing a letter, contacting a councilperson, or advocating for a program (like retiring gas-powered leaf blowers).
For many patients, their doctor is the only person they routinely interact with who has advanced scientific training. Rather than presenting dry data, Dr. Mosesón recommends framing changes and recommendations in ways that are meaningful to neighbors.
“Each physician or clinician is going to know the values of their community,” Dr. Mosesón said. If you’re in a military town, advocating for electric cars may be easier if framed around decreasing dependence on foreign oil. If the region recently experienced back-to-back heat events, advocating for a cooling center might be galvanizing.
What is Dr. Mosesón’s ultimate goal? Inform others so well that she can retire her podcasting equipment.
“I would love,” Dr. Mosesón said, “for every physician in their local community to be a clean air and climate advocate.”
------
Be sure to check out a special episode of the Air Health Our Health podcast, where Dr. Mosesón and CHEST Advocates Editor in Chief, Drew Harris, MD, FCCP, discuss the serious health issues impacting coal miners. They take a deep dive into black lung disease and silica dust, highlighting the science and research, prevention efforts and challenges to implementation, and the importance of advocacy work.
LISTEN NOW »
This article was adapted from the Winter 2024 online issue of CHEST Advocates. For the full article — and to engage with the other content from this issue — visit chestnet.org/chest-advocates.
For Erika Mosesón, MD, a pulmonologist and ICU doctor, advocacy for clean air and climate action started small: signing petitions and writing letters.
Even as she attended conferences and learned about the health impacts of air pollution, her impression was that experts were handling it. “I didn’t really think my voice was worth highlighting,” Dr. Mosesón said.
But her concerns grew with the repeal of the Clean Power Plan in 2019 and rolled-back federal protections around particulate matter and other environmental guidelines.
In response, Dr. Mosesón moved from writing letters to educating people in her home state of Oregon on the lung-related effects of pollution. She spoke at organization meetings and town halls and met with legislators. One way or another, she knew she needed to get the word out.
After all, problem-causing particulates are teeny-tiny; too small to be seen. “It’s literally invisible,” Dr. Mosesón said. But the impact on patients is not.
That’s how the Air Health Our Health podcast was born.
The podcast has a straightforward tagline — ”Clean air saves lives” — and a blunt recommendation: “If you do nothing else, don’t light things on fire and breathe them into your lungs.”
Giving a voice to the voiceless
In early 2017, the Oregon legislature was considering bills aimed at transitioning from diesel-fueled engines to cleaner alternatives. At the time, Dr. Mosesón was on the executive committee for the Oregon Thoracic Society, and, in partnership with the American Lung Association, she was tapped to speak to legislators about clean air and the health impacts of air pollution.
This role made it clear to her that lawmakers don’t hear diverse perspectives. A trucking company may budget for full-time lobbyists, whereas parents of kids with asthma aren’t in the room.
So there’s an asymmetry to who is and is not heard from, Dr. Mosesón said. That’s why in her conversations and presentations, she advocates for those who might not otherwise be represented in the rooms where big decisions are made.
Automating advocacy
Over time, Dr. Mosesón found her schedule was filling up with meetings and presentations.
“I’m a full-time clinician,” Dr. Mosesón noted. She’s also a parent to three kids. When she was asked to attend a hearing, sometimes her schedule required her to decline. And so, early in the pandemic, the Air Health Our Health podcast and the accompanying website were born.
“The podcast and website were honestly a way to automate advocacy,” Dr. Mosesón said.
In many ways, the pandemic was an ideal time to launch the podcast. For one thing, the idea of podcasting from your closet or living room (as opposed to a professional audio studio) became commonplace. Plus, for a pulmonologist, these years were full of relevant topics like how climate change and particulate matter interacted with COVID-19 , Dr. Mosesón noted.
Then, in 2020, the Labor Day fires led to Oregon’s having the worst air quality in the world. That same year, there were George Floyd protests around the country, including in Portland, which led to rampant use of tear gas and prompted Dr. Mosesón to dig into studies about these chemicals.
Given just how much air pollution affects health — and the continued extreme weather events (such as Oregon’s heat dome in summer 2021) — there was no shortage of topics for the podcast.
Next steps to empower physicians
Confronting climate change is daunting, and it is made more challenging by a partisan environment, distrust of experts, and disinformation. On her podcast, Dr. Mosesón aims to make it easier.
In each episode, she shares information and interviews experts. She shares how a patient might be affected by particular issues — radon, wildfires, and so on. The goal is to provide clinicians with a foundation on everyday issues.
“Every single doctor feels like they can talk to a patient about smoking, even if they don’t know all the deep nitty-gritty studies about it,” Dr. Mosesón said. The exact effects of smoking — cancer, heart disease, and lung disease — occur due to air pollution. “When I give talks, I tell people, if you can talk about smoking, you can talk about air pollution.”
Each podcast also features an array of action items.
Some steps are practical, such as creating a plan for heat events or encouraging radon testing. The solution could also be as simple as asking the right questions.
For example, at a doctor’s visit for asthma, common recommendations are to use a HEPA filter or place a sheet protector on the bed, Dr. Mosesón said. It won’t typically come up that a patient’s asthma may be caused or exacerbated by living beside a highway.
Dr. Mosesón also encourages advocacy. “There are all these different levels [of response],” she said. Next steps might involve writing a letter, contacting a councilperson, or advocating for a program (like retiring gas-powered leaf blowers).
For many patients, their doctor is the only person they routinely interact with who has advanced scientific training. Rather than presenting dry data, Dr. Mosesón recommends framing changes and recommendations in ways that are meaningful to neighbors.
“Each physician or clinician is going to know the values of their community,” Dr. Mosesón said. If you’re in a military town, advocating for electric cars may be easier if framed around decreasing dependence on foreign oil. If the region recently experienced back-to-back heat events, advocating for a cooling center might be galvanizing.
What is Dr. Mosesón’s ultimate goal? Inform others so well that she can retire her podcasting equipment.
“I would love,” Dr. Mosesón said, “for every physician in their local community to be a clean air and climate advocate.”
------
Be sure to check out a special episode of the Air Health Our Health podcast, where Dr. Mosesón and CHEST Advocates Editor in Chief, Drew Harris, MD, FCCP, discuss the serious health issues impacting coal miners. They take a deep dive into black lung disease and silica dust, highlighting the science and research, prevention efforts and challenges to implementation, and the importance of advocacy work.
LISTEN NOW »
This article was adapted from the Winter 2024 online issue of CHEST Advocates. For the full article — and to engage with the other content from this issue — visit chestnet.org/chest-advocates.
Fighting for fresh air: RSV’s connection to environmental pollution
Diffuse Lung Disease and Lung Transplant Network
Occupational and Environmental Health Section
Poor air quality has numerous health hazards for patients with chronic lung disease. Now mounting evidence from pediatric studies suggests a concerning link between air pollution and viral infections, specifically respiratory syncytial virus (RSV).
Multiple studies have shown increased incidence and severity of disease in children with exposure to air pollutants such as particulate matter and nitrogen dioxide.1,2,3 Researchers speculate that these pollutants potentiate viral entry to airway epithelium, increase viral load, and dysregulate the immune response.4 Air pollution, increasingly worsened by climate change, is also associated with acute respiratory infections in adults, though adult research remains sparse.5
The adoption of viral testing during the pandemic has revealed a previously under-recognized prevalence of RSV in adults.
RSV accounts for an estimated 60,000 to 160,000 hospitalizations and 6,000 to 10,000 deaths annually among elderly adults. This newfound awareness coincides with the exciting development of a new RSV vaccine that has shown around 85% efficacy at preventing symptomatic RSV infection in the first year, and new data suggest benefits persisting even into the second year after vaccination.6 With an estimated 60 million adults at high risk for RSV in the US, RSV prevention has become an increasingly important aspect of respiratory care.
While more research is needed to definitively quantify the link between air pollution and RSV in adults, the existing data offer valuable insights for all pulmonologists. These findings suggest a benefit in counseling patients with chronic lung conditions on taking steps to mitigate exposure to air pollutants, either through avoidance of outdoor activities or mask-wearing when air quality levels exceed healthy ranges, as well as promoting RSV vaccination for patients who are at risk.7
References
1. Milani GP, Cafora M, Favero C, et al. PM2.5, PM10 and bronchiolitis severity: a cohort study. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2022;33(10). https://doi.org/10.1111/pai.13853
2. Wrotek A, Badyda A, Czechowski PO, Owczarek T, Dąbrowiecki P, Jackowska T. Air pollutants’ concentrations are associated with increased number of RSV hospitalizations in Polish children. J Clin Med. 2021;10(15):3224. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10153224
3. Horne BD, Joy EA, Hofmann MG, et al. Short-term elevation of fine particulate matter air pollution and acute lower respiratory infection. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018;198(6):759-766. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201709-1883oc
4. Wrotek A, Jackowska T. Molecular mechanisms of RSV and air pollution interaction: a scoping review. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(20):12704. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232012704
5. Kirwa K, Eckert CM, Vedal S, Hajat A, Kaufman JD. Ambient air pollution and risk of respiratory infection among adults: evidence from the multiethnic study of atherosclerosis (MESA). BMJ Open Respir Res. 2021;8(1). https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjresp-2020-000866
6. Melgar M, Britton A, Roper LE, et al. Use of respiratory syncytial virus vaccines in older adults: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices — United States, 2023. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72(29):793-801. http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7229a4
7. Kodros JK, O’Dell K, Samet JM, L’Orange C, Pierce JR, Volckens J. Quantifying the health benefits of face masks and respirators to mitigate exposure to severe air pollution. GeoHealth. 2021;5(9). https://doi.org/10.1029/2021gh000482
Diffuse Lung Disease and Lung Transplant Network
Occupational and Environmental Health Section
Poor air quality has numerous health hazards for patients with chronic lung disease. Now mounting evidence from pediatric studies suggests a concerning link between air pollution and viral infections, specifically respiratory syncytial virus (RSV).
Multiple studies have shown increased incidence and severity of disease in children with exposure to air pollutants such as particulate matter and nitrogen dioxide.1,2,3 Researchers speculate that these pollutants potentiate viral entry to airway epithelium, increase viral load, and dysregulate the immune response.4 Air pollution, increasingly worsened by climate change, is also associated with acute respiratory infections in adults, though adult research remains sparse.5
The adoption of viral testing during the pandemic has revealed a previously under-recognized prevalence of RSV in adults.
RSV accounts for an estimated 60,000 to 160,000 hospitalizations and 6,000 to 10,000 deaths annually among elderly adults. This newfound awareness coincides with the exciting development of a new RSV vaccine that has shown around 85% efficacy at preventing symptomatic RSV infection in the first year, and new data suggest benefits persisting even into the second year after vaccination.6 With an estimated 60 million adults at high risk for RSV in the US, RSV prevention has become an increasingly important aspect of respiratory care.
While more research is needed to definitively quantify the link between air pollution and RSV in adults, the existing data offer valuable insights for all pulmonologists. These findings suggest a benefit in counseling patients with chronic lung conditions on taking steps to mitigate exposure to air pollutants, either through avoidance of outdoor activities or mask-wearing when air quality levels exceed healthy ranges, as well as promoting RSV vaccination for patients who are at risk.7
References
1. Milani GP, Cafora M, Favero C, et al. PM2.5, PM10 and bronchiolitis severity: a cohort study. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2022;33(10). https://doi.org/10.1111/pai.13853
2. Wrotek A, Badyda A, Czechowski PO, Owczarek T, Dąbrowiecki P, Jackowska T. Air pollutants’ concentrations are associated with increased number of RSV hospitalizations in Polish children. J Clin Med. 2021;10(15):3224. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10153224
3. Horne BD, Joy EA, Hofmann MG, et al. Short-term elevation of fine particulate matter air pollution and acute lower respiratory infection. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018;198(6):759-766. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201709-1883oc
4. Wrotek A, Jackowska T. Molecular mechanisms of RSV and air pollution interaction: a scoping review. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(20):12704. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232012704
5. Kirwa K, Eckert CM, Vedal S, Hajat A, Kaufman JD. Ambient air pollution and risk of respiratory infection among adults: evidence from the multiethnic study of atherosclerosis (MESA). BMJ Open Respir Res. 2021;8(1). https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjresp-2020-000866
6. Melgar M, Britton A, Roper LE, et al. Use of respiratory syncytial virus vaccines in older adults: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices — United States, 2023. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72(29):793-801. http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7229a4
7. Kodros JK, O’Dell K, Samet JM, L’Orange C, Pierce JR, Volckens J. Quantifying the health benefits of face masks and respirators to mitigate exposure to severe air pollution. GeoHealth. 2021;5(9). https://doi.org/10.1029/2021gh000482
Diffuse Lung Disease and Lung Transplant Network
Occupational and Environmental Health Section
Poor air quality has numerous health hazards for patients with chronic lung disease. Now mounting evidence from pediatric studies suggests a concerning link between air pollution and viral infections, specifically respiratory syncytial virus (RSV).
Multiple studies have shown increased incidence and severity of disease in children with exposure to air pollutants such as particulate matter and nitrogen dioxide.1,2,3 Researchers speculate that these pollutants potentiate viral entry to airway epithelium, increase viral load, and dysregulate the immune response.4 Air pollution, increasingly worsened by climate change, is also associated with acute respiratory infections in adults, though adult research remains sparse.5
The adoption of viral testing during the pandemic has revealed a previously under-recognized prevalence of RSV in adults.
RSV accounts for an estimated 60,000 to 160,000 hospitalizations and 6,000 to 10,000 deaths annually among elderly adults. This newfound awareness coincides with the exciting development of a new RSV vaccine that has shown around 85% efficacy at preventing symptomatic RSV infection in the first year, and new data suggest benefits persisting even into the second year after vaccination.6 With an estimated 60 million adults at high risk for RSV in the US, RSV prevention has become an increasingly important aspect of respiratory care.
While more research is needed to definitively quantify the link between air pollution and RSV in adults, the existing data offer valuable insights for all pulmonologists. These findings suggest a benefit in counseling patients with chronic lung conditions on taking steps to mitigate exposure to air pollutants, either through avoidance of outdoor activities or mask-wearing when air quality levels exceed healthy ranges, as well as promoting RSV vaccination for patients who are at risk.7
References
1. Milani GP, Cafora M, Favero C, et al. PM2.5, PM10 and bronchiolitis severity: a cohort study. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2022;33(10). https://doi.org/10.1111/pai.13853
2. Wrotek A, Badyda A, Czechowski PO, Owczarek T, Dąbrowiecki P, Jackowska T. Air pollutants’ concentrations are associated with increased number of RSV hospitalizations in Polish children. J Clin Med. 2021;10(15):3224. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10153224
3. Horne BD, Joy EA, Hofmann MG, et al. Short-term elevation of fine particulate matter air pollution and acute lower respiratory infection. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018;198(6):759-766. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201709-1883oc
4. Wrotek A, Jackowska T. Molecular mechanisms of RSV and air pollution interaction: a scoping review. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(20):12704. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232012704
5. Kirwa K, Eckert CM, Vedal S, Hajat A, Kaufman JD. Ambient air pollution and risk of respiratory infection among adults: evidence from the multiethnic study of atherosclerosis (MESA). BMJ Open Respir Res. 2021;8(1). https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjresp-2020-000866
6. Melgar M, Britton A, Roper LE, et al. Use of respiratory syncytial virus vaccines in older adults: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices — United States, 2023. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72(29):793-801. http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7229a4
7. Kodros JK, O’Dell K, Samet JM, L’Orange C, Pierce JR, Volckens J. Quantifying the health benefits of face masks and respirators to mitigate exposure to severe air pollution. GeoHealth. 2021;5(9). https://doi.org/10.1029/2021gh000482
A word of caution on e-cigarettes: Retracted paper
Editor’s note: On March 29, 2024, the authors of the study, “Efficacy of Electronic Cigarettes vs Varenicline and Nicotine Chewing Gum as an Aid to Stop Smoking: A Randomized Clinical Trial,” published in JAMA Internal Medicine, issued a formal retraction of their article. The CHEST Physician® Editorial Board apologizes for any confusion this may have caused.
An article in the April issue of the CHEST Physician publication headlined, “E-cigarettes beat nicotine gum for smoking cessation,” was based on an article in JAMA Internal Medicine by Liu Z and colleagues which was subsequently retracted by the author due to coding errors and discrepancies in calculations that cast doubt on the accuracy and reliability of the reported findings.
One should be cautious in evaluating claims of the benefits of electronic cigarettes (e-cigarettes). e-Cigarettes are a highly addictive and largely unregulated product. The fine print in previous clinical trials of e-cigarettes shows greater rates of stopping nicotine products—including e-cigarettes—in the groups assigned to recommendation for nicotine replacement therapy. e-Cigarettes have substantial acute and chronic harms.
Although much of the research to date is from animal models, there is a growing body of evidence in humans that validates the findings from the animal models. In laboratory animal models, e-cigarettes impair airway defenses, contribute to epithelial dysfunction, lead to apoptosis of airway cells, cause emphysematous changes, and lead to increased cancer rates.
Adverse effects on cardiovascular health have also been demonstrated. There is evidence of genotoxicity from e-cigarette exposure, with increased rates of DNA damage and decreased rates of DNA repair. Carcinogenic substances are present in e-cigarettes, and we may not see the carcinogenic effects in humans for several years or even decades. Commonly used flavoring chemicals have substantial pulmonary toxicity. There is evidence that the dual use of e-cigarettes and combustible tobacco can be more harmful than the use of combustible tobacco alone, as the person who smokes is now exposed to additional toxins unique to the e-cigarette.
E-cigarettes can cause severe acute lung disease; 14% of the severe e-cigarette or vaping product use-associated lung injury (EVALI) cases reported use of only nicotine-containing e-cigarette products. There are reports of people who used e-cigarettes who required lung transplant due to complications of their e-cigarette use.
The tobacco industry has a long history of “harm reduction” products that were anything but—from filter cigarettes (the “advanced” Kent Micronite filter contained asbestos) to the so-called low tar and nicotine cigarettes (which were no less harmful). There is a long history of physicians endorsing these products as “must be better.” The growing evidence that e-cigarettes carry distinct health risks of their own should prompt us to consider a broader picture beyond just comparing them with traditional cigarettes to assess their impact on health.
Physicians treating tobacco dependence should recommend US Food and Drug Administration-approved medications for pharmacotherapy. These have a robust evidence base documenting that they help people who smoke to break free of nicotine addiction. The goal of tobacco dependence treatment should be stopping ALL harmful tobacco/nicotine products—including e-cigarettes—not simply changing from one harmful product to another.
References
Liu Z. Notice of retraction: Lin HX et al. Efficacy of electronic cigarettes vs varenicline and nicotine chewing gum as an aid to stop smoking: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2024;184(3):291-299. JAMA Intern Med. Preprint. Posted online March 29, 2024. PMID: 38551593. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2024.1125
Farber HJ, Conrado Pacheco Gallego M, Galiatsatos P, Folan P, Lamphere T, Pakhale S. Harms of electronic cigarettes: what the healthcare provider needs to know. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2021;18(4):567-572. PMID: 33284731. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.202009-1113CME
Proctor RN. Golden Holocaust: Origins of the Cigarette Catastrophe and the Case for Abolition. University of California Press; 2011.
Auer R, Schoeni A, Humair JP, et al. Electronic nicotine-delivery systems for smoking cessation. N Engl J Med. 2024;390(7):601-610. PMID: 38354139. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2308815
Hajek P, Phillips-Waller A, Przulj D, et al. A randomized trial of e-cigarettes versus nicotine-replacement therapy. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(7):629-637. Preprint. Posted online January 30, 2019. PMID: 30699054. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1808779
Editor’s note: On March 29, 2024, the authors of the study, “Efficacy of Electronic Cigarettes vs Varenicline and Nicotine Chewing Gum as an Aid to Stop Smoking: A Randomized Clinical Trial,” published in JAMA Internal Medicine, issued a formal retraction of their article. The CHEST Physician® Editorial Board apologizes for any confusion this may have caused.
An article in the April issue of the CHEST Physician publication headlined, “E-cigarettes beat nicotine gum for smoking cessation,” was based on an article in JAMA Internal Medicine by Liu Z and colleagues which was subsequently retracted by the author due to coding errors and discrepancies in calculations that cast doubt on the accuracy and reliability of the reported findings.
One should be cautious in evaluating claims of the benefits of electronic cigarettes (e-cigarettes). e-Cigarettes are a highly addictive and largely unregulated product. The fine print in previous clinical trials of e-cigarettes shows greater rates of stopping nicotine products—including e-cigarettes—in the groups assigned to recommendation for nicotine replacement therapy. e-Cigarettes have substantial acute and chronic harms.
Although much of the research to date is from animal models, there is a growing body of evidence in humans that validates the findings from the animal models. In laboratory animal models, e-cigarettes impair airway defenses, contribute to epithelial dysfunction, lead to apoptosis of airway cells, cause emphysematous changes, and lead to increased cancer rates.
Adverse effects on cardiovascular health have also been demonstrated. There is evidence of genotoxicity from e-cigarette exposure, with increased rates of DNA damage and decreased rates of DNA repair. Carcinogenic substances are present in e-cigarettes, and we may not see the carcinogenic effects in humans for several years or even decades. Commonly used flavoring chemicals have substantial pulmonary toxicity. There is evidence that the dual use of e-cigarettes and combustible tobacco can be more harmful than the use of combustible tobacco alone, as the person who smokes is now exposed to additional toxins unique to the e-cigarette.
E-cigarettes can cause severe acute lung disease; 14% of the severe e-cigarette or vaping product use-associated lung injury (EVALI) cases reported use of only nicotine-containing e-cigarette products. There are reports of people who used e-cigarettes who required lung transplant due to complications of their e-cigarette use.
The tobacco industry has a long history of “harm reduction” products that were anything but—from filter cigarettes (the “advanced” Kent Micronite filter contained asbestos) to the so-called low tar and nicotine cigarettes (which were no less harmful). There is a long history of physicians endorsing these products as “must be better.” The growing evidence that e-cigarettes carry distinct health risks of their own should prompt us to consider a broader picture beyond just comparing them with traditional cigarettes to assess their impact on health.
Physicians treating tobacco dependence should recommend US Food and Drug Administration-approved medications for pharmacotherapy. These have a robust evidence base documenting that they help people who smoke to break free of nicotine addiction. The goal of tobacco dependence treatment should be stopping ALL harmful tobacco/nicotine products—including e-cigarettes—not simply changing from one harmful product to another.
References
Liu Z. Notice of retraction: Lin HX et al. Efficacy of electronic cigarettes vs varenicline and nicotine chewing gum as an aid to stop smoking: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2024;184(3):291-299. JAMA Intern Med. Preprint. Posted online March 29, 2024. PMID: 38551593. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2024.1125
Farber HJ, Conrado Pacheco Gallego M, Galiatsatos P, Folan P, Lamphere T, Pakhale S. Harms of electronic cigarettes: what the healthcare provider needs to know. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2021;18(4):567-572. PMID: 33284731. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.202009-1113CME
Proctor RN. Golden Holocaust: Origins of the Cigarette Catastrophe and the Case for Abolition. University of California Press; 2011.
Auer R, Schoeni A, Humair JP, et al. Electronic nicotine-delivery systems for smoking cessation. N Engl J Med. 2024;390(7):601-610. PMID: 38354139. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2308815
Hajek P, Phillips-Waller A, Przulj D, et al. A randomized trial of e-cigarettes versus nicotine-replacement therapy. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(7):629-637. Preprint. Posted online January 30, 2019. PMID: 30699054. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1808779
Editor’s note: On March 29, 2024, the authors of the study, “Efficacy of Electronic Cigarettes vs Varenicline and Nicotine Chewing Gum as an Aid to Stop Smoking: A Randomized Clinical Trial,” published in JAMA Internal Medicine, issued a formal retraction of their article. The CHEST Physician® Editorial Board apologizes for any confusion this may have caused.
An article in the April issue of the CHEST Physician publication headlined, “E-cigarettes beat nicotine gum for smoking cessation,” was based on an article in JAMA Internal Medicine by Liu Z and colleagues which was subsequently retracted by the author due to coding errors and discrepancies in calculations that cast doubt on the accuracy and reliability of the reported findings.
One should be cautious in evaluating claims of the benefits of electronic cigarettes (e-cigarettes). e-Cigarettes are a highly addictive and largely unregulated product. The fine print in previous clinical trials of e-cigarettes shows greater rates of stopping nicotine products—including e-cigarettes—in the groups assigned to recommendation for nicotine replacement therapy. e-Cigarettes have substantial acute and chronic harms.
Although much of the research to date is from animal models, there is a growing body of evidence in humans that validates the findings from the animal models. In laboratory animal models, e-cigarettes impair airway defenses, contribute to epithelial dysfunction, lead to apoptosis of airway cells, cause emphysematous changes, and lead to increased cancer rates.
Adverse effects on cardiovascular health have also been demonstrated. There is evidence of genotoxicity from e-cigarette exposure, with increased rates of DNA damage and decreased rates of DNA repair. Carcinogenic substances are present in e-cigarettes, and we may not see the carcinogenic effects in humans for several years or even decades. Commonly used flavoring chemicals have substantial pulmonary toxicity. There is evidence that the dual use of e-cigarettes and combustible tobacco can be more harmful than the use of combustible tobacco alone, as the person who smokes is now exposed to additional toxins unique to the e-cigarette.
E-cigarettes can cause severe acute lung disease; 14% of the severe e-cigarette or vaping product use-associated lung injury (EVALI) cases reported use of only nicotine-containing e-cigarette products. There are reports of people who used e-cigarettes who required lung transplant due to complications of their e-cigarette use.
The tobacco industry has a long history of “harm reduction” products that were anything but—from filter cigarettes (the “advanced” Kent Micronite filter contained asbestos) to the so-called low tar and nicotine cigarettes (which were no less harmful). There is a long history of physicians endorsing these products as “must be better.” The growing evidence that e-cigarettes carry distinct health risks of their own should prompt us to consider a broader picture beyond just comparing them with traditional cigarettes to assess their impact on health.
Physicians treating tobacco dependence should recommend US Food and Drug Administration-approved medications for pharmacotherapy. These have a robust evidence base documenting that they help people who smoke to break free of nicotine addiction. The goal of tobacco dependence treatment should be stopping ALL harmful tobacco/nicotine products—including e-cigarettes—not simply changing from one harmful product to another.
References
Liu Z. Notice of retraction: Lin HX et al. Efficacy of electronic cigarettes vs varenicline and nicotine chewing gum as an aid to stop smoking: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2024;184(3):291-299. JAMA Intern Med. Preprint. Posted online March 29, 2024. PMID: 38551593. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2024.1125
Farber HJ, Conrado Pacheco Gallego M, Galiatsatos P, Folan P, Lamphere T, Pakhale S. Harms of electronic cigarettes: what the healthcare provider needs to know. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2021;18(4):567-572. PMID: 33284731. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.202009-1113CME
Proctor RN. Golden Holocaust: Origins of the Cigarette Catastrophe and the Case for Abolition. University of California Press; 2011.
Auer R, Schoeni A, Humair JP, et al. Electronic nicotine-delivery systems for smoking cessation. N Engl J Med. 2024;390(7):601-610. PMID: 38354139. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2308815
Hajek P, Phillips-Waller A, Przulj D, et al. A randomized trial of e-cigarettes versus nicotine-replacement therapy. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(7):629-637. Preprint. Posted online January 30, 2019. PMID: 30699054. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1808779
Fellow to use diversity scholar mentorship to strengthen care in pediatric-to-adult transitions
During residency training at the Rush University Medical Center in Internal Medicine and Pediatrics, Esha Kapania, MD, quickly became interested in the pulmonary pathologies that span the life of a patient, beginning in childhood and lasting into adulthood.
Now in her first year of fellowship at the University of Louisville and as the recipient of the 2024 Medical Educator Scholar Diversity Fellowship from CHEST and the Association of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Program Directors (APCCMPD), Dr. Kapania will utilize the support of the program to explore this space.
“Recent advancements in pediatric pulmonary medicine have prolonged the expected lifespan of many previously fatal diagnoses, and I have realized that, despite these innovations, there remains very little communication between the adult and pediatric subspecialists,” Dr. Kapania said. “There is minimal education on congenital pulmonary pathology in adult medicine and, perhaps equally as important, negligible instruction on the cultural and social changes that patients experience when they transition from pediatric to adult providers.”
In residency, Dr. Kapania witnessed the success of cystic fibrosis (CF) clinics and hopes to leverage that experience to advance transitional care across disease states. Using the guidelines set to transition patients with CF from pediatric to adult care as a model, Dr. Kapania will focus her time on creating a streamlined process for patients living with severe asthma and patients with neuromuscular diseases who are chronically vented.
“Patients who are chronically vented tend not to have a lot of resources dedicated to them and are a resource- and time-heavy population,” Dr. Kapania said. “Because there is no defined process to transition these patients, we tend to see pediatric providers hold on to these patients for a lot longer than they do with [patients with CF]. A set of evidence-based practices would go a long way in this space.”
Through the APCCMPD and CHEST Medical Educator Scholar Diversity Fellowship, Dr. Kapania will work closely with the program’s selected mentor, Başak Çoruh, MD, FCCP, who is an Associate Professor of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine and Director of the Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine fellowship program at the University of Washington.
“I’m looking forward to working with Dr. Çoruh for career guidance and for support of my area of interest within [pulmonary and critical care medicine],” Dr. Kapania said. “She is an established physician who has a lot of insight to share, and this is a great opportunity to make the best of my fellowship.”
This is the first year for the APCCMPD and CHEST Medical Educator Scholar Diversity Fellowship. To learn more about the scholarship, visit the CHEST website.
During residency training at the Rush University Medical Center in Internal Medicine and Pediatrics, Esha Kapania, MD, quickly became interested in the pulmonary pathologies that span the life of a patient, beginning in childhood and lasting into adulthood.
Now in her first year of fellowship at the University of Louisville and as the recipient of the 2024 Medical Educator Scholar Diversity Fellowship from CHEST and the Association of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Program Directors (APCCMPD), Dr. Kapania will utilize the support of the program to explore this space.
“Recent advancements in pediatric pulmonary medicine have prolonged the expected lifespan of many previously fatal diagnoses, and I have realized that, despite these innovations, there remains very little communication between the adult and pediatric subspecialists,” Dr. Kapania said. “There is minimal education on congenital pulmonary pathology in adult medicine and, perhaps equally as important, negligible instruction on the cultural and social changes that patients experience when they transition from pediatric to adult providers.”
In residency, Dr. Kapania witnessed the success of cystic fibrosis (CF) clinics and hopes to leverage that experience to advance transitional care across disease states. Using the guidelines set to transition patients with CF from pediatric to adult care as a model, Dr. Kapania will focus her time on creating a streamlined process for patients living with severe asthma and patients with neuromuscular diseases who are chronically vented.
“Patients who are chronically vented tend not to have a lot of resources dedicated to them and are a resource- and time-heavy population,” Dr. Kapania said. “Because there is no defined process to transition these patients, we tend to see pediatric providers hold on to these patients for a lot longer than they do with [patients with CF]. A set of evidence-based practices would go a long way in this space.”
Through the APCCMPD and CHEST Medical Educator Scholar Diversity Fellowship, Dr. Kapania will work closely with the program’s selected mentor, Başak Çoruh, MD, FCCP, who is an Associate Professor of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine and Director of the Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine fellowship program at the University of Washington.
“I’m looking forward to working with Dr. Çoruh for career guidance and for support of my area of interest within [pulmonary and critical care medicine],” Dr. Kapania said. “She is an established physician who has a lot of insight to share, and this is a great opportunity to make the best of my fellowship.”
This is the first year for the APCCMPD and CHEST Medical Educator Scholar Diversity Fellowship. To learn more about the scholarship, visit the CHEST website.
During residency training at the Rush University Medical Center in Internal Medicine and Pediatrics, Esha Kapania, MD, quickly became interested in the pulmonary pathologies that span the life of a patient, beginning in childhood and lasting into adulthood.
Now in her first year of fellowship at the University of Louisville and as the recipient of the 2024 Medical Educator Scholar Diversity Fellowship from CHEST and the Association of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Program Directors (APCCMPD), Dr. Kapania will utilize the support of the program to explore this space.
“Recent advancements in pediatric pulmonary medicine have prolonged the expected lifespan of many previously fatal diagnoses, and I have realized that, despite these innovations, there remains very little communication between the adult and pediatric subspecialists,” Dr. Kapania said. “There is minimal education on congenital pulmonary pathology in adult medicine and, perhaps equally as important, negligible instruction on the cultural and social changes that patients experience when they transition from pediatric to adult providers.”
In residency, Dr. Kapania witnessed the success of cystic fibrosis (CF) clinics and hopes to leverage that experience to advance transitional care across disease states. Using the guidelines set to transition patients with CF from pediatric to adult care as a model, Dr. Kapania will focus her time on creating a streamlined process for patients living with severe asthma and patients with neuromuscular diseases who are chronically vented.
“Patients who are chronically vented tend not to have a lot of resources dedicated to them and are a resource- and time-heavy population,” Dr. Kapania said. “Because there is no defined process to transition these patients, we tend to see pediatric providers hold on to these patients for a lot longer than they do with [patients with CF]. A set of evidence-based practices would go a long way in this space.”
Through the APCCMPD and CHEST Medical Educator Scholar Diversity Fellowship, Dr. Kapania will work closely with the program’s selected mentor, Başak Çoruh, MD, FCCP, who is an Associate Professor of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine and Director of the Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine fellowship program at the University of Washington.
“I’m looking forward to working with Dr. Çoruh for career guidance and for support of my area of interest within [pulmonary and critical care medicine],” Dr. Kapania said. “She is an established physician who has a lot of insight to share, and this is a great opportunity to make the best of my fellowship.”
This is the first year for the APCCMPD and CHEST Medical Educator Scholar Diversity Fellowship. To learn more about the scholarship, visit the CHEST website.
Transesophageal ultrasound: The future of ultrasound in the ICU
Thoracic Oncology and Chest Procedures Network
Ultrasound and Chest Imaging Section
Historically, transesophageal ultrasound (TEE) has been regarded as a diagnostic and management tool for structural heart disease in relatively stable patients. However, TEE is more commonly being utilized by intensivists as a first-line tool in the diagnostics and management of patients in the ICU.
TEE, with its unobstructed superior cardiac views, facilitates rapid diagnosis in undifferentiated shock and guides appropriate resuscitation efforts. Studies have shown that TEE alters management strategies in 40% of cases, following transthoracic echocardiography with an extremely low complication rate of 2% to 3% (primarily in the form of self-limited gastrointestinal bleeding).1,2,3,4
TEE also provides ultrasonographic evaluation of the lungs through transesophageal lung ultrasound (TELUS). TELUS allows for visualization of all six traditional lung zones utilized in traditional lung ultrasound.5 Patients with severe acute respiratory distress syndrome may greatly benefit from TEE utilization. TEE enables early detection of right ventricular dysfunction, aids in fluid management, and assesses the severity of lung consolidation, thereby facilitating prompt utilization of prone positioning or adjustments in positive end-expiratory pressure.
Cardiac arrest is another unique opportunity for TEE utilization by providing real-time cardiac visualization during active cardiopulmonary resuscitation. This facilitates optimal chest compression positioning, early recognition of arrhythmia, timely identification of reversible cause, and procedural guidance for ECMO-assisted CPR.6 TEE is an invaluable tool for the modern-day intensivist, providing rapid and accurate assessments, and therefore holds the potential to become standard of care in the ICU.
References
1. Prager R, Bowdridge J, Pratte M, Cheng J, McInnes MD, Arntfield R. Indications, clinical impact, and complications of critical care transesophageal echocardiography: a scoping review. J Intensive Care Med. 2023;38(3):245-272. Preprint. Posted online July 19, 2022. PMID: 35854414; PMCID: PMC9806486. doi: 10.1177/08850666221115348
2. Hüttemann E, Schelenz C, Kara F, Chatzinikolaou K, Reinhart K. The use and safety of transoesophageal echocardiography in the general ICU – a minireview. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2004;48(7):827-36. PMID: 15242426. doi: 10.1111/j.0001-5172.2004.00423.x
3. Mayo PH, Narasimhan M, Koenig S. Critical care transesophageal echocardiography. Chest. 2015;148(5):1323-1332. PMID: 26204465. doi: 10.1378/chest.15-0260
4. Prager R, Ainsworth C, Arntfield R. Critical care transesophageal echocardiography for the resuscitation of shock: an important diagnostic skill for the modern intensivist. Chest. 2023;163(2):268-269. PMID: 36759112. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2022.09.001
5. Cavayas YA, Girard M, Desjardins G, Denault AY. Transesophageal lung ultrasonography: a novel technique for investigating hypoxemia. Can J Anaesth. 2016;63(11):1266-76. Preprint. Posted online July 29, 2016. PMID: 27473720. doi: 10.1007/s12630-016-0702-2
6. Teran F, Prats MI, Nelson BP, et al. Focused transesophageal echocardiography during cardiac arrest resuscitation: JACC review wopic of the Week. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;76(6):745-754. PMID: 32762909. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.05.074
Thoracic Oncology and Chest Procedures Network
Ultrasound and Chest Imaging Section
Historically, transesophageal ultrasound (TEE) has been regarded as a diagnostic and management tool for structural heart disease in relatively stable patients. However, TEE is more commonly being utilized by intensivists as a first-line tool in the diagnostics and management of patients in the ICU.
TEE, with its unobstructed superior cardiac views, facilitates rapid diagnosis in undifferentiated shock and guides appropriate resuscitation efforts. Studies have shown that TEE alters management strategies in 40% of cases, following transthoracic echocardiography with an extremely low complication rate of 2% to 3% (primarily in the form of self-limited gastrointestinal bleeding).1,2,3,4
TEE also provides ultrasonographic evaluation of the lungs through transesophageal lung ultrasound (TELUS). TELUS allows for visualization of all six traditional lung zones utilized in traditional lung ultrasound.5 Patients with severe acute respiratory distress syndrome may greatly benefit from TEE utilization. TEE enables early detection of right ventricular dysfunction, aids in fluid management, and assesses the severity of lung consolidation, thereby facilitating prompt utilization of prone positioning or adjustments in positive end-expiratory pressure.
Cardiac arrest is another unique opportunity for TEE utilization by providing real-time cardiac visualization during active cardiopulmonary resuscitation. This facilitates optimal chest compression positioning, early recognition of arrhythmia, timely identification of reversible cause, and procedural guidance for ECMO-assisted CPR.6 TEE is an invaluable tool for the modern-day intensivist, providing rapid and accurate assessments, and therefore holds the potential to become standard of care in the ICU.
References
1. Prager R, Bowdridge J, Pratte M, Cheng J, McInnes MD, Arntfield R. Indications, clinical impact, and complications of critical care transesophageal echocardiography: a scoping review. J Intensive Care Med. 2023;38(3):245-272. Preprint. Posted online July 19, 2022. PMID: 35854414; PMCID: PMC9806486. doi: 10.1177/08850666221115348
2. Hüttemann E, Schelenz C, Kara F, Chatzinikolaou K, Reinhart K. The use and safety of transoesophageal echocardiography in the general ICU – a minireview. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2004;48(7):827-36. PMID: 15242426. doi: 10.1111/j.0001-5172.2004.00423.x
3. Mayo PH, Narasimhan M, Koenig S. Critical care transesophageal echocardiography. Chest. 2015;148(5):1323-1332. PMID: 26204465. doi: 10.1378/chest.15-0260
4. Prager R, Ainsworth C, Arntfield R. Critical care transesophageal echocardiography for the resuscitation of shock: an important diagnostic skill for the modern intensivist. Chest. 2023;163(2):268-269. PMID: 36759112. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2022.09.001
5. Cavayas YA, Girard M, Desjardins G, Denault AY. Transesophageal lung ultrasonography: a novel technique for investigating hypoxemia. Can J Anaesth. 2016;63(11):1266-76. Preprint. Posted online July 29, 2016. PMID: 27473720. doi: 10.1007/s12630-016-0702-2
6. Teran F, Prats MI, Nelson BP, et al. Focused transesophageal echocardiography during cardiac arrest resuscitation: JACC review wopic of the Week. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;76(6):745-754. PMID: 32762909. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.05.074
Thoracic Oncology and Chest Procedures Network
Ultrasound and Chest Imaging Section
Historically, transesophageal ultrasound (TEE) has been regarded as a diagnostic and management tool for structural heart disease in relatively stable patients. However, TEE is more commonly being utilized by intensivists as a first-line tool in the diagnostics and management of patients in the ICU.
TEE, with its unobstructed superior cardiac views, facilitates rapid diagnosis in undifferentiated shock and guides appropriate resuscitation efforts. Studies have shown that TEE alters management strategies in 40% of cases, following transthoracic echocardiography with an extremely low complication rate of 2% to 3% (primarily in the form of self-limited gastrointestinal bleeding).1,2,3,4
TEE also provides ultrasonographic evaluation of the lungs through transesophageal lung ultrasound (TELUS). TELUS allows for visualization of all six traditional lung zones utilized in traditional lung ultrasound.5 Patients with severe acute respiratory distress syndrome may greatly benefit from TEE utilization. TEE enables early detection of right ventricular dysfunction, aids in fluid management, and assesses the severity of lung consolidation, thereby facilitating prompt utilization of prone positioning or adjustments in positive end-expiratory pressure.
Cardiac arrest is another unique opportunity for TEE utilization by providing real-time cardiac visualization during active cardiopulmonary resuscitation. This facilitates optimal chest compression positioning, early recognition of arrhythmia, timely identification of reversible cause, and procedural guidance for ECMO-assisted CPR.6 TEE is an invaluable tool for the modern-day intensivist, providing rapid and accurate assessments, and therefore holds the potential to become standard of care in the ICU.
References
1. Prager R, Bowdridge J, Pratte M, Cheng J, McInnes MD, Arntfield R. Indications, clinical impact, and complications of critical care transesophageal echocardiography: a scoping review. J Intensive Care Med. 2023;38(3):245-272. Preprint. Posted online July 19, 2022. PMID: 35854414; PMCID: PMC9806486. doi: 10.1177/08850666221115348
2. Hüttemann E, Schelenz C, Kara F, Chatzinikolaou K, Reinhart K. The use and safety of transoesophageal echocardiography in the general ICU – a minireview. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2004;48(7):827-36. PMID: 15242426. doi: 10.1111/j.0001-5172.2004.00423.x
3. Mayo PH, Narasimhan M, Koenig S. Critical care transesophageal echocardiography. Chest. 2015;148(5):1323-1332. PMID: 26204465. doi: 10.1378/chest.15-0260
4. Prager R, Ainsworth C, Arntfield R. Critical care transesophageal echocardiography for the resuscitation of shock: an important diagnostic skill for the modern intensivist. Chest. 2023;163(2):268-269. PMID: 36759112. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2022.09.001
5. Cavayas YA, Girard M, Desjardins G, Denault AY. Transesophageal lung ultrasonography: a novel technique for investigating hypoxemia. Can J Anaesth. 2016;63(11):1266-76. Preprint. Posted online July 29, 2016. PMID: 27473720. doi: 10.1007/s12630-016-0702-2
6. Teran F, Prats MI, Nelson BP, et al. Focused transesophageal echocardiography during cardiac arrest resuscitation: JACC review wopic of the Week. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;76(6):745-754. PMID: 32762909. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.05.074
















